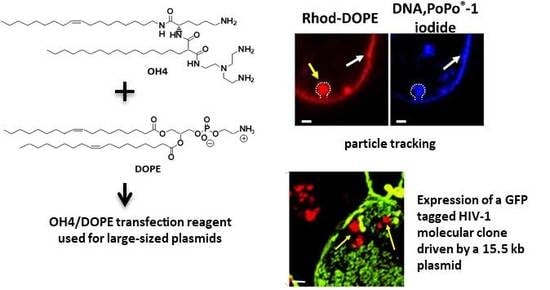
Efficient Transfection of Large Plasmids Encoding HIV-1 into Human Cells—A High Potential Transfection System Based on a Peptide Mimicking Cationic Lipid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of Cationic Vesicles
2.2.2. Lipoplex Preparation
2.2.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy with Negative Staining (Negative Stain TEM)
2.2.4. Cryogenic Transmission Electron Microscopy (CryoTEM)
2.2.5. Particle Size and Charge Measurements
2.2.6. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
2.2.7. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM) Experiments
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daley, J. Gene THerapy Arrives. Nature 2019, 576, S12–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sander, J.D.; Joung, J.K. CRISPR-Cas systems for editing, regulating and targeting genomes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Song, C.-Q.; Dorkin, J.R.; Zhu, L.J.; Li, Y.; Wu, Q.; Park, A.; Yang, J.; Suresh, S.; Bizhanova, A.; et al. Therapeutic genome editing by combined viral and non-viral delivery of CRISPR system components in vivo. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kay, M.A. State-of-the-art gene-based therapies: The road ahead. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vector Used in Gene Therapie Clinical Trails. Available online: http://abedia.com/wiley/vectors.php (accessed on 13 December 2019).
- Ibraheem, D.; Elaissari, A.; Fessi, H. Gene therapy and DNA delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 459, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yla-Herttuala, S. Glybera’s Second Act: The Curtain Rises on the High Cost of Therapy. Mol. Ther. 2015, 23, 217–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morrison, C. [dollar]1-million price tag set for Glybera gene therapy. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 217–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotterman, M.A.; Chalberg, T.W.; Schaffer, D.V. Viral Vectors for Gene Therapy: Translational and Clinical Outlook. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 17, 63–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Connor, T.P.; Crystal, R.G. Genetic medicines: Treatment strategies for hereditary disorders. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006, 7, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vhora, I.; Lalani, R.; Bhatt, P.; Patil, S.; Patel, H.; Patel, V.; Misra, A. Colloidally Stable Small Unilamellar Stearyl Amine Lipoplexes for Effective BMP-9 Gene Delivery to Stem Cells for Osteogenic Differentiation. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 3550–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Kanasty, R.L.; Eltoukhy, A.A.; Vegas, A.J.; Dorkin, J.R.; Anderson, D.G. Non-viral vectors for gene-based therapy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreiss, P.; Cameron, B.; Rangara, R.; Mailhe, P.; Aguerre-Charriol, O.; Airiau, M.; Scherman, D.; Crouzet, J.; Pitard, B. Plasmid DNA size does not affect the physicochemical properties of lipoplexes but modulates gene transfer efficiency. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 3792–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H.; Cheng, K. Delivery strategies of the CRISPR-Cas9 gene-editing system for therapeutic applications. J. Control. Release 2017, 266, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewert, K.; Ahmad, A.; Evans, H.M.; Safinya, C.R. Cationic lipid–DNA complexes for non-viral gene therapy: Relating supramolecular structures to cellular pathways. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2005, 5, 33–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, M.; Bhatt, P.; Chauhan, G.; Gupta, S.; Misra, A.; Mashru, R. IGF-II-Conjugated Nanocarrier for Brain-Targeted Delivery of p11 Gene for Depression. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuhorn, I.S.; Bakowsky, U.; Polushkin, E.; Visser, W.H.; Stuart, M.C.A.; Engberts, J.B.F.N.; Hoekstra, D. Nonbilayer phase of lipoplex–membrane mixture determines endosomal escape of genetic cargo and transfection efficiency. Mol. Ther. 2005, 11, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janich, C.; Wölk, C.; Taßler, S.; Drescher, S.; Meister, A.; Brezesinski, G.; Dobner, B.; Langner, A. Composites of malonic acid diamides and phospholipids—Structural parameters for optimal transfection efficiency in A549 cells. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2014, 116, 1184–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janich, C.; Wölk, C.; Erdmann, F.; Groth, T.; Brezesinski, G.; Dobner, B.; Langner, A. Composites of malonic acid diamides and phospholipids—Impact of lipoplex stability on transfection efficiency. J. Control. Release 2015, 220, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janich, C.; Taßler, S.; Meister, A.; Hause, G.; Schafer, J.; Bakowsky, U.; Brezesinski, G.; Wolk, C. Structures of malonic acid diamide/phospholipid composites and their lipoplexes. Soft Matter 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hübner, W.; Chen, P.; Portillo, A.D.; Liu, Y.; Gordon, R.E.; Chen, B.K. Sequence of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 (HIV-1) Gag Localization and Oligomerization Monitored with Live Confocal Imaging of a Replication-Competent, Fluorescently Tagged HIV-1. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 12596–12607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, P.; Hübner, W.; Spinelli, M.A.; Chen, B.K. Predominant Mode of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Transfer between T Cells Is Mediated by Sustained Env-Dependent Neutralization-Resistant Virological Synapses. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 12582–12595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ivanusic, D.; Madela, K.; Laue, M.; Denner, J. Three-Dimensional Imaging of CD63 Recruitment at the Virological Synapse: HIV-1. Aids Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2015, 31, 579–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanusic, D.; Madela, K.; Laue, M.; Denner, J. Visualization of HIV-1 Budding Structures. Aids Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2014, 30, 945–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Dai, L.; Wang, A.; Wölk, C.; Dobner, B.; Brezesinski, G.; Tang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, J. The Directional Observation of Highly Dynamic Membrane Tubule Formation Induced by Engulfed Liposomes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martens, T.F.; Remaut, K.; Demeester, J.; De Smedt, S.C.; Braeckmans, K. Intracellular delivery of nanomaterials: How to catch endosomal escape in the act. Nano Today 2014, 9, 344–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuhorn, I.S.; Hoekstra, D. On the Mechanism of Cationic Amphiphile-mediated Transfection. To Fuse or not to Fuse: Is that the Question? J. Membr. Biol. 2002, 189, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campeau, P.; Chapdelaine, P.; Seigneurin-Venin, S.; Massie, B.; Tremblay, J.P. Transfection of large plasmids in primary human myoblasts. Gene. Ther. 2001, 8, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuhorn, I.S.; Visser, W.H.; Bakowsky, U.; Engberts, J.B.F.N.; Hoekstra, D. Interference of serum with lipoplex–cell interaction: Modulation of intracellular processing. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Biomembr. 2002, 1560, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janich, C.; Pinnapireddy, S.R.; Erdmann, F.; Groth, T.; Langner, A.; Bakowsky, U.; Wölk, C. Fast therapeutic DNA internalization—A high potential transfection system based on a peptide mimicking cationic lipid. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 118, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Janich, C.; Ivanusic, D.; Giselbrecht, J.; Janich, E.; Pinnapireddy, S.R.; Hause, G.; Bakowsky, U.; Langner, A.; Wölk, C. Efficient Transfection of Large Plasmids Encoding HIV-1 into Human Cells—A High Potential Transfection System Based on a Peptide Mimicking Cationic Lipid. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 805. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12090805
Janich C, Ivanusic D, Giselbrecht J, Janich E, Pinnapireddy SR, Hause G, Bakowsky U, Langner A, Wölk C. Efficient Transfection of Large Plasmids Encoding HIV-1 into Human Cells—A High Potential Transfection System Based on a Peptide Mimicking Cationic Lipid. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(9):805. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12090805
Chicago/Turabian StyleJanich, Christopher, Daniel Ivanusic, Julia Giselbrecht, Elena Janich, Shashank Reddy Pinnapireddy, Gerd Hause, Udo Bakowsky, Andreas Langner, and Christian Wölk. 2020. "Efficient Transfection of Large Plasmids Encoding HIV-1 into Human Cells—A High Potential Transfection System Based on a Peptide Mimicking Cationic Lipid" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 9: 805. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12090805
APA StyleJanich, C., Ivanusic, D., Giselbrecht, J., Janich, E., Pinnapireddy, S. R., Hause, G., Bakowsky, U., Langner, A., & Wölk, C. (2020). Efficient Transfection of Large Plasmids Encoding HIV-1 into Human Cells—A High Potential Transfection System Based on a Peptide Mimicking Cationic Lipid. Pharmaceutics, 12(9), 805. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12090805