Recent Advances in Nanomaterial-Based Wound-Healing Therapeutics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Wound Infection
2.1. Types of Wounds
2.2. Normal Wound-Healing Process
2.3. Wound Dressing
2.4. Causes for Delayed Wound Healing
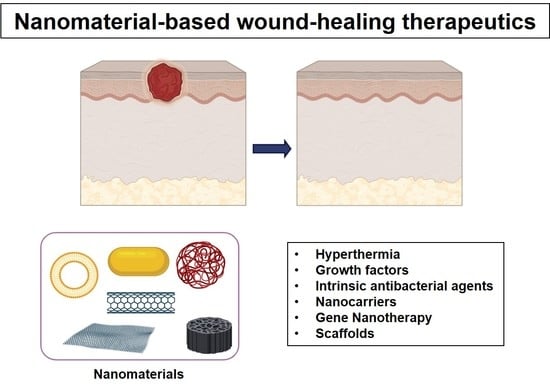
3. Nanomaterials in Wound Healing
3.1. Intrinsic Antibacterial Agents in Wound Healing
3.1.1. Metal and Metal Oxide Nanomaterials
Silver Nanoparticles
Gold Nanoparticles
Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles
3.1.2. Non-Metallic Nanomaterials
3.2. Nanomaterials as Nanocarriers for Wound Healing
3.2.1. Nanomaterials Combined with Antibiotics
3.2.2. Nanomaterials Containing Nitric Oxide
4. Nanomaterial-Based Scaffolds for Wound Healing
5. Nanomaterial-Based Growth Factors for Wound Healing
6. Nanomaterial-Based Innovative Strategies
6.1. Nanomaterials for Antibacterial Hyperthermia Treatment
6.2. Nanomaterial-Based Gene Nanotherapy
7. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, S.; DiPietro, L.A. Factors affecting wound healing. J. Dent. Res. 2010, 89, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eming, S.A.; Martin, P.; Canic, M.T. Wound repair and regeneration: Mechanisms, signaling, and translation. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 265sr6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gurtner, G.C.; Werner, S.; Barrandon, Y.; Longaker, M.T. Wound repair and regeneration. Nature 2008, 453, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, R.; Harding, K. Bacteria and wound healing. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 17, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.-H. Nanoparticle-Based Therapies for Wound Biofilm Infection: Opportunities and Challenges. IEEE Trans. NanoBiosci. 2016, 15, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamdan, S.; Pastar, I.; Drakulich, S.; Dikici, E.; Tomic-Canic, M.; Deo, S.; Daunert, S. Nanotechnology-Driven Therapeutic Interventions in Wound Healing: Potential Uses and Applications. ACS Cent. Sci. 2017, 3, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veves, A.; Falanga, V.; Armstrong, D.G.; Sabolinski, M.L. Graftskin, a human skin equivalent, is effective in the management of noninfected neuropathic diabetic foot ulcers: A prospective randomized multicenter clinical trial. Diabetes Care 2001, 24, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marston, W.A.; Hanft, J.; Norwood, P.; Pollak, R. The efficacy and safety of Dermagraft in improving the healing of chronic diabetic foot ulcers: Results of a prospective randomized trial. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 1701–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Driver, V.R.; Lavery, L.A.; Reyzelman, A.M.; Dutra, T.G.; Dove, C.R.; Kotsis, S.V.; Kim, H.M.; Chung, K.C. A clinical trial of Integra Template for diabetic foot ulcer treatment. Wound Repair Regen. 2015, 23, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiell, J.M.; Wieman, T.J.; Steed, D.L.; Perry, B.H.; Sampson, A.R.; Schwab, B.H. Efficacy and safety of becaplermin (recombinant human platelet-derived growth factor-BB) in patients with nonhealing, lower extremity diabetic ulcers: A combined analysis of four randomized studies. Wound Repair Regen. 1999, 7, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embil, J.M.; Nagai, M.K. Becaplermin: Recombinant platelet derived growth factor, a new treatment for healing diabetic foot ulcers. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2002, 2, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonder, M.A.; Lazarus, G.S.; Cowan, D.A.; Aronson-Cook, B.; Kohli, A.R.; Mamelak, A.J. Treating the chronic wound: A practical approach to the care of nonhealing wounds and wound care dressings. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2008, 58, 185–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalashnikova, I.; Das, S.; Seal, S. Nanomaterials for wound healing: Scope and advancement. Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 2593–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihai, M.M.; Dima, M.B.; Dima, B.; Holban, A. Nanomaterials for Wound Healing and Infection Control. Materials 2019, 12, 2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Naskar, A.; Kim, K.-S. Nanomaterials as Delivery Vehicles and Components of New Strategies to Combat Bacterial Infections: Advantages and Limitations. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiao, M.; Zhang, P.; Meng, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Luo, X.; Gao, M. Recent advancements in biocompatible inorganic nanoparticles towards biomedical applications. Biomater. Sci. 2018, 6, 726–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naskar, A.; Kim, K.-S. Black phosphorus nanomaterials as multi-potent and emerging platforms against bacterial infections. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 137, 103800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Mei, X.; Wang, Y.; Weng, X.; Liang, R.; Wei, M. Two-Dimensional nanomaterials: Fascinating materials in biomedical field. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 1707–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajendran, N.K.; Kumar, S.S.D.; Houreld, N.N.; Abrahamse, H. A review on nanoparticle based treatment for wound healing. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 44, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lu, K.-J.; Yu, C.-H.; Huang, Q.-L.; Du, Y. Nano-drug delivery systems in wound treatment and skin regeneration. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 17, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Gupta, A. Noninvasive red and near-infrared wavelength-induced photobiomodulation: Promoting impaired cutaneous wound healing. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2017, 33, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Junka, A.F.; Rakoczy, R.; Szymczyk, P.; Bartoszewicz, M.; Sedghizadeh, P.P.; Fijałkowski, K. Application of rotating magnetic fields increase the activity of antimicrobials against wound biofilm pathogens. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Upton, D.; Solowiej, K.; Hender, C.; Woo, K. Stress and pain associated with dressing change in patients with chronic wounds. J. Wound Care 2012, 21, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caló, E.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Biomedical applications of hydrogels: A review of patents and commercial products. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 65, 252–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landén, N.X.; Li, D.; Ståhle, M. Transition from inflammation to proliferation: A critical step during wound healing. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 3861–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dreifke, M.B.; Jayasuriya, A.A.; Jayasuriya, A.C. Current wound healing procedures and potential care. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 48, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matica, M.A.; Aachmann, F.L.; Tondervik, A.; Sletta, H.; Ostafe, V. Chitosan as a Wound Dressing Starting Material: Antimicrobial Properties and Mode of Action. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Xu, P.; Yao, Z.; Fang, Q.; Feng, L.; Guo, R.; Cheng, B. Preparation of Antimicrobial Hyaluronic Acid/Quaternized Chitosan Hydrogels for the Promotion of Seawater-Immersion Wound Healing. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Baker, A.B. Biomaterials and nanotherapeutics for enhancing skin wound healing. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2016, 4, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, M.; Ali, M.N.; Barakullah, A.; Gulzar, A.; Arshad, M.; Fatima, S.; Asad, M. Synthetic polymeric biomaterials for wound healing: A review. Prog. Biomater. 2018, 7, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinho, E.; Soares, G. Functionalization of cotton cellulose for improved wound healing. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 1887–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Sun, X.; Liang, L.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.-N. Gelatin-Based Hydrogels Blended with Gellan as an Injectable Wound Dressing. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 4766–4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fukuda, M.; Sasaki, H. Effects of Fluoroquinolone-Based Antibacterial Ophthalmic Solutions on Corneal Wound Healing. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 31, 536–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirilä, E.; Ramamurthy, N.; Maisi, P.; McClain, S.; Kucine, A.; Wahlgren, J.; Golub, L.; Salo, T.; Sorsa, T. Wound healing in ovariectomized rats: Effects of chemically modified tetracycline (CMT-8) and estrogen on matrix metalloproteinases −8, −13 and type I collagen expression. Curr. Med. Chem. 2001, 8, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, U.S.M.; Vishnu, V.; Sharmila, S.; Kumar, A. Formulation and evaluation of cefixime trihydrate topical gel for wound infections. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2018, 11, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heal, C.; Banks, J.; Lepper, P.D.; Kontopantelis, E.; Van Driel, M.L. Topical antibiotics for preventing surgical site infection in wounds healing by primary intention. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 2016, 011426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mori, H.M.; Kawanami, H.; Kawahata, H.; Aoki, M. Wound healing potential of lavender oil by acceleration of granulation and wound contraction through induction of TGF-beta in a rat model. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naderi, N.; Karponis, D.; Mosahebi, A.; Seifalian, A. Nanoparticles in wound healing from hope to promise from promise to routine. Front. Biosci. 2018, 23, 1038–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boroumand, Z.; Golmakani, N.; Boroumand, S. Clinical trials on silver nanoparticles for wound healing. Nanomed. J. 2018, 5, 186–191. [Google Scholar]
- Dissemond, J.; Böttrich, J.G.; Braunwarth, H.; Hilt, J.; Wilken, P.; Münter, K.C. Evidence for silver in wound care-meta-analysis of clinical studies from 2000–2015. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2017, 15, 524–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.S.D.; Rajendran, N.K.; Houreld, N.N.; Abrahamse, H. Recent advances on silver nanoparticle and biopolymer-based biomaterials for wound healing applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 115, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naskar, A.; Khan, H.; Sarkar, R.; Kumar, S.; Halder, D.; Jana, S. Anti-Biofilm activity and food packaging application of room temperature solution process based polyethylene glycol capped Ag-ZnO-Graphene nanocomposite. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 91, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burdușel, A.-C.; Gherasim, O.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Mogoantă, L.; Ficai, A.; Andronescu, E. Biomedical Applications of Silver Nanoparticles: An Up-to-Date Overview. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rangaraj, A.; Harding, K.; Leaper, D. Role of collagen in wound management. Wounds UK 2011, 7, 54–63. [Google Scholar]
- GhavamiNejad, A.; Unnithan, A.; Sasikala, A.R.K.; Samarikhalaj, M.; Thomas, R.G.; Jeong, Y.Y.; Nasseri, S.; Murugesan, P.; Wu, N.; Park, C.; et al. Mussel-Inspired Electrospun Nanofibers Functionalized with Size-Controlled Silver Nanoparticles for Wound Dressing Application. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 12176–12183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Sonshine, D.A.; Shervani, S.; Hurt, R.H. Controlled Release of Biologically Active Silver from Nanosilver Surfaces. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 6903–6913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, R.; He, T.; Xu, K.; Du, D.; Zhao, N.; Cheng, X.; Yang, J.; Shi, H.; Lin, Y. Biomedical Potential of Ultrafine Ag/AgCl Nanoparticles Coated on Graphene with Special Reference to Antimicrobial Performances and Burn Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 15067–15075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Jia, Y.; Qin, C.C.; Zhan, L.; Yan, X.; Cui, L.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, X.; Long, Y.-Z. In situ deposition of a personalized nanofibrous dressing via a handy electrospinning device for skin wound care. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 3482–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.; Zou, W.; Ning, W.; Fan, J.; Li, L.; Liu, B.; Liu, X. Synthesis of DNA-guided silver nanoparticles on a graphene oxide surface: Enhancing the antibacterial effect and the wound healing activity. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 28238–28248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vijayakumar, V.; Samal, S.K.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. Recent advancements in biopolymer and metal nanoparticle-based materials in diabetic wound healing management. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 122, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, R.; Prabaharan, M.; Kumar, P.S.; Nair, S.; Tamura, H. Biomaterials based on chitin and chitosan in wound dressing applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 322–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akturk, O.; Yasti, A.C.; Kuru, S.; Duymus, M.E.; Kaya, F.; Hucumenoglu, S.; Kismet, K.; Caydere, M.; Keskin, D. Collagen/gold nanoparticle nanocomposites: A potential skin wound healing biomaterial. J. Biomater. Appl. 2016, 31, 283–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, S.-H.; Chang, Y.-B.; Tsai, C.-L.; Fu, K.-Y.; Wang, S.-H.; Tseng, H.-J. Characterization and biocompatibility of chitosan nanocomposites. Colloids Surf. B: Biointerfaces 2011, 85, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkova, N.; Yukhta, M.; Pavlovich, O.; Goltsev, A.M. Application of Cryopreserved Fibroblast Culture with Au Nanoparticles to Treat Burns. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sherwani, M.A.; Tufail, S.; Khan, A.A.; Owais, M. Gold Nanoparticle-Photosensitizer Conjugate Based Photodynamic Inactivation of Biofilm Producing Cells: Potential for Treatment of C. albicans Infection in BALB/c Mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-A.; Chen, H.-M.; Yao, Y.-D.; Hung, C.-F.; Tu, C.-S.; Liang, Y.-J. Topical treatment with anti-oxidants and Au nanoparticles promote healing of diabetic wound through receptor for advance glycation end-Products. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 47, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, X.; Tan, L.; Cui, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhua, S.; Li, Z.; Yuan, X.; Zheng, Y.; Yeung, K.W.K.; et al. Controlled-temperature photothermal and oxidative bacteria killing and acceleration of wound healing by polydopamine-assisted Au-hydroxyapatite nanorods. Acta Biomater. 2018, 77, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randeria, P.S.; Seeger, M.; Wang, X.-Q.; Wilson, H.M.; Shipp, D.; Mirkin, C.A.; Paller, A.S. siRNA-based spherical nucleic acids reverse impaired wound healing in diabetic mice by ganglioside GM3 synthase knockdown. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5573–5578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.-W.; Wei, J.-J.; Zhang, M.-Y.; Zhang, X.-L.; Yin, X.-F.; Lu, C.; Song, J.; Bai, S.-M.; Yang, H. Water-Based Black Phosphorus Hybrid Nanosheets as a Moldable Platform for Wound Healing Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 35495–35502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Xiang, Y.; Liu, X.; Cui, Z.; Yang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhua, S.; Zheng, Y.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Wua, S. Repeatable Photodynamic Therapy with Triggered Signaling Pathways of Fibroblast Cell Proliferation and Differentiation to Promote Bacteria-Accompanied Wound Healing. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 1747–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajji, S.; Ben Khedir, S.; Hamza-Mnif, I.; Hamdi, M.; Jedidi, I.; Kallel, R.; Boufi, S.; Nasri, M. Biomedical potential of chitosan-silver nanoparticles with special reference to antioxidant, antibacterial, hemolytic and in vivo cutaneous wound healing effects. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2019, 1863, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holban, A.M.; Grumezescu, V.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Vasile, B.S.; Trusca, R.; Cristescu, R.; Socol, G.; Iordache, F. Antimicrobial nanospheres thin coatings prepared by advanced pulsed laser technique. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 872–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, P.T.S.; Lakshmanan, V.-K.; Anilkumar, T.; Ramya, C.; Reshmi, P.; Unnikrishnan, A.; Nair, S.V.; Jayakumar, R. Flexible and Microporous Chitosan Hydrogel/Nano ZnO Composite Bandages for Wound Dressing: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 2618–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholipour-Kanani, A.; Bahrami, S.H.; Rabbani, S. Effect of novel blend nanofibrous scaffolds on diabetic wounds healing. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopal, A.; Kant, V.; Gopalakrishnan, A.; Tandan, S.K.; Kumar, D. Chitosan-based copper nanocomposite accelerates healing in excision wound model in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 731, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasile, B.S.; Oprea, O.; Voicu, G.; Ficai, A.; Andronescu, E.; Teodorescu, A.; Holban, A. Synthesis and characterization of a novel controlled release zinc oxide/gentamicin–chitosan composite with potential applications in wounds care. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 463, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Joslin, S.; Dellinger, A.; Ehrich, M.; Brooks, B.; Ren, Q.; Rodeck, U.; Lenk, R.; Kepley, C.L. A novel class of compounds with cutaneous wound healing properties. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2010, 6, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Guo, B.; Wu, H.; Liang, Y.; Ma, P.X. Injectable antibacterial conductive nanocomposite cryogels with rapid shape recovery for noncompressible hemorrhage and wound healing. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.; Wang, H.-L.; Iyer, R. Suppression of Proinflammatory Cytokines in Functionalized Fullerene-Exposed Dermal Keratinocytes. J. Nanomater. 2010, 2010, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, M.S.; NasserAbdelhamidab, H.; Wu, H.-F. Near infrared (NIR) laser mediated surface activation of graphene oxide nanoflakes for efficient antibacterial, antifungal and wound healing treatment. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 127, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anghel, I.; Holban, A.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Andronescu, E.; Ficai, A.; Anghel, A.G.; Maganu, M.; Lazăr, V.; Chifiriuc, M.C. Modified wound dressing with phyto-nanostructured coating to prevent staphylococcal and pseudomonal biofilm development. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abenojar, E.C.; Wickramasinghe, S.; Ju, M.; Uppaluri, S.; Klika, A.; George, J.; Barsoum, W.; Frangiamore, S.J.; Higuera-Rueda, C.A.; Samia, A.C.S. Magnetic Glycol Chitin-Based Hydrogel Nanocomposite for Combined Thermal and d-Amino-Acid-Assisted Biofilm Disruption. ACS Infect. Dis. 2018, 4, 1246–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, L.A.; Dekker, L.; Kallumadil, M.; Southern, P.; Wilson, M.; Nair, S.P.; Pankhurst, Q.A.; Parkin, I.P. Carboxylic acid-stabilised iron oxide nanoparticles for use in magnetic hyperthermia. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 6529–6535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-H.; Yamayoshi, I.; Mathew, S.; Lin, H.; Nayfach, J.; Simon, S.I.; Liln, H. Magnetic nanoparticle targeted hyperthermia of cutaneous Staphylococcus aureus infection. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 41, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mugabe, C.; Azghani, A.O.; Omri, A. Liposome-mediated gentamicin delivery: Development and activity against resistant strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from cystic fibrosis patients. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2005, 55, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Huang, X.; Wang, X.; Liao, G.; Chen, Z. Preparation and characterization of flexible nanoliposomes loaded with daptomycin, a novel antibiotic, for topical skin therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 1285–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chereddy, K.K.; Vandermeulen, G.; Preat, V. PLGA based drug delivery systems: Promising carriers for wound healing activity. Wound Repair Regen. 2016, 24, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.-W.; Nurhasni, H.; Cao, J.; Choi, M.; Kim, I.; Lee, B.L.; Jung, Y. Nitric oxide-releasing poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)-polyethylenimine nanoparticles for prolonged nitric oxide release, antibacterial efficacy, and in vivo wound healing activity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 3065–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shahverdi, S.; Hajimiri, M.; Esfandiari, M.A.; Larijani, B.; Atyabi, F.; Rajabiani, A.; Dehpour, A.R.; Gharehaghaji, A.A.; Dinarvand, R. Fabrication and structure analysis of poly(lactide-co-glycolic acid)/silk fibroin hybrid scaffold for wound dressing applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 473, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetrick, E.M.; Shin, J.H.; Paul, H.S.; Schoenfisch, M.H. Anti-biofilm efficacy of nitric oxide-releasing silica nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2782–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balaure, P.C.; Holban, A.M.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Mogosanu, G.D.; Bălşeanu, T.A.; Stan, M.; Dinischiotu, A.; Volceanov, A.; Mogoantă, L. In vitro and in vivo studies of novel fabricated bioactive dressings based on collagen and zinc oxide 3D scaffolds. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 557, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Han, Y.; Cui, M.; Tey, H.L.; Wang, L.; Xu, C. ZnO nanoparticles as an antimicrobial tissue adhesive for skin wound closure. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 4535–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naskar, A.; Lee, S.; Kim, K.-S. Easy One-Pot Low-Temperature Synthesized Ag-ZnO Nanoparticles and Their Activity Against Clinical Isolates of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Naskar, A.; Bera, S.; Bhattacharya, R.; Roy, S.S.; Jana, S. Effect of bovine serum albumin immobilized Au–ZnO–graphene nanocomposite on human ovarian cancer cell. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 734, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naskar, A.; Lee, S.; Kim, K.-S. Antibacterial potential of Ni-doped zinc oxide nanostructure: Comparatively more effective against Gram-negative bacteria including multi-drug resistant strains. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 1232–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paladini, F.; Pollini, M. Antimicrobial Silver Nanoparticles for Wound Healing Application: Progress and Future Trends. Materials 2019, 12, 2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elahi, N.; Kamali, M.; Baghersad, M.H. Recent biomedical applications of gold nanoparticles: A review. Talanta 2018, 184, 537–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niska, K.; Zielinska, E.; Radomski, M.W.; Inkielewicz-Stepniak, I. Metal nanoparticles in dermatology and cosmetology: Interactions with human skin cells. Chem. Interact. 2018, 295, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arafa, M.G.; El-Kased, R.; Elmazar, M.M. Thermoresponsive gels containing gold nanoparticles as smart antibacterial and wound healing agents. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naskar, A.; Saha, P.; Roy, S.S.; Jana, S.; Bera, S.; Bhattacharya, R.; Sen, T. Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of Ag incorporated ZnO–graphene nanocomposites. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 88751–88761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korrapati, P.S.; Karthikeyan, K.; Satish, A.; Krishnaswamy, V.R.; Venugopal, J.R.; Ramakrishna, S. Recent advancements in nanotechnological strategies in selection, design and delivery of biomolecules for skin regeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 67, 747–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singla, R.; Soni, S.; Patial, V.; Kulurkar, P.M.; Kumari, A.; Mahesh, S.; Padwad, Y.S.; Yadav, S.K. In vivo diabetic wound healing potential of nanobiocomposites containing bamboo cellulose nanocrystals impregnated with silver nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadinoto, K.; Sundaresan, A.; Cheow, W.S. Lipid–polymer hybrid nanoparticles as a new generation therapeutic delivery platform: A review. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 85, 427–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheow, W.S.; Hadinoto, K. Factors affecting drug encapsulation and stability of lipid–Polymer hybrid nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 85, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Chang, H.-Y.; Lu, J.-K.; Huang, Y.-C.; Harroun, S.G.; Tseng, Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, C.-C.; Chang, H.-T. Self-Assembly of Antimicrobial Peptides on Gold Nanodots: Against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria and Wound-Healing Application. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 7189–7199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, E.; Muller, R.H. SLN and NLC for topical delivery of ketoconazole. J. Microencapsul. 2005, 22, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severino, P.; Fangueiro, J.; Chaud, M.V.; Cordeiro, J.; Silva, A.; Souto, E. Advances in nanobiomaterials for topical administrations: New galenic and cosmetic formulations. In Nanobiomaterials in Galenic Formulations and Cosmetics, 1st ed.; Grumezescu, A., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 10, pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, P.; Nie, X.; Zou, M.; Shi, Y.; Cheng, G. Recent advances in materials for extended-release antibiotic delivery system. J. Antibiot. 2011, 64, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gould, L. Topical Collagen-Based Biomaterials for Chronic Wounds: Rationale and Clinical Application. Adv. Wound Care 2016, 5, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Englander, L.; Friedman, A. Nitric Oxide Nanoparticle Technology: A novel antimicrobial agent in the context of current treatment of skin and soft tissue infection. J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2010, 3, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Barraud, N.; Hassett, D.J.; Hwang, S.-H.; Rice, S.A.; Kjelleberg, S.; Webb, J.S. Involvement of Nitric Oxide in Biofilm Dispersal of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 7344–7353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, H.W.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.; Song, H.B.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, K.; Kim, W.J. Light-Induced Acid Generation on a Gatekeeper for Smart Nitric Oxide Delivery. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 4199–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihu, M.R.; Sandkovsky, U.; Han, G.; Friedman, J.M.; Martinez, L.R.; Nosanchuk, J.D. The use of nitric oxide releasing nanoparticles as a treatment against Acinetobacter baumannii in wound infections. Virulence 2010, 1, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Macherla, C.; Sanchez, D.A.; Ahmadi, M.S.; Vellozzi, E.M.; Friedman, A.; Nosanchuk, J.D.; Martinez, L.R. Nitric Oxide Releasing Nanoparticles for Treatment of Candida Albicans Burn Infections. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poinern, G.; Fawcett, D.; Ng, Y.J.; Ali, N.; Brundavanam, R.K.; Jiang, Z.-T. Nanoengineering a biocompatible inorganic scaffold for skin wound healing. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2010, 6, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Gu, H.; Mi, H.; Rao, C.; Fu, J.; Turng, L.-S. Fabrication of scaffolds in tissue engineering: A review. Front. Mech. Eng. 2017, 13, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Meng, X.-H.; Fan, J.; Yang, L.; Wen, Q.-L.; Ye, S.-J.; Lin, S.; Wang, B.-Q.; Chen, L.-L.; Wu, J.; et al. Acceleration of dermal wound healing by using electrospun curcumin-loaded poly(ε-caprolactone)-poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(ε-caprolactone) fibrous mats. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2013, 102, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongargaonkar, A.A.; Bowlin, G.L.; Yang, H. Electrospun Blends of Gelatin and Gelatin–Dendrimer Conjugates As a Wound-Dressing and Drug-Delivery Platform. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 4038–4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rigo, C.; Ferroni, L.; Tocco, I.; Roman, M.; Munivrana, I.; Gardin, C.; Cairns, W.R.L.; Vindigni, V.; Azzena, B.; Barbante, C.; et al. Active Silver Nanoparticles for Wound Healing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 4817–4840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Auddy, R.G.; Abdullah, F.; Das, S.; Roy, P.; Datta, S.; Mukherjee, A. New Guar Biopolymer Silver Nanocomposites for Wound Healing Applications. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, L.; Fu, R.; Li, C.; Yu, C.; Li, Z.; Guan, H.; Hu, D.; Zhao, D. Silver nanoparticle/chitosan oligosaccharide/poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibers as wound dressings: A preclinical study. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 4131–4145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.N.; Hong, Y.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, S.M.; Suh, K.-Y. Effect of orientation and density of nanotopography in dermal wound healing. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 8782–8792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Y.; Yu, D.; Wang, P.; Xu, J.; Li, D.; Ding, M. Nanotechnology promotes the full-thickness diabetic wound healing effect of recombinant human epidermal growth factor in diabetic rats. Wound Repair Regen. 2010, 18, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, Y.; Mou, Y. A fibrin gel loaded with chitosan nanoparticles for local delivery of rhEGF: Preparation and in vitro release studies. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2011, 22, 1221–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Paras, C.B.; Weng, H.; Punnakitikashem, P.; Su, L.-C.; Vu, K.; Tang, L.; Yang, J.; Nguyen, K.T. Dual growth factor releasing multi-functional nanofibers for wound healing. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 9351–9359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, K.; Yao, K.; Xu, Z.-K. Nanomaterials with a photothermal effect for antibacterial activities: An overview. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 8680–8691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Cai, Q.; Qi, W.; Jia, Y.; Xiong, T.; Fan, Z.; Liu, S.; Yang, J.; Li, N.; Chang, B. BSA-CuS Nanoparticles for Photothermal Therapy of Diabetic Wound Infection In Vivo. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 9510–9516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, W.-L.; Lin, T.-T.; Sureshbabu, R.; Chia, W.-T.; Hsiao, H.-C.; Liu, H.-Y.; Yang, C.-M.; Sung, H. A rapid drug release system with a NIR light-activated molecular switch for dual-modality photothermal/antibiotic treatments of subcutaneous abscesses. J. Control. Release 2015, 199, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankhurst, Q.A.; Connolly, J.; Jones, S.K.; Dobson, J. Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, R167–R181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Ma, L.; Gaoa, C. Design of gene-activated matrix for the repair of skin and cartilage. Polym. J. 2014, 46, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.S.; Kim, H.S.; Yoo, H.S. Electrospinning strategies of drug-incorporated nanofibrous mats for wound recovery. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2013, 5, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobsa, S.; Kristofik, N.J.; Sawyer, A.; Bothwell, A.L.; Kyriakides, T.R.; Saltzman, W.M. An electrospun scaffold integrating nucleic acid delivery for treatment of full-thickness wounds. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 3891–3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Phases | 1st: Hemostasis (Few Minutes) | 2nd: Inflammatory (0–5 Days) | 3rd: Proliferative (5 Days–3 Weeks) | 4th: Remodeling (3 Weeks–≥2 Years) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specific events |
|
|
|
|
| Nanomaterials |
|
|
|
|
| Nanomaterials | Role in Wound Healing | References |
|---|---|---|
| Ag NPs |
| [40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47] [48] [49] |
| Au NPs |
| [50,51,52,53,54,55] [56] [57] [58] |
| BP |
| [59] [60] |
| Chitosan |
| [27,61,62] [53,61,63] [64,65,66] |
| CNTs |
| [13,67] [68] |
| Fullerene |
| [67,69] |
| Graphene |
| [47] [70] [49] |
| Iron oxide NPs |
| [71] [72,73,74] |
| Liposomes |
| [60,75,76] |
| PLGA NPs |
| [77] [78] [79] |
| Silica NPs |
| [80] |
| ZnO NPs |
| [81,82] [66] |
| Scaffold Material | Activity | References |
|---|---|---|
| PLGA/silk fibroin | Diabetic wound healing | [79] |
| Chitosan-PVA | Treated diabetic wounds in rats | [64] |
| Nanofiber with Ag NPs | Reduced inflammation, increased wound healing, low cytotoxicity and long-term antibacterial action | [48] |
| Fe3O4@C16 | Showed antibacterial and anti-adherence properties, which are essential for wound regeneration | [71] |
| Gel containing gentamicin, ZnO NPs and chitosan | Showed synergistic antibacterial activity and can be beneficial for wound healing | [66] |
| Ag NPs in polyethylene cloth | Fast regeneration of cutaneous layer in vivo | [109] |
| Guar gum with Ag NPs | Enhanced wound closure | [110] |
| PVA, chitosan oligosaccharides with Ag NPs | Excellent antibacterial activity within wound site and no toxicity | [111] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Naskar, A.; Kim, K.-s. Recent Advances in Nanomaterial-Based Wound-Healing Therapeutics. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12060499
Naskar A, Kim K-s. Recent Advances in Nanomaterial-Based Wound-Healing Therapeutics. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(6):499. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12060499
Chicago/Turabian StyleNaskar, Atanu, and Kwang-sun Kim. 2020. "Recent Advances in Nanomaterial-Based Wound-Healing Therapeutics" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 6: 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12060499
APA StyleNaskar, A., & Kim, K. -s. (2020). Recent Advances in Nanomaterial-Based Wound-Healing Therapeutics. Pharmaceutics, 12(6), 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12060499