Therapeutic Use of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes: From Basic Science to Clinics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Components of MSC-Exos and Their Role in MSC-Exo-Mediated Biological Effects
3. Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms Responsible for Immunomodulatory Effects of MSC-Exos
3.1. MSC-Exo-Based Inhibition of Inflammatory Macrophages
3.2. Effects of Aging on MSC-Exo-Dependent Generation of Immunosuppressive Phenotype in Macrophages
3.3. MSC-Exo-Mediated Generation of Immunosuppressive Phenotype in Microglial Cells
3.4. Effects of MSC-Exos on Antigen-Presenting Properties of DCs
3.5. MSC-Exo-Dependent Modulation of T Cells
3.6. Effects of MSC-Exos on Phenotype and Function of B Cells
4. Signaling Pathways Responsible for MSC-Exo-Dependent Enhanced Survival and Regeneration of Injured Parenchymal Cells
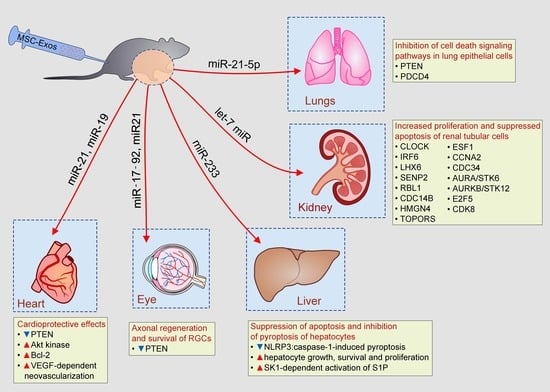
4.1. MSC-Exo-Based Protection of Lung Epithelial Cells, Renal Tubular Cells, and Hepatocytes
4.2. MSC-Exo-Dependent Modulation of Apoptosis and Autophagy in Injured Parenchymal Cells
5. Clinical Use of MSC-Exos
6. Concluding Remarks and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Volarevic, V.; Ljujic, B.; Stojkovic, P.; Lukic, A.; Arsenijevic, N.; Stojkovic, M. Human stem cell research and regenerative medicine-present and future. Br. Med. Bull. 2011, 99, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fu, Y.; Karbaat, L.; Wu, L.; Leijten, J.; Both, S.K.; Karperien, M. Trophic Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Tissue Regeneration. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2017, 23, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrell, C.R.; Jankovic, M.G.; Fellabaum, C.; Volarevic, A.; Djonov, V.; Arsenijevic, A.; Volarevic, V. Molecular Mechanisms Responsible for Anti-inflammatory and Immunosuppressive Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Factors. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1084, 187–206. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gazdic, M.; Volarevic, V.; Arsenijevic, N.; Stojkovic, M. Mesenchymal stem cells: A friend or foe in immune-mediated diseases. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2015, 11, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volarevic, V.; Markovic, B.S.; Gazdic, M.; Volarevic, A.; Jovicic, N.; Arsenijevic, N.; Armstrong, L.; Djonov, V.; Lako, M.; Stojkovic, M. Ethical and Safety Issues of Stem Cell-Based Therapy. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 15, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Breitbach, M.; Bostani, T.; Roell, W.; Xia, Y.; Dewald, O.; Nygren, J.M.; Fries, J.W.; Tiemann, K.; Bohlen, H.; Hescheler, J.; et al. Potential risks of bone marrow cell transplantation into infarcted hearts. Blood 2007, 110, 1362–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, Y.S.; Park, J.S.; Tkebuchava, T.; Luedeman, C.; Losordo, D.W. Unexpected severe calcification after transplantation of bone marrow cells in acute myocardial infarction. Circulation 2004, 109, 3154–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berglund, A.K.; Fortier, L.A.; Antczak, D.F.; Schnabel, L.V. Immunoprivileged no more: Measuring the immunogenicity of allogeneic adult mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harrell, C.R.; Fellabaum, C.; Jovicic, N.; Djonov, V.; Arsenijevic, N.; Volarevic, V. Molecular Mechanisms Responsible for Therapeutic Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Secretome. Cells 2019, 8, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phinney, D.G.; Pittenger, M.F. Concise Review: MSC-Derived Exosomes for Cell-Free Therapy. Stem Cells 2017, 35, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vizoso, F.J.; Eiro, N.; Cid, S.; Schneider, J.; Perez-Fernandez, R. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome: Toward Cell-Free Therapeutic Strategies in Regenerative Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deng, H.; Sun, C.; Sun, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, L.; Wu, D.; Gao, Q.; Jiang, X. Lipid, Protein, and MicroRNA Composition Within Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes. Cell. Reprogram. 2018, 20, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, G.; Zheng, G.; Ge, M.; Wang, J.; Huang, R.; Shu, Q.; Xu, J. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles affect disease outcomes via transfer of microRNAs. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrell, C.R.; Jovicic, N.; Djonov, V.; Arsenijevic, N.; Volarevic, V. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes and Other Extracellular Vesicles as New Remedies in the Therapy of Inflammatory Diseases. Cells 2019, 8, 1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.; Fan, H.; Shou, Z.; Xu, M.; Chen, Q.; Ai, C.; Dong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Nan, Z.; Wang, Y.; et al. Extracellular vesicles containing miR-146a attenuate experimental colitis by targeting TRAF6 and IRAK1. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 68, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, F.; Wu, Y.; Tang, X.; Kang, J.; Zhang, B.; Yan, Y.; Qian, H.; Zhang, X.; Xu, W. Exosomes Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Relieve Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Mice. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 5356760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannella, K.M.; Wynn, T.A. Mechanisms of Organ Injury and Repair by Macrophages. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2017, 79, 593–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.W.; Wei, L.; Han, Z.; Chen, Z. Mesenchymal stromal cells-derived exosomes alleviate ischemia/reperfusion injury in mouse lung by transporting anti-apoptotic miR-21-5p. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 852, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Qin, C.; Wang, J.; Hu, Y.; Zheng, G.; Qiu, G.; Ge, M.; Tao, H.; Shu, Q.; Xu, J. Differential effects of extracellular vesicles from aging and young mesenchymal stem cells in acute lung injury. Aging (Albany NY) 2019, 11, 7996–8014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulestreau, J.; Maumus, M.; Rozier, P.; Jorgensen, C.; Noël, D. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Aging. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Fu, B.; Sun, X.; Li, D.; Huang, Q.; Zhao, W.; Chen, X. Differentially expressed microRNAs in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived microvesicles in young and older rats and their effect on tumor growth factor-β1-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition in HK2 cells. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2015, 6, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fafián-Labora, J.; Lesende-Rodriguez, I.; Fernández-Pernas, P.; Sangiao-Alvarellos, S.; Monserrat, L.; Arntz, O.J.; van de Loo, F.J.; Mateos, J.; Arufe, M.C. Effect of age on pro-inflammatory miRNAs contained in mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ding, M.; Shen, Y.; Wang, P.; Xie, Z.; Xu, S.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lyu, Y.; Wang, D.; Xu, L.; et al. Exosomes Isolated From Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviate Neuroinflammation and Reduce Amyloid-Beta Deposition by Modulating Microglial Activation in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurochem. Res. 2018, 43, 2165–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laso-García, F.; Ramos-Cejudo, J.; Carrillo-Salinas, F.J.; Otero-Ortega, L.; Feliú, A.; Gómez-de Frutos, M.; Mecha, M.; Díez-Tejedor, E.; Guaza, C.; Gutiérrez-Fernández, M. Therapeutic potential of extracellular vesicles derived from human mesenchymal stem cells in a model of progressive multiple sclerosis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shahir, M.; Mahmoud Hashemi, S.; Asadirad, A.; Varahram, M.; Kazempour-Dizaji, M.; Folkerts, G.; Garssen, J.; Adcock, I.; Mortaz, E. Effect of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes on the induction of mouse tolerogenic dendritic cells. J. Cell Physiol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cho, K.S.; Kang, S.A.; Kim, S.D.; Mun, S.J.; Yu, H.S.; Roh, H.J. Dendritic cells and M2 macrophage play an important role in suppression of Th2-mediated inflammation by adipose stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles. Stem Cell Res. 2019, 39, 101500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.; Zhang, T.; Xu, X.; Lu, Z.; Yu, X.; Fang, Y.; Hu, J.; Jia, P.; Teng, J.; Ding, X. miR-21 Protects Against Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced Acute Kidney Injury by Preventing Epithelial Cell Apoptosis and Inhibiting Dendritic Cell Maturation. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigemoto-Kuroda, T.; Oh, J.Y.; Kim, D.K.; Jeong, H.J.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Park, J.W.; Kim, T.W.; An, S.Y.; Prockop, D.J.; et al. MSC-derived Extracellular Vesicles Attenuate Immune Responses in Two Autoimmune Murine Models: Type 1 Diabetes and Uveoretinitis. Stem Cell Rep. 2017, 8, 1214–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fathollahi, A.; Hashemi, S.M.; Haji Molla Hoseini, M.; Yeganeh, F. In vitro analysis of immunomodulatory effects of mesenchymal stem cell- and tumor cell –derived exosomes on recall antigen-specific responses. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 67, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nojehdehi, S.; Soudi, S.; Hesampour, A.; Rasouli, S.; Soleimani, M.; Hashemi, S.M. Immunomodulatory effects of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes on experimental type-1 autoimmune diabetes. J. Cell Biochem. 2018, 119, 9433–9443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Yeo, R.W.Y.; Lai, R.C.; Sim, E.W.K.; Chin, K.C.; Lim, S.K. Mesenchymal stromal cell exosome-enhanced regulatory T-cell production through an antigen-presenting cell-mediated pathway. Cytotherapy 2018, 20, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosenza, S.; Toupet, K.; Maumus, M.; Luz-Crawford, P.; Blanc-Brude, O.; Jorgensen, C.; Noël, D. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes are more immunosuppressive than microparticles in inflammatory arthritis. Theranostics 2018, 8, 1399–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, V.; Sánchez-Margallo, F.M.; Macías-García, B.; Gómez-Serrano, M.; Jorge, I.; Vázquez, J.; Blázquez, R.; Casado, J.G. The immunomodulatory activity of extracellular vesicles derived from endometrial mesenchymal stem cells on CD4+ T cells is partially mediated by TGFbeta. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2018, 12, 2088–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crain, S.K.; Robinson, S.R.; Thane, K.E.; Davis, A.M.; Meola, D.M.; Barton, B.A.; Yang, V.K.; Hoffman, A.M. Extracellular Vesicles from Wharton’s Jelly Mesenchymal Stem Cells Suppress CD4 Expressing T Cells Through Transforming Growth Factor Beta and Adenosine Signaling in a Canine Model. Stem Cells Dev. 2019, 28, 212–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bright, J.J.; Kerr, L.D.; Sriram, S. TGF-beta inhibits IL-2-induced tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of Jak-1 and Stat 5 in T lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 1997, 159, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fu, S.; Zhang, N.; Yopp, A.C.; Chen, D.; Mao, M.; Chen, D.; Zhang, H.; Ding, Y.; Bromberg, J.S. TGF-beta induces Foxp3 + T-regulatory cells from CD4 + CD25—Precursors. Am. J. Transplant. 2004, 4, 1614–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Fu, L.; Liang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Wang, L.; Ma, C.; Wang, H. Exosomes originating from MSCs stimulated with TGF-β and IFN-γ promote Treg differentiation. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 6832–6840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volarevic, V.; Gazdic, M.; Simovic Markovic, B.; Jovicic, N.; Djonov, V.; Arsenijevic, N. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived factors: Immuno-modulatory effects and therapeutic potential. Biofactors 2017, 43, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acovic, A.; Gazdic, M.; Jovicic, N.; Harrell, C.R.; Fellabaum, C.; Arsenijevic, N.; Volarevic, V. Role of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in pathology of the gastrointestinal tract. Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2018, 11, 1756284818815334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, Y.M.; Zhuansun, Y.X.; Chen, R.; Lin, L.; Lin, Y.; Li, J.G. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes promote immunosuppression of regulatory T cells in asthma. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 363, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrell, C.R.; Miloradovic, D.; Sadikot, R.; Fellabaum, C.; Simovic Markovic, B.; Miloradovic, D.; Acovic, A.; Djonov, V.; Arsenijevic, N.; Volarevic, V. Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms Responsible for Beneficial Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Derived Product “Exo-d-MAPPS” in Attenuation of Chronic Airway Inflammation. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2020, 3153891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khare, D.; Or, R.; Resnick, I.; Barkatz, C.; Almogi-Hazan, O.; Avni, B. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Derived Exosomes Affect mRNA Expression and Function of B-Lymphocytes. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bai, L.; Shao, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Su, C.; Dong, L.; Yu, B.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, X. Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes on Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, A.; Zhang, X.; He, H.; Zhou, L.; Naito, Y.; Sugita, S.; Lee, J.W. Therapeutic potential of stem/stromal cell-derived secretome and vesicles for lung injury and disease. Expert. Opin. Biol. 2020, 20, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, S.; Grange, C.; Deregibus, M.C.; Calogero, R.A.; Saviozzi, S.; Collino, F.; Morando, L.; Busca, A.; Falda, M.; Bussolati, B.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived microvesicles protect against acute tubular injury. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 1053–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bruno, S.; Tapparo, M.; Collino, F.; Chiabotto, G.; Deregibus, M.C.; Soares Lindoso, R.; Neri, F.; Kholia, S.; Giunti, S.; Wen, S.; et al. Renal Regenerative Potential of Different Extracellular Vesicle Populations Derived from Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Tissue Eng. Part A 2017, 23, 1262–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, C.D.; Esquela-Kerscher, A.; Stefani, G.; Byrom, M.; Kelnar, K.; Ovcharenko, D.; Wilson, M.; Wang, X.; Shelton, J.; Shingara, J.; et al. The let-7 microRNA represses cell proliferation pathways in human cells. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 7713–7722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gatti, S.; Bruno, S.; Deregibus, M.C.; Sordi, A.; Cantaluppi, V.; Tetta, C.; Camussi, G. Microvesicles derived from human adult mesenchymal stem cells protect against ischaemia-reperfusion-induced acute and chronic kidney injury. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 1474–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Xiang, B.; Wang, X.; Xiang, C. Exosomes derived from human menstrual blood-derived stem cells alleviate fulminant hepatic failure. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Lin, S.; Wan, B.; Velani, B.; Zhu, Y. Pyroptosis in Liver Disease: New Insights into Disease Mechanisms. Aging Dis. 2019, 10, 1094–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nojima, H.; Freeman, C.M.; Schuster, R.M.; Japtok, L.; Kleuser, B.; Edwards, M.J.; Gulbins, E.; Lentsch, A.B. Hepatocyte exosomes mediate liver repair and regeneration via sphingosine-1-phosphate. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Du, Y.; Li, D.; Han, C.; Wu, H.; Xu, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X. Exosomes from Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (hiPSC-MSCs) Protect Liver against Hepatic Ischemia/ Reperfusion Injury via Activating Sphingosine Kinase and Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Signaling Pathway. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 611–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakovljevic, J.; Harrell, C.R.; Fellabaum, C.; Arsenijevic, A.; Jovicic, N.; Volarevic, V. Modulation of autophagy as new approach in mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 104, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.; Liu, W.; Zhang, B.; Wang, J.; Wu, P.; Tandra, N.; Liang, Z.; Ji, C.; Yin, L.; Hu, X.; et al. HucMSC exosomes-delivered 14-3-3ζ enhanced autophagy via modulation of ATG16L in preventing cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Ding, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Ji, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, X. Exosomes derived from PEDF modified adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulation of autophagy and apoptosis. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 371, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Jia, H.; Zhang, B.; Wang, J.; Ji, C.; Zhu, X.; Yan, Y.; Yin, L.; Yu, J.; Qian, H.; et al. Pre-incubation with hucMSC-exosomes prevents cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by activating autophagy. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mead, B.; Tomarev, S. Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Exosomes Promote Survival of Retinal Ganglion Cells Through miRNA-Dependent Mechanisms. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 1273–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Jiang, Z.; Webster, K.A.; Chen, J.; Hu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, Z.; et al. Enhanced Cardioprotection by Human Endometrium Mesenchymal Stem Cells Driven by Exosomal MicroRNA-21. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiue, S.J.; Rau, R.H.; Shiue, H.S.; Hung, Y.W.; Li, Z.X.; Yang, K.D.; Cheng, J.K. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes as a cell-free therapy for nerve injury-induced pain in rats. Pain 2019, 160, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendt, M.; Rezvani, K.; Shpall, E. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes for clinical use. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2019, 54, 789–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, B.; Amaral, J.; Tomarev, S. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Promote Neuroprotection in Rodent Models of Glaucoma. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2018, 59, 702–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassar, W.; El-Ansary, M.; Sabry, D.; Mostafa, M.A.; Fayad, T.; Kotb, E.; Temraz, M.; Saad, A.N.; Essa, W.; Adel, H. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells derived extracellular vesicles can safely ameliorate the progression of chronic kidney diseases. Biomater. Res. 2016, 20, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Yang, G. Exosome Mediated Delivery of miR-124 Promotes Neurogenesis after Ischemia. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids. 2017, 7, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harrell, C.R.; Simovic Markovic, B.; Fellabaum, C.; Arsenijevic, A.; Djonov, V.; Arsenijevic, N.; Volarevic, V. Therapeutic Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes in the Treatment of Eye Diseases. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1089, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hao, Q.; Gudapati, V.; Monsel, A.; Park, J.H.; Hu, S.; Kato, H.; Lee, J.H.; Zhou, L.; He, H.; Lee, J.W. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Decrease Lung Injury in Mice. J. Immunol. 2019, 203, 1961–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Target Cell | Molecular Mechanism | Effect on Cell Phenotype and Function | Therapeutic Potential | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 macrophages | miR-146a-dependent inhibition TRAF6/IRAK1/NF-κB-signaling | Reduced expression of iNOS and inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6) | DSS-induced colitis | [15] |
| HSCs | miR-181-5p-dependent induction of autophagy and apoptosis | Increased expression of Beclin-1 and suppression of Bcl-2 | Liver fibrosis | [17] |
| M2 macrophages and microglial cells | miR-223-5p-dependent expression of Arginase-1 | Increased secretion of IL-10 and TGF-β | I/R-induced lung injury; AD and MS | [18,23,24] |
| DCs | miR-21-based suppression of NF-κB signaling | Reduced expression of co-stimulatory molecules (CD40, CD80, CD86), decreased production of Th1 and Th17-related cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-12) | EAU; EAE; STZ-T1DM | [28,29,30] |
| Th1 and Th17 cells | TGF-β-dependent inhibition of JAK/STAT signaling | G1 cell cycle arrest and reduced proliferation | EAE; STZ-T1DM | [29,30] |
| Tregs | TGF-β and IDO-dependent activation of GCN2 kinase | Reduced transdifferentiation of Tregs in Th17 cells | STZ-T1DM; chronic airway inflammation | [30,40] |
| B cells | miR-dependent down-regulation of JCHAIN, PTGS2, POU2AF1, TNFRSF13B, SH2D1A, LTA genes | Suppressed proliferation and reduced production of IgM. | B cell-mediated autoimmune diseases | [42] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Harrell, C.R.; Jovicic, N.; Djonov, V.; Volarevic, V. Therapeutic Use of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes: From Basic Science to Clinics. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12050474
Harrell CR, Jovicic N, Djonov V, Volarevic V. Therapeutic Use of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes: From Basic Science to Clinics. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(5):474. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12050474
Chicago/Turabian StyleHarrell, Carl Randall, Nemanja Jovicic, Valentin Djonov, and Vladislav Volarevic. 2020. "Therapeutic Use of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes: From Basic Science to Clinics" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 5: 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12050474
APA StyleHarrell, C. R., Jovicic, N., Djonov, V., & Volarevic, V. (2020). Therapeutic Use of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes: From Basic Science to Clinics. Pharmaceutics, 12(5), 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12050474