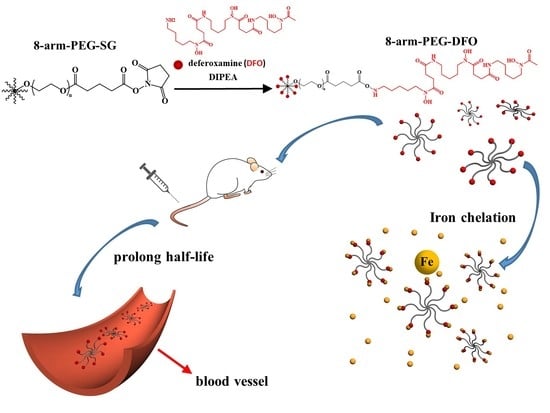
A Novel Star Like Eight-Arm Polyethylene Glycol-Deferoxamine Conjugate for Iron Overload Therapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. The Synthesis of 8-Arm-PEG-DFO Conjugates
2.3. The Characterization of the 8-Arm-PEG-DFO Conjugates
2.4. Iron Binding Properties of the 8-Arm-PEG-DFO Conjugates
2.5. In Vitro Hemolysis Test
2.6. In Vitro Metabolism Studies
2.7. Cell Culture
2.8. Cell Viability Analysis
2.9. Iron Chelation Studies in Iron-Overload Macrophages
2.10. Pharmacokinetics Study
2.10.1. Animal Studies
2.10.2. Sample Preparation and Chromatography Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. The Synthesis and Characterization of 8-Arm-PEG-DFO Conjugates
3.2. In Vitro Hemolysis Test
3.3. In Vitro Metabolism Test
3.4. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Test
3.5. Iron Chelation Efficacy Studies in Iron-Overload Macrophages
3.6. Pharmacokinetics Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Codd, R.; Richardson-Sanchez, T.; Telfer, T.J.; Gotsbacher, M.P. Advances in the Chemical Biology of Desferrioxamine B. Acs Chem. Biol. 2018, 13, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridharan, K.; Sivaramakrishnan, G. Efficacy and safety of iron chelators in thalassemia and sickle cell disease: A multiple treatment comparison network meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 11, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgnapignatti, C.; Rugolotto, S.; De Stefano, P.; Zhao, H.; Cappellini, M.D.; Del Vecchio, G.C.; Romeo, M.A.; Forni, G.L.; Gamberini, M.R.; Ghilardi, R. Survival and complications in patients with thalassemia major treated with transfusion and deferoxamine. Haematologica 2004, 89, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar]
- You, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Han, X.; Wang, T.; Guo, S.; Dong, T.; Xu, J.; Anderson, G.J.; et al. Targeted Brain Delivery of Rabies Virus Glycoprotein 29-Modified Deferoxamine-Loaded Nanoparticles Reverses Functional Deficits in Parkinsonian Mice. Acs Nano 2018, 12, 4123–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappellini, M.D.; Pattoneri, P. Oral Iron Chelators. Annu. Rev. Med. 2009, 60, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merali, S.; Chin, K.; Angel, L.D.; Grady, R.W.; Armstrong, M.; Clarkson, A.B. Clinically achievable plasma deferoxamine concentrations are therapeutic in a rat model of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1995, 39, 2023–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Imran Ul-Haq, M.; Hamilton, J.L.; Lai, B.F.L.; Shenoi, R.A.; Horte, S.; Constantinescu, I.; Leitch, H.A.; Kizhakkedathu, J.N. Design of Long Circulating Nontoxic Dendritic Polymers for the Removal of Iron in Vivo. Acs Nano 2013, 7, 10704–10716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallaway, P.E.; Eaton, J.W.; Panter, S.S.; Hedlund, B.E. Modulation of deferoxamine toxicity and clearance by covalent attachment to biocompatible polymers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 10108–10112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Modell, B.; Khan, M.; Darlison, M. Survival in Beta-thalassaemia major in the UK: Data from the UK Thalassaemia Register. Lancet 2000, 355, 2051–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubourg, L.; Laurain, C.; Ranchin, B.; Pondarré, C.; Hadj-Aïssa, A.; Sigaudo-Roussel, D.; Cochat, P. Deferasirox-induced renal impairment in children: An increasing concern for pediatricians. Pediatric Nephrol. 2012, 27, 2115–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsey, W.T.; Olin, B.R. Deferasirox for Transfusion-Related Iron Overload: A Clinical Review. Clin. Ther. 2007, 29, 2154–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvaruso, G.; Vitrano, A.; Di Maggio, R.; Lai, E.; Colletta, G.; Quota, A.; Calogera, G.; Luciana, C.R.; Massimiliano, S.; Lorella, P.; et al. Deferiprone versus deferoxamine in thalassemia intermedia: Results from a 5-year long-term Italian multicenter randomized clinical trial. Am. J. Hematol. 2015, 90, 634–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sammaraiee, Y.; Banerjee, G.; Farmer, S.; Hylton, B.; Cowley, P.; Eleftheriou, P.; Porter, J.; Werring, D.J. Risks associated with oral deferiprone in the treatment of infratentorial superficial siderosis. J. Neurol. 2020, 267, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tricta, F.; Uetrecht, J.; Galanello, R.; Connelly, J.; Rozova, A.; Spino, M.; Palmblad, J. Deferiprone-induced agranulocytosis: 20 years of clinical observations. Am. J. Hematol. 2016, 91, 1026–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, J.L.; Ul-Haq, M.I.; Abbina, S.; Kalathottukaren, M.T.; Kizhakkedathu, J.N. In vivo efficacy, toxicity and biodistribution of ultra-long circulating desferrioxamine based polymeric iron chelator. Biomaterials 2016, 102, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, J.L.; ul-haq, M.I.; Creagh, A.L.; Haynes, C.A.; Kizhakkedathu, J.N. Iron Binding and Iron Removal Efficiency of Desferrioxamine Based Polymeric Iron Chelators: Influence of Molecular Size and Chelator Density. Macromol. Biosci. 2017, 17, 1600244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panter, S.S.; Braughler, J.M.; Hall, E.D. Dextran-Coupled Deferoxamine Improves Outcome in a Murine Model of Head Injury. J. Neurotrauma 1992, 9, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, T.M.; Purro, M.; Xiong, M.P. Enzymatically Biodegradable Polyrotaxane-Deferoxamine Conjugates for Iron Chelation. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 25788–25797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, Z.; Gao, D.; Al-Zubaydi, F.; Li, S.; Singh, Y.; Rivera, K.; Holloway, J.; Szekely, Z.; Love, S.; Sinko, P.J. The effect of size and polymer architecture of doxorubicin-poly(ethylene) glycol conjugate nanocarriers on breast duct retention, potency and toxicity. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 121, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasut, G.; Canal, F.; Via, L.D.; Arpicco, S.; Veronese, F.M.; Schiavon, O. Antitumoral activity of PEG–gemcitabine prodrugs targeted by folic acid. J. Control. Release 2008, 127, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavon, O.; Pasut, G.; Moro, S.; Orsolini, P.; Guiotto, A.; Veronese, F.M. PEG–Ara-C conjugates for controlled release. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 39, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, N.A.; Mustafa, I.; Jackson, J.K.; Burt, H.M.; Horte, S.A.; Scott, M.D.; Kizhakkedathu, J.N. In vitro chelating, cytotoxicity, and blood compatibility of degradable poly(ethylene glycol)-based macromolecular iron chelators. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 638–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilks, M.Q.; Normandin, M.D.; Yuan, H.; Cho, H.; Guo, Y.; Herisson, F.; Ayata, C.; Wooten, D.W.; EI Fakhri, G.; Josephson, L. Imaging PEG-like nanoprobes in tumor, transient ischemia, and inflammatory disease models. Bioconjugate Chem. 2015, 26, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dai, L.; Wang, L.; Deng, L.; Liu, J.; Lei, J.; Li, D.; He, J. Novel Multiarm Polyethylene glycol-Dihydroartemisinin Conjugates Enhancing Therapeutic Efficacy in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapra, P.; Zhao, H.; Mehlig, M.; Malaby, J.; Kraft, P.; Longley, C.; Greenberger, L.M.; Horak, I.D. Novel delivery of SN38 markedly inhibits tumor growth in xenografts, including a camptothecin-11-refractory model. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 1888–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, H.; Rubio, B.; Sapra, P.; Wu, D.; Reddy, P.; Sai, P.; Martinez, A.; Gao, Y.; Lozanguiez, Y.; Longley, C. Novel prodrugs of SN38 using multiarm poly(ethylene glycol) linkers. Bioconjugate Chem. 2008, 19, 849–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Chen, X.; Gu, Z.; Li, H.; Ma, L.; Qi, X.; Tan, H.; You, C. Synthesis and evaluation of oxidation-responsive alginate-deferoxamine conjugates with increased stability and low toxicity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 144, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Purro, M.; Xiong, M.P. Oxidation-Induced Degradable Nanogels for Iron Chelation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Mondjinou, Y.; Hyun, S.-H.; Kulkarni, A.; Lu, Z.-R.; Thompson, D.H. Gd3+ -1,4,7,10-Tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7-triacetic-2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin/Pluronic Polyrotaxane as a Long Circulating High Relaxivity MRI Contrast Agent. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 40, 22272–22276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Gao, H.; Zhou, S.; Kuang, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H.; Sun, J. Optimization and evaluation of lipid emulsions for intravenous co-delivery of artemether and lumefantrine in severe malaria treatment. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.-C.; Zhang, Q.; Li, H.; Larregieu, C.A.; Zhang, N.; Chu, T.; Jin, H.; Mao, S.-J. Development of intravenous lipid emulsion of α-asarone with significantly improved safety and enhanced efficacy. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 450, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.J.; Hao, S.-J.; Liu, Y.-D.; Hu, T.; Zhang, G.-F.; Zhang, X.; Qi, Q.-S.; Ma, G.-H.; Su, Z.-G. PEGylation markedly enhances the in vivo potency of recombinant human non-glycosylated erythropoietin: A comparison with glycosylated erythropoietin. J. Control. Release 2010, 145, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; White, J.B.; Peterson, N.C.; Rickert, K.W.; Lloyd, C.O.; Allen, K.L.; Rosenthal, K.; Gao, X.; Wu, H.; Dall’Acqua, W.F.; et al. Tumor uptake of pegylated diabodies: Balancing systemic clearance and vascular transport. J. Control. Release 2018, 279, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Tao, J.; Baumgarten, K.M.; Sun, H. Hypoxia-Mimicking Nanofibrous Scaffolds Promote Endogenous Bone Regeneration. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 32450–32459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Selvaratnam, B.; Koodali, R.T.; Sun, H. Mesoporous silicate nanoparticles/3D nanofibrous scaffold-mediated dual-drug delivery for bone tissue engineering. J. Control. Release 2018, 279, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.; Han, M.; Xue, J.; Baek, Y.; Chang, J.; Hu, S.; Nam, H.; Jo, M.J.; EIFakhri, G.; Hutchens, M.P.; et al. Renal clearable nanochelators for iron overload therapy. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, P.; Mohammed, N.; Marshall, L.; Abeysinghe, R.D.; Hider, R.C.; Porter, J.B.; Singh, S. Intravenous infusion pharmacokinetics of desferrioxamine in thalassaemic patients. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1993, 21, 640–644. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, G.; Keberle, H.; Schmid, K.; Brunner, H. Distribution and renal excretion of desferrioxamine and ferrioxamine in the dog and in the rat. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1966, 15, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Conjugate | 8-Arm-PEG20k-DFO | 8-Arm-PEG40k-DFO |
|---|---|---|
| Eq. DFO AUC(0-t) (mg/L*h) | 102.07 ± 10.72 | 122.81 ± 28.22 |
| Eq. DFO Cmax (mg/L) | 19.39 ± 5.03 | 33.93 ± 10.80 |
| Eq. DFO t1/2α(h) | 0.18 ± 0.062 | 0.26 ± 0.14 |
| Eg. DFO t1/2β(h) | 17.58 ± 8.11 | 10.13 ± 3.31 |
| Eq. DFO V (L/kg) | 0.73 ± 0.60 | 0.50 ± 0.36 |
| Eq. DFO CL (L/h/kg) | 0.21 ± 0.06 | 0.27 ± 0.04 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, B.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhan, A.; Yang, Y.; Liu, H. A Novel Star Like Eight-Arm Polyethylene Glycol-Deferoxamine Conjugate for Iron Overload Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12040329
Yu B, Yang Y, Liu Q, Zhan A, Yang Y, Liu H. A Novel Star Like Eight-Arm Polyethylene Glycol-Deferoxamine Conjugate for Iron Overload Therapy. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(4):329. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12040329
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Bohong, Yinxian Yang, Qi Liu, Aiyan Zhan, Yang Yang, and Hongzhuo Liu. 2020. "A Novel Star Like Eight-Arm Polyethylene Glycol-Deferoxamine Conjugate for Iron Overload Therapy" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 4: 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12040329
APA StyleYu, B., Yang, Y., Liu, Q., Zhan, A., Yang, Y., & Liu, H. (2020). A Novel Star Like Eight-Arm Polyethylene Glycol-Deferoxamine Conjugate for Iron Overload Therapy. Pharmaceutics, 12(4), 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12040329