Influence of Lactobacillus Biosurfactants on Skin Permeation of Hydrocortisone
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Production and Isolation of L. crispatus BC1 and L. gasseri BC9 Biosurfactants
2.3. Surface-Activity and Critical Micelle Concentration of BC1-BS and BC9-BS
2.4. HC Solubility
2.5. HPLC Analytical Assay
2.6. Influence of BC1-BS and BC9-BS on HC Solubility
2.7. Tissue Preparation
2.8. Effect of BS on Skin Hydration
2.9. Influence of BC1-BS and BC9-BS on HC Permeation
2.10. Differential Scanning Calorimetry Analysis (DSC) of Stratum Corneum
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Surface-Activity Determination and Critical Micelle Concentration of Biosurfactants
3.2. HC Solubility
3.3. Influence of BC1-BS and BC9-BS on HC Solubility
3.4. Effect of BS on Skin Hydration
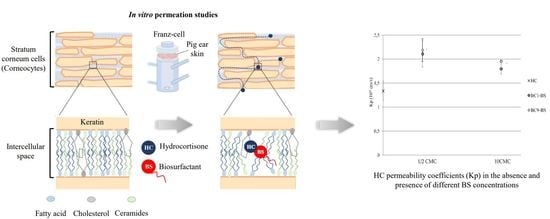
3.5. Influence of BC1-BS and BC9-BS on HC Permeation
3.6. Differential Scanning Calorimetry Analysis (DSC) of Stratum Corneum
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marwah, H.; Garg, T.; Goyal, A.K.; Rath, G. Permeation enhancer strategies in transdermal drug delivery. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 564–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.B.; Martin, G.P.; Jones, S.A.; Akomeah, F.K. Dermal and Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems: Current and Future Prospects. Drug Deliv. 2006, 13, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prausnitz, M.R.; Mitragotri, S.; Langer, R. Current status and future potential of transdermal drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjadi, M.; Mostaghaci, B.; Sitti, M. Recent Advances in Skin Penetration Enhancers for Transdermal Gene and Drug Delivery. Curr. Gen. Ther. 2017, 17, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, K.W. Penetration enhancement of topical formulations. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luppi, B.; Bigucci, F.; Baldini, M.; Abruzzo, A.; Cerchiara, T.; Corace, G.; Zecchi, V. Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose films for prolonged delivery of the antipsychotic drug chlorpromazine. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 62, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Cagno, M.; Luppi, B. Drug supersaturation states induced by polymeric micelles and liposomes: A mechanistic investigation into permeability enhancements. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 48, 775–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seweryn, A. Interactions between surfactants and the skin—Theory and practice. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 256, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adu, S.A.; Naughton, P.J.; Marchant, R.; Banat, I.M. Microbial Biosurfactants in Cosmetic and Personal Skincare Pharmaceutical Formulations. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoth, D.; Rincón-Fontán, M.; Stahr, P.L.; Pelikh, O.; Eckert, R.W.; Dietrich, H.; Cruz, J.M.; Moldes, A.B.; Keck, C.M. Evaluation of a Biosurfactant Extract Obtained from Corn for Dermal Application. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 10, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hamme, J.; Singh, A.; Ward, O. Physiological aspects. Part 1 in a series of papers devoted to surfactants in microbiology and biotechnology. Biotechnol. Adv. 2006, 24, 604–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchant, R.; Banat, I. Microbial biosurfactants: Challenges and opportunities for future exploitation. Trends Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelik, P.A.; Manga, E.B.; Çabuk, A.; Banat, I.M. Biosurfactants’ Potential Role in Combating COVID-19 and Similar Future Microbial Threats. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 334. [Google Scholar]
- Ohadi, M.; Shahravan, A.; Dehghannoudeh, N.; Eslaminejad, T.; Banat, I.M.; Dehghannoudeh, G. Potential Use of Microbial Surfactant in Microemulsion Drug Delivery System: A Systematic Review. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2020, 14, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abruzzo, A.; Giordani, B.; Parolin, C.; Vitali, B.; Protti, M.; Mercolini, L.; Cappelletti, M.; Fedi, S.; Bigucci, F.; Cerchiara, T.; et al. Novel mixed vesicles containing lactobacilli biosurfactant for vaginal delivery of an anti-Candida agent. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 112, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordani, B.; Costantini, P.E.; Fedi, S.; Cappelletti, M.; Abruzzo, A.; Parolin, C.; Foschi, C.; Frisco, G.; Calonghi, N.; Cerchiara, T.; et al. Liposomes containing biosurfactants isolated from Lactobacillus gasseri exert antibiofilm activity against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 139, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anestopoulos, I.; Kiousi, D.E.; Klavaris, A.; Galanis, A.; Salek, K.; Euston, S.R.; Pappa, A.; Panayiotidis, M.I. Surface Active Agents and Their Health-Promoting Properties: Molecules of Multifunctional Significance. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gregorio, P.R.; Parolin, C.; Abruzzo, A.; Luppi, B.; Protti, M.; Mercolini, L.; Silva, J.A.; Giordani, B.; Marangoni, A.; Nader-Macías, M.E.F.; et al. Biosurfactant from vaginal Lactobacillus crispatus BC1 as a promising agent to interfere with Candida adhesion. Microb. Cell Fact. 2020, 19, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abruzzo, A.; Giordani, B.; Parolin, C.; De Gregorio, P.R.; Foschi, C.; Cerchiara, T.; Bigucci, F.; Vitali, B.; Luppi, B. Lactobacillus crispatus BC1 Biosurfactant Delivered by Hyalurosomes: An Advanced Strategy to Counteract Candida Biofilm. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abruzzo, A.; Armenise, N.; Bigucci, F.; Cerchiara, T.; Gösser, M.B.; Samorì, C.; Galletti, P.; Tagliavini, E.; Brown, D.M.; Johnston, H.J.; et al. Surfactants from itaconic acid: Toxicity to HaCaT keratinocytes in vitro, micellar solubilization, and skin permeation enhancement of hydrocortisone. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 524, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Som, I.; Bhatia, K.; Yasir, M. Status of surfactants as penetration enhancers in transdermal drug delivery. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2012, 4, 2–9. [Google Scholar]
- Todo, H. Transdermal permeation of drugs in various animal species. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simon, G.A.; Maibach, H.I. The pig as an experimental animal model of percutaneous permeation in man: Qualitative and quantitative observations-an overview. Skin Pharmacol. Appl. Skin Physiol. 2000, 13, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, D.J.; Ward, R.J.; Heylings, J.R. Multi-species assessment of electrical resistance as a skin integrity marker for in vitro percutaneous absorption studies. Toxicol. Vitro 2004, 18, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimura, T.; Shimotoyodome, Y.; Nishijima, T.; Sugata, K.; Taguchi, H.; Moriwaki, S. Changes in hydration of the stratum corneum are the most suitable indicator to evaluate the irritation of surfactants on the skin. Skin Res. Technol. 2017, 23, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abruzzo, A.; Cerchiara, T.; Bigucci, F.; Gallucci, M.C.; Luppi, B. Mucoadhesive buccal tablets based on Chitosan/Gelatin microparticles for delivery of propranolol hydrochloride. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 4365–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Doh, H.J.; Choi, M.K.; Chung, S.J.; Shim, C.K.; Kim, D.D.; Kim, J.S.; Yong, C.S.; Choi, H.G. Skin permeation enhancement of diclofenac by fatty acids. Drug Deliv. 2008, 15, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baby, A.R.; Lacerda, A.C.; Velasco, M.V.; Lopes, P.S.; Kawano, Y.; Kaneko, T.M. Evaluation of the interaction of surfactants with stratum corneum model membrane from Bothrops jararaca by DSC. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 317, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panchagnula, R.; Salve, P.R.; Thomas, N.S.; Jain, A.K.; Ramarao, P. Transdermal delivery of naloxone: Effect of water, propylene glycol, ethanol and their binary combinations on permeation through rat skin. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 219, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staszak, K.; Wieczorek, D.; Michocka, K. Effect of Sodium Chloride on the Surface and Wetting Properties of Aqueous Solutions of Cocamidopropyl Betaine. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2015, 18, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qazi, M.J.; Liefferink, R.W.; Schlegel, S.J.; Backus, E.H.G.; Bonn, D.; Shahidzadeh, N. Influence of Surfactants on Sodium Chloride Crystallization in Confinement. Langmuir 2017, 3, 4260–4268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, E.; Najjar, S.; Sallam, A. Aqueous solubility of diclofenac diethylamine in the presence of pharmaceutical additives: A comparative study with diclofenac sodium. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2000, 26, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergström, C.A.; Luthman, K.; Artursson, P. Accuracy of calculated pH-dependent aqueous drug solubility. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 22, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fini, A.; Bergamante, V.; Ceschel, G.C.; Ronchi, C.; De Moraes, C.A. Control of transdermal permeation of hydrocortisone acetate from hydrophilic and lipophilic formulations. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 2008, 9, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhat, P.A.; Dar, A.A.; Rather, G.M. Solubilization capabilities of some cationic, anionic, and nonionic surfactants toward the poorly water-soluble antibiotic drug erythromycin. J. Chem. Eng. Data. 2008, 53, 1271–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, J.T.; Manoukian, E. Micellar solubilization of timobesone acetate in aqueous and aqueous propylene glycol solutions of nonionic surfactants. Pharm. Res. 1988, 5, 704–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, A.K.; Flanagan, D.R. Micellar solubilization of a new antimalarial drug, beta-arteether. J. Pharm. Sci. 1989, 78, 574–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Gao, H.; Babu, S.; Garad, S. Co-Amorphous Formation of High-Dose Zwitterionic Compounds with Amino Acids to Improve Solubility and Enable Parenteral Delivery. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, E.B.; Almeida, A.J.; Müller, R.H. Lipid nanoparticles (SLN®, NLC®) for cutaneous drug delivery: Structure, protection and skin effects. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2007, 3, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wissing, S.; Müller, R.H. The influence of the crystallinity of lipid nanoparticles on their occlusive properties. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 242, 377–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wissing, S.A.; Müller, R.H. The influence of solid lipid nanoparticles on skin hydration and viscoelasticity—In vivo study. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2003, 56, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakizawa, Y.; Kataoka, K. Block copolymer micelles for delivery of gene and related compounds. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, R.; Katiyar, S.S.; Kushwah, V.; Jain, S. Solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carrier-based nanotherapeutics in treatment of psoriasis: A comparative study. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2017, 14, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, W.S.; Cho, H.I.; Lee, H.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Choi, Y.W. Enhanced occlusiveness of nanostructured lipid carrier (NLC)-based carbogel as a skin moisturizing vehicle. J. Pharm. Investig. 2010, 40, 373–378. [Google Scholar]
- Raghavan, S.L.; Kiepfer, B.; Davis, A.F.; Kazarian, S.G.; Hadgraft, J. Membrane transport of hydrocortisone acetate from supersaturated solutions; the role of polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 19, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, S.L.; Trividic, A.; Davis, A.F.; Hadgraft, J. Effect of cellulose polymers on supersaturation and in vitro membrane transport of hydrocortisone acetate. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 193, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.; Sharma, O.P.; Mehta, T. Nanocrystal: A novel approach to overcome skin barriers for improved topical drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 351–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, G.B.; Chen, R.; Keck, C.M.; Müller, R.H. Industrial concentrates of dermal hesperidin smartCrystals®–production, characterization & long-term stability. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 482, 54–60. [Google Scholar]
- Nokhodchi, A.; Shokri, J.; Dashbolaghi, A.; Hassan-Zadeh, D. The enhancement effect of surfactants on the penetration of lorazepam through rat skin. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 250, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarheed, O. Combination treatments of chemical enhancers with low frequency ultrasound for the transdermal delivery of hydrocortisone. Can. J. Pure Appl. Sci. 2013, 7, 2463–2473. [Google Scholar]
- Carelli, V.; Colo, G.D.; Nannipieri, E.; Serafini, M.F. Bile acids as enhancers of steroid penetration through excised hairless mouse skin. Int. J. Pharm. 1993, 89, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden, G.M.; Guzek, D.B.; Harris, R.R.; McKie, J.E.; Potts, R.O. Lipid thermotropic transitions in human stratum corneum. J. Invest. Dermatol. 1986, 86, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Golden, G.M.; Guzek, D.B.; Kennedy, A.H.; McKie, J.E.; Potts, R.O. Stratum corneum lipid phase transitions and water barrier properties. Biochemistry 1987, 26, 2382–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.C.; Cho, C.W.; Oh, I. Effects of non-ionic surfactants as permeation enhancers towards piroxicam from the poloxamer gel through rat skins. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 222, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapra, B.; Jain, S.; Tiwary, A.K. Percutaneous permeation enhancement by terpenes: Mechanistic view. AAPS J. 2008, 10, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abruzzo, A.; Parolin, C.; Corazza, E.; Giordani, B.; di Cagno, M.P.; Cerchiara, T.; Bigucci, F.; Vitali, B.; Luppi, B. Influence of Lactobacillus Biosurfactants on Skin Permeation of Hydrocortisone. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 820. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13060820
Abruzzo A, Parolin C, Corazza E, Giordani B, di Cagno MP, Cerchiara T, Bigucci F, Vitali B, Luppi B. Influence of Lactobacillus Biosurfactants on Skin Permeation of Hydrocortisone. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(6):820. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13060820
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbruzzo, Angela, Carola Parolin, Elisa Corazza, Barbara Giordani, Massimiliano Pio di Cagno, Teresa Cerchiara, Federica Bigucci, Beatrice Vitali, and Barbara Luppi. 2021. "Influence of Lactobacillus Biosurfactants on Skin Permeation of Hydrocortisone" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 6: 820. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13060820
APA StyleAbruzzo, A., Parolin, C., Corazza, E., Giordani, B., di Cagno, M. P., Cerchiara, T., Bigucci, F., Vitali, B., & Luppi, B. (2021). Influence of Lactobacillus Biosurfactants on Skin Permeation of Hydrocortisone. Pharmaceutics, 13(6), 820. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13060820