Improvement of Butamben Anesthetic Efficacy by the Development of Deformable Liposomes Bearing the Drug as Cyclodextrin Complex
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Phase Solubility Studies
2.3. Preparation of BTB–CD Solid Systems
- (a)
- Physical mixtures (PMs) were obtained through 15 min tumble mixing of the sieved components (75–150 µm granulometric fraction).
- (b)
- Kneaded products (KN) were obtained by adding a small volume of an ethanol:water 50:50 v/v solution to a given amount of PM, and then were kneaded thoroughly with a pestle to obtain an homogeneous slurry; this continued until the solvent was completely removed. The obtained product was kept 24 h in an oven at 40 °C for removing traces of solvent.
- (c)
- Coground products (GR) were prepared using a high-energy vibrational micromill (Mixer Mill MM 200 Retsch GmbH, Düsseldorf, Germany) where PMs were ball milled for 30 min at 24 Hz.
- (d)
- Coevaporated products (COE) were obtained by coevaporation in a rotary evaporator (Heidolph Laborota 4000, Schwabach, Germany) at 55 °C of equimolar BTB–CD solutions in ethanol:water 50:50 v/v. The resulting products were kept 24 h in a vacuum desiccator to remove solvent traces.
- (e)
- Colyophilized products (COL) were obtained by freeze-drying (Lyovac GT2, Leybold-Heraeus, Cologne, Germany) equimolar BTB–CD aqueous solutions placed in Petri dishes (20 cm diameter, 18 mm height).
2.4. Characterization of Drug–CD Binary Systems
2.5. Dissolution Studies
2.6. Preparation of Liposomes
2.7. Characterization of Liposomes
2.8. Stability Studies
2.9. Gel Preparation
2.10. In Vitro Permeation Studies through Excised Animal Membrane
2.11. In Vivo Studies
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Phase-Solubility Studies
3.2. Solid-State Characterization of Drug–CD Systems
3.3. Dissolution Studies of BTB–RAMEB Systems
3.4. Development and Characterization of Liposomal Formulations
3.5. Stability Studies of Liposomal Formulations
3.6. In Vitro Drug Permeation Studies
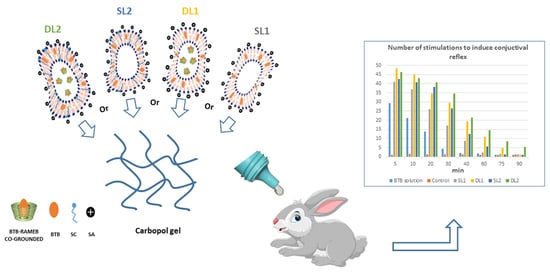
3.7. In Vivo Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FDA Code of Federal Regulations, Title 21, vol. 4, revised April 1 2020, Sec. 216.24. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/CFRSearch.cfm?fr=216.24 (accessed on 12 June 2021).
- Akbarzadeh, A.; Rezaei-Sadabady, R.; Davaran, S.; Joo, S.W.; Zarghami, N.; Hanifehpour, Y.; Samiei, M.; Kouhi, M.; Nejati-Koshki, K. Liposome: Classification, preparation, and applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sercombe, L.; Veerati, T.; Moheimani, F.; Wu, S.Y.; Sood, A.K.; Hua, S. Advances and Challenges of Liposome Assisted Drug Delivery. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zylberberg, C.; Matosevic, S. Pharmaceutical liposomal drug delivery: A review of new delivery systems and a look at the regulatory landscape. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 3319–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sinico, C.; Fadda, A.M. Vesicular carriers for dermal drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2009, 6, 813–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierre, M.B.R.; Costa, I.D.S.M. Liposomal systems as drug delivery vehicles for dermal and transdermal applications. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2011, 303, 607–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, N. Vesicles: A recently developed novel carrier for enhanced topical drug delivery. Curr. Drug. Deliv. 2014, 11, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.; Alam, K.; Beg, S.; Anwar, F.; Kumar, V. Liposomes as topical drug delivery systems: State of the arts. In Biomedical Applications of Nanoparticles; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Chapter 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.; Mackeben, S.; Müller-Goymann, C.C. Physicochemical characterisation of liposomes with encapsulated local anaesthetics. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 274, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.O.; Kim, S.J.; Pouliot, R.; Baek, W.Y. Enhanced transdermal delivery of local anaesthetics by liposome formulation of local anaesthetic mixture. Trans Tech. Publ. 2005, 277, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Cereda, C.M.; Brunetto, G.B.; Ribeiro, D.; de Paula, E. Liposomal formulations of prilocaine, lidocaine and mepivacaine prolong analgesic duration. Can. J. Anesth. 2006, 53, 1092–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mura, P.; Maestrelli, F.; Gonzalez-Rodrıguez, M.L.; Michelacci, I.; Ghelardini, C.; Rabasco, A.M. Development, characterization and in vivo evaluation of benzocaine-loaded liposomes. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2007, 67, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Araujo, D.R.; Cereda, C.M.; Brunetto, G.B.; Vomero, V.U.; Pierucci, A.; Neto, H.S.; de Oliveira, A.L.; Fraceto, L.F.; Braga Ade, F.; de Paula, E. Pharmacological and local toxicity studies of a liposomal formulation for the novel local anaesthetic ropivacaine. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2008, 60, 1449–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahar, P.; Cummings, K.C. Liposomal bupivacaine: A review of a new bupivacaine formulation. J. Pain Res. 2012, 5, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Lu, W.L.; Gu, W.; Lu, S.S.; Chen, Z.P.; Cai, B.C.; Yang, X.X. Drug-in-cyclodextrin-in-liposomes: A promising delivery system for hydrophobic drugs. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2014, 11, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maestrelli, F.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, M.L.; Rabasco, A.M.; Mura, P. Preparation and characterization of liposomes encapsulating ketoprofen-cyclodextrin complexes for transdermal drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 298, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Gao, J.; Wang, F.; Liang, W. Preparation, characterization and pharmacokinetics of liposomes-encapsulated cyclodextrins inclusion complexes for hydrophobic drugs. Drug Deliv. 2007, 14, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Q.; Guo, T.; Xia, D.; Li, X.; Zhu, C.; Li, H.; Ouyang, D.; Zhang, J.; Gan, Y. Pluronic F127-modified liposome containing tacrolimus-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes: Improved solubility, cellular uptake and intestinal penetration. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2013, 65, 1107–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Liu, X.; Hu, W.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, L. Preparation and evaluation of naringenin-loaded sulfobutylether-β-cyclodextrin/chitosan nanoparticles for ocular drug delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 149, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Bao, X.; Fang, A.; Li, H.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, C.; Wu, J.; Song, X. Nanoliposome-encapsulated brinzolamide-hydropropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex: A potential therapeutic ocular drug delivery system. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vieira, A.L.N.; Franz-Montan, M.; Cabeça, L.F.; de Paula, E. Anaesthetic benefits of a ternary drug delivery system (ropivacaine-in cyclodextrin-in liposomes): In vitro and in vivo evaluation. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2020, 72, 396–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, H.A. Transfersomes for transdermal drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2006, 3, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Singh, S.; Sharma, D.; Webster, T.J.; Shafaat, K.; Faruk, A. Elastic liposomes as novel carriers: Recent advances in drug delivery. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 5087–5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karande, P.; Mitragotri, S. Enhancement of transdermal drug delivery via synergistic action of chemicals. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1788, 2362–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El Zaafarany, G.M.; Awad, G.A.; Holayel, S.M.; Mortada, N.D. Role of “edge activators” and surface charge in developing ultradeformable vesicles with enhanced skin delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 397, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cereda, C.M.S.; Franz-Montan, M.; Da Silva, C.M.G.; Casadei, B.R.; Domingues, C.C.; Tofoli, G.R.; De Araujo, D.R.; De Paula, E. Transdermal delivery of butamben using elastic and conventional liposomes. J. Liposome Res. 2013, 23, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, H.A.E. Elastic liposomes for topical and transdermal drug delivery. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1522, 107–117. [Google Scholar]
- Alomrani, A.H.; Shazly, G.A.; Amara, A.A.; Badran, M.M. Itraconazole-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin loaded deformable liposomes: In vitro skin penetration studies and antifungal efficacy using Candida albicans as model. Colloids Surf. B 2014, 121, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mura, P.; Bragagni, M.; Mennini, N.; Cirri, M.; Maestrelli, F. Development of liposomal and microemulsion formulations for transdermal delivery of clonazepam: Effect of randomly methylated β-cyclodextrin. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 475, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestrelli, F.; González-Rodríguez, M.L.; Rabasco, A.M.; Ghelardini, C.; Mura, P. New “drug-in cyclodextrin-in deformable liposomes” formulations to improve the therapeutic efficacy of local anaesthetics. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 395, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragagni, M.; Maestrelli, F.; Mennini, N.; Ghelardini, C.; Mura, P. Liposomal formulations of prilocaine: Effect of complexation with hydroxypropyl-ß-cyclodextrin on drug anaesthetic efficacy. J. Liposome Res. 2010, 20, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, P.; Lalani, R.; Vhora, I.; Patil, S.; Amrutiya, J.; Misra, A.; Mashru, R. Liposomes encapsulating native and cyclodextrin enclosed paclitaxel: Enhanced loading efficiency and its pharmacokinetic evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 536, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Romero, A.M.; Maestrelli, F.; Mura, P.; Rabasco, A.M.; González-Rodríguez, M.L. Novel findings about double-loaded curcumin-in-HPβcyclodextrin-in liposomes: Effects on the lipid bilayer and drug release. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jhan, S.; Pethe, A.M. Double-loaded liposomes encapsulating lycopene β-cyclodextrin complexes: Preparation, optimization, and evaluation. J. Liposome Res. 2020, 30, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piel, G.; Piette, M.; Barillaro, V.; Castagne, D.; Evrard, B.; Delattre, L. Betamethasone -in cyclodextrin- in liposome: The effect of cyclodextrins on encapsulation efficiency and release kinetics. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 312, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakavets, I.; Lassalle, H.P.; Scheglmann, D.; Wiehe, A.; Zorin, V.; Bezdetnaya, L. Temoporfin -in cyclodextrin- in liposome—A new approach for anticancer drug delivery: The optimization of composition. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fatouros, D.G.; Hatzidimitriou, K.; Antimisiaris, S.G. Liposomes encapsulating prednisolone and prednisolone-cyclodextrin complexes: Comparison of membrane integrity and drug release. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 13, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manosroi, A.; Kongkaneramit, L.; Manosroi, J. Stability and transdermal absorption of topical amphotericin B liposome formulations. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 270, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higuchi, T.; Connors, A.K. Phase solubility techniques. Adv. Anal. Chem. Instr. 1965, 4, 117–210. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, K.A. The concept of dissolution efficiency. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1975, 27, 48–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGrath, J.C.; Lilley, E. Implementing guidelines on reporting research using animals (ARRIVE etc.): New requirements for publication in BJP. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 3189–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Marzouqi, A.; Jobe, B.; Corti, G.; Cirri, M.; Mura, P. Physicochemical characterization of drug-cyclodextrin complexes prepared by supercritical carbon dioxide and by conventional techniques. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2007, 57, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestrelli, F.; Cecchi, M.; Cirri, M.; Capasso, G.; Mennini, N.; Mura, P. Comparative study of oxaprozin complexation with natural and chemically modified cyclodextrins in solution and in the solid state. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2009, 63, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piemi, M.P.Y.; Korner, D.; Benita, S.; Marty, J.P. Positively and negatively charged submicron emulsions for enhanced topical delivery of antifungal drugs. J. Control. Release 1999, 58, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahara, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Yoshida, S.; Onodera, R.; Inoue, N.; Takeuchi, H. Effects of cationic liposomes with stearylamine against virus infection. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 543, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency. Background Review for Cyclodextrins Used as Excipients; EMA/CHMP/333892/2013, November 20th; European Medicines Agency: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bragagni, M.; Mennini, N.; Maestrelli, F.; Cirri, M.; Mura, P. Comparative study of liposomes, transfersomes and ethosomes as carriers for improving topical delivery of celecoxib. Drug Deliv. 2012, 19, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scognamiglio, I.; De Stefano, D.; Campani, V.; Mayol, L.; Carnuccio, R.; Fabbrocini, G.; Ayala, F.; La Rotonda, M.I.; De Rosa, G. Nanocarriers for topical administration of resveratrol: A comparative study. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 440, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, G.H.R.; Lemes, J.B.P.; Geronimo, G.; de Lima, F.F.; de Moura, L.D.; dos Santos, A.C.; Carvalho, N.S.; Malange, K.F.; Breitkreitz, M.C.; Paradab, C.A.; et al. Lipid nanoparticles loaded with butamben and designed to improve anesthesia at inflamed tissues. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 3378–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, R.J.; Pandit, J.K. Effect of cyclodextrins on the complexation and transdermal delivery of bupranolol through rat skin. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 271, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, T.M. Bile salts as skin permeation enhancer. Pharm. Ind. 2000, 62, 157–160. [Google Scholar]
- Karande, P.; Mitragotri, S. High throughput screening of transdermal formulations. Pharm. Res. 2002, 19, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Type of CD | K1:1, M−1 | Solubilizing Efficiency at 12.5 mM CD * | Solubilizing Efficiency at 25 mM CD * |
|---|---|---|---|
| αCd | 480 ± 30 | 5.7 | 9.2 |
| βCD | 1390 ± 90 | 8.7 | --- § |
| γCD | 80 ± 10 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
| HPαCD | 540 ± 40 | 6.1 | 10.5 |
| HPβCD | 1910 ± 100 | 10.2 | 19.2 |
| RAMEB | 10460 ± 220 | 13.0 | 27.2 |
| SBEβCD | 3590 ± 130 | 11.9 | 23.6 |
| Sample | PD10 | DE60 |
|---|---|---|
| BTB | 2.3 | 3.7 |
| BTB–RAMEB PM | 19.5 | 22.4 |
| BTB–RAMEB KN | 41.7 | 45.1 |
| BTB–RAMEB COE | 63.3 | 65.9 |
| BTB–RAMEB GR | 87.7 | 86.3 |
| BTB–RAMEB COL | 89.9 | 88.0 |
| Formul. Code | Bilayer Composition (Molar Ratios) | Drug Loading Mode | Vesicle Size (nm ± SD) | PDI | Z-Pot. (mV ± SD) | Deformability | EE% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC | CH | SA | SC | |||||||
| SL1 | 5.5 | 1.0 | 1.5 | SL | 240 ± 65 | 0.22 | +30.2 ± 3.9 | 1.10 ± 0.02 | 92.2 ± 3.8 | |
| DL1 | 5.5 | 1.0 | 1.5 | DL | 280 ± 60 | 0.24 | +39.8 ± 2.8 | 1.08 ± 0.03 | 93.8 ± 3.0 | |
| SL2 | 5.5 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 1.0 | SL | 260 ± 40 | 0.23 | +5.1 ±0.5 | 1.05 ± 0.04 | 94.6 ± 2.6 |
| DL2 | 5.5 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 1.0 | DL | 290 ± 56 | 0.25 | +12.1 ± 0.5 | 1.03 ± 0.03 | 99.8 ± 1.3 |
| Formulation | Kp (cm/h) |
|---|---|
| SL1 | 0.0433 ± 0.0038 |
| SL2 | 0.0516 ± 0.0047 |
| DL1 | 0.0630 ± 0.0054 |
| DL2 | 0.0672 ± 0.0057 |
| SL1 in gel | 0.0426 ± 0.0034 |
| SL2 in gel | 0.0491 ± 0.0041 |
| DL1 in gel | 0.0601 ± 0.0050 |
| DL2 in gel | 0.0652 ± 0.0054 |
| BTB solution in gel | 0.0181 ± 0.0015 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mura, P.; Maestrelli, F.; Cirri, M.; Nerli, G.; Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Ghelardini, C.; Mennini, N. Improvement of Butamben Anesthetic Efficacy by the Development of Deformable Liposomes Bearing the Drug as Cyclodextrin Complex. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13060872
Mura P, Maestrelli F, Cirri M, Nerli G, Di Cesare Mannelli L, Ghelardini C, Mennini N. Improvement of Butamben Anesthetic Efficacy by the Development of Deformable Liposomes Bearing the Drug as Cyclodextrin Complex. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(6):872. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13060872
Chicago/Turabian StyleMura, Paola, Francesca Maestrelli, Marzia Cirri, Giulia Nerli, Lorenzo Di Cesare Mannelli, Carla Ghelardini, and Natascia Mennini. 2021. "Improvement of Butamben Anesthetic Efficacy by the Development of Deformable Liposomes Bearing the Drug as Cyclodextrin Complex" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 6: 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13060872
APA StyleMura, P., Maestrelli, F., Cirri, M., Nerli, G., Di Cesare Mannelli, L., Ghelardini, C., & Mennini, N. (2021). Improvement of Butamben Anesthetic Efficacy by the Development of Deformable Liposomes Bearing the Drug as Cyclodextrin Complex. Pharmaceutics, 13(6), 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13060872