Deep Tumor Penetration of Doxorubicin-Loaded Glycol Chitosan Nanoparticles Using High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound
Abstract
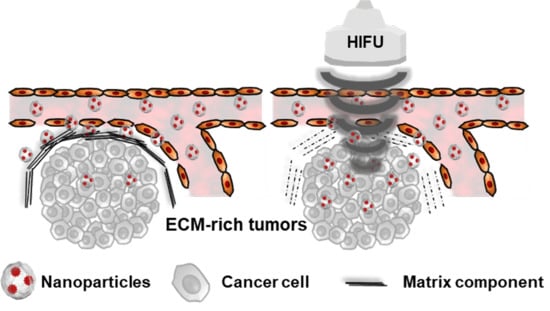
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis and Characterization of Doxorubicin-Loaded Glycol Chitosan Nanoparticles (DOX-CNPs)
2.3. In Vitro Release Profile of HIFU-Triggered DOX-CNPs
2.4. Cellular Uptake Behavior of HIFU-Triggered DOX-CNPs
2.5. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Test of HIFU-Triggered DOX-CNPs
2.6. In Vivo Biodistribution of HIFU-Triggered DOX-CNPs in A549 Tumor-Bearing Mice
2.7. Antitumor Efficacy of DOX-CNPs with HIFU Treatment
2.8. Histological Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. In Vitro Characterization of DOX-Loaded Glycol Chitosan Nanoparticles (DOX-CNPs)
3.2. In Vitro Cellular Uptake and Cytotoxicity of HIFU-Triggred DOX-CNPs
3.3. In Vivo Biodistribution and Therapeutic Efficacy of HIFU-Triggered DOX-CNPs
3.4. In Vivo Therapeutic Efficacy Using HIFU-Triggered DOX-CNPs in A549 Tumor-Bearing Mice
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, K.; Kim, J.H.; Park, H.; Kim, Y.S.; Park, K.; Nam, H.; Lee, S.; Park, J.H.; Park, R.W.; Kim, I.S.; et al. Tumor-homing multifunctional nanoparticles for cancer theragnosis: Simultaneous diagnosis, drug delivery, and therapeutic monitoring. J. Control. Release 2010, 146, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, H. The enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect in tumor vasculature: The key role of tumor-selective macromolecular drug targeting. Adv. Enzym. Regul. 2001, 41, 189–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazak, R.; Houri, M.; Achy, S.E.; Hussein, W.; Refaat, T. Passive targeting of nanoparticles to cancer: A comprehensive review of the literature. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 2, 904–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nel, A.; Ruoslahti, E.; Meng, H. New Insights into “Permeability” as in the Enhanced Permeability and Retention Effect of Cancer Nanotherapeutics; ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.; Nakamura, H.; Maeda, H. The EPR effect: Unique features of tumor blood vessels for drug delivery, factors involved, and limitations and augmentation of the effect. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.J.; Yang, S.C.; Liu, X.L.; Gao, Y.H.; Dong, X.; Lai, X.; Zhu, M.H.; Feng, H.Y.; Zhu, X.D.; Lu, Q.; et al. Nanobowl-Supported Liposomes Improve Drug Loading and Delivery. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 4177–4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, S.; Ko, H.; Rao, N.V.; Yoon, H.Y.; You, D.G.; Han, H.S.; Um, W.; Saravanakumar, G.; Park, J.H. A versatile gold cross-linked nanoparticle based on triblock copolymer as the carrier of doxorubicin. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 70352–70360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.; Park, B.C.; Lim, S.; Yoon, H.Y.; Jeon, Y.S.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, K. Heat-Generating Iron Oxide Multigranule Nanoclusters for Enhancing Hyperthermic Efficacy in Tumor Treatment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 33483–33491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabielska-Koczywas, K.; Lechowski, R. The Use of Liposomes and Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery Systems to Improve Cancer Treatment in Dogs and Cats. Molecules 2017, 22, 2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Denison, T.A.; Bae, Y.H. Tumor heterogeneity and its implication for drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2012, 164, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenblum, D.; Joshi, N.; Tao, W.; Karp, J.M.; Peer, D. Progress and challenges towards targeted delivery of cancer therapeutics. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fisher, R.; Pusztai, L.; Swanton, C. Cancer heterogeneity: Implications for targeted therapeutics. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, F.; Leunig, M.; Huang, S.K.; Berk, D.A.; Papahadjopoulos, D.; Jain, R.K. Microvascular permeability and interstitial penetration of sterically stabilized (stealth) liposomes in a human tumor xenograft. Cancer Res. 1994, 54, 3352–3356. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jain, R.K. Delivery of molecular and cellular medicine to solid tumors. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 46, 149–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yhee, J.Y.; Jeon, S.; Yoon, H.Y.; Shim, M.K.; Ko, H.; Min, J.; Na, J.H.; Chang, H.; Han, H.; Kim, J.H.; et al. Effects of tumor microenvironments on targeted delivery of glycol chitosan nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2017, 267, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, V.P.; Jain, R.K. Strategies for advancing cancer nanomedicine. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 958–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Junttila, M.R.; de Sauvage, F.J. Influence of tumour micro-environment heterogeneity on therapeutic response. Nature 2013, 501, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonsen, T.G.; Gaustad, J.V.; Leinaas, M.N.; Rofstad, E.K. High Interstitial Fluid Pressure Is Associated with Tumor-Line Specific Vascular Abnormalities in Human Melanoma Xenografts. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netti, P.A.; Berk, D.A.; Swartz, M.A.; Grodzinsky, A.J.; Jain, R.K. Role of extracellular matrix assembly in interstitial transport in solid tumors. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 2497–2503. [Google Scholar]
- Song, G.N.; Darr, D.B.; Santos, C.M.; Ross, M.; Valdivia, A.; Jordan, J.L.; Midkiff, B.R.; Cohen, S.; Nikolaishvili-Feinberg, N.; Miller, C.R.; et al. Effects of Tumor Microenvironment Heterogeneity on Nanoparticle Disposition and Efficacy in Breast Cancer Tumor Models. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 6083–6095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, C.; Stylianopoulos, T.; Cui, J.A.; Martin, J.; Chauhan, V.P.; Jiang, W.; Popovic, Z.; Jain, R.K.; Bawendi, M.G.; Fukumura, D. Multistage nanoparticle delivery system for deep penetration into tumor tissue. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2426–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, Y.; Nam, G.H.; Koh, E.; Jeon, S.; Kim, G.B.; Jeong, C.; Kim, D.H.; Yang, Y.; Kim, I.S. Exosome as a Vehicle for Delivery of Membrane Protein Therapeutics, PH20, for Enhanced Tumor Penetration and Antitumor Efficacy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1703074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parodi, A.; Haddix, S.G.; Taghipour, N.; Scaria, S.; Taraballi, F.; Cevenini, A.; Yazdi, I.K.; Corbo, C.; Palomba, R.; Khaled, S.Z.; et al. Bromelain Surface Modification Increases the Diffusion of Silica Nanopartides in the Tumor Extracellular Matrix. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 9874–9883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Q.; Kou, L.F.; Tu, Y.; Zhu, L. MMP-Responsive ‘Smart’ Drug Delivery and Tumor Targeting. Trends Pharm. Sci. 2018, 39, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talbert, J.N.; Goddard, J.M. Enzymes on material surfaces. Colloids Surf. B 2012, 93, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, K.S.; Han, H.; Yoon, B.D.; Lee, M.; Kim, H.; Seo, D.W.; Seo, J.H.; Kim, K.; Kwon, I.C.; Yuk, S.H. Effect of HIFU treatment on tumor targeting efficacy of docetaxel-loaded Pluronic nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B 2014, 119, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Shin, I.S.; Hancock, H.; Jang, B.S.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, S.M.; Zderic, V.; Frenkel, V.; Pastan, I.; Paik, C.H.; et al. Pulsed high intensity focused ultrasound increases penetration and therapeutic efficacy of monoclonal antibodies in murine xenograft tumors. J. Control. Release 2012, 162, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.; Han, H.; Koo, H.; Na, J.H.; Yoon, H.Y.; Lee, K.E.; Lee, H.; Kim, H.; Kwon, I.C.; Kim, K. Extracellular matrix remodeling in vivo for enhancing tumor-targeting efficiency of nanoparticle drug carriers using the pulsed high intensity focused ultrasound. J. Control. Release 2017, 263, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, D.G.; Yoon, H.Y.; Jeon, S.; Um, W.; Son, S.; Park, J.H.; Kwon, I.C.; Kim, K. Deep tissue penetration of nanoparticles using pulsed-high intensity focused ultrasound. Nano Converg. 2017, 4, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doherty, G.J.; Tempero, M.; Corrie, P.G. HALO-109–301: A Phase III trial of PEGPH20 (with gemcitabine and nab-paclitaxel) in hyaluronic acid-high stage IV pancreatic cancer. Future Oncol. 2018, 14, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, S.; Tavares, A.J.; Dai, Q.; Ohta, S.; Audet, J.; Dvorak, H.F.; Chan, W.C. Analysis of nanoparticle delivery to tumours. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, D.K.; Shapka, S.N.; Amsden, B.G. Structure, depolymerization, and cytocompatibility evaluation of glycol chitosan. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A Off. J. Soc. Biomater. Jpn. Soc. Biomater. Aust. Soc. Biomater. Korean Soc. Biomater. 2007, 83, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.E.; Kim, H.-J.; Rhee, J.-K.; Park, K. Versatile chemical derivatizations to design glycol chitosan-based drug carriers. Molecules 2017, 22, 1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-S.; Kim, S.; Park, J.H.; Kim, K.; Choi, K.; Chung, H.; Jeong, S.Y.; Park, R.-W.; Kim, I.-S. Hydrophobically modified glycol chitosan nanoparticles as carriers for paclitaxel. J. Control. Release 2006, 111, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, H.-Y.; Kim, I.-S.; Kwon, I.C.; Kim, Y.-H. Tumor targetability and antitumor effect of docetaxel-loaded hydrophobically modified glycol chitosan nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2008, 128, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Key, J.; Cooper, C.; Kim, A.Y.; Dhawan, D.; Knapp, D.W.; Kim, K.; Park, J.H.; Choi, K.; Kwon, I.C.; Park, K. In vivo NIRF and MR dual-modality imaging using glycol chitosan nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2012, 163, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.Y.; Son, S.; Lee, S.J.; You, D.G.; Yhee, J.Y.; Park, J.H.; Swierczewska, M.; Lee, S.; Kwon, I.C.; Kim, S.H. Glycol chitosan nanoparticles as specialized cancer therapeutic vehicles: Sequential delivery of doxorubicin and Bcl-2 siRNA. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, K.; Kim, J.H.; Nam, Y.S.; Lee, S.; Nam, H.Y.; Kim, K.; Park, J.H.; Kim, I.S.; Choi, K.; Kim, S.Y.; et al. Effect of polymer molecular weight on the tumor targeting characteristics of self-assembled glycol chitosan nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2007, 122, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.; Park, J.H.; Chung, H.; Kwon, I.C.; Jeong, S.Y.; Kim, I.S. Physicochemical characteristics of self-assembled nanoparticles based on glycol chitosan bearing 5 beta-cholanic acid. Langmuir 2003, 19, 10188–10193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, J.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, S.; Koo, H.; Min, K.H.; Jeong, S.Y.; Yuk, S.H.; Kim, K.; Kwon, I.C. Effect of the stability and deformability of self-assembled glycol chitosan nanoparticles on tumor-targeting efficiency. J. Control. Release 2012, 163, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, J.H.; Koo, H.; Lee, S.; Han, S.J.; Lee, K.E.; Kim, S.; Lee, H.; Lee, S.; Choi, K.; Kwon, I.C.; et al. Precise Targeting of Liver Tumor Using Glycol Chitosan Nanoparticles: Mechanisms, Key Factors, and Their Implications. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 3700–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, H.Y.; Kwon, S.M.; Chung, H.; Lee, S.Y.; Kwon, S.H.; Jeon, H.; Kim, Y.; Park, J.H.; Kim, J.; Her, S.; et al. Cellular uptake mechanism and intracellular fate of hydrophobically modified glycol chitosan nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2009, 135, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Lee, S.J.; Chung, H.; Her, S.; Choi, Y.; Kim, K.; Choi, K.; Kwon, I.C. Cellular Uptake Pathway and Drug Release Characteristics of Drug-Encapsulated Glycol Chitosan Nanoparticles in Live Cells. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2010, 73, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yhee, J.Y.; Yoon, H.Y.; Kim, H.; Jeon, S.; Hergert, P.; Im, J.; Panyam, J.; Kim, K.; Nho, R.S. The effects of collagen-rich extracellular matrix on the intracellular delivery of glycol chitosan nanoparticles in human lung fibroblasts. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 6089–6105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitragotri, S. Innovation—Healing sound: The use of ultrasound in drug delivery and other therapeutic applications. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karshafian, R.; Bevan, P.D.; Williams, R.; Samac, S.; Burns, P.N. Sonoporation by Ultrasound-Activated Microbubble Contrast Agents: Effect of Acoustic Exposure Parameters on Cell Membrane Permeability and Cell Viability. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2009, 35, 847–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borden, M.A.; Zhang, H.; Gillies, R.J.; Dayton, P.A.; Ferrara, K.W. A stimulus-responsive contrast agent for ultrasound molecular imaging. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frenkel, V. Ultrasound mediated delivery of drugs and genes to solid tumors. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1193–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, Y.; Han, H.; Jeon, S.; Yoon, H.Y.; Kim, H.; Kwon, I.C.; Kim, K. Deep Tumor Penetration of Doxorubicin-Loaded Glycol Chitosan Nanoparticles Using High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12100974
Choi Y, Han H, Jeon S, Yoon HY, Kim H, Kwon IC, Kim K. Deep Tumor Penetration of Doxorubicin-Loaded Glycol Chitosan Nanoparticles Using High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(10):974. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12100974
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Yongwhan, Hyounkoo Han, Sangmin Jeon, Hong Yeol Yoon, Hyuncheol Kim, Ick Chan Kwon, and Kwangmeyung Kim. 2020. "Deep Tumor Penetration of Doxorubicin-Loaded Glycol Chitosan Nanoparticles Using High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 10: 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12100974
APA StyleChoi, Y., Han, H., Jeon, S., Yoon, H. Y., Kim, H., Kwon, I. C., & Kim, K. (2020). Deep Tumor Penetration of Doxorubicin-Loaded Glycol Chitosan Nanoparticles Using High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound. Pharmaceutics, 12(10), 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12100974