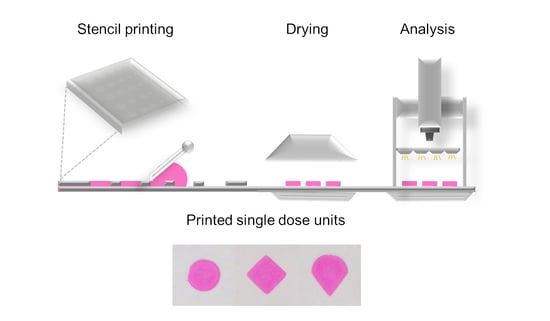
Stencil Printing—A Novel Manufacturing Platform for Orodispersible Discs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Stencil Printing Set-Up
2.2. Ink Formulation
2.3. Stencil Printing
2.4. Rheology
2.5. Visual Print Evaluation
2.6. pH
2.7. Disintegration
2.8. Drug Assay
2.9. Uniformity of Mass of Single-Dose Preparations
2.10. Uniformity of Content of Single Dose Preparations
2.11. Polarized Light Microscopy
2.12. X-ray Powder Diffraction
2.13. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.14. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
3. Results
3.1. Stencil Preparation
3.2. Ink Formulation Development
3.3. Ink Rheology and Printability
3.4. Disintegration of Discs
3.5. pH of Ink Formulations and Disc Surfaces
3.6. Quantification of Haloperidol by HPLC
3.7. Uniformity of Mass and Content
3.8. Polarized Light Microscopy
3.9. X-ray Diffraction
3.10. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3.11. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Srai, J.S.; Badman, C.; Krumme, M.; Futran, M.; Johnston, C. Future supply chains enabled by continuous processing—Opportunities and challenges. May 20–21, 2014 Continuous Manufacturing Symposium. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 840–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Metwali, B.; Mulla, H. Personalised dosing of medicines for children. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2017, 69, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Florence, A.T.; Lee, V.H. Personalised medicines: More tailored drugs, more tailored delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 415, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgensen, A.L.; Prince, C.; Fitzgerald, G.; Hanson, A.; Downing, J.; Reynolds, J.; Zhang, J.E.; Alfirevic, A.; Pirmohamed, M. Implementation of genotype-guided dosing of warfarin with point-of-care genetic testing in three UK clinics: A matched cohort study. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edinger, M.; Bar-Shalom, D.; Sandler, N.; Rantanen, J.; Genina, N. QR encoded smart oral dosage forms by inkjet printing. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 536, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arya, A.; Chandra, A.; Sharma, V.; Pathak, K. Fast dissolving oral films: An innovative drug delivery system and dosage form. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 2010, 2, 576–583. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann, E.M.; Breitenbach, A.; Breitkreutz, J. Advances in orodispersible films for drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2011, 8, 299–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thabet, Y.; Breitkreutz, J. Orodispersible films: Product transfer from lab-scale to continuous manufacturing. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 535, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woertz, C.; Kleinebudde, P. Development of orodispersible polymer films containing poorly water soluble active pharmaceutical ingredients with focus on different drug loadings and storage stability. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 493, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niese, S.; Breitkreutz, J.; Quodbach, J. Development of a dosing device for individualized dosing of orodispersible warfarin films. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 561, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Guo, X.; Sun, Y.; Yang, M. Anti-solvent Precipitation Method Coupled Electrospinning Process to Produce Poorly Water-Soluble Drug-Loaded Orodispersible Films. Aaps Pharmscitech 2019, 20, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janßen, E.M.; Schliephacke, R.; Breitenbach, A.; Breitkreutz, J. Drug-printing by flexographic printing technology—A new manufacturing process for orodispersible films. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 441, 818–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genina, N.; Fors, D.; Palo, M.; Peltonen, J.; Sandler, N. Behavior of printable formulations of loperamide and caffeine on different substrates—Effect of print density in inkjet printing. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 453, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buanz, A.B.; Saunders, M.H.; Basit, A.W.; Gaisford, S. Preparation of personalized-dose salbutamol sulphate oral films with thermal ink-jet printing. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickström, H.; Hilgert, E.; Nyman, J.; Desai, D.; Şen Karaman, D.; de Beer, T.; Sandler, N.; Rosenholm, J. Inkjet printing of drug-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles—A platform for drug development. Molecules 2017, 22, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Planchette, C.; Pichler, H.; Wimmer-Teubenbacher, M.; Gruber, M.; Gruber-Wölfler, H.; Mohr, S.; Mohr, S.; Tetyczka, C.; Hsiao, W.-K.; Paudel, A.; et al. Printing medicines as orodispersible dosage forms: Effect of substrate on the printed micro-structure. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 509, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alomari, M.; Vuddanda, P.R.; Trenfield, S.J.; Dodoo, C.C.; Velaga, S.; Basit, A.W.; Gaisford, S. Printing T3 and T4 oral drug combinations as a novel strategy for hypothyroidism. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 549, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöholm, E.; Sandler, N. Additive manufacturing of personalized orodispersible warfarin films. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 564, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musazzi, U.M.; Selmin, F.; Ortenzi, M.A.; Mohammed, G.K.; Franzé, S.; Minghetti, P.; Cilurzo, F. Personalized orodispersible films by hot melt ram extrusion 3D printing. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 551, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamróz, W.; Kurek, M.; Łyszczarz, E.; Szafraniec, J.; Knapik-Kowalczuk, J.; Syrek, K.; Paluch, M.; Jachowicz, R. 3D printed orodispersible films with Aripiprazole. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 533, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, R.; Desmulliez, M. A review of stencil printing for microelectronic packaging. Solder. Surf. Mt. Technol. 2012, 24, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Yerga, D.; Álvarez-Martos, I.; Blanco-López, M.C.; Henry, C.S.; Fernández-Abedul, M.T. Point-of-need simultaneous electrochemical detection of lead and cadmium using low-cost stencil-printed transparency electrodes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 981, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kay, R.W.; De Gourcuff, E.; Desmulliez, M.P.Y.; Jackson, G.J.; Steen, H.A.H.; Liu, C.; Conway, P.P. Stencil printing technology for wafer level bumping at sub-100 micron pitch using Pb-free alloys. In Proceedings of the Electronic Components and Technology, Lake Buena Vista, FL, USA, 31 May 2005; pp. 848–854. [Google Scholar]
- Lazarus, N.; Bedair, S.S.; Kierzewski, I.M. Ultrafine pitch stencil printing of liquid metal alloys. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 1178–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, D.; Jiang, N.R.; Liu, Y.F.; Zhang, X.L.; Li, A.W.; Feng, J.; Sun, H.B. Mechanically robust stretchable organic optoelectronic devices built using a simple and universal stencil-pattern transferring technology. Light Sci. Appl. 2018, 7, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amalu, E.H.; Ekere, N.N.; Mallik, S. Evaluation of rheological properties of lead-free solder pastes and their relationship with transfer efficiency during stencil printing process. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 3189–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krammer, O.; Gyarmati, B.; Szilágyi, A.; Illés, B.; Bušek, D.; Dušek, K. The effect of solder paste particle size on the thixotropic behaviour during stencil printing. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2018, 262, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipphan, H. Handbook of Print Media: Technologies and production Methods; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; pp. 55–58. [Google Scholar]
- Lääketietokeskus. Available online: https://laakeinfo.fi/Medicine.aspx?m=1360&d=3098906 (accessed on 16 November 2019).
- Ingelman-Sundberg, M. Genetic polymorphisms of cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6): Clinical consequences, evolutionary aspects and functional diversity. Pharm. J. 2005, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Pharmacopoeia, 9th ed.; Council of Europe: Strasbourg, France, 2016.
- Öler, M.; Hakyemez, G. Investigations of some physicochemical properties of haloperidol which may affect its activity. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 1988, 13, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ream, R.L.; Moore, D.M. Saliva stimulating chewing gum composition, Patent and Trademark Office. U.S. Patent 4,088,788, 8 May 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, B.; Lee, N.C. Solder bumping via paste reflow for area array packages. In Proceedings of the 27th Annual IEEE/SEMI International Electronics Manufacturing Technology Symposium, San Jose, CA, USA, 17–18 July 2002; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Yehia, S.A.; El-Gazayerly, O.N.; Basalious, E.B. Fluconazole mucoadhesive buccal films: In vitro/in vivo performance. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2009, 6, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumal, V.A.; Lutchman, D.; Mackraj, I.; Govender, T. Formulation of monolayered films with drug and polymers of opposing solubilities. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 358, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Tonkay, G.L.; Storer, R.H.; Sallade, R.M.; Leandri, D.J. Critical variables of solder paste stencil printing for micro-BGA and fine-pitch QFP. IEEE Trans. Electron. Packag. Manuf. 2004, 27, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maing, I.Y.; Parliment, T.H.; Soukup, R.J. Stabilization of erythrosine in aqueous acidic food systems, Patent and Trademark Office. U.S. Patent 4,133,900, 9 January 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Cassanas, G.; Morssli, M.; Fabregue, E.; Bardet, L. Vibrational spectra of lactic acid and lactates. J. Raman Spectrosc. 1991, 22, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saluja, H.; Mehanna, A.; Panicucci, R.; Atef, E. Hydrogen bonding: Between strengthening the crystal packing and improving solubility of three haloperidol derivatives. Molecules 2016, 21, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preis, M.; Gronkowsky, D.; Grytzan, D.; Breitkreutz, J. Comparative study on novel test systems to determine disintegration time of orodispersible films. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2014, 66, 1102–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguty, T.A.; Ekere, N.N.; Adebayo, A. Correlating solder paste composition with stencil printing performance. In Proceedings of the Twenty Fourth IEEE/CPMT International Electronics Manufacturing Technology Symposium (Cat. No. 99CH36330), Austin, TX, USA, 19 October 1999; pp. 304–312. [Google Scholar]











| Formulations | Lactic Acid (LA) | Haloperidol (HAL) |
|---|---|---|
| HPMC 16% | − | − |
| HPMC 16% LA | + | − |
| HPMC 16% LA HAL | + | + |
| HPMC 16% HAL | − | + |
| Ingredient | Function | Quantity (%) |
|---|---|---|
| HAL | API | 1 |
| HPMC E5 | Matrix former | 12–18 |
| Erythrosine | Colorant | 1 |
| Glycerol | Plasticizer | 3.5 |
| Ethanol | Solvent | 50 |
| Lactic acid 1% (aq.) | Solvent, pH modifier, saliva stimulant | Ad 100 |
| Formulation | Ink Formulation (n = 3) | Surface pH (n = 3) |
|---|---|---|
| HPMC 16% | 7.10 ± 0.02 | 6.02 ± 0.28 |
| HPMC 16% LA | 3.23 ± 0.06 | 4.18 ± 0.45 |
| HPMC 16% LA HAL | 4.24 ± 0.09 | 4.08 ± 0.15 |
| HPMC 16% HAL | 8.00 ± 0.06 | 5.59 ± 0.14 |
| Discs (Ø mm) | Uniformity of Mass (mg ± sd) | Uniformity of Content (mg ± sd) |
|---|---|---|
| 10.8 | 10.78 ± 0.20 | 0.49 ± 0.01 |
| 14.4 | 18.70 ± 0.53 | 0.87 ± 0.02 |
| 18.0 | 29.43 ± 0.83 | 1.43 ± 0.03 |
| 21.6 | 42.59 ± 1.11 | 1.97 ± 0.04 |
| 25.2 | 55.30 ± 1.34 | 2.56 ± 0.07 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wickström, H.; Koppolu, R.; Mäkilä, E.; Toivakka, M.; Sandler, N. Stencil Printing—A Novel Manufacturing Platform for Orodispersible Discs. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12010033
Wickström H, Koppolu R, Mäkilä E, Toivakka M, Sandler N. Stencil Printing—A Novel Manufacturing Platform for Orodispersible Discs. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(1):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12010033
Chicago/Turabian StyleWickström, Henrika, Rajesh Koppolu, Ermei Mäkilä, Martti Toivakka, and Niklas Sandler. 2020. "Stencil Printing—A Novel Manufacturing Platform for Orodispersible Discs" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 1: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12010033
APA StyleWickström, H., Koppolu, R., Mäkilä, E., Toivakka, M., & Sandler, N. (2020). Stencil Printing—A Novel Manufacturing Platform for Orodispersible Discs. Pharmaceutics, 12(1), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12010033