Chitosan Derivatives with Mucoadhesive and Antimicrobial Properties for Simultaneous Nanoencapsulation and Extended Ocular Release Formulations of Dexamethasone and Chloramphenicol Drugs
Abstract
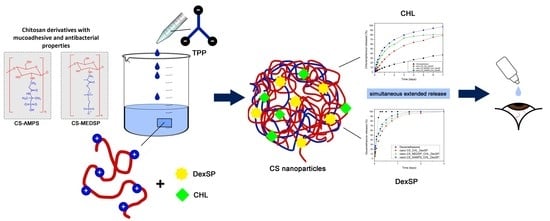
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of CS Derivatives
2.3. Preparation of CS Nanoparticles
2.4. Characterization of Chitosan Derivatives
2.4.1. Fourier-Transformed Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.4.2. Wide angle X-Ray Scattering
2.4.3. Swelling Study
2.4.4. 3-[4,5-Dimethylthiazole-2-yl]-2,5-Diphenyltetrazolium Bromide (MTT) Assay
2.4.5. Mucoadhesive Strength
2.4.6. In Vitro Antibacterial Activity Testing
2.5. Characterisation of Encapsulated Nanoparticles in CS Derivatives
2.5.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.5.2. Size Measurements of Nanoparticles
2.5.3. Differential Scanning Calorimeter (DSC)
2.5.4. Drug Loading
2.5.5. In Vitro Dissolution Studies
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of CS Derivatives
3.2. Characterization of Drug-Loaded Nanoparticles
3.3. Drug Release
3.4. Modeling of Drug Release Data
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Silva, M.M.; Calado, R.; Marto, J.; Bettencourt, A.; Almeida, J.; Gonçalves, L.M.D. Chitosan Nanoparticles as a Mucoadhesive Drug Delivery System for Ocular Administration. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gaudana, R.; Ananthula, H.K.; Parenky, A.; Mitra, A.K. Ocular Drug Delivery. AAPS J. 2010, 12, 348–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urtti, A. Challenges and obstacles of ocular pharmacokinetics and drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2006, 58, 1131–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Yañez, F.; Concheiro, A. Ocular drug delivery from molecularly-imprinted contact lenses. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2010, 20, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Cholkar, K.; Agrahari, V.; Mitra, A.K. Ocular drug delivery systems: An overview. World J. Pharmacol. 2013, 2, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumelle, C.; Gholizadeh, S.; Annabi, N.; Dana, R. Advances and limitations of drug delivery systems formulated as eye drops. J. Control. Release 2020, 321, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudana, R.; Jwala, J.; Boddu, S.H.S.; Mitra, A.K. Recent Perspectives in Ocular Drug Delivery. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 1197–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Achouri, D.; Alhanout, K.; Piccerelle, P. Recent advances in ocular drug delivery. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2012, 39, 1599–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duxfield, L.; Sultana, R.; Wang, R.; Englebretsen, V.; Deo, S.; Rupenthal, I.D.; Al-kassas, R. Ocular delivery systems for topical application of anti-infective agents. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2015, 42, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensign, L.M.; Cone, R.; Hanes, J. Oral Drug Delivery with Polymeric Nanoparticles: The Gastrointestinal Mucus Barriers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 64, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roy, S.; Pal, K.; Anis, A.; Pramanik, K.; Prabhakar, B. Polymers in Mucoadhesive Drug-Delivery Systems: A Brief Note. Des. Monomers Polym. 2009, 12, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaikh, R.; Raghu, T.; Singh, R.; Garland, M.J.; David, A.; Donnelly, R.F. Mucoadhesive drug delivery systems. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2011, 3, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- van der Lubben, I.M.; Verhoef, J.C.; van Aelst, A.C.; Borchard, G.; Junginger, H.E. Chitosan microparticles for oral vaccination: Preparation, characterization and preliminary in vivo uptake studies in murine Peyer’s patches. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, A.; Lanthaler, M.; Laffleur, F.; Huck, C.W.; Bernkop-schnürch, A. Thiolated chitosan micelles: Highly mucoadhesive drug carriers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 167, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontillo, A.R.N.; Detsi, A. Nanoparticles for ocular drug delivery: Modified and non-modified chitosan as a promising biocompatible carrier. Nanomedicine 2019, 14, 1889–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ways, T.M.M.; Lau, W.M. Chitosan and Its Derivatives for Application in Mucoadhesive Drug Delivery Systems. Polymers 2018, 10, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhavsar, C.; Momin, M.; Gharat, S.A.; Omri, A. Functionalized and graft copolymers of chitosan and its pharmaceutical applications. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2017, 14, 1189–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, S.; Mahdi, S.; Kaur, J.; Iqbal, Z.; Talegaonkar, S.; Ahmad, F.J. Advances and potential applications of chitosan derivatives as mucoadhesive biomaterials in modern drug delivery. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2006, 58, 1021–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzzarelli, R.A.A.; Tanfani, F. The N-Permethylation of Chitosan and the Preparation of N-Trimethyl Chitosan Iodide. Carbohydr. Polym. 1985, 5, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karavasili, C.; Katsamenis, O.L.; Bouropoulos, N.; Nazar, H.; Thurner, P.J.; van der Merwe, S.M.; Fatouros, D.G. Preparation and Characterization of Bioadhesive Microparticles Comprised of Low Degree of Quaternization Trimethylated Chitosan for Nasal Administration: Effect of Concentration and Molecular Weight. Langmuir 2014, 30, 12337–12344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Upadhyaya, L.; Singh, J.; Agarwal, V.; Tewari, R.P. The implications of recent advances in carboxymethyl chitosan based targeted drug delivery and tissue engineering applications. J. Control. Release 2014, 186, 54–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayakumar, R.; Prabaharan, M.; Nair, S.V.; Tokura, S.; Tamura, H. Novel carboxymethyl derivatives of chitin and chitosan materials and their biomedical applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2010, 55, 675–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langoth, N.; Kahlbacher, H.; Schöffmann, G.; Schmerold, I.; Schuh, M.; Franz, S.; Kurka, P.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Thiolated Chitosans: Design and In Vivo Evaluation of a Mucoadhesive Buccal Peptide Drug Delivery System. Pharm. Res. 2006, 23, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernkop-Schnurch, A.; Steininger, S. Synthesis and characterisation of mucoadhesive thiolated polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 194, 39–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernkop-Schnurch, A.; Hornof, M.; Guggi, D. Thiolated chitosans. J. Pharm. Biopharm 2004, 57, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michailidou, G.; Christodoulou, E.; Nanaki, S.; Barmpalexis, P.; Karavas, E.; Vergkizi-Nikolakaki, S.; Bikiaris, D.N. Super-hydrophilic and high strength polymeric foam dressings of modified chitosan blends for topical wound delivery of chloramphenicol. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 208, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerantzaki, M.; Kehagias, N.; Francone, A.; Fernández, A.; Sotomayor Torres, C.M.; Papi, R.; Choli-Papadopoulou, T.; Bikiaris, D.N. Design of a Multifunctional Nanoengineered PLLA Surface by Maximizing the Synergies between Biochemical and Surface Design Bactericidal Effects. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 1509–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiou, A.D.; Nerantzaki, M.; Brown, A.P.; Jha, A.; Bikiaris, D.N. Drug loading capacity of microporous β-pyrophosphate crystals. Mater. Des. 2019, 168, 107661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todoran, N.; Ciurba, A.; Redai, E.; Ion, V.; Lazar, L.; Sipos, E. Limitations when use chloramphenicol-b-cyclodextrins complexes in ophtalmic solutions buffered with boric acid/borax system. Acta Medica Marisiensis 2014, 60, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mandal, B.; Halder, K.; Dey, S.; Bhowmik, M.; Debnath, M.; Ghosh, L. Development and physical characterization of chloramphenicol loaded biodegradable nanoparticles for prolonged release. Pharmazie 2009, 64, 445–449. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, A.A.A.; Khidr, S.H.; Ahmed, S.M.; Aboutaleb, A.E. Evaluation of chloramphenicol-b-cyclodextrin inclusion complex. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1991, 37, 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- Aiassa, V.; Zoppi, A.; Becerra, M.C.; Albesa, I.; Longhi, M.R. Enhanced inhibition of bacterial biofilm formation and reduced leukocyte toxicity by chloramphenicol: ²-cyclodextrin: N-acetylcysteine complex. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 152, 672–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiassa, V.; Zoppi, A.; Albesa, I.; Longhi, M.R. Inclusion complexes of chloramphenicol with β-cyclodextrin and aminoacids as a way to increase drug solubility and modulate ROS production. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbu, E.; Verestiuc, L.; Iancu, M.; Jatariu, A. Hybrid polymeric hydrogels for ocular drug delivery: Nanoparticulate systems from copolymers of acrylic acid-functionalized chitosan and N-isopropylacrylamide or 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 225108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Gans, J.; van de Beek, D. Dexamethasone in adults with bacterial meningitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 1549–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrero-Vanrell, R.; Cardillo, J.A. Clinical applications of the sustained-release dexamethasone implant for treatment of macular edema. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2011, 5, 139–146. [Google Scholar]
- Villanueva, J.R.; Villanueva, L.R.; Navarro, M.G. Pharmaceutical technology can turn a traditional drug, dexamethasone into a first-line ocular medicine. A global perspective and future trends. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 516, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eljarrat-Binstock, E.; Raiskup, F.; Frucht-Pery, J.; Domb, A.J. Transcorneal and transscleral iontophoresis of dexamethasone phosphate using drug loaded hydrogel. J. Control. Release 2005, 106, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weijtens, O.; Schoemaker, R.C.; Romijn, F.P.H.T.M.; Cohen, A.F. Intraocular Penetration and Systemic Dexamethasone Disodium Phosphate. Opthalmology 2002, 109, 1887–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yellepeddi, V.K.; Palakurthi, S. Recent Advances in Topical Ocular Drug Delivery. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 32, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Han, Z. Injectable hydrogels for ophthalmic applications. J. Control. Release 2017, 268, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Fang, L.; Cao, F. Multifunctional carboxymethyl chitosan derivatives-layered double hydroxide hybrid nanocomposites for efficient drug delivery to the posterior segment of the eye. Acta Biomater. 2020, 104, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Sun, L.; Zhou, L.; Cheng, Y.; Cao, F. Functional chitosan oligosaccharide nanomicelles for topical ocular drug delivery of dexamethasone. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 227, 115356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, A.; Shi, H.; Liu, H.; Bao, Z.; Lin, D.; Lin, D. Mucoadhesive dexamethasone-glycol chitosan nanoparticles for ophthalmic drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Campos, A.M.; Diebold, Y.; Carvalho, E.L.S.; Sánchez, A.; Alonso, M.J. Chitosan Nanoparticles as New Ocular Drug Delivery Systems: In Vitro Stability, in Vivo Fate, and Cellular Toxicity. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, E.A.; Abdel-salam, E.T.; el Rayes, S.M.; Mohamed, N.S. Facile synthesis of graft copolymers of maltodextrin and chitosan with 2-acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propanesulfonic acid for efficient removal of Ni ( II ), Fe ( III ), and Cd ( II ) ions from aqueous media. J. Polym. Res. 2019, 26, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaridou, M.; Christodoulou, E.; Nerantzaki, M.; Kostoglou, M.; Lambropoulou, D.A.; Katsarou, A.; Pantopoulos, K.; Bikiaris, D.N. Formulation and In-Vitro Characterization of Chitosan-Nanoparticles Loaded with the Iron Chelator Deferoxamine Mesylate (DFO). Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karavas, E.; Georgarakis, E.; Bikiaris, D. Application of PVP/HPMC miscible blends with enhanced mucoadhesive properties for adjusting drug release in predictable pulsatile chronotherapeutics. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2006, 64, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siafaka, P.I.; Zisi, A.P.; Exindari, M.K.; Karantas, I.D.; Bikiaris, D.N. Porous dressings of modified chitosan with poly (2-hydroxyethyl acrylate) for topical wound delivery of levofloxacin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 143, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Dong, P.; Wei, Y.; Qian, J.; Hua, D. Synthesis of poly(sulfobetaine methacrylate)-grafted chitosan under γ-ray irradiation for alamethicin assembly. Colloids Surf. B. Biointerfaces 2015, 132, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Neoh, K.; Kang, E.-T. Integration of antifouling and bactericidal moieties for optimizing the efficacy of antibacterial coatings. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 438, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazaridis, N.K.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Vassiliou, A.A.; Bikiaris, D.N. Chitosan Derivatives as Biosorbents for Basic Dyes. Langmuir 2007, 23, 7634–7643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, B.C. Organic Nitrogen Compounds V: Amine Salts. Spectroscopy 2019, 34, 30–37. [Google Scholar]
- Verestiuc, L.; Nastasescu, O.; Barbu, E.; Sarvaiya, I.; Green, K.L.; Tsibouklis, J. Functionalized chitosan/NIPAM (HEMA) hybrid polymer networks as inserts for ocular drug delivery: Synthesis, in vitro assessment, and in vivo evaluation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2006, 77, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siafaka, P.I.; Titopoulou, A.; Koukaras, E.N.; Kostoglou, M.; Koutris, E.; Karavas, E.; Bikiaris, D.N. Chitosan derivatives as effective nanocarriers for ocular release of timolol drug. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 49, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siafaka, P.I.; Mone, M.; Koliakou, I.G.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Bikiaris, D.N. Synthesis and physicochemical properties of a new biocompatible chitosan grafted with 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 222, 268–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzopoulou, Z.; Baciu, D.; Gounari, E.; Steriotis, T.; Charalambopoulou, G.; Bikiaris, D. Biocompatible Nanobioglass Reinforced Poly(ε-Caprolactone) Composites Synthesized via In Situ Ring Opening Polymerization Zoi. Polymers 2018, 10, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christodoulou, E.; Nerantzaki, M.; Nanaki, S.; Barmpalexis, P.; Anastasiou, A.D.; Bikiaris, D.N. Paclitaxel Magnetic Core-Shell Nanoparticles Based on Poly(lactic acid) Semitelechelic Novel Block Copolymers for Combined Hyperthermia and Chemotherapy Treatment of Cancer. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Filippousi, M.; Siafaka, P.I.; Amanatiadou, E.P.; Nanaki, S.G.; Nerantzaki, M. Modified chitosan coated mesoporous strontium hydroxyapatite nanorods as drug carriers †. J. Mater. Chem. 2015, 3, 5991–6000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabea, E.I.; Stevens, C.V.; Smagghe, G.; Steurbaut, W. Chitosan as Antimicrobial Agent: Applications and Mode of Action. Biomacromolecules 2003, 4, 1457–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matica, M.A.; Aachmann, F.L.; Tøndervik, A. Chitosan as a Wound Dressing Starting Material: Antimicrobial Properties and Mode of Action. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, H.; Zhan, P.; Kieft, T.L.; Ryan, S.J.; Baker, S.M.; Wiesmann, W.P.; Rogelj, S. Antibacterial action of a novel functionalized chitosan-arginine against Gram-negative bacteria. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 2562–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sadeghi, A.; Amini, M.; Avadi, M.R.; Siedi, F.; Junginger, H.E. Synthesis, Characterization, and Antibacterial Effects of Trimethylated and Triethylated 6-NH2-6-Deoxy Chitosan. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2008, 23, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rúnarsson, Ö.V.; Holappa, J.; Nevalainen, T.; Hjálmarsdóttir, M.; Järvinen, T.; Loftsson, T.; Einarsson, J.M.; Jónsdóttir, S.; Valdimarsdóttir, M.; Másson, M. Antibacterial activity of methylated chitosan and chitooligomer derivatives: Synthesis and structure activity relationships. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 2660–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Britto, D.; Goy, R.C.; Paulo, S.; Filho, C.; Assis, O.B.G. Quaternary Salts of Chitosan: History, Antimicrobial Features, and Prospects. Int. J. Carbohydr. Chem. 2011, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Tan, W.; Luan, F.; Yin, X.; Dong, F.; Li, Q. Synthesis of Quaternary Ammonium Salts of Chitosan Bearing Halogenated Acetate for Antifungal and Antibacterial Activities. Polymers 2018, 10, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jadhav, R.L.; Yadav, A.V.; Patil, M.V. Poly Sulfoxyamine Grafted Chitosan as Bactericidal Dressing for Wound Healing RAHUL. Asian J. Chem. 2020, 32, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, A.M.M.; Dorkoosh, F.A.; Avadi, M.R.; Saadat, P.; Rafiee-tehrani, M.; Junginger, H.E. Preparation, characterization and antibacterial activities of chitosan, N-trimethyl chitosan (TMC) and N-diethylmethyl chitosan (DEMC) nanoparticles loaded with insulin using both the ionotropic gelation and polyelectrolyte complexation methods. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 355, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Meng, W.; Wang, S.; Sun, Y.; Ashraf, M.A. Quaternary ammonium salt of chitosan: Preparation and antimicrobial property for paper. Open Med. 2015, 10, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Xin, M.; Li, M.; Huang, H.; Zhou, S.; Liu, J. Synthesis, characterization, and antibacterial activity of N,O-quaternary ammonium chitosan. Carbohydr. Res. 2011, 346, 2445–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, V.K.; Yadav, N.P.; Sinha, P.; Mishra, N.; Luqman, S.; Dwivedi, H.; Kymonil, K.M.; Saraf, S.A. Development of cellulosic polymer based gel of novel ternary mixture of miconazole nitrate for buccal delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 103, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, S.K.; Wang, Y.; Hanes, J. Mucus-penetrating nanoparticles for drug and gene delivery to mucosal tissues. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rossi, S.; Ferrari, F.; Bonferoni, M.C.; Caramella, C. Characterization of chitosan hydrochloride-mucin rheological interaction: Influence of polymer concentration and polymer:mucin weight ratio. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 12, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdziok, J.; Bajerová, M.; Chalupová, Z.; Rabišková, M. Oxycellulose as mucoadhesive polymer in buccal tablets. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2010, 36, 1115–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutroumanis, K.P.; Avgoustakis, K.; Bikiaris, D. Synthesis of cross-linked N-(2-carboxybenzyl) chitosan pH sensitive polyelectrolyte and its use for drug controlled delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 82, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raafat, A.I.; Mahmoud, G.A.; Ali, A.E.; Badawy, N.A. In vitro evaluation of mucoadhesive and self-disinfection efficiency of (acrylic acid/polyethylene glycol)-silver nanocomposites for buccal drug delivery. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2018, 33, 95–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellaway, I. In vitro test methods for the measurement of mucoadhesion. In Bioadhesion Possibilities and Future Trends (APV, Band 25); Gurny, R., Junginger, H., Eds.; Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft mbH: Stuttgart, Germany, 1990; pp. 86–92. [Google Scholar]
- Bassi, J.; Barbosa, S.; Ferreira, D.S.; de Freitas, O.; Bruschi, M.L. A critical review about methodologies for the analysis of mucoadhesive properties of drug delivery systems. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2017, 43, 1053–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, F.; Eberth, K.; Smart, J.D. A rheological assessment of the nature of interactions between mucoadhesive polymers and a homogenised mucus gel. Biomaterials 1998, 19, 1083–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehr, C.-M.; Bouwstra, J.A.; Schacht, E.H.; Junginger, H.E. In vitro evaluation of mucoadhesive properties of chitosan and some other natural polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 1992, 78, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaei, A.H.; Paulson, J.; Honary, S. Evaluation of poly(acrylic acid-co-ethylhexyl acrylate) films for mucoadhesive transbuccal drug delivery: Factors affecting the force of mucoadhesion. J. Control. Release 2000, 67, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafee, N.A.; Ismail, F.A.; Boraie, N.A. Mucoadhesive Delivery Systems. I. Evaluation of Mucoadhesive Polymers for Buccal Tablet Formulation. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2004, 30, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sá, L.L.F.; Nogueira, N.C.; Filho, E.C.D.S.; Figueiras, A.; Veiga, F.; Nunes, L.C.C.; Soares-Sobrinho, J.L. Design of buccal mucoadhesive tablets: Understanding and development. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 8, 150–163. [Google Scholar]
- Nafee, N.A.; Boraie, N.A.; Ismail, F.A.; Mortada, L.M. Design and characterization of mucoadhesive buccal patches containing Cetylpyridinium chloride. Acta Pharm. 2003, 53, 199–212. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Huwaij, R.; Obaidat, R.M.; Sweidan, K.; Al-hiari, Y. Formulation and In Vitro Evaluation of Xanthan Gum or Carbopol 934-Based Mucoadhesive Patches, Loaded with Nicotine. AAPS PharmSciTech 2011, 12, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kolawole, O.M.; Lau, W.M.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Methacrylated chitosan as a polymer with enhanced mucoadhesive properties for transmucosal drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 550, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng-Lund, E.; Muff-westergaard, C.; Sander, C.; Madelung, P.; Jacobsen, J. A mechanistic based approach for enhancing buccal mucoadhesion of chitosan. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 461, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogias, I.A.; Williams, A.C.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Chitosan-based mucoadhesive tablets for oral delivery of ibuprofen. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 436, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabovac, V.; Guggi, D.; Bernkop-schnu, A. Comparison of the mucoadhesive properties of various polymers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 1713–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, G.P.; Laverty, T.P.; Jones, D.S. Mucoadhesive polymeric platforms for controlled drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 71, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Advances in Mucoadhesion and Mucoadhesive Polymers. Macromol. Biosci. 2011, 11, 748–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikos, A.; Peppas, N. Scaling concepts and molecular theories of adhesion of synthetic polymers to glycoproteinic networks. In Bioadhesive Drug Delivery Systems; Lenaerts, V., Gurny, R., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1990; pp. 25–42. [Google Scholar]
- Peppas, N.A.; Buri, P.A. Surface, interfacial and molecular aspects of polymer bioadhesion on soft tissues. J. Control. Release 1985, 2, 257–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fefelova, N.A.; Nurkeeva, Z.S.; Mun, G.A.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Mucoadhesive interactions of amphiphilic cationic copolymers based on [2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl] trimethylammonium chloride. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 339, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.I.N.W.; Park, J.A.E.H.A.N.; Robinson, J.R. Bioadhesive-Based Dosage Forms: The Next Generation. J. Pharm. Sci. 2000, 89, 850–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edsman, K.; Ha, H. Pharmaceutical applications of mucoadhesion for the non-oral routes. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2005, 57, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosnik, A.; Neves, J.; Sarmento, B. Mucoadhesive polymers in the design of nano-drug delivery systems for administration by non-parenteral routes: A review. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 2030–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, S.; Bikiaris, D.; Avgoustakis, K.; Karavas, E.; Georgarakis, M. Chitosan nanoparticles loaded with dorzolamide and pramipexole. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 73, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukaras, E.N.; Papadimitriou, A.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Froudakis, G.E. Insight on the Formation of Chitosan Nanoparticles through Ionotropic Gelation with Tripolyphosphate. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 2856–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukaras, E.N.; Papadimitriou, S.A.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Froudakis, G.E. Properties and energetics for design and characterization of chitosan nanoparticles used for drug encapsulation. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 12653–12661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, H.; Helena, M.; Lobão, P.; Silva, A.C.; Manuel, J.; Lobo, S. Applications of Polymeric and Lipid Nanoparticles in Ophthalmic Pharmaceutical Formulations: Present and Future Considerations. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 17, 278–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, S.K.; Wang, Y.Y.; Hida, K.; Cone, R.; Hanes, J. Nanoparticles reveal that human cervicovaginal mucus is riddled with pores larger than viruses. Proc. Natl. Aacad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, S.K.; O’Hanlon, D.E.; Harrold, S.; Man, S.T.; Wang, Y.Y.; Cone, R.; Hanes, J. Rapid transport of large polymeric nanoparticles in fresh undiluted human mucus. Proc. Natl. Aacad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 1482–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ponchel, G.; Montisci, M.-J.; Dembri, A.; Durrer, C.; Duchene, D. Mucoadhesion of colloidal particulate systems in the gastro-intestinal tract. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1997, 44, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Batchelor, H.; Hanson, P.; Saleem, I.Y.; Perrie, Y.; Mohammed, A.R. Dissolution rate enhancement, in vitro evaluation and investigation of drug release kinetics of chloramphenicol and sulphamethoxazole solid dispersions. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2013, 39, 704–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnitzler, E.; Carvalho, M.; Stadler, C.; Volpato, A.; Ionashiro, M. Application of differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) in the thermal characterization of dexamethasone acetate, Excipients and dexamethasone cream. Eclet. Quim. 2000, 26, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, A.; Sahoo, R.N.; Nanda, A.; Singh, R.; Mallick, S. Ocular Permeation and Sustained Anti-inflammatory Activity of Dexamethasone from Kaolin Nanodispersion Hydrogel System. Curr. Eye Res. 2018, 43, 828–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaeei, S.; Alizadeh, M. Design and Evaluation of Soluble Ocular Insert For Controlled Release of Chloramphenicol. J. Reports Pharm. Sci. 2017, 6, 123–133. [Google Scholar]
- Faccia, P.A.; Pardini, F.M.; Amalvy, J.I. Uptake and release of Dexamethasone using pH-responsive poly (2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate-co-2-(diisopropylamino)ethyl methacrylate) hydrogels for potential use in ocular drug delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 51, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, A.; Mei, W.; Zhu, R.; Li, K.; Sun, X. Dexamethasone sodium phosphate intercalated layered double hydroxides and their therapeutic efficacy in a murine asthma model. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 23826–23834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranch, K.; Patel, H.; Chavda, L.; Koli, A.; Maulvi, F.; Parikh, R.K. Development of in situ Ophthalmic gel of Dexamethasone Sodium Phosphate and Chloramphenicol: A Viable Alternative to Conventional Eye Drops. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 7, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Liu, X.; Hu, W.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, L. Preparation and evaluation of naringenin-loaded sulfobutylether-β-cyclodextrin/ chitosan nanoparticles for ocular drug delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 149, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Hu, G. Chloramphenicol/sulfobutyl ether-β-cyclodextrin complexes in an ophthalmic delivery system: Prolonged residence time and enhanced bioavailability in the conjunctival sac. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Feky, G.S.; Zayed, G.M.; Elshaier, Y.A.M.M.; Alsharif, F.M. Chitosan-Gelatin Hydrogel Crosslinked With Oxidized Sucrose for the Ocular Delivery of Timolol Maleate. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 107, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamcerencu, M.; Desbrieres, J.; Popa, M. Thermo-sensitive gellan maleate/N-isopropylacrylamide hydrogels: Initial ‘in vitro’ and ‘in vivo’ evaluation as ocular inserts. Polym. Bull. 2019, 77, 741–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, G.; Yu, S.; Li, J.; Pan, W. Development and characterization of nanostructured lipid carriers based chitosan thermosensitive hydrogel for delivery of dexamethasone. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 103, 941–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, X.; Deng, G.; Hou, D.; Chen, Y.; Lu, Z. Corneal permeation properties of a charged lipid nanoparticle carrier containing dexamethasone. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 1329–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, B.; Tang, Y.; Oh, Y.; Suarez, M.J.; Meng, T.; Kulkarni, V. Controlled release of dexamethasone sodium phosphate with biodegradable nanoparticles for preventing experimental corneal neovascularization. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2019, 17, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arranz-Romera, A.; Davis, B.M.; Bravo-Osuna, I.; Esteban-Pérez, S.; Molina-Martínez, I. Simultaneous co-delivery of neuroprotective drugs from multi-loaded PLGA microspheres for the treatment of glaucoma. J. Control. Release J. 2019, 297, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awwad, S.; Day, R.M.; Khaw, P.T.; Brocchini, S.; Fadda, H. Sustained release ophthalmic dexamethasone: In vitro in vivo correlations derived from the PK-Eye. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 552, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brooks, C.C.; Jabbehdari, S.; Gupta, P.K. Dexamethasone 0.4 mg Sustained-Release Ocular Inflammation and Pain Following Intracanalicular Insert in the Management of Ophthalmic Surgery: Design, Development and Place in Therapy. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2020, 14, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- da Silva, G.R.; Lima, T.H.; Fernandes-Cunha, G.M.; Oréfice, R.L.; da Silva-Cunha, A.; Zhao, M.; Behar-Cohen, F. Ocular biocompatibility of dexamethasone acetate loaded poly (ɛ-caprolactone) nanofibers. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 142, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, Y.; Haruna, Y.; Otsuka, M. Dissolution process analysis using model-free Noyes-Whitney integral equation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 102, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsmeyer, R.W.; Gumy, R.; Doelker, E.; Buri, P.; Peppas, N.A. Mechanisms of solute release from porous hydrophilic polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 1983, 15, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tien, C. Calculations and Modeling; Butterworth-Heinemann: Boston, MA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Crank, J. The Mathematics of Diffusion, 2nd ed.; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]















| Polymer | Area of Inhibition (Diameter mm) | |
|---|---|---|
| E. coli | S. aureus | |
| CS | 6 ± 1 | 7 ± 1 |
| CS-AAMPS | 7 ± 1 | 12 ± 2 |
| AAMPS monomer | 8 ± 1 | 13 ± 2 |
| CS-MEDSP | 9 ± 2 | 14 ± 3 |
| MEDSP monomer | 8 ± 1 | 13 ± 2 |
| Neomycin | 12 ± 2 | 10 ± 1 |
| Polymer | Mucoadhesive Strength (N/cm2) |
|---|---|
| CS | 0.27 ± 0.02 |
| CS-AAMPS | 0.46 ± 0.05 |
| CS-MEDPS | 0.72 ± 0.07 |
| Sample | Yield (%) | Drug Loading (%) | Entrapment Efficiency (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHL | DexSP | CHL | DexSP | ||
| CS/TPP | 55.1 ± 5.4 | 23.7 ± 2.1 | 10.1 ± 0.6 | 29.28 ± 2.3 | 24.96 ± 2.7 |
| CCS/TPP-AAMPS | 46.8 ± 3.7 | 25.2 ± 1.9 | 9.7 ± 0.6 | 28.78 ± 1.5 | 22.15 ± 1.4 |
| CS/TPP-MEDSP | 43.5 ± 3.8 | 22.6 ± 1.5 | 11.8 ± 0.8 | 25.98 ± 1.9 | 27.13 ± 1.5 |
| Drug | Matrix | φ | Κ1(1/day) | Κ2(1/day) | Rmax |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DexSP | CS | 0.21 | 10.28 | 1.9 | 100 |
| DexSP | CS-MEDSP | 0.31 | 23.18 | 2.15 | 100 |
| DexSP | CS-AAMPS | 0.23 | 49.5 | 3 | 100 |
| CHL | CS | 0 | - | 0.14 | 81.7 |
| CHL | CS-MEDSP | 0.05 | 13.34 | 0.72 | 80.5 |
| CHL | CS-AAMPS | 0.28 | 2.9 | 0.46 | 97.5 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karava, A.; Lazaridou, M.; Nanaki, S.; Michailidou, G.; Christodoulou, E.; Kostoglou, M.; Iatrou, H.; Bikiaris, D.N. Chitosan Derivatives with Mucoadhesive and Antimicrobial Properties for Simultaneous Nanoencapsulation and Extended Ocular Release Formulations of Dexamethasone and Chloramphenicol Drugs. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12060594
Karava A, Lazaridou M, Nanaki S, Michailidou G, Christodoulou E, Kostoglou M, Iatrou H, Bikiaris DN. Chitosan Derivatives with Mucoadhesive and Antimicrobial Properties for Simultaneous Nanoencapsulation and Extended Ocular Release Formulations of Dexamethasone and Chloramphenicol Drugs. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(6):594. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12060594
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarava, Aikaterini, Maria Lazaridou, Stavroula Nanaki, Georgia Michailidou, Evi Christodoulou, Margaritis Kostoglou, Hermis Iatrou, and Dimitrios N. Bikiaris. 2020. "Chitosan Derivatives with Mucoadhesive and Antimicrobial Properties for Simultaneous Nanoencapsulation and Extended Ocular Release Formulations of Dexamethasone and Chloramphenicol Drugs" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 6: 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12060594
APA StyleKarava, A., Lazaridou, M., Nanaki, S., Michailidou, G., Christodoulou, E., Kostoglou, M., Iatrou, H., & Bikiaris, D. N. (2020). Chitosan Derivatives with Mucoadhesive and Antimicrobial Properties for Simultaneous Nanoencapsulation and Extended Ocular Release Formulations of Dexamethasone and Chloramphenicol Drugs. Pharmaceutics, 12(6), 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12060594