Montelukast Nanocrystals for Transdermal Delivery with Improved Chemical Stability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of MTK Nanocrystal Suspension and Hydrogel
2.3. Preparation of Drug Solution and Conventional Hydrogel
2.4. Morphological and Physicochemical Characterization of MTK Nanocrystal Formulations
2.4.1. Particle Size and Zeta Potential of MTK Nanocrystals
2.4.2. Morphology of MTK Nanocrystals
2.4.3. X-ray Powder Diffraction Analysis
2.4.4. Thermal Analysis
2.4.5. Drug Content in the Nanocrystal Suspension
2.5. In Vitro Dissolution Profiles of MTK Nanocrystal Formulations
2.6. Photo-Stability of MTK Nanocrystal Formulations
2.7. In Vivo Transdermal Delivery of MTK Nanocrystal Formulations
2.7.1. Animals and Experimental Protocols
2.7.2. LC/MS-MS Analysis and Calculation of Pharmacokinetic Parameters
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Selection of Steric Stabilizer of MTK Nanocrystal Suspension
3.2. Effect of Process Parameters on Size and Homogeneity of MTK Nanocrystal Suspension
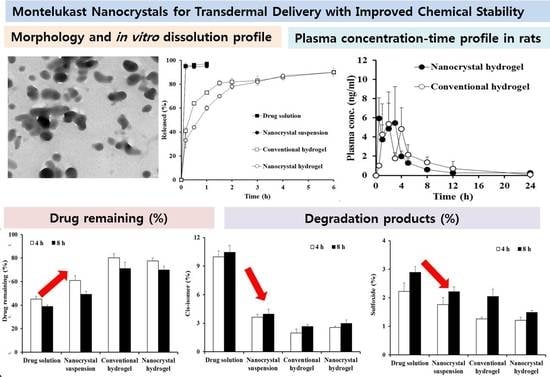
3.3. Morphological and Physicochemical Characteristics of MTK Nanocrystal Suspension and Hydrogel
3.4. In Vitro Drug Release Profile from MTK Nanocrystal Suspension and Hydrogel
3.5. Photo-Stability of MTK Nanocrystal Formulations
3.6. In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Profile after Topical Administration of MTK Nanocrystal Hydrogel in Rats
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diamant, Z.; Mantzouranis, E.; Bjermer, L. Montelukast in the treatment of asthma and beyond. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 5, 639–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lambiase, A.; Bonini, S.; Rasi, G.; Coassin, M.; Bruscolini, A.; Bonini, S. Montelukast, a leukotriene receptor antagonist, in vernal keratoconjunctivitis associated with asthma. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2003, 121, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reiss, T.F.; Chervinsky, P.; Dockhorn, R.J.; Shingo, S.; Seidenberg, B.; Edwards, T.B. Montelukast, a once-daily leukotriene receptor antagonist, in the treatment of chronic asthma: A multicenter, randomized, double-blind trial. Montelukast Clinical Research Study Group. Arch. Intern. Med. 1998, 158, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rahman, S.O.; Singh, R.K.; Hussain, S.; Akhtar, M.; Najmi, A.K. A novel therapeutic potential of cysteinyl leukotrienes and their receptors modulation in the neurological complications associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 842, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, M.A.; Abdelsalam, R.M.; Kenawy, S.A.; Attia, A.S. Montelukast, a cysteinyl leukotriene receptor-1 antagonist protects against hippocampal injury induced by transient global cerebral ischemia and reperfusion in rats. Neurochem. Res. 2015, 40, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschallinger, J.; Schäffner, I.; Klein, B.; Gelfert, R.; Rivera, F.J.; Illes, S.; Grassner, L.; Janssen, M.; Rotheneichner, P.; Schmuckermair, C.; et al. Structural and functional rejuvenation of the aged brain by an approved anti-asthmatic drug. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.W.; Kim, Y.H.; Yousaf, A.M.; Kim, D.S.; Kwon, T.K.; Park, J.H.; Kim, Y.I.; Park, J.H.; Jin, S.G.; Kim, K.S.; et al. Novel montelukast sodium-loaded stable oral suspension bioequivalent to the commercial granules in rats. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2016, 39, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumu, A.; DiMaso, M.; Löbenberg, R. Dynamic dissolution testing to establish in vitro/in vivo correlations for montelukast sodium, a poorly soluble drug. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 2778–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, H.S.; Gundare, S.A. Preparation, characterization and pulmonary pharmacokinetics of xyloglucan microspheres as dry powder inhalation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 102, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balani, S.K.; Xu, X.; Pratha, V.; Koss, M.A.; Amin, R.D.; Dufresne, C.; Miller, R.R.; Arison, B.H.; Doss, G.A.; Chiba, M.; et al. Metabolic profiles of montelukast sodium (Singulair), a potent cysteinyl leukotriene1 receptor antagonist, in human plasma and bile. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1997, 25, 1282–1287. [Google Scholar]
- Al Omari, M.M.; Zoubi, R.M.; Hasan, E.I.; Khader, T.Z.; Badwan, A.A. Effect of light and heat on the stability of montelukast in solution and in its solid state. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 45, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bos, J.D.; Meinardi, M.M. The 500 dalton rule for the skin penetration of chemical compounds and drugs. Exp. Dermatol. 2000, 9, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madison, K.C. Barrier function of the skin: “la raison d’être” of the epidermis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2003, 121, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kong, Q.; Higasijima, K.; Wakabayashi, R.; Tahara, Y.; Kitaoka, M.; Obayashi, H.; Hou, Y.; Kamiya, N.; Goto, M. Transcutaneous delivery of immunomodulating pollen extract-galactomannan conjugate by solid-in-oil nanodispersions for pollinosis immunotherapy. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeb, A.; Arif, S.T.; Malik, M.; Shah, F.A.; Din, F.U.; Qureshi, O.S.; Lee, E.S.; Lee, G.Y.; Kim, J.K. Potential of nanoparticulate carriers for improved drug delivery via skin. J. Pharm. Investig. 2019, 49, 485–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hajjar, B.; Zier, K.I.; Khalid, N.; Azarmi, S.; Löbenberg, R. Evaluation of a microemulsion-based gel formulation for topical drug delivery of diclofenac sodium. J. Pharm. Investig. 2018, 48, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, C.; Ito, Y.; Nagai, N. Enhanced percutaneous absorption of cilostazol nanocrystals using aqueous gel patch systems and clarification of the absorption mechanism. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 3501–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pireddu, R.; Sinico, C.; Ennas, G.; Marongiu, F.; Muzzalupo, R.; Lai, F.; Fadda, A.M. Novel nanosized formulations of two diclofenac acid polymorphs to improve topical bioavailability. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 77, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, V.K.; Singh, Y.; Meher, J.G.; Gupta, S.; Chourasia, M.K. Engineered nanocrystal technology: In-vivo fate, targeting and applications in drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2014, 183, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Parmar, P.K.; Bansal, A.K. Evaluation of different techniques for size determination of drug nanocrystals: A case study of celecoxib nanocrystalline solid dispersion. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chogale, M.M.; Ghodake, V.N.; Patravale, V.B. Performance parameters and characterizations of nanocrystals: A brief review. Pharmaceutics 2016, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shegokar, R.; Müller, R.H. Nanocrystals: Industrially feasible multifunctional formulation technology for poorly soluble actives. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 399, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patzelt, A.; Richter, H.; Knorr, F.; Schäfer, U.; Lehr, C.M.; Dähne, L.; Sterry, W.; Lademann, J. Selective follicular targeting by modification of the particle sizes. J. Control. Release 2011, 150, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Rosso, J.Q.; Harper, J.; Pillai, R.; Moore, R. Tretinoin photostability: Comparison of micronized tretinoin (0.05%) gel and tretinoin (0.025%) gel following exposure to ultraviolet a light. J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2012, 5, 27–29. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, F.; Pireddu, R.; Corrias, F.; Fadda, A.M.; Valenti, D.; Pini, E.; Sinico, C. Nanosuspension improves tretinoin photostability and delivery to the skin. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 458, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, A.; Chen, D.; Jiang, L.; Pan, Y.; Tao, Y.; Huang, L.; Liu, Z.; Xie, S.; Yuan, Z. Preparation, characterization and pharmacokinetics of cyadox nanosuspension. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Permana, A.D.; McCrudden, M.T.C.; Donnelly, R.F. Enhanced intradermal delivery of nanosuspensions of antifilariasis drugs using dissolving microneedles: A proof of concept study. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, H.; Ichikawa, A.; Ikeuchi-Takahashi, Y.; Hattori, Y.; Onishi, H. Nanogels of succinylated glycol chitosan-succinyl prednisolone conjugate: Preparation, in vitro characteristics and therapeutic potential. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, S.W.; Shin, D.H.; Kim, J.S. Liposomal itraconazole formulation for the treatment of glioblastoma using inclusion complex with HP-β-CD. J. Pharm. Investig. 2019, 49, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniyar, M.G.; Kokare, C.R. Formulation and evaluation of spray dried liposomes of lopinavir for topical application. J. Pharm. Investig. 2019, 49, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.H.; Na, Y.G.; Lee, H.K.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, H.J.; Bang, K.H.; Wang, M.; Pyo, Y.C.; Huh, H.W.; Cho, C.W. Effect of surfactant on the preparation and characterization of gemcitabine-loaded particles. J. Pharm. Investig. 2019, 49, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okafor, N.I.; Nkanga, C.I.; Walker, R.B.; Noundou, X.S.; Krause, R.W.M. Encapsulation and physicochemical evaluation of efavirenz in liposomes. J. Pharm. Investig. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpagaus, C.J. PLA/PLGA nanoparticles prepared by nano spray drying. J. Pharm. Investig. 2019, 49, 405–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montelukast Sodium USP-NF. Available online: https://www.uspnf.com/sites/default/files/usp_pdf/EN/USPNF/2009-10USPMontelukastSodiumProspectiveHarmonization.pdf (accessed on 13 November 2019).
- Kim, D.Y. Development and Validation of a Sensitive LC-MS/MS Method to Determine Montelukast in Rat Plasma Using Liquid-Liquid Extraction and Multiple Reaction Monitoring. Master’s Thesis, Dankook University, Cheonan, Korea, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, L.S.; Zografi, G. Spectroscopic characterization of interactions between PVP and indomethacin in amorphous molecular dispersions. Pharm. Res. 1997, 14, 1691–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, H.; Morris, K.R.; Park, K. Study on the interactions between polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) and acetaminophen crystals: Partial dissolution pattern change. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 94, 2166–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, M.J.; Lee, D.R.; Im, S.H.; Yoon, J.A.; Shin, C.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Jang, S.W.; Choi, Y.W.; Han, Y.T.; Kang, M.J. Design and in vivo evaluation of entecavir-3-palmitate microcrystals for subcutaneous sustained delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 130, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pireddu, R.; Caddeo, C.; Valenti, D.; Marongiu, F.; Scano, A.; Ennas, G.; Lai, F.; Fadda, A.M.; Sinico, C. Diclofenac acid nanocrystals as an effective strategy to reduce in vivo skin inflammation by improving dermal drug bioavailability. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 143, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Lu, S.; Zeng, L.; Wang, Y.; Song, W.; Liu, J. Pramipexole nanocrystals for transdermal permeation: Characterization and its enhancement micro-mechanism. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 124, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faramarzi, P.; Haririan, I.; Ghanbarzadeh, S.; Yaqoubi, S.; Hamishehkar, H. Development of carrier free montelukast dry powder inhalation formulation. Pharm. Ind. 2015, 77, 1535–1542. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelghany, S.; Tekko, I.A.; Vora, L.; Larrañeta, E.; Permana, A.D.; Donnelly, R.F. Nanosuspension-based dissolving microneedle arrays for intradermal delivery of curcumin. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.H.; Kwon, T.K.; Kim, Y.I.; Park, J.H.; Woo, J.S. Syrup formulation with enhanced light stability comprising montelukast or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof and method for preparing the same. U.S. Patent Application number 1020130115650, 27 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Aslanian, R.G. Case studies in modern drug discovery and development. In Discovery and Development of Montelukast (Singulair®); Young, R.N., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; Chapter 8; pp. 154–195. [Google Scholar]
- Ita, K.B. Transdermal drug delivery: Progress and challenges. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2014, 24, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso Jde, O.; Oliveira, R.V.; Lu, J.B.; Desta, Z. In vitro metabolism of montelukast by cytochrome P450s and UDP-Glucuronosyltransferases. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2015, 43, 1905–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





| Stabilizer (% w/v) 1 | Crystal Size (nm) 2 | Homogeneity (PDI) 2,3 | Dispersibility 4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| - 5 | 1614.3 ± 402.5 | 0.961 ± 0.067 | Aggregated |
| PVP K30 | 129.7 ± 1.1 | 0.281 ± 0.007 | Re-dispersible |
| Kollidon VA64 | 587.1 ± 177.7 | 0.556 ± 0.119 | Re-dispersible |
| HPMC-2910 | 319.3 ± 2.1 | 0.308 ± 0.065 | Aggregated |
| Poloxamer-188 | 89.9 ± 0.3 | 0.269 ± 0.006 | Aggregated |
| Poloxamer-407 | 100.6 ± 1.0 | 0.353 ± 0.046 | Aggregated |
| Tween 20 | 89.9 ± 0.4 | 0.290 ± 0.002 | Aggregated |
| Tween 80 | 97.6 ± 0.6 | 0.275 ± 0.011 | Aggregated |
| Kolliphor RH40 | 97.9 ± 0.6 | 0.451 ± 0.007 | Aggregated |
| Cremophor EL | 117.6 ± 0.5 | 0.184 ± 0.006 | Aggregated |
| Solutol HS15 | 145.7 ± 0.8 | 0.251 ± 0.009 | Aggregated |
| Parameters | MTK Nanocrystal Suspension |
|---|---|
| MTK concentration (mg/mL) | 10.93 ± 0.23 |
| Suspended (mg/mL) | 10.88 ± 0.20 |
| Dissolved (mg/mL) | 0.05 ± 0.01 |
| Particle size (nm) | 102.3 ± 3.0 |
| PDI | 0.238 ± 0.056 |
| Zeta potential (mV) | −3.6 ± 0.7 |
| pH | 4.1 ± 0.1 |
| Parameters | Nanocrystal Hydrogel | Conventional Hydrogel |
|---|---|---|
| AUC(0–24 h) (ng·h/mL) | 20.1 ± 5.2 | 23.5 ± 7.0 |
| AUC(0–inf) (ng·h/mL) | 20.8 ± 5.7 | 26.6 ± 8.1 |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 5.9 ± 2.1 | 5.3 ± 2.2 |
| Tmax (h) | 0.5 | 2.0 |
| t1/2 (h) | 9.7 ± 3.3 | 6.2 ± 5.4 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Im, S.H.; Jung, H.T.; Ho, M.J.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, H.T.; Kim, D.Y.; Lee, H.C.; Choi, Y.S.; Kang, M.J. Montelukast Nanocrystals for Transdermal Delivery with Improved Chemical Stability. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12010018
Im SH, Jung HT, Ho MJ, Lee JE, Kim HT, Kim DY, Lee HC, Choi YS, Kang MJ. Montelukast Nanocrystals for Transdermal Delivery with Improved Chemical Stability. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(1):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12010018
Chicago/Turabian StyleIm, Sung Hyun, Hoe Taek Jung, Myoung Jin Ho, Jeong Eun Lee, Hyung Tae Kim, Dong Yoon Kim, Hyo Chun Lee, Yong Seok Choi, and Myung Joo Kang. 2020. "Montelukast Nanocrystals for Transdermal Delivery with Improved Chemical Stability" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 1: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12010018
APA StyleIm, S. H., Jung, H. T., Ho, M. J., Lee, J. E., Kim, H. T., Kim, D. Y., Lee, H. C., Choi, Y. S., & Kang, M. J. (2020). Montelukast Nanocrystals for Transdermal Delivery with Improved Chemical Stability. Pharmaceutics, 12(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12010018