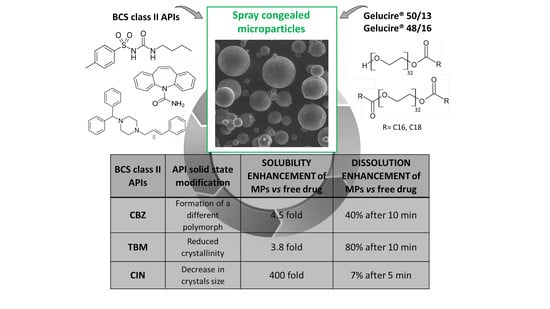
Different BCS Class II Drug-Gelucire Solid Dispersions Prepared by Spray Congealing: Evaluation of Solid State Properties and In Vitro Performances
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Samples
2.3. Morphological Analysis of MPs and Drug Content Determination
2.3.1. Morphological Analysis
2.3.2. Analytical Methods
2.3.3. Determination of Drug Content
2.4. Solid State Characterization of MPs
2.4.1. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Studies
2.4.2. Fourier Transform-Infrared Spectra (FT-IR) Analysis
2.4.3. Hot Stage Microscopy (HSM) Analysis
2.4.4. Powder X-Ray Diffraction (PXRD) Analysis
2.5. Solubility and Dissolution Tests of MPs
2.5.1. Solubility Studies
2.5.2. Dissolution Studies
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphology and Drug Content of the Microparticles
3.2. Solid State Characterization of the MPs
3.2.1. Characterization of MPs containing CBZ
3.2.2. Characterization of MPs Containing TBM
3.2.3. Characterization of MPs Containing CIN
3.3. Solubility and Dissolution Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Duong, T.; Van den Mooter, G. The role of the carrier in the formulation of pharmaceutical solid dispersions. Part I: Crystalline and semi-crystalline carriers. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 1583–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Harris, M.T.; Taylor, L.S. Modification of Crystallization Behavior in Drug/Polyethylene Glycol Solid Dispersions. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Taylor, L.S.; Harris, M.T. Evaluation of the Microstructure of Semicrystalline Solid Dispersions. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Duong, T.; Reekmans, G.; Venkatesham, A.; Van Aerschot, A.; Adriaensens, P.; Van Humbeeck, J.; Van den Mooter, G. Spectroscopic Investigation of the Formation and Disruption of Hydrogen Bonds in Pharmaceutical Semicrystalline Dispersions. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 1726–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Duong, T.; Goderis, B.; Van Humbeeck, J.; Van den Mooter, G. Microstructure of Pharmaceutical Semicrystalline Dispersions: The Significance of Polymer Conformation. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Duong, T.; Van Humbeeck, J.; Van den Mooter, G. Crystallization Kinetics of Indomethacin/Polyethylene Glycol Dispersions Containing High Drug Loadings. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 2493–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmpalexis, P.; Kachrimanis, K.; Georgarakis, E. Physicochemical characterization of nimodipine–polyethylene glycol solid dispersion systems. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2014, 40, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Duong, T.; Lüdeker, D.; Van Bockstal, P.-J.; De Beer, T.; Van Humbeeck, J.; Van den Mooter, G. Polymorphism of Indomethacin in Semicrystalline Dispersions: Formation, Transformation, and Segregation. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 1037–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, W.S.; Chan, K.L. FTIR Spectroscopic Study of Poly(Ethylene Glycol)–Nifedipine Dispersion Stability in Different Relative Humidities. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, T.; Ding, W.; Dong, C.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Li, Y. Dissolution and oral bioavailability enhancement of praziquantel by solid dispersions. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2018, 8, 580–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Real, D.; Orzan, L.; Leonardi, D.; Salomon, C.J. Improving the Dissolution of Triclabendazole from Stable Crystalline Solid Dispersions Formulated for Oral Delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 21, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahi, K.C.; Patra, C.N.; Jena, G.K.; Ghose, D.; Jena, J.; Panda, S.K.; Sahu, M. Gelucire: A versatile polymer for modified release drug delivery system. Future J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 4, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Marchaud, D.; Craig, D.Q.M. An investigation into the mechanism of dissolution rate enhancement of poorly water-soluble drugs from spray chilled gelucire 50/13 microspheres. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Badry, M. Physicochemical characterization and dissolution properties of meloxicam-gelucire 50/13 binary systems. Sci. Pharm. 2011, 79, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaker, M.A. Dissolution and bioavailability enhancement of Atorvastatin: Gelucire semi-solid binary system. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 43, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, D.Q.M. The mechanisms of drug release from solid dispersions in water-soluble polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 231, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutananta, W.; Craig, D.Q.M.; Newton, J.M. An Evaluation of the Mechanisms of Drug Release from Glyceride Bases. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1995, 47, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutananta, W.; Craig, D.Q.M.; Newton, J.M. An Investigation into the Effects of Preparation Conditions and Storage on the Rate of Drug Release from Pharmaceutical Glyceride Bases. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1995, 47, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Craig, D.Q.M. Role of blooming in determining the storage stability of lipid-based dosage forms. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 93, 2962–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoni, S.; Albertini, B.; Passerini, N. Spray Congealing: An Emerging Technology to Prepare Solid Dispersions with Enhanced Oral Bioavailability of Poorly Water Soluble Drugs. Molecules 2019, 24, 3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertoni, S.; Dolci, L.S.; Albertini, B.; Passerini, N. Spray congealing: A versatile technology for advanced drug delivery systems. Ther. Deliv. 2018, 9, 833–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoni, S.; Albertini, B.; Ferraro, L.; Beggiato, S.; Dalpiaz, A.; Passerini, N. Exploring the use of spray congealing to produce solid dispersions with enhanced indomethacin bioavailability: In vitro characterization and in vivo study. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 139, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jannin, V.; Di Cuia, M.; Chevrier, S.; Faure, A.; Chavant, Y.; Voutsinas, C.; Demarne, F. Characterization of new self-emulsifying excipient to expand formulation options for poorly soluble drugs: Gelucire 48/16. In Proceedings of the AAPS Annual Meeting and Exposition, Chicago, IL, USA, 14–18 October 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passerini, N.; Perissutti, B.; Moneghini, M.; Voinovich, D.; Albertini, B.; Cavallari, C.; Rodriguez, L. Characterization of Carbamazepine–Gelucire 50/13 Microparticles Prepared by a Spray-congealing Process Using Ultrasounds. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 91, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingone, G.; Rubessa, F. Release of carbamazepine from solid dispersions with polyvinylpyrrolidone/vinylacetate copolymer (PVP/VA). STP Pharma Sci. J. 1994, 4, 122–127. [Google Scholar]
- Grzesiak, A.L.; Lang, M.; Kim, K.; Matzger, A.J. Comparison of the Four Anhydrous Polymorphs of Carbamazepine and the Crystal Structure of Form I. J. Pharm. Sci. 2003, 92, 2260–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, N.; Craig, D.Q.M. The influence of drug incorporation on the structure and release properties of solid dispersions in lipid matrices. J. Control. Release 2003, 93, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Bao, Y.; Wang, J.; Rohani, S. In situ focused beam reflectance measurement (FBRM), attenuated total reflectance fourier transform infrared (ATR-FTIR) and Raman characterization of the polymorphic transformation of carbamazepine. Pharmaceutics 2012, 4, 164–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.W.; Yeo, S. Do Antisolvent crystallization of carbamazepine from organic solutions. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2012, 90, 2202–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallari, C.; Fini, A.; Ceschel, G. Design of olanzapine/lutrol solid dispersions of improved stability and performances. Pharmaceutics 2013, 5, 570–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naima, Z.; Siro, T.; Juan-Manuel, G.-D.; Chantal, C.; René, C.; Jerome, D. Interactions between carbamazepine and polyethylene glycol (PEG) 6000: Characterisations of the physical, solid dispersed and eutectic mixtures. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 12, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perissutti, B.; Rubessa, F.; Princivalle, F. Solid dispersions of carbamazepine with Gelucire 44/14 and 50/13. STP Pharma Sci. J. 2000, 10, 479–484. [Google Scholar]
- Parambil, J.V.; Poornachary, S.K.; Hinder, S.J.; Tan, R.B.H.; Heng, J.Y.Y. Establishing template-induced polymorphic domains for API crystallisation: The case of carbamazepine. CrystEngComm 2015, 17, 6384–6392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, R.M.; Siqueira, S.; Machado, M.O.; Freitas, L.A.P. The effect of homogenization method on the properties of carbamazepine microparticles prepared by spray congealing. J. Microencapsul. 2013, 30, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, R.M.; Siqueira, S.; Tacon, L.A.; Freitas, L.A.P. Microstructured ternary solid dispersions to improve carbamazepine solubility. Powder Technol. 2012, 215–216, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, R.; Gonen, S.; Hoag, S.W. Influence of polyethylene glycol and povidone on the polymorphic transformation and solubility of carbamazepine. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 240, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustichelli, C.; Gamberini, G.; Ferioli, V.; Gamberini, M.C.; Ficarra, R.; Tommasini, S. Solid-state study of polymorphic drugs: Carbamazepine. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2000, 23, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowes, M.M.J.; Caira, M.R.; Lötter, A.P.; Van Der Watt, J.G. Physicochemical Properties and X-ray Structural Studies of the Trigonal Polymorph of Carbamazepine. J. Pharm. Sci. 1987, 76, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirunahari, S.; Aitipamula, S.; Chow, P.S.; Tan, R.B.H. Conformational polymorphism of tolbutamide: A structural, spectroscopic, and thermodynamic characterization of Burger’s Forms I-IV. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 2975–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, G.; Komasaka, T.; Bando, R.; Yoshihashi, Y.; Yonemochi, E.; Fujii, K.; Uekusa, H.; Terada, K. Reevaluation of solubility of tolbutamide and polymorphic transformation from Form I to unknown crystal form. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 369, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türk, M.; Bolten, D. Polymorphic properties of micronized mefenamic acid, nabumetone, paracetamol and tolbutamide produced by rapid expansion of supercritical solutions (RESS). J. Supercrit. Fluids 2016, 116, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, J.A.; Taylor, L.S. Evaluation and modeling of the eutectic composition of various drug-polyethylene glycol solid dispersions. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2011, 16, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martı́nez-Ohárriz, M.C.; Martı́n, C.; Goñi, M.M.; Rodrı́guez-Espinosa, C.; Tros-Ilarduya, M.C.; Zornoza, A. Influence of polyethylene glycol 4000 on the polymorphic forms of diflunisal. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 1999, 8, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, K.; Hirayama, F.; Uekama, K. Characterization of Tolbutamide Polymorphs (Burger’s Forms II and IV) and Polymorphic Transition Behavior. J. Pharm. Sci. 1999, 88, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedzierewicz, F.; Huffman, M.; Maincent, P. Comparison of tolbutamide β-cyclodextrin inclusion compounds and solid dispersions: Physicochemical characteristics and dissolution studies. Int. J. Pharm. 1990, 58, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedzierewicz, F.; Villieras, F.; Zinutti, C.; Hoffman, M.; Maincent, P. A 3 year stability study of tolbutamide solid dispersions and β-cyclodextrin complex. Int. J. Pharm. 1995, 117, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira Jørgensen, S.; Rades, T.; Mu, H.; Graeser, K.; Müllertz, A. Exploring the utility of the Chasing Principle: Influence of drug-free SNEDDS composition on solubilization of carvedilol, cinnarizine and R3040 in aqueous suspension. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditzinger, F.; Price, D.J.; Ilie, A.-R.; Köhl, N.J.; Jankovic, S.; Tsakiridou, G.; Aleandri, S.; Kalantzi, L.; Holm, R.; Nair, A.; et al. Lipophilicity and hydrophobicity considerations in bio-enabling oral formulations approaches—A PEARRL review. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2019, 71, 464–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baird, J.A.; Van Eerdenbrugh, B.; Taylor, L.S. A Classification System to Assess the Crystallization Tendency of Organic Molecules from Undercooled Melts. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 3787–3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eerdenbrugh, B.; Raina, S.; Hsieh, Y.; Augustijns, P.; Taylor, L.S. Classification of the Crystallization Behavior of Amorphous Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients in Aqueous Environments. Pharm. Res. 2014, 31, 969–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eerdenbrugh, B.; Baird, J.A.; Taylor, L.S. Crystallization tendency of active pharmaceutical ingredients following rapid solvent evaporation—Classification and comparison with crystallization tendency from undercooled melts. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 3826–3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paus, R.; Hart, E.; Ji, Y.; Sadowski, G. Solubility and Caloric Properties of Cinnarizine. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2015, 60, 2256–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Samples | Constituents (%, w/w) | Actual Drug Content (%, w/w) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gelucire® 50/13 | Gelucire® 48/16 | API | CBZ | CIN | TBM | |
| MPs A | 90 | - | 10 | 10.32 ± 0.13 | 9.38 ± 0.76 | 10.72 ± 0.87 |
| MPs B | 45 | 45 | 10.14 ± 0.06 | 9.37 ± 0.97 | 9.76 ± 0.11 | |
| MPs C | 27 | 63 | 9.71 ± 0.37 | 8.19 ± 0.94 | 9.76 ± 0.27 | |
| Nomenclature | Crystal Structure | Morphology | XRD Diagnostic Peaks (°, 2θ) | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | Triclinic | Fine needles | 7.9, 8.6, 9.4, 12.2, 13.1, 19.9 | Stable form at high temperature |
| II | Trigonal | Long and thick needles | 8.7, 13.3, 15.0, 18.5, 20.1, 24.5 | Metastable form, considered an impurity of form III |
| III | P-Monoclinic | Plate-shaped prisms | 15.3, 15.9, 17.2, 19.5, 25.0 | Commercial form. Stable form at room temperature, highly hygroscopic |
| IV | C-Monoclinic | Spherical plates | 14.1, 17.9, 21.8, 33.1 | Considered an impurity of form III, less soluble |
| dihydrate | - | Fine needles | 8.8, 12.1, 18.8, 19.4 | Formed in humid conditions, less soluble than form III |
| Nomenclature | Crystal Structure | Morphology | XRD Diagnostic Peaks (°, 2θ) | Melting Point (°C), ΔHfus (kJ/mol) | Transition Point (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IH | - | - | - | 128, 23.8 | - |
| IL | Orthorhombic | Prism | 8.7, 12.1, 19.9. 20.9 | - | 40 |
| II | Monoclinic | Plate | 10.3, 11.3, 19.6 | 117, 26.0 | - |
| III | Monoclinic | Needle | 11.2, 15.4, 18.2 | - | 106 |
| IV | Monoclinic | Needle | 10.6, 18.0, 18.9 | - | 88 |
| API | DSC | HSM | PXRD | FT-IR | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBZ | Absence of the API melting endotherm | Drug crystals in the melted carrier (solubilization at 60 °C–140 °C) | Definite peaks at different 2θ position | No evidence of drug – carrier interaction | Partial API solubilization in the carrier and recrystallization in different polymorph |
| TBM | Absence of the API melting endotherm | No drug crystals in the melted carrier (60 °C) | Broader and less intense peaks | Evidence of drug-carrier interactions | Partial API solubilization in the carrier with reduced crystallinity |
| CIN | Absence of the API melting endotherm | Drug crystals in the melted carrier (solubilization at 60 °C–100 °C) | Broader and less intense peaks | No evidence of drug – carrier interaction | Partial API solubilization in the carrier with formation of smaller drug crystals |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bertoni, S.; Albertini, B.; Passerini, N. Different BCS Class II Drug-Gelucire Solid Dispersions Prepared by Spray Congealing: Evaluation of Solid State Properties and In Vitro Performances. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 548. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12060548
Bertoni S, Albertini B, Passerini N. Different BCS Class II Drug-Gelucire Solid Dispersions Prepared by Spray Congealing: Evaluation of Solid State Properties and In Vitro Performances. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(6):548. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12060548
Chicago/Turabian StyleBertoni, Serena, Beatrice Albertini, and Nadia Passerini. 2020. "Different BCS Class II Drug-Gelucire Solid Dispersions Prepared by Spray Congealing: Evaluation of Solid State Properties and In Vitro Performances" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 6: 548. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12060548
APA StyleBertoni, S., Albertini, B., & Passerini, N. (2020). Different BCS Class II Drug-Gelucire Solid Dispersions Prepared by Spray Congealing: Evaluation of Solid State Properties and In Vitro Performances. Pharmaceutics, 12(6), 548. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12060548