Urinary Metabolomic Profiling after Administration of Corydalis Tuber and Pharbitis Seed Extract in Healthy Korean Volunteers
Abstract
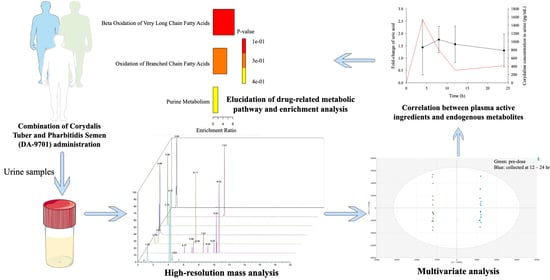
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Clinical Study and Sample Collection
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.4. Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry Conditions
2.5. Data Processing and Multivariate Analysis
2.6. Metabolites Identification
2.7. Pathway Analysis and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis and Candidate Selection
3.2. Metabolite Identification
3.3. Pathway Analysis
3.4. Statistical Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tack, J.; Bisschops, R.; Sarnelli, G. Pathophysiology and treatment of functional dyspepsia. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, 1239–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Enck:, P.; Azpiroz, F.; Boeckxstaens, G.; Elsenbruch, S.; Feinle-Bisset, C.; Holtmann, G.; Lackner, J.M.; Ronkainen, J.; Schemann, M.; Stengel, A. Functional dyspepsia. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllou, K.; Kourikou, A.; Gazouli, M.; Karamanolis, G.; Dimitriadis, G. Functional dyspepsia susceptibility is related to CD 14, GNB 3, MIF, and TRPV 1 gene polymorphisms in the Greek population. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 29, e12913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.E.; Park, H.K.; Kim, N.; Joo, Y.-E.; Baik, G.-H.; Shin, J.E.; Seo, G.S.; Kim, G.H.; Kim, H.-U.; Kim, H.Y.; et al. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Functional Dyspepsia: A Nationwide Multicenter Prospective Study in Korea. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 48, e12–e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tack, J.; Talley, N.J.; Camilleri, M.; Holtmann, G.; Hu, P.; Malagelada, J.-R.; Stanghellini, V. Functional Gastroduodenal Disorders. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 1466–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Flockhart, D.A.; Desta, Z.; Mahal, S.K. Selection of Drugs to Treat Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2000, 39, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.H.; Choi, J.J.; Kim, D.H.; Choi, S.; Lee, K.R.; Son, M.; Jin, M. Gastroprokinetic effects of DA-9701, a new prokinetic agent formulated with Pharbitis Semen and Corydalis Tuber. Phytomedicine 2008, 15, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Liang, Y.; Yang, J.; Bai, X.; Hao, X.-Y.; Yang, F.-M.; Sun, Q.-Y. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors from Corydalis yanhusuo. Nat. Prod. Res. 2011, 25, 1418–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.H.; Kim, H.-S.; Lee, S.K. Effects of the new prokinetic agent DA-9701 formulated with corydalis tuber and pharbitis seed in patients with minimal change esophagitis: A bicenter, randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled study. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2014, 20, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lim, C.-H.; Choi, M.-G.; Park, H.; Baeg, M.K.; Park, J.M. Effect of DA-9701 on gastric emptying in a mouse model: Assessment by 13C-octanoic acid breath test. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Son, M.; Kim, S.Y. Effects of corydaline from Corydalis tuber on gastric motor function in an animal model. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 33, 958–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, Y.S.; Kim, M.Y.; Lee, H.; Park, S.; Lee, K. Effect of DA-9701, a novel prokinetic agent, on stress-induced delayed gastric emptying and hormonal changes in rats. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2013, 25, 254-e166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.R.; Min, B.H.; Lee, S.O.; Lee, T.H.; Son, M.; Rhee, P.L. Effects of DA-9701, a novel prokinetic agent, on gastric accommodation in conscious dogs. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 27, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corona, G.; Rizzolio, F.; Giordano, A.; Toffoli, G. Pharmaco-metabolomics: An emerging “omics” tool for the personalization of anticancer treatments and identification of new valuable therapeutic targets. J. Cell. Physiol. 2012, 227, 2827–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellero-Simatos, S.; Lewis, J.P.; Georgiades, A.; Yerges-Armstrong, L.M.; Beitelshees, A.L.; Horenstein, R.B.; Dane, A.; Harms, A.C.; Ramaker, R.; Vreeken, R.J.; et al. Pharmacometabolomics Reveals That Serotonin Is Implicated in Aspirin Response Variability. CPT Pharmacomet. Syst. Pharmacol. 2014, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Lee, J.W.; Hong, K.T.; Yu, K.-S.; Jang, I.-J.; Park, K.D.; Shin, H.Y.; Ahn, H.S.; Cho, J.-Y.; Kang, H.J. Pharmacometabolomics for predicting variable busulfan exposure in paediatric haematopoietic stem cell transplantation patients. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, L.; Hu, M.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Lu, B.; Xie, Z.; Liao, Q. Association between metabolic profile and microbiomic changes in rats with functional dyspepsia. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 20166–20181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Su, X.; Li, Y.; Zhu, J.; Song, Y.; Zhang, P.; Chen, J.D.Z.; Wei, R.; et al. 1H NMR-Based Metabonomic Study of Functional Dyspepsia in Stressed Rats Treated with Chinese Medicine Weikangning. Evid. Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 4039425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jardines, D.; Correa, T.; Ledea, O.; Zamora, Z.; Rosado, A.; Molerio, J. Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry profile of urinary organic acids of Wistar rats orally treated with ozonized unsaturated triglycerides and ozonized sunflower oil. J. Chromatogr. B 2003, 783, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumazawa, Y.; Sakamoto, H.; Kawajiri, H.; Seguro, K.; Motoki, M. Determination of ε-(γ-glutamyl) lysine in several fish eggs and muscle proteins. Fish. Sci. 1996, 62, 331–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fesus, L.; Piacentini, M. Transglutaminase 2: An enigmatic enzyme with diverse functions. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2002, 27, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley, A.J.; Coggan, M.; Board, P.G. Identification and Characterization of γ-Glutamylamine Cyclotransferase, an Enzyme Responsible for γ-Glutamyl-ϵ-lysine Catabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 9642–9648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pfeffer, K.D.; Huecksteadt, T.P.; Hoidal, J.R. Xanthine dehydrogenase and xanthine oxidase activity and gene expression in renal epithelial cells. Cytokine and steroid regulation. J. Immunol. 1994, 153, 1789–1797. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Harrison, R. Structure and function of xanthine oxidoreductase: Where are we now? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2002, 33, 774–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhu, D.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Su, G.; Lin, L.; Wang, X.; Dong, Y. In Vitro and In Vivo Studies on Adlay-Derived Seed Extracts: Phenolic Profiles, Antioxidant Activities, Serum Uric Acid Suppression, and Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitory Effects. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 7771–7778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Shen, H.; Wang, L.; Meng, Q.; Liu, W. Analyses of total alkaloid extract of Corydalis yanhusuo by comprehensive RP× RP liquid chromatography with pH difference. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2016, 2016, 9752735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiao, W.-P.; Yang, Y.-F.; Wu, H.-Z.; Xiong, Y.-y. Predicting the Mechanism of the Analgesic Property of Yanhusuo Based on Network Pharmacology. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2019, 14, 1934578X19883071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tillhon, M.; Guamán Ortiz, L.M.; Lombardi, P.; Scovassi, A.I. Berberine: New perspectives for old remedies. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 84, 1260–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, M.M.; Talley, N.J. The role of duodenal inflammation in functional dyspepsia. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2017, 51, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Chen, B.; Kim, J.; Chen, X.; Dai, N. Micro-inflammation in functional dyspepsia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 30, e13304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanheel, H.; Vicario, M.; Vanuytsel, T.; Van Oudenhove, L.; Martinez, C.; Keita, Å.V.; Pardon, N.; Santos, J.; Söderholm, J.D.; Tack, J.; et al. Impaired duodenal mucosal integrity and low-grade inflammation in functional dyspepsia. Gut 2014, 63, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, M.; Son, M. DA-9701 (Motilitone): A Multi-Targeting Botanical Drug for the Treatment of Functional Dyspepsia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Min, Y.W.; Min, B.-H.; Kim, S.; Choi, D.; Rhee, P.-L. Effect of DA-9701 on gastric motor function assessed by magnetic resonance imaging in healthy volunteers: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.Y.; Woo, H.S.; Kim, K.O.; Choi, S.H.; Kwon, K.A.; Chung, J.W.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.J.; Park, D.K. DA-9701 improves colonic transit time and symptoms in patients with functional constipation: A prospective study. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 32, 1943–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Characteristics | Group A | Group B | Group C |
|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 4) | (n = 6) | (n = 6) | |
| Age | 24.25 ± 1.50 | 23.83 ± 1.47 | 25.33 ± 3.78 |
| (23–26) | (22–26) | (20–30) | |
| Height (cm) | 174.9 ± 5.08 | 171.9 ± 2.26 | 173.6 ± 7.37 |
| (168.0–179.1) | (169.3–175.4) | (162.2–183.5) | |
| Weight (kg) | 68.35 ± 10.5 | 67.65 ± 8.90 | 72.32 ± 14.4 |
| (59.3–77.6) | (56.4–83.8) | (58.3–98.4) | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.23 ± 2.37 | 22.83 ± 2.74 | 23.78 ± 2.89 |
| (19.5–24.4) | (19.6–27.9) | (21.0–29.2) |
| Metabolites | Retention Time (min) | Molecular Weight (g/mol) | VIP Value | Related Pathway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| l-acetylcarnitine | 0.66 | 204.12303 | 5.66 | lipid transport and metabolism |
| fatty acid metabolism | ||||
| lipid peroxidation | ||||
| Azelaic acid | 7.44 | 188.10429 | 4.75 | lipid transport and metabolism |
| fatty acid metabolism | ||||
| lipid peroxidation | ||||
| Ophthalmic acid | 0.94 | 289.12739 | 3.92 | unclear |
| Uric acid | 0.68 | 168.02844 | 3.69 | purine metabolism |
| Suberic acid | 5.95 | 174.08862 | 3.69 | lipid transport and metabolism |
| fatty acid metabolism | ||||
| lipid peroxidation | ||||
| ε-(γ-glutamyl)-lysine | 1.83 | 275.14819 | 3.26 | unclear |
| Pimelic acid | 4.09 | 160.07276 | 3.17 | lipid transport and metabolism |
| fatty acid metabolism | ||||
| lipid peroxidation |
| Identified | 0–4 h | 4–8 h | 8–12 h | 12–24 h |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Candidates | ||||
| Uric acid | 1.43 ± 1.12 | 1.75 ± 0.53 * | 1.56 ± 0.74 * | 1.31 ± 0.67 |
| ε-(γ-glutamyl)-lysine # | 0.18 ± 0.11 * | 0.03 ± 0.02 * | 0.01 ± 0.01 * | 0.01 ± 0.01 * |
| Ophthalmic acid | 0.42 ± 0.23 * | 0.40 ± 0.28 * | 1.07 ± 0.61 | 0.99 ± 0.56 |
| Pimelic acid # | 0.25 ± 0.14 * | 0.41 ± 0.31 * | 0.66 ± 0.34 * | 0.63 ± 0.52 * |
| Suberic acid | 0.48 ± 0.23 * | 0.51 ± 0.30 * | 0.84 ± 0.54 | 0.90 ± 0.89 |
| Azelaic acid | 0.11 ± 0.05 * | 0.59 ± 0.37 * | 0.96 ± 0.65 | 0.60 ± 0.56 * |
| L-acetylcarnitine | 1.22 ± 0.89 | 0.92 ± 0.52 | 0.59 ± 0.25 * | 0.68 ± 0.23 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, H.-C.; Park, J.E.; Seo, Y.; Kim, M.-G.; Shin, K.-H. Urinary Metabolomic Profiling after Administration of Corydalis Tuber and Pharbitis Seed Extract in Healthy Korean Volunteers. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13040522
Jeong H-C, Park JE, Seo Y, Kim M-G, Shin K-H. Urinary Metabolomic Profiling after Administration of Corydalis Tuber and Pharbitis Seed Extract in Healthy Korean Volunteers. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(4):522. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13040522
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Hyeon-Cheol, Jung Eun Park, Yohan Seo, Min-Gul Kim, and Kwang-Hee Shin. 2021. "Urinary Metabolomic Profiling after Administration of Corydalis Tuber and Pharbitis Seed Extract in Healthy Korean Volunteers" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 4: 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13040522
APA StyleJeong, H. -C., Park, J. E., Seo, Y., Kim, M. -G., & Shin, K. -H. (2021). Urinary Metabolomic Profiling after Administration of Corydalis Tuber and Pharbitis Seed Extract in Healthy Korean Volunteers. Pharmaceutics, 13(4), 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13040522