MRI/Photoluminescence Dual-Modal Imaging Magnetic PLGA Nanocapsules for Theranostics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Synthesis of PLGA-BPLP Copolymer
2.2. Synthesis of Oleic Acid Coated SPIONs
2.3. Fabrication of Functional PLGA-BPLP NCs and Encapsulation of BSA
2.4. Physicochemical Characterization of PLGA-BPLP, SPIONs, and NCs
2.4.1. Absorption Spectroscopies of the Polymers
2.4.2. Size Distribution and Disperse Stability of the NCs
2.4.3. Electron Microscopies
2.4.4. Magnetometry
2.4.5. Fluorescence Properties
2.5. MRI Phantoms of the NCs
2.6. In Vitro Toxicity Evaluation of the NCs
2.7. In Vitro Observation of NCs Cellular Uptake
2.8. BSA Loading in NCs and Release Kinetics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Photoluminescent PLGA-BPLP Copolymer
3.2. Fabrication of PLGA-BPLP NCs Combining Other Functional Moieties
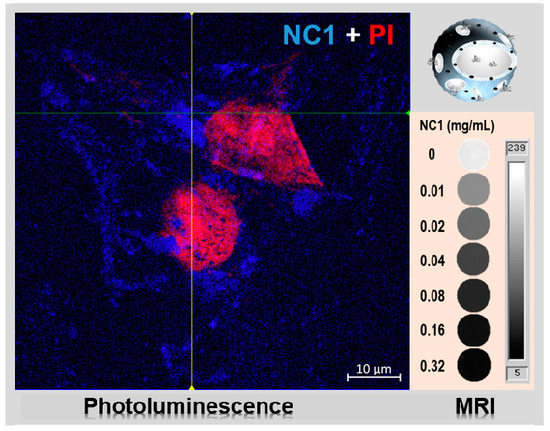
3.3. Imaging Performance of the Magnetic Photoluminescent NCs
3.4. Cell Viability after NCs Uptake
3.5. Protein Loading and In Vitro Release
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, D.; Shin, K.; Kwon, S.G.; Hyeon, T. Synthesis and biomedical applications of multifunctional nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1802309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, L.J.; Stammes, M.A.; Que, I.; van Beek, E.R.; Knol-Blankevoort, V.T.; Snoeks, T.J.A.; Chan, A.; Kaijzel, E.L.; Lowik, C. Effect of PLGA NP size on efficiency to target traumatic brain injury. J. Control. Release 2016, 223, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, H.; Tang, X.; Xu, J.; Jin, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, S.; Gou, J.; Jin, X. Simple and tunable surface coatings via polydopamine for modulating pharmacokinetics, cell uptake and biodistribution of polymeric nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 15864–15876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zeng, F.; Jin, H.; Xu, Q.; Huang, Y. Dual-targeting magnetic PLGA nanoparticles for codelivery of paclitaxel and curcumin for brain tumor therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 32159–32169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danhier, F.; Ansorena, E.; Silva, J.M.; Coco, R.; Le Breton, A.; Préat, V. PLGA-based nanoparticles: An overview of biomedical applications. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 505–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swider, E.; Koshkina, O.; Tel, J.; Cruz, L.J.; de Vries, I.J.M.; Srinivas, M. Customizing poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) particles for biomedical applications. Acta. Biomater. 2018, 73, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mir, M.; Ahmed, N.; ur Rehman, A. Recent applications of PLGA based nanostructures in drug delivery. Coll. Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 159, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, Z.; Tan, T.; Liu, C.; Duan, J.; Wang, W.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Z.; Huang, Q.; Dou, P. Targeted delivery of hesperetin to cartilage attenuates osteoarthritis by bimodal imaging with Gd2 (CO3) 3@ PDA nanoparticles via TLR-2/NF-κB/Akt signaling. Biomaterials 2019, 205, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Xu, J.; Xu, L.; Sun, X.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, R.; Liu, Z. Cancer cell membrane-coated adjuvant nanoparticles with mannose modification for effective anticancer vaccination. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 5121–5129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, D.X.; Householder, K.T.; Ceton, R.; Kovalik, T.; Heffernan, J.M.; Shankar, R.V.; Bowser, R.P.; Wechsler-Reya, R.J.; Sirianni, R.W. Optical barcoding of PLGA for multispectral analysis of nanoparticle fate in vivo. J. Control. Release 2017, 253, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.K.; Utsumi, T.; Seo, Y.E.; Deng, Y.; Satoh, A.; Saltzman, W.M.; Iwakiri, Y. Cellular distribution of injected PLGA-nanoparticles in the liver. Nanomedicine 2016, 12, 1365–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdel-Mottaleb, M.M.; Beduneau, A.; Pellequer, Y.; Lamprecht, A. Stability of fluorescent labels in PLGA polymeric nanoparticles: Quantum dots versus organic dyes. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 494, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, R.L.; Householder, K.T.; Chung, E.P.; Prakapenka, A.V.; DiPerna, D.M.; Sirianni, R.W. A critical evaluation of drug delivery from ligand modified nanoparticles: Confounding small molecule distribution and efficacy in the central nervous system. J. Control. Release 2015, 220, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jaiswal, J.K.; Mattoussi, H.; Mauro, J.M.; Simon, S.M. Long-term multiple color imaging of live cells using quantum dot bioconjugates. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamieson, T.; Bakhshi, R.; Petrova, D.; Pocock, R.; Imani, M.; Seifalian, A.M. Biological applications of quantum dots. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 4717–4732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gautam, S.; Liu, L.; Dey, J.; Chen, W.; Mason, R.P.; Serrano, C.A.; Schug, K.A.; Tang, L. Development of aliphatic biodegradable photoluminescent polymers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 10086–10091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, J.; Guo, J.; Xie, Z.; Shan, D.; Gerhard, E.; Qian, G.; Yang, J. Fluorescence imaging enabled poly(lactide-co-glycolide). Acta Biomater. 2016, 29, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, W.; Zeng, X.; Wu, J.; Zhu, X.; Yu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, G.; Mei, L. Polydopamine-based surface modification of novel nanoparticle-aptamer bioconjugates for in vivo breast cancer targeting and enhanced therapeutic effects. Theranostics 2016, 6, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Van Treuren, T.; Ranjan, A.P.; Chaudhary, P.; Vishwanatha, J.K. In vivo imaging and biodistribution of near infrared dye loaded brain-metastatic-breast-cancer-cell-membrane coated polymeric nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 265101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Moragas, L.; Yu, S.-M.; Murillo-Cremaes, N.; Laromaine, A.; Roig, A. Scale-up synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles by microwave-assisted thermal decomposition. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 281, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzyk, W.; Bednarz, S.; Bogdał, D. Luminescence phenomena of biodegradable photoluminescent poly(diol citrates). Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 6445–6447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carenza, E.; Jordan, O.; Martinez-San Segundo, P.; Jiřík, R.; Starčuk Jr, Z.; Borchard, G.; Rosell, A.; Roig, A. Encapsulation of VEGF 165 into magnetic PLGA nanocapsules for potential local delivery and bioactivity in human brain endothelial cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 2538–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gref, R.; Lück, M.; Quellec, P.; Marchand, M.; Dellacherie, E.; Harnisch, S.; Blunk, T.; Müller, R. ‘Stealth’corona-core nanoparticles surface modified by polyethylene glycol (PEG): Influences of the corona (PEG chain length and surface density) and of the core composition on phagocytic uptake and plasma protein adsorption. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2000, 18, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butoescu, N.; Seemayer, C.A.; Palmer, G.; Guerne, P.-A.; Gabay, C.; Doelker, E.; Jordan, O. Magnetically retainable microparticles for drug delivery to the joint: Efficacy studies in an antigen-induced arthritis model in mice. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11, R72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.-X.J. Superparamagnetic iron oxide based MRI contrast agents: Current status of clinical application. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2011, 1, 35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pakulska, M.M.; Donaghue, I.E.; Obermeyer, J.M.; Tuladhar, A.; McLaughlin, C.K.; Shendruk, T.N.; Shoichet, M.S. Encapsulation-free controlled release: Electrostatic adsorption eliminates the need for protein encapsulation in PLGA nanoparticles. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1600519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]









| NCs Type | Shell Polymers (wt%) | SPIONs Loading (wt%) | Ms (eum/g) | Size (DLS) | BSA Loading (wt%) | BSA EE% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLGA | PLGA-BPLP * | PLGA-PEG | d. nm | PdI | |||||
| NC1.non-PEGylated | 10 | 90 | / | 5.7 | 4.0 | 272 | 0.11 | 0.96 | 38.5 |
| NC2.PEGylated | 3 | 90 | 7 | 6.0 | 4.2 | 265 | 0.05 | 1.01 | 41.3 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; García-Gabilondo, M.; Rosell, A.; Roig, A. MRI/Photoluminescence Dual-Modal Imaging Magnetic PLGA Nanocapsules for Theranostics. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12010016
Zhang Y, García-Gabilondo M, Rosell A, Roig A. MRI/Photoluminescence Dual-Modal Imaging Magnetic PLGA Nanocapsules for Theranostics. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yajie, Miguel García-Gabilondo, Anna Rosell, and Anna Roig. 2020. "MRI/Photoluminescence Dual-Modal Imaging Magnetic PLGA Nanocapsules for Theranostics" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12010016
APA StyleZhang, Y., García-Gabilondo, M., Rosell, A., & Roig, A. (2020). MRI/Photoluminescence Dual-Modal Imaging Magnetic PLGA Nanocapsules for Theranostics. Pharmaceutics, 12(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12010016