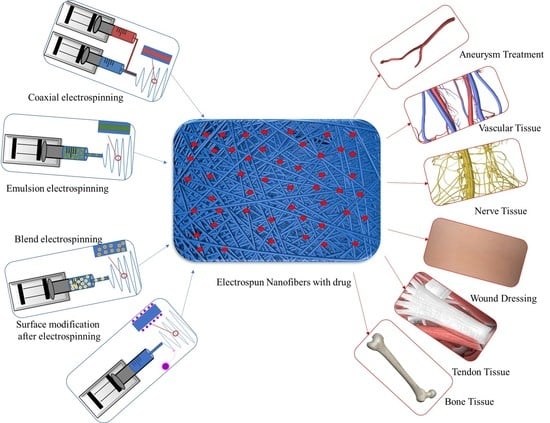
Electrospun Nanofibers for Tissue Engineering with Drug Loading and Release
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Electrospun Scaffolds for Aneurysm Treatment
3. Electrospun Scaffolds for Nerve Tissue Engineering
4. Electrospun Scaffolds for Vascular Tissue Engineering
5. Electrospun Scaffolds for Wound Dressing Application
6. Electrospun Scaffolds for Tendon Tissue Engineering
7. Electrospun Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering
8. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qasim, S.B.; Zafar, M.S.; Najeeb, S.; Khurshid, Z.; Shah, A.H.; Husain, S.; Rehman, I.U. Electrospinning of chitosan-based solutions for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 407. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Thomopoulos, S.; Xia, Y. Electrospun nanofibers for regenerative medicine. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2012, 1, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zamani, R.; Aval, S.F.; Pilehvar-Soltanahmadi, Y.; Nejati-Koshki, K.; Zarghami, N. Recent advances in cell electrospining of natural and synthetic nanofibers for regenerative medicine. Drug Res. 2018, 68, 425–435. [Google Scholar]
- Greiner, A.; Wendorff, J.H. Electrospinning: A fascinating method for the preparation of ultrathin fibers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 5670–5703. [Google Scholar]
- Zafar, M.; Najeeb, S.; Khurshid, Z.; Vazirzadeh, M.; Zohaib, S.; Najeeb, B.; Sefat, F. Potential of electrospun nanofibers for biomedical and dental applications. Materials 2016, 9, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flemming, R.G.; Murphy, C.J.; Abrams, G.A.; Goodman, S.L.; Nealey, P.F. Effects of synthetic micro- and nano-structured surfaces on cell behavior. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 573–588. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Von Recum, A.F.; Shannon, C.E.; Cannon, C.E.; Long, K.J.; van Kooten, T.G.; Meyle, J. Surface roughness, porosity, and texture as modifiers of cellular adhesion. Tissue Eng. 1996, 2, 241–253. [Google Scholar]
- Green, A.M.; Jansen, J.A.; van der Waerden, J.P.C.M.; Von Recum, A.F. Fibroblast response to microtextured silicone surfaces: Texture orientation into or out of the surface. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 1994, 28, 647–653. [Google Scholar]
- Mitragotri, S.; Anderson, D.G.; Chen, X.; Chow, E.K.; Ho, D.; Kabanov, A.V.; Karp, J.M.; Kataoka, K.; Mirkin, C.A.; Petrosko, S.H.; et al. Accelerating the translation of nanomaterials in biomedicine. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 6644–6654. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Stiadle, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Li, Q.; Shen, C.; Thibeault, S.L.; Turng, L.-S. Electrospun nanofibrous thermoplastic polyurethane/poly(glycerol sebacate) hybrid scaffolds for vocal fold tissue engineering applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 94, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campiglio, C.; Marcolin, C.; Draghi, L. Electrospun ECM macromolecules as biomimetic scaffold for regenerative medicine: Challenges for preserving conformation and bioactivity. AIMS J. 2017, 4, 638–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bölgen, N.; Vargel, I.; Korkusuz, P.; Menceloğlu, Y.Z.; Pişkin, E. In vivo performance of antibiotic embedded electrospun PCL membranes for prevention of abdominal adhesions. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2010, 81B, 530–543. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.M.; Yang, C.L.H. Encapsulating drugs in biodegradable ultrafine fibers through co-axial electrospinning. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2010, 77A, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Luu, Y.K.; Chang, C.; Fang, D.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B.; Hadjiargyrou, M. Incorporation and controlled release of a hydrophilic antibiotic using poly(lactide-co-glycolide)-based electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds. J. Control. Release 2004, 98, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nie, H.; Wang, C.H. Fabrication and characterization of PLGA/HAp composite scaffolds for delivery of BMP-2 plasmid DNA. J. Control. Release 2007, 120, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chew, S.Y.; Jie, W.; Yim, E.K.F.; Leong, K.W. Sustained release of proteins from electrospun biodegradable fibers. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 2017–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, A.; Moztarzadeh, F.; Aghazadeh Mohandesi, J. Investigating the effect of chitosan on hydrophilicity and bioactivity of conductive electrospun composite scaffold for neural tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 121, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, E.; Rajeswaran, N.; Sahanand, K.S.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Rajendran, S. In vitro evaluation of phytochemical loaded electrospun gelatin nanofibers for application in bone and cartilage tissue engineering. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 14, 015004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Z.; Zanjanizadeh Ezazi, N.; Liu, D.; Santos, H.A. Electrospun fibrous architectures for drug delivery, tissue engineering and cancer therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1802852. [Google Scholar]
- Sill, T.J.; Von Recum, H.A. Electrospinning: Applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1989–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenawy, E.R.; Bowlin, G.L.; Mansfield, K.; Layman, J.; Simpson, D.G.; Sanders, E.H.; Wnek, G.E. Release of tetracycline hydrochloride from electrospun poly(ethylene-co-vinylacetate), poly(lactic acid), and a blend. J. Control. Release 2002, 81, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Ju, Y.M.; Son, J.S.; Ahn, K.D.; Dong, K.H. Surface modification of biodegradable electrospun nanofiber scaffolds and their interaction with fibroblasts. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2007, 18, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, K.; Liu, D.; Kuang, H.; Cai, J.; Chen, W.; Sun, B.; Xia, L.; Fang, B.; Morsi, Y.; Mo, X. Three-dimensional electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds displaying bone morphogenetic protein-2-derived peptides for the promotion of osteogenic differentiation of stem cells and bone regeneration. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 534, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Wang, J.; Liu, C. Biomaterials act as enhancers of growth factors in bone regeneration. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 8810–8823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Jiang, H.H.; Zhu, K.; Chen, W. Biodegradable fibrous scaffolds composed of gelatin coated poly(epsilon-caprolactone) prepared by coaxial electrospinning. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2010, 83A, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Wang, X.; Feng, Y.; Li, J.; Lim, C.T.; Ramakrishna, S. Coaxial electrospinning of (fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated bovine serum albumin)-encapsulated poly(epsilon-caprolactone) nanofibers for sustained release. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.I. A facile technique to prepare biodegradable coaxial electrospun nanofibers for controlled release of bioactive agents. J. Control. Release 2005, 108, 237–243. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; He, C.; Mo, X. Fabrication and characterization of biodegradable nanofibrous mats by mix and coaxial electrospinning. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2009, 20, 2285–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado-Prone, G.; Silva-Bermudez, P.; Almaguer-Flores, A.; García-Macedo, J.A.; García, V.I.; Rodil, S.E.; Ibarra, C.; Velasquillo, C. Enhanced antibacterial nanocomposite mats by coaxial electrospinning of polycaprolactone fibers loaded with Zn-based nanoparticles. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2018, 14, 1695–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Zhong, Q.; Ge, Y.; Guo, Z.; Tian, J.; Zhou, Y.; Ding, S.; Li, H.; Zhou, C. Dual drug loaded coaxial electrospun PLGA/PVP fiber for guided tissue regeneration under control of infection. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 90, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Mo, X.; Ramakrishna, S. Controlled release of dual drugs from emulsion electrospun nanofibrous mats. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2009, 73, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Li, R.; Li, X.; Xie, J. Electrospinning: An enabling nanotechnology platform for drug delivery and regenerative medicine. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 132, 188–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, A.; Suliman, A.; Angle, N. Spontaneous dissection of the carotid and vertebral arteries: The 10-year UCSD experience. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2007, 21, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoder, M.; Cartes-Zumelzu, F.; Grabenwöger, M.; Cejna, M.; Funovics, M.; Krenn, C.G.; Hutschala, D.; Wolf, F.; Thurnher, S.; et al. Elective endovascular stent-graft repair of atherosclerotic thoracic aortic aneurysms: Clinical results and midterm follow-up. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2003, 180, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabenwöger, M.; Hutschala, D.; Cartes-Zumelzu, F.; Ehrlich, M.; Grimm, M.; Thurnher, S.; Lammer, J.; Wolner, E.; Havel, M. Behandlung von thorakalen Aortenaneurysmen mit selbstexpandierenden endoluminalen Gefäßprothesen. Acta Chir. Austriaca 1999, 31, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golshani, K.; Ferrel, A.; Lessne, M.; Shah, P.; Chowdhary, A.; Choulakian, A.; Alexander, M.J.; Smith, T.P.; Enterline, D.S.; Zomorodi, A.R. Stent-assisted coil emboilization of ruptured intracranial aneurysms: A retrospective multicenter review. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2012, 3, 84. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; An, Q.; Li, D.; Jing, W.; He, L.; Chen, H.; Yu, L.; Wei, Z.; Mo, X. A novel heparin loaded poly(l-lactide-co-caprolactone) covered stent for aneurysm therapy. Mater. Lett. 2014, 116, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; An, Q.; Li, D.; Wu, T.; Chen, W.; Sun, B.; El-Hamshary, H.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Zhu, W.; Mo, X. Heparin and vascular endothelial growth factor loaded poly(l-lactide-co-caprolactone) nanofiber covered stent-graft for aneurysm treatment. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2015, 11, 1947–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Liu, P.; Yin, H.; Gu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, W.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Mo, X. Heparin and rosuvastatin calcium loaded ploy(l-lactide-co-caprolactone) nanofiber covered stent-graft for aneurysm treatment. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 9014–9023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondo, S.; Fornaro, M.; Tos, P.; Battiston, B.; Giacobini-Robecchi, M.G.; Geuna, S. Perspectives in regeneration and tissue engineering of peripheral nerves. Ann. Anat. 2011, 193, 334–340. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, G.R.D.; Brandt, K.; Widmer, M.S.; Lu, L.; Meszlenyi, R.K.; Gupta, P.K.; Mikos, A.G.; Hodges, J.; Williams, J.; Gürlek, A. In vivo evaluation of poly(l-lactic acid) porous conduits for peripheral nerve regeneration. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, C.-C.; Serio, A.; Amdursky, N.; Besnard, C.; Stevens, M.M. Fabrication of hemin-doped serum albumin-based fibrous scaffolds for neural tissue engineering applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 5305–5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Z. Application of self-assembling peptide nanofiber scaffold in nerve tissue engineering. Chin. J. Repar. Reconstr. Surg. 2009, 23, 861–863. [Google Scholar]
- Chun-Yang, W.; Jun-Jian, L.; Cun-Yi, F.; Xiu-Mei, M.; Hong-Jiang, R.; Feng-Feng, L. The effect of aligned core-shell nanofibres delivering NGF on the promotion of sciatic nerve regeneration. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2012, 23, 167–184. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, C.; Fan, C.; Mo, X. Aligned SF/P(LLA-CL)-blended nanofibers encapsulating nerve growth factor for peripheral nerve regeneration. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2014, 102, 2680–2691. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.; Li, X.; Tian, L.; Chen, H.; Xiumei, M. Poly(l-lactide-co-ε-caprolactone) electrospun nanofibers for encapsulating and sustained releasing proteins. Polymer 2009, 50, 4212–4219. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, B.; Wu, T.; He, L.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, X.; El-Hamshary, H.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Xu, T.; Mo, X. Development of dual neurotrophins-encapsulated electrosupun nanofibrous scaffolds for peripheral nerve regeneration. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2016, 12, 1987–2000. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bhutto, M.A.; Wu, T.; Sun, B.; Ei-Hamshary, H.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Mo, X. Fabrication and characterization of vitamin B5 loaded poly (l-lactide-co-caprolactone)/silk fiber aligned electrospun nanofibers for Schwann cell proliferation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 144, 108–117. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, W.; Li, D.; Wang, Y.; Sun, B.; Li, D.; Morsi, Y.; Hamshary, H.A.E.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Mo, X.M. Laminin-coated nerve guidance conduits based on poly(l-lactide-co-glycolide) fibers and yarns for promoting Schwann cells proliferation and migration. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 3186–3194. [Google Scholar]
- Junka, R.; Valmikinathan, C.M.; Kalyon, D.M.; Yu, X. Laminin functionalized biomimetic nanofibers for nerve tissue engineering. J. Biomater. Tissue Eng. 2013, 3, 494–502. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Q.; Li, X.; Xu, F.; Yao, X.; Wang, M. Incorporation and release of dual growth factors for nerve tissue engineering using nanofibrous bicomponent scaffolds. Biomed. Mater. 2013, 13, 044107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canver, C.C. Conduit options in coronary artery bypass surgery. Chest 1995, 108, 1150–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chlupác, J.; Filová, E.; Bacáková, L. Vascular prostheses: 50 years of advancement from synthetic towards tissue engineering and cell therapy. Rozhledy 2010, 89, 85–94. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Wang, S.; Qiu, L.; Ke, Q.; Zhai, W.; Mo, X. Heparin loading and pre-endothelialization in enhancing the patency rate of electrospun small-diameter vascular grafts in a canine model. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 2220–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, J.; An, Q.; Li, D.; Liu, P.; Zhu, W.; Mo, X. Electrospun poly(l-lactic acid-co-ɛ-caprolactone) fibers loaded with heparin and vascular endothelial growth factor to improve blood compatibility and endothelial progenitor cell proliferation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 128, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, A.; Bowlin, G.L.; Luo, R.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Mo, X. Electrospun silk fibroin/poly(l-lactide-ε-caplacton) graft with platelet-rich growth factor for inducing smooth muscle cell growth and infiltration. Regen. Biomater. 2016, 3, 239–245. [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, H.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J.; Wang, C.; Lu, S.; Mo, X. A method for preparation of an internal layer of artificial vascular graft co-modified with Salvianolic acid B and heparin. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 19365–19372. [Google Scholar]
- Guex, A.G.; Hegemann, D.; Giraud, M.N.; Tevaearai, H.T.; Popa, A.M.; Rossi, R.M.; Fortunato, G. Covalent immobilisation of VEGF on plasma-coated electrospun scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 123, 724–733. [Google Scholar]
- Gurtner, G.C.; Sabine, W.; Yann, B.; Longaker, M.T. Wound repair and regeneration. Nature 2008, 453, 314–321. [Google Scholar]
- Zahedi, P.; Rezaeian, I.; Ranaei-Siadat, S.O.; Jafari, S.H.; Supaphol, P. A review on wound dressings with an emphasis on electrospun nanofibrous polymeric bandages. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2010, 21, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng-Xiao, C.; Xiu-Mei, M.; Kui-Hua, Z.; Lin-Peng, F.; An-Lin, Y.; Chuang-Long, H.; Hong-Sheng, W. Fabrication of chitosan/silk fibroin composite nanofibers for wound-dressing applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 3529–3539. [Google Scholar]
- Alhusein, N.; Blagbrough, I.S.; De Bank, P.A. Electrospun matrices for localised controlled drug delivery: Release of tetracycline hydrochloride from layers of polycaprolactone and poly(ethylene-co-vinyl acetate). Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2012, 2, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhusein, N.; Blagbrough, I.S.; Beeton, M.L.; Bolhuis, A.; De Bank, P.A. Electrospun zein/PCL fibrous matrices release tetracycline in a controlled manner, killing Staphylococcus aureus both in biofilms and ex vivo on pig skin, and are compatible with human skin cells. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhusein, N.; Blagbrough, I.S.; De Bank, P.A. Zein/polycaprolactone electrospun matrices for localised controlled delivery of tetracycline. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2013, 3, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosal, K.; Agatemor, C.; Thomas, S.; Kny, E. Electrospinning tissue engineering and wound dressing scaffolds from polymer–titanium dioxide nanocomposites. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 358, 1262–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhai, D.; Lv, F.; Yu, Q.; Ma, H.; Yin, J.; Yi, Z.; Liu, M.; Chang, J.; Wu, C. Preparation of copper-containing bioactive glass/eggshell membrane nanocomposites for improving angiogenesis, antibacterial activity and wound healing. Acta Biomater. 2016, 36, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eming, S.A.; Martin, P.; Tomic-Canic, M. Wound repair and regeneration: Mechanisms, signaling, and translation. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 265sr6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaoxing Luo, M.D.; Jin, T.M.; He, W.; Jun Wu, M.D.; Bing, M.M.; Xihua Wang, M.D.; Chen, X.; Yi, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, X. Antibacterial effect of dressings containing multivalent silver ion carried by zirconium phosphate on experimental rat burn wounds. Wound Repair Regen. 2010, 16, 800–804. [Google Scholar]
- Brett, B.; Sampson, E.M.; Schultz, G.S.; Parnell, L.K.S. Wound dressing components degrade proteins detrimental to wound healing. Int. Wound J. 2010, 5, 543–551. [Google Scholar]
- Ignatova, M.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I. Electrospinning of poly(vinyl pyrrolidone)–iodine complex and poly(ethylene oxide)/poly(vinyl pyrrolidone)–iodine complex—A prospective route to antimicrobial wound dressing materials. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 1609–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhusein, N.; De Bank, P.A.; Blagbrough, I.S.; Bolhuis, A. Killing bacteria within biofilms by sustained release of tetracycline from triple-layered electrospun micro/nanofibre matrices of polycaprolactone and poly(ethylene-co-vinyl acetate). Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2013, 3, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román-Doval, R.; Tellez-Cruz, M.M.; Rojas-Chávez, H.; Cruz-Martínez, H.; Carrasco-Torres, G.; Vásquez-Garzón, V.R. Enhancing electrospun scaffolds of PVP with polypyrrole/iodine for tissue engineering of skin regeneration by coating via a plasma process. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 3342–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, X.; Fan, L.; He, C.; Zhang, K.; Mo, X.; Wang, H. Vitamin E-loaded silk fibroin nanofibrous mats fabricated by green process for skin care application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 56, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Aassar, M.R.; El Fawal, G.F.; El-Deeb, N.M.; Hassan, H.S.; Mo, X. Electrospun polyvinyl alcohol/ pluronic F127 blended nanofibers containing titanium dioxide for antibacterial wound dressing. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 178, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, F.; Wang, J.; Xu, P.; Han, Y.; Ma, H.; Xu, H.; Chen, S.; Chang, J.; Ke, Q.; Liu, M. A conducive bioceramic/polymer composite biomaterial for diabetic wound healing. Acta Biomater. 2017, 60, 128–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagnaninchi, P.O.; Yang, Y.; El Haj, A.J.; Maffulli, N. Tissue engineering for tendon repair. Br. J. Sports Med. 2007, 41, e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Deng, G.; Chen, W.; Ye, X.; Mo, X. A novel electrospun-aligned nanoyarn-reinforced nanofibrous scaffold for tendon tissue engineering. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 122, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Wang, J.; Ye, K.; Li, D.; Ai, C.; Sheng, D.; Jin, W.; Liu, X.; Zhi, Y.; Jiang, J. Dual-layer aligned-random nanofibrous scaffolds for improving gradient microstructure of tendon-to-bone healing in a rabbit extra-articular model. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 3481–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Dong, S.; Zhou, Q.; Mo, X.; Song, L.; Hou, T.; Wu, J.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Li, P. The effect of mechanical stimulation on the maturation of TDSCs-poly(l-lactide-co-ε-caprolactone)/collagen scaffold constructs for tendon tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 2760–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, S.; Ang, L.T.; Goh, J.C.H.; Toh, S.-L. Growth factor delivery through electrospun nanofibers in scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2010, 93A, 1539–1550. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Y.J.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Jing, Z.Y.; Liu, Y.Y.; Yin, D.C. Electrospun heparin-loaded core-shell nanofiber sutures for achilles tendon regeneration in vivo. Macromol. Biosci. 2018, 18, 1800041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; Di, N.; Song, L.; Li, S.; Li, D.; Xiang, Y.; Liu, W. Fabrication of electrospun poly(l-lactide-co-ε-caprolactone)/collagen nanoyarn network as a novel, three-dimensional, macroporous, aligned scaffold for tendon tissue engineering. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2013, 19, 925–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riggin, C.N.; Qu, F.; Dong, H.K.; Huegel, J.; Steinberg, D.R.; Kuntz, A.F.; Soslowsky, L.J.; Mauck, R.L.; Bernstein, J. Electrospun PLGA nanofiber scaffolds release ibuprofen faster and degrade slower after in vivo implantation. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 45, 2348–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tellado, S.F.; Balmayor, E.R.; Griensven, M.V. Strategies to engineer tendon/ligament-to-bone interface: Biomaterials, cells and growth factors. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 94, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, S.; Toh, S.L.; Goh, J.C.H. A bFGF-releasing silk/PLGA-based biohybrid scaffold for ligament/tendon tissue engineering using mesenchymal progenitor cells. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 2990–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, C.N.; Schwartz, A.G.; Liu, W.; Xie, J.; Havlioglu, N.; Sakiyamaelbert, S.E.; Silva, M.J.; Xia, Y.; Gelberman, R.H.; Thomopoulos, S. Controlled delivery of mesenchymal stem cells and growth factors using a nanofiber scaffold for tendon repair. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 6905–6914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Blackwood, K.; Doustgani, A.; Poh, P.; Steck, R.M.; Stevens, M.; Woodruff, M. Melt-electrospun polycaprolactone strontium-substituted bioactive glass scaffolds for bone regeneration. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2014, 102, 3140–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Cosme, J.G.; Xu, T.; Miszuk, J.M.; Picciani, P.H.; Fong, H.; Sun, H. Three dimensional electrospun PCL/PLA blend nanofibrous scaffolds with significantly improved stem cells osteogenic differentiation and cranial bone formation. Biomaterials 2016, 115, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poologasundarampillai, G.; Wang, D.; Li, S.; Nakamura, J.; Bradley, R.; Lee, P.D.; Stevens, M.M.; McPhail, D.S.; Kasuga, T.; Jones, J.R. Cotton-wool-like bioactive glasses for bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 3733–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Miszuk, J.M.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, H.; Fong, H. Electrospun polycaprolactone 3D nanofibrous scaffold with interconnected and hierarchically structured pores for bone tissue engineering. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2015, 4, 2238–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Chen, S.; Morsi, Y.; Elhamshary, H.; El-newehy, M.; Fan, C.; Mo, X. Superabsorbent 3D scaffold based on electrospun nanofibers for cartilage tissue engineering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 24415–24425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Yu, J.; Tang, X.; Ge, J.; Ding, B. Ultralight nanofibre-assembled cellular aerogels with superelasticity and multifunctionality. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, F.R.; Hou, Q.; Oreffo, R.O. Delivery systems for bone growth factors—The new players in skeletal regeneration. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2004, 56, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberman, J.R.; Daluiski, A.; Einhorn, T.A. The role of growth factors in the repair of bone. Biology and clinical applications. JBJS 2002, 84-A, 1032–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Su, Q.; Liu, W.; Lim, M.; Venugopal, J.R.; Mo, X.; Ramakrishna, S.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; El-Newehy, M. Controlled release of bone morphogenetic protein 2 and dexamethasone loaded in core–shell PLLACL–collagen fibers for use in bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimer, A.L.; Öner, F.C.; Vaccaro, A.R. Spinal reconstruction and bone morphogenetic proteins: Open questions. Injury 2009, 40, S32–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.Y.; Duan, Z.X.; Guo, X.D.; Li, J.F.; Lu, H.W.; Zheng, Q.X.; Quan, D.P.; Yang, S.H. Bone induction by biomimetic PLGA-(PEG-ASP)n copolymer loaded with a novel synthetic BMP-2-related peptide in vitro and in vivo. J. Control. Release 2010, 144, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, Y.; Tanihara, M.; Suzuki, K.; Saitou, A.; Sufan, W.; Nishimura, Y. Alginate hydrogel linked with synthetic oligopeptide derived from BMP-2 allows ectopic osteoinduction in vivo. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2015, 50, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, L.; Boda, S.K.; Wang, H.; Teusink, M.J.; Shuler, F.D.; Xie, J. Novel 3D hybrid nanofiber aerogels coupled with BMP-2 peptides for cranial bone regeneration. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1701415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Feng, W.; Qiu, K.; Chen, L.; Wang, W.; Nie, W.; Mo, X.; He, C. BMP-2 derived peptide and dexamethasone incorporated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for enhanced osteogenic differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 15777–15789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, K.; Kuang, H.; You, Z.; Morsi, Y.; Mo, X. Electrospun Nanofibers for Tissue Engineering with Drug Loading and Release. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11040182
Ye K, Kuang H, You Z, Morsi Y, Mo X. Electrospun Nanofibers for Tissue Engineering with Drug Loading and Release. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(4):182. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11040182
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Kaiqiang, Haizhu Kuang, Zhengwei You, Yosry Morsi, and Xiumei Mo. 2019. "Electrospun Nanofibers for Tissue Engineering with Drug Loading and Release" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 4: 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11040182
APA StyleYe, K., Kuang, H., You, Z., Morsi, Y., & Mo, X. (2019). Electrospun Nanofibers for Tissue Engineering with Drug Loading and Release. Pharmaceutics, 11(4), 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11040182