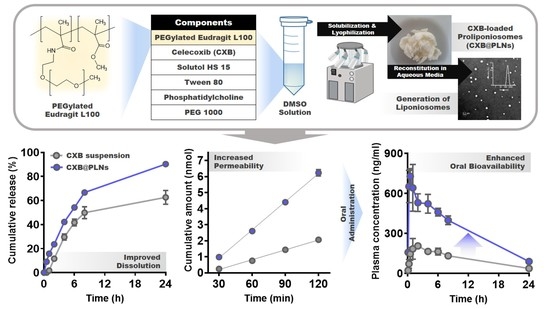
Preparation and Evaluation of Eudragit L100-PEG Proliponiosomes for Enhanced Oral Delivery of Celecoxib
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis and Characterization of Eudragit L100-PEGs
2.3. Preparation and Characterization of CXB-Loaded Proliponiosomes (CXB@PLNs)
2.4. Release Test
2.5. Cytotoxicity and Permeability Assays
2.6. Pharmacokinetic Study and Blood Biochemistry Test
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of ELPs
3.2. Preparation and Characterization of CXB@PLNs in Solid State
3.3. Characterization of LNs Generated by Reconstitution of CXB@PLNs
3.4. In Vitro CXB Release from CXB@PLNs
3.5. Cytotoxicity of ELPs and Permeability of CXB@PLNs
3.6. Pharmacokinetic Study and Blood Biochemistry Test
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McCormack, P.L. Celecoxib. Drugs 2011, 71, 2457–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, D.; Kim, K.-T.; Baek, M.-J.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, D.-D. Preparation and evaluation of celecoxib-loaded proliposomes with high lipid content. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 141, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frampton, J.E.; Keating, G.M. Celecoxib: A review of its use in the management of arthritis and acute pain. Drugs 2007, 67, 2433–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulson, S.K.; Vaughn, M.B.; Jessen, S.M.; Lawal, Y.; Gresk, C.J.; Yan, B.; Maziasz, T.J.; Cook, C.S.; Karim, A. Pharmacokinetics of celecoxib after oral administration in dogs and humans: Effect of food and site of absorption. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001, 297, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hammouda, B. Temperature Effect on the Nanostructure of SDS Micelles in Water. J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. 2013, 118, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.J.; Heo, E.-J.; Kim, Y.-H.; Kim, S.; Hwang, Y.-H.; Byun, J.-M.; Cheon, S.H.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Cho, K.H. Development and evaluation of poorly water-soluble celecoxib as solid dispersions containing nonionic surfactants using fluidized-bed granulation. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrews, G.P.; Abu-Diak, O.; Kusmanto, F.; Hornsby, P.; Hui, Z.; Jones, D.S. Physicochemical characterization and drug-release properties of celecoxib hot-melt extruded glass solutions. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 62, 1580–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, M.J.; Yoon, H.; Shim, C.R.; Ko, H.A.; Cho, S.A.; Lee, D.; Khang, G. Enhanced dissolution rate of celecoxib using PVP and/or HPMC-based solid dispersions prepared by spray drying method. J. Pharm. Investig. 2013, 43, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgen, M.; Bloom, C.; Beyerinck, R.; Bello, A.; Song, W.; Wilkinson, K.; Steenwyk, R.; Shamblin, S. Polymeric nanoparticles for increased oral bioavailability and rapid absorption using celecoxib as a model of a low-solubility, high-permeability drug. Pharm. Res. 2012, 29, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kishore, N.; Raja, M.D.; Kumar, C.S.; Dhanalekshmi, U.; Srinivasan, R. Lipid carriers for delivery of celecoxib: In vitro, in vivo assessment of nanomedicine in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2016, 118, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deniz, A.; Sade, A.; Severcan, F.; Keskin, D.; Tezcaner, A.; Banerjee, S. Celecoxib-loaded liposomes: Effect of cholesterol on encapsulation and in vitro release characteristics. Biosci. Rep. 2010, 30, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guzmán, H.R.; Tawa, M.; Zhang, Z.; Ratanabanangkoon, P.; Shaw, P.; Gardner, C.R.; Chen, H.; Moreau, J.P.; Almarsson, O.; Remenar, J.F. Combined use of crystalline salt forms and precipitation inhibitors to improve oral absorption of celecoxib from solid oral formulations. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 96, 2686–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouwers, J.; Brewster, M.E.; Augustijns, P. Supersaturating drug delivery systems: The answer to solubility-limited oral bioavailability? J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 98, 2549–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Dai, W.-G. Drug precipitation inhibitors in supersaturable formulations. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 453, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Pollock-Dove, C.; Dong, L.C.; Chen, J.; Creasey, A.A.; Dai, W.G. Enhanced bioavailability of a poorly water-soluble weakly basic compound using a combination approach of solubilization agents and precipitation inhibitors: A case study. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 1100–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, W.-G.; Dong, L.C.; Li, S.; Deng, Z. Combination of Pluronic/Vitamin E TPGS as a potential inhibitor of drug precipitation. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 355, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, Y.; Haruna, Y.; Otsuka, M. Dissolution process analysis using model-free Noyes–Whitney integral equation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 102, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Lu, Y.; Qi, J.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, Z.; Wu, W. Adapting liposomes for oral drug delivery. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajera, R.; Nagpal, K.; Singh, S.K.; Mishra, D.N. Niosomes: A controlled and novel drug delivery system. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 34, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brandelli, A.; Pinilla, C.M.B.; Lopes, N.A. Nanoliposomes as a Platform for Delivery of Antimicrobials. In Nanotechnology Applied To Pharmaceutical Technology; Rai, M., Alves dos Santos, C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 55–90. [Google Scholar]
- Zeb, A.; Arif, S.T.; Malik, M.; Shah, F.A.; Din, F.U.; Qureshi, O.S.; Lee, E.-S.; Lee, G.-Y.; Kim, J.-K. Potential of nanoparticulate carriers for improved drug delivery via skin. J. Pharm. Investig. 2019, 49, 485–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asgharkhani, E.; Fathi Azarbayjani, A.; Irani, S.; Chiani, M.; Saffari, Z.; Norouzian, D.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Atyabi, S.M. Artemisinin-loaded niosome and pegylated niosome: Physico-chemical characterization and effects on MCF-7 cell proliferation. J. Pharm. Investig. 2018, 48, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Hanning, S.; Falconer, J.; Locke, M.; Wen, J. Recent advances in non-ionic surfactant vesicles (niosomes): Fabrication, characterization, pharmaceutical and cosmetic applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 144, 18–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ge, X.; Wei, M.; He, S.; Yuan, W.E. Advances of Non-Ionic Surfactant Vesicles (Niosomes) and Their Application in Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramadan, A.A.; Eladawy, S.A.; El-Enin, A.S.M.A.; Hussein, Z.M. Development and investigation of timolol maleate niosomal formulations for the treatment of glaucoma. J. Pharm. Investig. 2020, 50, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, S.; Chaudhary, A.; Chaudhary, A.; Kumar, A. Proniosomes: The effective and efficient drug-carrier system. Ther. Deliv. 2020, 11, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan-yu, X.; Yun-mei, S.; Zhi-peng, C.; Qi-neng, P. Preparation of silymarin proliposome: A new way to increase oral bioavailability of silymarin in beagle dogs. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 319, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Zheng, H.-N.; Jiang, C.; Li, K.; Xiao, S.-J. EDC/NHS activation mechanism of polymethacrylic acid: Anhydride versus NHS-ester. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 69939–69947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.W.; Hawley, M.; Smith, M.; Geiger, B.M.; Pfund, W. Characterization of a novel polymorphic form of celecoxib. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 95, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopp, B.; Smausz, T.; Tombácz, E.; Wittmann, T.; Ignácz, F. Solid state and liquid ablation of polyethylene-glycol 1000: Temperature dependence. Opt. Commun. 2000, 181, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drazenovic, J.; Wang, H.; Roth, K.; Zhang, J.; Ahmed, S.; Chen, Y.; Bothun, G.; Wunder, S.L. Effect of lamellarity and size on calorimetric phase transitions in single component phosphatidylcholine vesicles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2015, 1848, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiang, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, R.; Zhou, Z.; Peng, C.; Zhu, M. Synthesis and characterization of an environmentally friendly PHBV/PEG copolymer network as a phase change material. Sci. China Chem. 2013, 56, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Haghirosadat, B.F.; Larypoor, M.; Ehsani, R.; Yazdian, F.; Rashedi, H.; Jahanizadeh, S.; Rahmani, A. Synthesis, Characterization and Evaluation of Liponiosome Containing Ginger Extract as a New Strategy for Potent Antifungal Formulation. J. Clust. Sci. 2020, 31, 971–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderinezhad, S.; Amoabediny, G.; Haghiralsadat, F. Co-delivery of hydrophilic and hydrophobic anticancer drugs using biocompatible pH-sensitive lipid-based nano-carriers for multidrug-resistant cancers. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 30008–30019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scholfield, C.R. Composition of soybean lecithin. J. Am. Oil Chem.’ Soc. 1981, 58, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.C.; Barry, B.W. Penetration enhancers. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 2012, 64, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danaei, M.; Dehghankhold, M.; Ataei, S.; Hasanzadeh Davarani, F.; Javanmard, R.; Dokhani, A.; Khorasani, S.; Mozafari, M.R. Impact of Particle Size and Polydispersity Index on the Clinical Applications of Lipidic Nanocarrier Systems. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, X.-J.; Wang, J.-L.; Iqbal, S.; Li, H.-J.; Cao, Z.-T.; Wang, Y.-C.; Du, J.-Z.; Wang, J. The effect of surface charge on oral absorption of polymeric nanoparticles. Biomater. Sci. 2018, 6, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Qi, J.; Gogoi, R.; Wong, J.; Mitragotri, S. Role of nanoparticle size, shape and surface chemistry in oral drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2016, 238, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Longer and safer gastric residence. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 963–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Jiang, H.; Jiang, T.; Zhi, Z.; Wu, C.; Sun, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S. Inclusion of celecoxib into fibrous ordered mesoporous carbon for enhanced oral bioavailability and reduced gastric irritancy. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 45, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohr, A.; Kristensen, J.; Stride, E.; Dyas, M.; Edirisinghe, M. Preparation of microspheres containing low solubility drug compound by electrohydrodynamic spraying. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 412, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawla, G.; Gupta, P.; Thilagavathi, R.; Chakraborti, A.K.; Bansal, A.K. Characterization of solid-state forms of celecoxib. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2003, 20, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, M. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of proniosomes containing celecoxib for oral administration. AAPS PharmSciTech 2010, 11, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, G.; Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Wei, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Tao, L. Cytotoxicity study of polyethylene glycol derivatives. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 18252–18259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohammadzadeh, R.; Baradaran, B.; Valizadeh, H.; Yousefi, B.; Zakeri-Milani, P. Reduced ABCB1 Expression and Activity in the Presence of Acrylic Copolymers. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 4, 219–224. [Google Scholar]
- Battisti, W.P.; Katz, N.P.; Weaver, A.L.; Matsumoto, A.K.; Kivitz, A.J.; Polis, A.B.; Geba, G.P. Pain management in osteoarthritis: A focus on onset of efficacy—A comparison of rofecoxib, celecoxib, acetaminophen, and nabumetone across four clinical trials. J. Pain 2004, 5, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Formulation | Mean Diameter | Polydispersity Index | Zeta Potential | Encapsulation Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 231.7 ± 1.5 nm | 0.27 ± 0.01 | 1.87 ± 0.13 mV | 80.8 ± 0.3% |
| F2 | 292.0 ± 3.5 nm | 0.25 ± 0.01 | −5.41 ± 0.94 mV | 89.2 ± 2.5% |
| Parameter 1 | CXB Suspension | F1 | F2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| AUC (μg∙h/mL) | 2.66 ± 0.10 | 7.98 ± 0.64 †,‡ | 4.46 ± 1.41 † |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 222 ± 27 | 765 ± 72 †,‡ | 407 ± 149 |
| Tmax (h) | 2.50 ± 2.30 | 0.56 ± 0.31 | 0.63 ± 0.25 |
| Relative bioavailability (%) | 100 | 300 | 168 |
| Parameter 1 | No Treatment | F1 | F2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALT (U/L) | 126.5 ± 76.3 | 163.3 ± 53.8 | 147.0 ± 24.5 |
| ALB (g/dL) | 2.7 ± 0.3 | 2.4 ± 0.4 | 2.6 ± 0.3 |
| TP (g/dL) | 4.2 ± 0.5 | 4.3 ± 0.3 | 4.5 ± 0.3 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 23.7 ± 9.3 | 24.0 ± 12.9 | 28.9 ± 1.3 |
| SCr (mg/dL) | 0.20 ± 0.01 | 0.17 ± 0.03 | 0.18 ± 0.02 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, M.-H.; Kim, D.H.; Nguyen, D.-T.; Lee, H.S.; Kang, N.-W.; Baek, M.-J.; An, J.; Yoo, S.-Y.; Mun, Y.-H.; Lee, W.; et al. Preparation and Evaluation of Eudragit L100-PEG Proliponiosomes for Enhanced Oral Delivery of Celecoxib. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 718. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12080718
Kim M-H, Kim DH, Nguyen D-T, Lee HS, Kang N-W, Baek M-J, An J, Yoo S-Y, Mun Y-H, Lee W, et al. Preparation and Evaluation of Eudragit L100-PEG Proliponiosomes for Enhanced Oral Delivery of Celecoxib. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(8):718. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12080718
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Min-Hwan, Dong Hyun Kim, Duy-Thuc Nguyen, Han Sol Lee, Nae-Won Kang, Min-Jun Baek, Jiseon An, So-Yeol Yoo, Yong-Hyeon Mun, Wonhwa Lee, and et al. 2020. "Preparation and Evaluation of Eudragit L100-PEG Proliponiosomes for Enhanced Oral Delivery of Celecoxib" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 8: 718. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12080718
APA StyleKim, M. -H., Kim, D. H., Nguyen, D. -T., Lee, H. S., Kang, N. -W., Baek, M. -J., An, J., Yoo, S. -Y., Mun, Y. -H., Lee, W., Kim, K. -T., Cho, C. -W., Lee, J. -Y., & Kim, D. -D. (2020). Preparation and Evaluation of Eudragit L100-PEG Proliponiosomes for Enhanced Oral Delivery of Celecoxib. Pharmaceutics, 12(8), 718. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12080718