Enhanced Anticancer Efficacy of Dual Drug-Loaded Self-Assembled Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Mediated by pH-Responsive Folic Acid and Human-Derived Cell Penetrating Peptide dNP2
Abstract
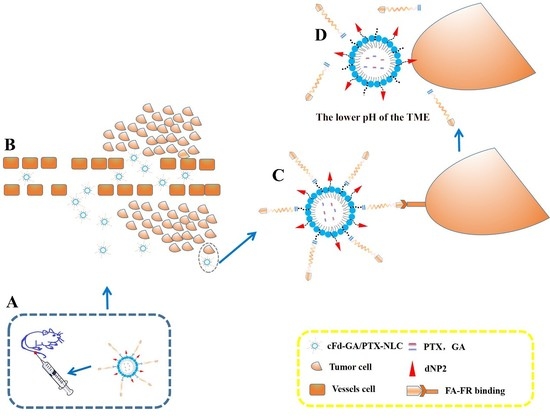
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials, Cell Lines, and Animals
2.2. Preparation of NLC
2.3. Particle Size, Zeta Potential, and Morphology
2.4. Entrapment Efficiency and Drug Loading
2.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
2.6. In Vitro Stability
2.7. Cellular Uptake
2.8. In Vivo Bio-Distribution Study
2.9. Cytotoxicity Study
2.10. Caspase Activity Assay
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Particle Size, Zeta Potential, and Morphology
3.2. Entrapment Efficiency and Drug Loading
3.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
3.4. In Vitro Stability
3.5. Cellular Uptake Study
3.6. In Vivo Bio-Distribution Study
3.7. Cytotoxicity Study
3.8. Caspase Activity Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Ca A Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zheng, R.; Baade, P.D.; Zhang, S.; Zeng, H.; Bray, F.; Jemal, A.; Yu, X.Q.; He, J. Cancer Statistics in China, 2015. Ca A Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Fan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Kebebe, D.; Zhang, B.; Lu, P.; Pi, J.; Liu, Z. Traditional Chinese medicine-combination therapies utilizing nanotechnology-based targeted delivery systems: A new strategy for antitumor treatment. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 2029–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, F.; Dahmani, F.Z.; Qiao, J.; Ni, J.; Xiong, H.; Liu, T.; Zhou, J.; Yao, J. A targeted nanoplatform co-delivering chemotherapeutic and antiangiogenic drugs as a tool to reverse multidrug resistance in breast cancer. Acta Biomater. 2018, 75, 398–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, M. Gambogic acid-loaded pH-sensitive mixed micelles for overcoming breast cancer resistance. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 495, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreusel, K.-M.; Bechrakis, N.E.; Wiegel, T.; Krause, L.; Foerster, M.H. Incidence and clinical characteristics of symptomatic choroidal metastasis from lung cancer. Acta Ophthalmol. 2008, 86, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Li, N.; Zhang, B.; Hui, Y.; Lu, P.; Pi, J.; Liu, Z. Dual drug-loaded nano-platform for targeted cancer therapy: Toward clinical therapeutic efficacy of multifunctionality. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zhang, B.; Fan, Y.; Wang, M.; Kebebe, D.; Li, J.; Liu, Z. Traditional Chinese medicine combined with hepatic targeted drug delivery systems: A new strategy for the treatment of liver diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 117, 109128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Üner, M. Preparation, characterization and physico-chemical properties of solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) and nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC): Their benefits as colloidal drug carrier systems. Die Pharm. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 61, 375–386. [Google Scholar]
- Carbone, C.; Leonardi, A.; Cupri, S.; Puglisi, G.; Pignatello, R. Pharmaceutical and biomedical applications of lipid-based nanocarriers. Pharm. Pat. Anal. 2014, 3, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidotti, G.; Brambilla, L.; Rossi, D. Cell-Penetrating Peptides: From Basic Research to Clinics. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 38, 406–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kebebe, D.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Vilakhamxay, M.; Liu, Z.; Li, J. Tumor-targeting delivery of herb-based drugs with cell-penetrating/tumor-targeting peptide-modified nanocarriers. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 1425–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albanese, A.; Tang, P.S.; Chan, W.C.W. The Effect of Nanoparticle Size, Shape, and Surface Chemistry on Biological Systems. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Kim, W.-J.; Kim, Y.-H.; Lee, S.; Koo, J.-H.; Lee, J.-A.; Yoon, H.; Kim, D.-H.; Park, H.-J.; Kim, H.-M.; et al. dNP2 is a blood–brain barrier-permeable peptide enabling ctCTLA-4 protein delivery to ameliorate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Shan, W.; Huang, Y. Improved anticancer efficacy of doxorubicin mediated by human-derived cell-penetrating peptide dNP2. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 551, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Mei, L.; Xu, C.; Yu, Q.; Shi, K.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, H.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Dual Receptor Recognizing Cell Penetrating Peptide for Selective Targeting, Efficient Intratumoral Diffusion and Synthesized Anti-Glioma Therapy. Theranostics 2016, 6, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, N.; Turk, M.J.; Westrick, E.; Lewis, J.D.; Low, P.S.; Leamon, C.P. Folate receptor expression in carcinomas and normal tissues determined by a quantitative radioligand binding assay. Anal. Biochem. 2005, 338, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosio, F.; Arpicco, S.; Stella, B.; Brusa, P.; Cattel, L. Folate-mediated targeting of albumin conjugates of paclitaxel obtained through a heterogeneous phase system. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 382, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, M.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Y.; Liu, T.; Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, T. Expression of folate receptors in nasopharyngeal and laryngeal carcinoma and folate receptor-mediated endocytosis by molecular targeted nanomedicine. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 2443–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ran, R.; Chen, J.; Kuang, Q.; Tang, J.; Mei, L.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, H.; Zhang, Z.; He, Q. Paclitaxel loaded liposomes decorated with a multifunctional tandem peptide for glioma targeting. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 4835–4847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Shi, K.; Tang, X.; Wei, J.; Cun, X.; Chen, X.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; He, Q. pH-sensitive folic acid and dNP2 peptide dual-modified liposome for enhanced targeted chemotherapy of glioma. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. Off. J. Eur. Fed. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 124, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Shi, K.; Tang, X.; Wei, J.; Cun, X.; Long, Y.; Zhang, Z.; He, Q. Synergistic tumor microenvironment targeting and blood-brain barrier penetration via a pH-responsive dual-ligand strategy for enhanced breast cancer and brain metastasis therapy. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2018, 14, 1833–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Li, J.; Kebebe, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Z. Cell penetrating peptides functionalized gambogic acid-nanostructured lipid carrier for cancer treatment. Drug Deliv. 2018, 25, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Meng, T.; Shi, N.; Zhuang, H.; Yang, Z.; Qi, X. Targeting and Microenvironment-Responsive Lipid Nanocarrier for the Enhancement of Tumor Cell Recognition and Therapeutic Efficiency. Adv. Health Mater. 2015, 4, 748–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Sun, Z.; Li, Y.; Guo, Y.; Liao, Y.; Liu, M.; Wang, X. Folate-modified Annonaceous acetogenins nanosuspensions and their improved antitumor efficacy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 5053–5067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soe, Z.C.; Thapa, R.K.; Ou, W.; Gautam, M.; Nguyen, H.T.; Jin, S.G.; Ku, S.K.; Oh, K.T.; Choi, H.-G.; Yong, C.S.; et al. Folate receptor-mediated celastrol and irinotecan combination delivery using liposomes for effective chemotherapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 170, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-H.; Lim, S.-J.; Park, J.-S.; Lee, M.-K. Folate-tethered emulsion for the target delivery of retinoids to cancer cells. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 68, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.; Fournier, P.G.J.; Mendoza-Lavaniegos, V.; Sengar, P.; Guerra-Olvera, F.M.; Iñiguez, E.; Kretzschmar, T.G.; Hirata, G.A.; Juárez, P. Functionalized rare earth-doped nanoparticles for breast cancer nanodiagnostic using fluorescence and CT imaging. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhye, S.G.; Nagarsenker, M.S. Simvastatin Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Oral Delivery: Formulation Development and In vivo Evaluation. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 75, 591–598. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, I.; Zielińska, A.; Ferreira, N.R.; Silva, A.M.; Souto, E.B. Optimization of linalool-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles using experimental factorial design and long-term stability studies with a new centrifugal sedimentation method. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 549, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebebe, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Yang, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Ma, Z.; Lu, P.; Liu, Z.; Li, J. Dimeric c(RGD) peptide conjugated nanostructured lipid carriers for efficient delivery of Gambogic acid to breast cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 6179–6195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Preparation | Size (nm) | PDI | ZP (mV) | EE% (GA) | EE% (PTX) | DL% (GA) | DL% (PTX) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GA/PTX-NLC | 23.62 ± 0.36 | 0.16 ± 0.03 | −3.59 ± 1.80 | 95.13 ± 0.64 | 96.14 ± 0.23 | 7.45 ± 0.07 | 6.43 ± 0.04 |
| dNP2-GA/PTX-NLC | 21.28 ± 0.33 | 0.18 ± 0.06 | −2.96 ± 0.43 | 98.15 ± 0.63 | 95.18 ± 0.21 | 7.54 ± 0.06 | 6.33 ± 0.05 |
| FA-GA/PTX-NLC | 21.93 ± 0.58 | 0.22 ± 0.07 | −2.78 ± 0.86 | 96.07 ± 0.74 | 96.79 ± 0.49 | 7.50 ± 0.07 | 6.47 ± 0.04 |
| FA/dNP2-GA/PTX-NLC | 19.38 ± 0.89 | 0.25 ± 0.09 | −4.01 ± 0.26 | 95.69 ± 0.88 | 97.17 ± 0.27 | 7.48 ± 0.05 | 6.47 ± 0.08 |
| cFA/dNP2-GA/PTX-NLC | 20.36 ± 0.78 | 0.23 ± 0.05 | −3.88 ± 0.96 | 97.36 ± 0.56 | 95.69 ± 0.58 | 7.51 ± 0.06 | 6.39 ± 0.05 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Z.; Pi, J.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, H.; Zhang, B.; Li, N.; Li, Z.; Liu, Z. Enhanced Anticancer Efficacy of Dual Drug-Loaded Self-Assembled Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Mediated by pH-Responsive Folic Acid and Human-Derived Cell Penetrating Peptide dNP2. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 600. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13050600
Ma Z, Pi J, Zhang Y, Qin H, Zhang B, Li N, Li Z, Liu Z. Enhanced Anticancer Efficacy of Dual Drug-Loaded Self-Assembled Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Mediated by pH-Responsive Folic Acid and Human-Derived Cell Penetrating Peptide dNP2. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(5):600. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13050600
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Zhe, Jiaxin Pi, Ying Zhang, Huan Qin, Bing Zhang, Nan Li, Zheng Li, and Zhidong Liu. 2021. "Enhanced Anticancer Efficacy of Dual Drug-Loaded Self-Assembled Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Mediated by pH-Responsive Folic Acid and Human-Derived Cell Penetrating Peptide dNP2" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 5: 600. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13050600
APA StyleMa, Z., Pi, J., Zhang, Y., Qin, H., Zhang, B., Li, N., Li, Z., & Liu, Z. (2021). Enhanced Anticancer Efficacy of Dual Drug-Loaded Self-Assembled Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Mediated by pH-Responsive Folic Acid and Human-Derived Cell Penetrating Peptide dNP2. Pharmaceutics, 13(5), 600. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13050600