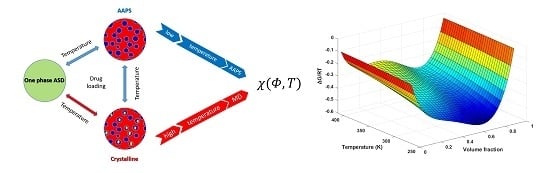
The Investigation of Flory–Huggins Interaction Parameters for Amorphous Solid Dispersion Across the Entire Temperature and Composition Range
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theory and Experimental Treatments
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Sample Preparation
3.2.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
3.2.3. Dynamic Vapor Absorption (DVS)
3.2.4. Thermal Analysis
3.2.5. Raman Chemical Mapping
3.2.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. Variations of Drug-polymer Interaction at Different Drug Loading
4.2. The Issues Associated with the Prediction of Drug Solubility Limits in Polymer
4.3. Measurements for χ13 and χ23 Using DVS
4.4. Detection of AAPS in aFD-PVPK15-Water Ternary System
4.5. F–H Interaction Parameters for aFD-PVPK15 at Various Conditions
4.6. FD-PVPK15 Binary Phase Diagram
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kawabata, Y.; Wada, K.; Nakatani, M.; Yamada, S.; Onoue, S. Formulation design for poorly water-soluble drugs based on biopharmaceutics classification system: Basic approaches and practical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 420, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalepu, S.; Nekkanti, V. Insoluble drug delivery strategies: Review of recent advances and business prospects. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2015, 5, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rams-Baron, M.; Jachowicz, R.; Boldyreva, E.; Zhou, D.; Jamroz, W.; Paluch, M. Amorphous Drugs: Benefits and Challenges; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; ISBN 9783319720029. [Google Scholar]
- Vasconcelos, T.; Marques, S.; das Neves, J.; Sarmento, B. Amorphous solid dispersions: Rational selection of a manufacturing process. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 100, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Dai, W.-G. Fundamental aspects of solid dispersion technology for poorly soluble drugs. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2014, 4, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baghel, S.; Cathcart, H.; O’Reilly, N.J. Polymeric Amorphous Solid Dispersions: A Review of Amorphization, Crystallization, Stabilization, Solid-State Characterization, and Aqueous Solubilization of Biopharmaceutical Classification System Class II Drugs. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2527–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jermain, S.V.; Brough, C.; Williams, R.O. Amorphous solid dispersions and nanocrystal technologies for poorly water-soluble drug delivery–An update. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 535, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmkemper, K.; Kyeremateng, S.O.; Heinzerling, O.; Degenhardt, M.; Sadowski, G. Long-Term Physical Stability of PVP- and PVPVA-Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.D.; Wildfong, P.L.D. Informatics calibration of a molecular descriptors database to predict solid dispersion potential of small molecule organic solids. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 418, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laitinen, R.; Löbmann, K.; Strachan, C.J.; Grohganz, H.; Rades, T. Emerging trends in the stabilization of amorphous drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 453, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luebbert, C.; Klanke, C.; Sadowski, G. Investigating phase separation in amorphous solid dispersions via Raman mapping. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 535, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Taylor, L.S. Microstructure Formation for Improved Dissolution Performance of Lopinavir Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 1751–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Jones, D.S.; Donnelly, C.; Brannigan, T.; Li, S.; Andrews, G.P. A New Method of Constructing a Drug-Polymer Temperature-Composition Phase Diagram Using Hot-Melt Extrusion. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 1379–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahieu, A.; Willart, J.F.; Dudognon, E.; Daneìde, F.; Descamps, M. A new protocol to determine the solubility of drugs into polymer matrixes. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsac, P.J.; Shamblin, S.L.; Taylor, L.S. Theoretical and practical approaches for prediction of drug-polymer miscibility and solubility. Pharm. Res. 2006, 23, 2417–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Booth, J.; Meehan, E.; Jones, D.S.D.S.; Li, S.; Andrews, G.P.G.P. Construction of drug-polymer thermodynamic phase diagrams using flory-huggins interaction theory: Identifying the relevance of temperature and drug weight fraction to phase separation within solid dispersions. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, C.; Tian, Y.; Potter, C.C.C.; Jones, D.S.D.S.; Andrews, G.P.G.P. Probing the Effects of Experimental Conditions on the Character of Drug-Polymer Phase Diagrams Constructed Using Flory-Huggins Theory. Pharm. Res. 2014, 32, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, H.; Wakabayashi, S.; Kikuchi, J.; Ida, Y.; Kadota, K.; Tozuka, Y. Anomalous role change of tertiary amino and ester groups as hydrogen acceptors in eudragit E based solid dispersion depending on the concentration of naproxen. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 1050–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarode, A.L.; Sandhu, H.; Shah, N.; Malick, W.; Zia, H. Hot Melt Extrusion for Amorphous Solid Dispersions: Temperature and Moisture Activated Drug−Polymer Interactions for Enhanced Stability. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 3665–3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, P.; Mohapatra, S.; Gopinath, T.; Vogt, F.G.; Suryanarayanan, R. Role of the Strength of Drug-Polymer Interactions on the Molecular Mobility and Crystallization Inhibition in Ketoconazole Solid Dispersions. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 3339–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karavas, E.; Ktistis, G.; Xenakis, A.; Georgarakis, E. Effect of hydrogen bonding interactions on the release mechanism of felodipine from nanodispersions with polyvinylpyrrolidone. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2006, 63, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzybowska, K.; Chmiel, K.; Knapik-Kowalczuk, J.; Grzybowski, A.; Jurkiewicz, K.; Paluch, M. Molecular factors governing the liquid and glassy states recrystallization of celecoxib in binary mixtures with excipients of different molecular weights. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 1154–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Nollenberger, K.; Albers, J.; Moffat, J.; Craig, D.; Qi, S. The effect of processing on the surface physical stability of amorphous solid dispersions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 88, 897–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, S.P.; Arora, K.K.; Kwong, E.; Templeton, A.; Clas, S.D.; Suryanarayanan, R. Correlation between molecular mobility and physical stability of amorphous itraconazole. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Jones, D.S.D.S.; Andrews, G.P.G.P. An investigation into the role of polymeric carriers on crystal growth within amorphous solid dispersion systems. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 150306122810000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raina, S.A.; Alonzo, D.E.; Zhang, G.G.Z.; Gao, Y.; Taylor, L.S. Impact of polymers on the crystallization and phase transition kinetics of amorphous nifedipine during dissolution in aqueous media. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 3565–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Yoreo, J.J.; Gilbert, P.U.P.A.; Sommerdijk, N.A.J.M.; Penn, R.L.; Whitelam, S.; Joester, D.; Zhang, H.; Rimer, J.D.; Navrotsky, A.; Banfield, J.F.; et al. Crystallization by particle attachment in synthetic, biogenic, and geologic environments. Science 2015, 349, aaa6760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebauer, D.; Cölfen, H. Prenucleation clusters and non-classical nucleation. Nano Today 2011, 6, 564–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rieger, J.; Frechen, T.; Cox, G.; Heckmann, W.; Schmidt, C.; Thieme, J. Precursor structures in the crystallization/precipitation processes of CaCO3 and control of particle formation by polyelectrolytes. Faraday Discuss. 2007, 136, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Taylor, L.S. Nanoscale Infrared, Thermal, and Mechanical Characterization of Telaprevir-Polymer Miscibility in Amorphous Solid Dispersions Prepared by Solvent Evaporation. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 1123–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumondor, A.C.F.; Wikstroem, H.; Van Eerdenbrugh, B.; Taylor, L. Understanding the Tendency of Amorphous Solid Dispersions to Undergo Amorphous-Amorphous Phase Separation in the Presence of Absorbed Moisture. AAPS PharmSciTech 2011, 12, 1209–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumondor, A.C.F.; Taylor, L.S. Effect of polymer hygroscopicity on the phase behavior of amorphous solid dispersions in the presence of moisture. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luebbert, C.; Sadowski, G. Moisture-induced phase separation and recrystallization in amorphous solid dispersions. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 532, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, T.; Wang, T.T.; Kwei, T.K. Thermally Induced Phase Separation Behavior of Compatible Polymer Mixtures. Macromolecules 1975, 8, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.D.S. Phase Transitions in Polymers: The Role of Metastable States; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 2008; ISBN 9780444519115. [Google Scholar]
- Davey, R.J.; Schroeder, S.L.M.; Ter Horst, J.H. Nucleation of organic crystals - A molecular perspective. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 2167–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahn, J.W.; Hilliard, J.E. Free Energy of a Nonuniform System. III. Nucleation in a Two-Component Incompressible Fluid. J. Chem. Phys. 1959, 31, 688–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnett, P.E.; Carpenter, K.J.; Dawson, S.; Davey, R.J. Solution crystallisation via a submerged liquid–liquid phase boundary: Oiling out. Chem. Commun. 2003, 698–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deneau, E.; Steele, G. An in-line study of oiling out and crystallization. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2005, 9, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajula, K.; Taskinen, M.; Lehto, V.-P.P.; Ketolainen, J.; Korhonen, O. Predicting the Formation and Stability of Amorphous Small Molecule Binary Mixtures from Computationally Determined Flory-Huggins Interaction Parameter and Phase Diagram. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsac, P.J.; Li, T.; Taylor, L.S. Estimation of drug-polymer miscibility and solubility in amorphous solid dispersions using experimentally determined interaction parameters. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tompa, H. Polymer Solutions; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Duarte, Í.; Santos, J.L.; Pinto, J.F.; Temtem, M. Screening methodologies for the development of spray-dried amorphous solid dispersions. Pharm. Res. 2015, 32, 222–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, K.J.; Zografi, G. Water Vapor Absorption into Amorphous Hydrophobic Drug/Poly(vinylpyrrolidone) Dispersions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 91, 2150–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulte, A.M.W.; Naafs, E.M.; van Eeten, F.; Mulder, M.H.V.; Smolders, C.A.; Strathmann, H. Equilibrium thermodynamics of the ternary membrane-forming system nylon, formic acid and water. Polymer 1996, 37, 1647–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barzin, J.; Sadatnia, B. Theoretical phase diagram calculation and membrane morphology evaluation for water/solvent/polyethersulfone systems. Polymer 2007, 48, 1620–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzin, J.; Sadatnia, B. Correlation between macrovoid formation and the ternary phase diagram for polyethersulfone membranes prepared from two nearly similar solvents. J. Memb. Sci. 2008, 325, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuld, N.; Wolf, B.A. Solvent quality as reflected in concentration- and temperature-dependent Flory-Huggins interaction parameters. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2001, 39, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Pui, Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, Z.; Su, C.C.; Hageman, M.; Hussain, M.; Haskell, R.; Stefanski, K.; Foster, K.; et al. Moisture-Induced Amorphous Phase Separation of Amorphous Solid Dispersions: Molecular Mechanism, Microstructure, and Its Impact on Dissolution Performance. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 107, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.C.; Prausnitz, J.M. Thermodynamics of Polymer Compatibility in Ternary Systems. Macromolecules 1974, 7, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, C.B.; Davis, M.T.; Albadarin, A.B.; Walker, G.M. Investigation of the Dependence of the Flory-Huggins Interaction Parameter on Temperature and Composition in a Drug-Polymer System. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 5327–5335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luebbert, C.; Wessner, M.; Sadowski, G. Mutual Impact of Phase Separation/Crystallization and Water Sorption in Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, M.; Taylor, J.S. Ideal Copolymers and the Second-Order Transitions of Synthetic Rubbers. I. Noncrystalline Copolymers. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2011, 26, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knopp, M.M.M.M.; Tajber, L.; Tian, Y.; Olesen, N.E.; Jones, D.S.D.S.; Kozyra, A.; Löbmann, K.; Paluch, K.; Brennan, C.M.C.M.; Holm, R.; et al. A comparative study of different methods for the prediction of drug-polymer solubility. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 150727172228007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.P.; Lipson, J.E.G. Polymer Free Volume and Its Connection to the Glass Transition. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 3987–4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, M.I.; Tomka, I. Effects of the degree of substitution in ethyl cellulose on the clustering of sorbed water. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B 2007, 36, 19–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meere, M.; Pontrelli, G.; McGinty, S. Modelling phase separation in amorphous solid dispersions. Acta Biomater 2019, 94, 410–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, H.; Steinacher, M.; Borca, C.N.; Huthwelker, T.; Murello, A.; Stellacci, F.; Amstad, E. Amorphous CaCO3: Influence of the formation time on its degree of hydration and stability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, jacs.8b08298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratke, L.; Diefenbach, S. Liquid immiscible alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 1995, 15, 263–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Caron, V.; Jones, D.S.D.S.; Healy, A.-M.A.M.; Andrews, G.P.G.P. Using Flory-Huggins phase diagrams as a pre-formulation tool for the production of amorphous solid dispersions: A comparison between hot-melt extrusion and spray drying. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2014, 66, 256–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazhnov, I.V.; Magazù, S.; Maisano, G.; Malomuzh, N.P.; Migliardo, F. Macro- and microdefinitions of fragility of hydrogen-bonded glass-forming liquids. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2006, 73, 031201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B.D. Predicting Solubility/Miscibility in Amorphous Dispersions: It Is Time to Move Beyond Regular Solution Theories. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 107, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumondor, A.C.F.; Stanford, L.A.; Taylor, L.S. Effects of polymer type and storage relative humidity on the kinetics of felodipine crystallization from amorphous solid dispersions. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 2599–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karavas, E.; Ktistis, G.; Xenakis, A.; Georgarakis, E. Miscibility behavior and formation mechanism of stabilized felodipine-polyvinylpyrrolidone amorphous solid dispersions. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2005, 31, 473–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Χ | Temperature of Dynamic Vapor Absorption Experiment (°C) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | |||||
| χ13 (aFD-water) | 5.68 ± 0.05 | 3.73 ± 0.07 | 2.16 ± 0.37 | 2.06 ± 0.31 | ||||
| χ23 (PVPK15-water) | 0.497 ± 0.01 | 0.404 ± 0.03 | 0.169 ± 0.05 | −0.116 ± 0.02 | ||||
| B | A | a0 | a1 | b0 | b1 | c0 | c1 | |
| aFD-water | 1.27 × 104 | −36.5 | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| PVPK15-water | / | / | −68.5 | 2.16 × 104 | 185 | −5.79 × 104 | −120 | 3.76 × 104 |
| Number of Glass Transition | Temperature of one Phase to AAPS (°C) at Different Drug Loadings | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 35% | 40% | 45% | 50% | |
| One glass transition | 60 | 55 | 50 | 48 |
| Two glass transitions | 58 | 53 | 48 | 46 |
| Temper-ature (°C) | Volume Fraction (%) | F–H interaction Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FD | PVPK15 | Water | χ12 * (aFD-PVPK15) | χ13 (aFD-Water) | χ23 (PVPK15-Water) | |
| 47 | 44.5 ± 0.2 | 45.2 ± 0.4 | 10.2 ± 0.4 | −0.284 | 3.11 | 0.651 |
| 49 | 39.9 ± 1.0 | 49.5 ± 1.0 | 10.7 ± 1.0 | −0.219 | 2.86 | 0.662 |
| 54 | 34.8 ± 0.5 | 53.0 ± 0.5 | 12.3 ± 0.5 | −0.0823 | 2.26 | 0.693 |
| 59 | 29.9 ± 0.8 | 56.4 ± 0.8 | 13.7 ± 0.8 | 0.0293 | 1.68 | 0.724 |
| Temperature (°C) | Volume Fraction (%) | χ12 Derived from Two Different Methods | |
|---|---|---|---|
| FD | PVPK15 | ||
| 141.5 ± 0.2 | 94.9 | 5.08 | −2.66 * |
| 140.5 ± 0.1 | 89.9 | 10.1 | −1.84 * |
| 139.2 ± 0.4 | 84.8 | 15.2 | −1.48 * |
| 137.3 ± 0.3 | 79.8 | 20.2 | −1.40 * |
| 59 | 34.6 ± 0.8 | 65.4 ± 0.8 | 0.0293 § |
| 54 | 39.6 ± 0.5 | 60.4 ± 0.5 | −0.0823 § |
| 49 | 44.6 ± 1.0 | 55.4 ± 1.0 | −0.219 § |
| 47 | 49.6 ± 0.4 | 50.4 ± 0.4 | −0.284 § |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, Y.; Qian, K.; Jacobs, E.; Amstad, E.; Jones, D.S.; Stella, L.; Andrews, G.P. The Investigation of Flory–Huggins Interaction Parameters for Amorphous Solid Dispersion Across the Entire Temperature and Composition Range. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11080420
Tian Y, Qian K, Jacobs E, Amstad E, Jones DS, Stella L, Andrews GP. The Investigation of Flory–Huggins Interaction Parameters for Amorphous Solid Dispersion Across the Entire Temperature and Composition Range. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(8):420. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11080420
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Yiwei, Kaijie Qian, Esther Jacobs, Esther Amstad, David S. Jones, Lorenzo Stella, and Gavin P. Andrews. 2019. "The Investigation of Flory–Huggins Interaction Parameters for Amorphous Solid Dispersion Across the Entire Temperature and Composition Range" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 8: 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11080420
APA StyleTian, Y., Qian, K., Jacobs, E., Amstad, E., Jones, D. S., Stella, L., & Andrews, G. P. (2019). The Investigation of Flory–Huggins Interaction Parameters for Amorphous Solid Dispersion Across the Entire Temperature and Composition Range. Pharmaceutics, 11(8), 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11080420