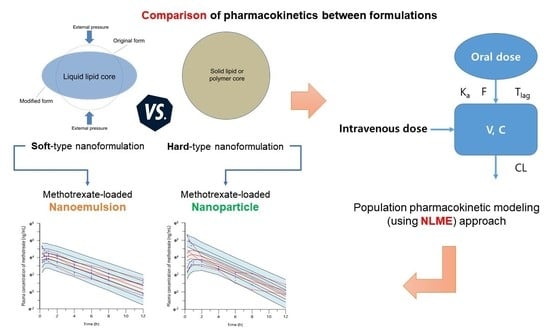
Pharmacokinetic Comparison between Methotrexate-Loaded Nanoparticles and Nanoemulsions as Hard- and Soft-Type Nanoformulations: A Population Pharmacokinetic Modeling Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Pharmacokinetic Analysis
2.3. Population Pharmacokinetic Model Development
2.4. Population Pharmacokinetic Model Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Comparison of Pharmacokinetic Results between Free Methotrexate Solution and Methotrexate-Loaded Nanoformulations
3.2. Population Pharmacokinetic Modeling Approach to Comparing Free Methotrexate Solution and Methotrexate-Loaded Nanoformulations
3.3. Comparison of Pharmacokinetic Results between Methotrexate-Loaded Nanoparticles and Nanoemulsions
3.4. Population Pharmacokinetic Modeling Approach to Comparing Methotrexate-Loaded Nanoparticles and Nanoemulsions
3.5. Evaluation of the Population Pharmacokinetic Model for Comparing Methotrexate-Loaded Nanoparticles and Nanoemulsions
3.6. Pharmacokinetic Comparison between Nanoformulations of Different Drugs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| UHPLC-ESI-MS/MS | Ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| NLME | Nonlinear mixed effects model |
| AIC | Akaike information criterion |
| SC | Schwarz criterion |
| WRSS | Weighted residual sum of squares |
| IIV | Interindividual variability |
| OFV | Objective function value |
| SE | Standard error |
| RSE | Relative standard error |
| MRT | Mean residence time |
| AUMC | Area under the first moment curve |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| RES | Reticuloendothelial system |
References
- Yoo, M.-K.; Kang, S.-K.; Choi, J.-H.; Park, I.-K.; Na, H.-S.; Lee, H.-C.; Kim, E.-B.; Lee, N.-K.; Nah, J.-W.; Choi, Y.-J.; et al. Targeted delivery of chitosan nanoparticles to Peyer’s patch using M cell-homing peptide selected by phage display technique. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 7738–7747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janer, G.; Mas del Molino, E.; Fernández-Rosas, E.; Fernández, A.; Vázquez-Campos, S. Cell uptake and oral absorption of titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 228, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.-H.; Jang, J.-H.; Lee, Y.-B. Oral delivery of topotecan in polymeric nanoparticles: Lymphatic distribution and pharmacokinetics. J. Control. Release 2021, 335, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, N.R.; Piroyan, A.; Ganta, S.; Morse, A.B.; Candiloro, K.M.; Solon, A.L.; Nack, A.H.; Galati, C.A.; Bora, C.; Maglaty, M.A. In vitro and In vivo evaluation of a novel folate-targeted theranostic nanoemulsion of docetaxel for imaging and improved anticancer activity against ovarian cancers. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2018, 19, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mandal, D.; Shaw, T.K.; Dey, G.; Pal, M.M.; Mukherjee, B.; Bandyopadhyay, A.K.; Mandal, M. Preferential hepatic uptake of paclitaxel-loaded poly-(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles—A possibility for hepatic drug targeting: Pharmacokinetics and biodistribution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol 2018, 112, 818–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.-H.; Jeong, S.-H.; Lee, Y.-B. Preparation and in vitro/in vivo characterization of polymeric nanoparticles containing methotrexate to improve lymphatic delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jang, J.-H.; Jeong, S.-H.; Lee, Y.-B. Enhanced lymphatic delivery of methotrexate using W/O/W nanoemulsion: In vitro characterization and pharmacokinetic study. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiei, P.; Haddadi, A. Docetaxel-loaded PLGA and PLGA-PEG nanoparticles for intravenous application: Pharmacokinetics and biodistribution profile. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valicherla, G.R.; Dave, K.M.; Syed, A.A.; Riyazuddin, M.; Gupta, A.P.; Singh, A.; Mitra, K.; Datta, D.; Gayen, J.R. Formulation optimization of docetaxel loaded self-emulsifying drug delivery system to enhance bioavailability and anti-tumor activity. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangeni, R.; Choi, S.W.; Jeon, O.-C.; Byun, Y.; Park, J.W. Multiple nanoemulsion system for an oral combinational delivery of oxaliplatin and 5-fluorouracil: Preparation and in vivo evaluation. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 6379–6399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Mattos, A.C.; Altmeyer, C.; Tominaga, T.T.; Khalil, N.M.; Mainardes, R.M. Polymeric nanoparticles for oral delivery of 5-fluorouracil: Formulation optimization, cytotoxicity assay and pre-clinical pharmacokinetics study. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 84, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.-Y.; Kang, J.-H.; Ngo, L.; Tran, P.; Lee, Y.-B. Preparation and evaluation of solid-self-emulsifying drug delivery system containing paclitaxel for lymphatic delivery. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.-Y.; Choi, J.-H.; Oh, I.-J.; Lee, Y.-B. Self-emulsifying drug delivery system for enhancing bioavailability and lymphatic delivery of tacrolimus. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol 2015, 15, 1831–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, K.S.; Schorzman, A.N.; Finniss, M.C.; Bowerman, C.J.; Peng, L.; Luft, J.C.; Madden, A.J.; Wang, A.Z.; Zamboni, W.C.; DeSimone, J.M. Nanoparticle drug loading as a design parameter to improve docetaxel pharmacokinetics and efficacy. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 8424–8429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zabaleta, V.; Ponchel, G.; Salman, H.; Agüeros, M.; Vauthier, C.; Irache, J.M. Oral administration of paclitaxel with pegylated poly (anhydride) nanoparticles: Permeability and pharmacokinetic study. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 81, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shin, S.-B.; Cho, H.-Y.; Kim, D.-D.; Choi, H.-G.; Lee, Y.-B. Preparation and evaluation of tacrolimus-loaded nanoparticles for lymphatic delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2010, 74, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.-H.; Jang, J.-H.; Cho, H.-Y.; Lee, Y.-B. Soft-and hard-lipid nanoparticles: A novel approach to lymphatic drug delivery. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2018, 41, 797–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.-H.; Jeong, S.-H.; Cho, H.-Y.; Lee, Y.-B. Population pharmacokinetics of cis-, trans-, and total cefprozil in healthy male Koreans. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeong, S.-H.; Jang, J.-H.; Cho, H.-Y.; Lee, Y.-B. Population pharmacokinetic analysis of tiropramide in healthy Korean subjects. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, K.; Stolk, P.; De Bruin, M.L.; Leufkens, H.G.M.; Crommelin, D.J.A.; De Vlieger, J.S.B. The EU regulatory landscape of non-biological complex drugs (NBCDs) follow-on products: Observations and recommendations. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 133, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wani, T.U.; Raza, S.N.; Khan, N.A. Nanoparticle opsonization: Forces involved and protection by long chain polymers. Polym. Bull. 2020, 77, 3865–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, D.E.; Peppas, N.A. Opsonization, biodistribution, and pharmacokinetics of polymeric nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 307, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










| Model | Description | n-Parameter | −2LL | AIC | Δ − 2LL | ΔAIC | Compared with | Residual Error Model | Compartment Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absorption model | |||||||||
| 01 | No Tlag | 9 | 3255.48 | 3280.13 | - | additive error model | 1-compartment | ||
| 02 * | Add Tlag | 11 | 2442.04 | 2464.04 | −813.44 | −816.08 | 01 | additive error model | 1-compartment |
| Residual error model | |||||||||
| 02 | Additive | 11 | 2442.04 | 2464.04 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 02 | additive error model | 1-compartment |
| 02-01 | Proportional | 11 | 2192.37 | 2214.37 | −249.67 | −249.67 | 02 | proportional error model | 1-compartment |
| 02-02 | Power | 11 | 2442.04 | 2464.04 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 02 | power error model | 1-compartment |
| 02-03 | Mixed | 12 | 2150.31 | 2174.31 | −291.73 | −289.73 | 02 | mixed error model | 1-compartment |
| 02-04 * | Log-additive | 11 | 759.13 | 781.13 | −1682.91 | −1682.91 | 02 | log-additive error model | 1-compartment |
| IIV model | |||||||||
| 02-04-01 | Remove IIV V | 10 | 1060.56 | 1080.56 | 301.43 | 299.43 | 02-04 | log-additive error model | 1-compartment |
| 02-04-02 | Remove IIV CL | 10 | 1154.02 | 1174.02 | 394.89 | 392.89 | 02-04 | log-additive error model | 1-compartment |
| 02-04-03 | Remove IIV Ka | 10 | 789.73 | 809.73 | 30.60 | 28.60 | 02-04 | log-additive error model | 1-compartment |
| 02-04-04 | Remove IIV Tlag | 10 | 1085.34 | 1105.34 | 326.21 | 324.21 | 02-04 | log-additive error model | 1-compartment |
| 02-04-05 | Remove IIV F | 10 | 860.97 | 880.97 | 101.84 | 99.84 | 02-04 | log-additive error model | 1-compartment |
| Model | Description | OFV | ΔOFV | Compared with | n-Parameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 02-04 | Base model | 759.128 | 11 | ||
| 02-04-C1 | Formulation on V | 754.284 | −4.843 | 02-04 | 12 |
| 02-04-C2 | Formulation on CL | 752.102 | −7.026 | 02-04 | 12 |
| 02-04-C3 | Formulation on Tlag | 761.168 | 2.040 | 02-04 | 12 |
| 02-04-C4 | Formulation on Ka | 754.534 | −4.594 | 02-04 | 12 |
| 02-04-C5 | Formulation on F | 754.132 | −4.995 | 02-04 | 12 |
| 02-04-C6 | Formulation on CL & V | 742.395 | −9.707 | 02-04-C2 | 13 |
| 02-04-C7 | Formulation on CL & Ka | 745.284 | −6.818 | 02-04-C2 | 13 |
| 02-04-C8 | Formulation on CL & F | 744.399 | −7.703 | 02-04-C2 | 13 |
| 02-04-C9 | Formulation on CL & V & F | 732.588 | −9.807 | 02-04-C6 | 14 |
| 02-04-C10 | Formulation on CL & V & Ka | 735.805 | −6.590 | 02-04-C6 | 14 |
| 02-04-C11 * | Formulation on CL & V & F & Ka | 722.746 | −9.842 | 02-04-C9 | 15 |
| Parameters | Units | Estimate | SE | RSE (%) | Shrinkage (%) | IIV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tvV | L/kg | 14.889 | 1.388 | 9.320 | - | - |
| tvCL | L/h/kg | 14.577 | 1.572 | 10.785 | - | - |
| tvTlag | h | 0.000 | 0.000 | 31.713 | - | - |
| tvKa | 1/h | 0.582 | 0.147 | 25.291 | - | - |
| tvF | - | 0.272 | 0.030 | 11.055 | - | - |
| dVdFormulation | - | 0.429 | 0.136 | 31.591 | - | - |
| dCLdFormulation | - | −0.355 | 0.086 | 24.316 | - | - |
| dKadFormulation | - | 10.883 | 1.574 | 14.465 | - | - |
| dFdFormulation | - | 4.246 | 1.233 | 29.027 | - | - |
| ω2V | - | 0.000 | 0.000 | 7.332 | 0.393 | 0.252 |
| ω2CL | - | 0.338 | 0.153 | 45.227 | 0.173 | 58.130 |
| ω2Tlag | - | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.014 | 0.600 | 0.052 |
| ω2Ka | - | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.014 | 0.465 | 0.002 |
| ω2F | - | 0.386 | 0.121 | 31.254 | 0.316 | 62.161 |
| σ | - | 1.269 | 0.132 | 10.374 | - | - |
| Parameters | Units | Final Model | Bootstrapping | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate | 95% Confidence Interval | Median | 95% Confidence Interval | ||
| tvV | L/kg | 14.889 | 12.169–17.608 | 13.267 | 10.004–16.531 |
| tvCL | L/h/kg | 14.577 | 11.496–17.659 | 12.840 | 9.142–16.537 |
| tvTlag | h | 0.000 | 0.000–0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000–0.000 |
| tvKa | 1/h | 0.582 | 0.293–0.870 | 0.554 | 0.207–0.900 |
| tvF | - | 0.272 | 0.213–0.331 | 0.239 | 0.168–0.309 |
| dVdFormulation | - | 0.429 | 0.164–0.695 | 0.407 | 0.088–0.726 |
| dCLdFormulation | - | −0.355 | −0.524–−0.186 | −0.362 | −0.565–−0.159 |
| dKadFormulation | - | 10.883 | 7.797–13.968 | 9.999 | 6.296–13.701 |
| dFdFormulation | - | 4.246 | 1.830–6.662 | 3.910 | 1.011–6.809 |
| ω2V | - | 0.000 | 0.000–0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000–0.000 |
| ω2CL | - | 0.338 | 0.038–0.637 | 0.338 | 0.022–0.697 |
| ω2Tlag | - | 0.000 | 0.000–0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000–0.000 |
| ω2Ka | - | 0.000 | 0.000–0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000–0.000 |
| ω2F | - | 0.386 | 0.150–0.623 | 0.386 | 0.102–0.670 |
| σ | - | 1.269 | 1.011–1.527 | 1.262 | 0.952–1.572 |
| Properties | Methotrexate-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles | Methotrexate-Loaded Nanoemulsions |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | 163.7 ± 10.25 nm | 173.77 ± 5.76 nm |
| Zeta potential | −20.4 ± 1.54 mV | −35.63 ± 0.78 mV |
| Encapsulation efficiency | 93.3 ± 0.5% | 90.37 ± 0.96% |
| Shape | Spherical form | Spherical form |
| References | Jang et al. (2019) [6] | Jang et al. (2020) [7] |
| Parameters | Oral (5 mg/kg as Methotrexate) | Oral (0.06 mg/kg as Methotrexate) | Intravenous (5 mg/kg as Methotrexate) | Intravenous (0.024 mg/kg as Methotrexate) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nanoparticles | Nanoemulsions | Nanoparticles | Nanoemulsions | |
| AUC0-t (ng·h/mL) | 142.05 ± 7.00 | 288.35 ± 51.14 * | 720.15 ± 81.74 | 268.94 ± 41.85 ** |
| AUC0-∞ (ng·h/mL) | 148.44 ± 7.43 | 291.34 ± 54.01 * | 722.53 ± 82.58 | 300.56 ± 36.10 ** |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 31.19 ± 5.15 | 81.72 ± 23.01 * | 713.07 ± 62.83 | 180.05 ± 24.79 ** |
| C0 (ng/mL) | - | - | 1344.57 ± 200.87 | 366.10 ± 76.22 ** |
| AUC0-t/Dose (h·kg/mL) | 2.84 10−5 ± 1.40 10−6 | 4.81 10−3 ± 8.52 10−4 * | 1.44 10−4 ± 1.64 10−5 | 1.12 10−2 ± 1.74 10−3 ** |
| AUC0-∞/Dose (h·kg/mL) | 2.97 10−5 ± 1.49 10−6 | 4.86 10−3 ± 9.00 10−4 * | 1.45 10−4 ± 1.65 10−5 | 1.25 10−2 ± 1.50 10−3 ** |
| Cmax/Dose (kg/mL) | 6.24 10−6 ± 1.03 10−6 | 1.36 10−3 ± 3.83 10−4 * | 1.43 10−4 ± 1.26 10−5 | 7.50 10−3 ± 1.03 10−3 ** |
| Tmax (h) | 0.92 ± 0.14 | 1.35 ± 0.60 | 0.25 ± 0.00 | 0.25 ± 0.00 |
| T1/2 (h) | 2.59 ± 0.66 | 1.58 ± 0.30* | 1.62 ± 0.61 | 6.38 ± 1.77 ** |
| CL (mL/h/kg) | - | - | 6984.15 ± 840.71 | 80.94 ± 11.38 ** |
| V (mL/kg) | - | - | 16146.33 ± 5631.17 | 748.38 ± 232.69 ** |
| MRT (h) | 4.27 ± 0.76 | 2.99 ± 0.37 * | 0.91 ± 0.05 | 4.12 ± 1.56 ** |
| Vss (mL/kg) | - | - | 6301.14 ± 404.35 | 338.68 ± 146.77 ** |
| F (%) | 20.54 | 38.77 * | - | - |
| Model | Description | n-Parameter | −2LL | AIC | Δ − 2LL | ΔAIC | Compared with | Residual Error Model | Compartment Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absorption model | |||||||||
| 01 | No Tlag | 9 | 1545.89 | 1563.89 | - | - | - | additive error model | 1-compartment |
| 02 * | Add Tlag | 11 | 1505.72 | 1527.72 | −40.17 | −36.17 | 01 | additive error model | 1-compartment |
| Residual error model | |||||||||
| 02 | Additive | 11 | 1505.72 | 1527.72 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 02 | additive error model | 1-compartment |
| 02-01 | Proportional | 11 | 1412.20 | 1434.20 | −93.52 | −93.52 | 02 | proportional error model | 1-compartment |
| 02-02 | Power | 11 | 1545.72 | 1567.72 | 40.00 | 40.00 | 02 | power error model | 1-compartment |
| 02-03 | Mixed | 12 | 1545.72 | 1569.72 | 40.00 | 42.00 | 02 | mixed error model | 1-compartment |
| 02-04 * | Log-additive | 11 | 498.53 | 520.53 | −1007.19 | −1007.19 | 02 | log-additive error model | 1-compartment |
| IIV model | |||||||||
| 02-04-01 | Remove IIV V | 10 | 595.61 | 615.61 | 97.08 | 95.08 | 02-04 | log-additive error model | 1-compartment |
| 02-04-02 | Remove IIV CL | 10 | 595.60 | 615.60 | 97.07 | 95.07 | 02-04 | log-additive error model | 1-compartment |
| 02-04-03 | Remove IIV Ka | 10 | 595.61 | 615.61 | 97.08 | 95.08 | 02-04 | log-additive error model | 1-compartment |
| 02-04-04 | Remove IIV Tlag | 10 | 595.61 | 615.61 | 97.08 | 95.08 | 02-04 | log-additive error model | 1-compartment |
| 02-04-05 | Remove IIV F | 10 | 534.28 | 554.28 | 35.75 | 33.75 | 02-04 | log-additive error model | 1-compartment |
| Model | Description | OFV | ΔOFV | Compared with | n-Parameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 02-04 | Base model | 498.535 | 11 | ||
| 02-04-C1 | Formulation on V | 338.410 | −160.125 | 02-04 | 12 |
| 02-04-C2 | Formulation on CL | 492.153 | −6.382 | 02-04 | 12 |
| 02-04-C3 | Formulation on Tlag | 496.267 | −2.267 | 02-04 | 12 |
| 02-04-C4 | Formulation on Ka | 493.304 | −5.231 | 02-04 | 12 |
| 02-04-C5 | Formulation on F | 465.927 | −32.608 | 02-04 | 12 |
| 02-04-C6 | Formulation on V & F | 331.262 | −7.148 | 02-04-C1 | 13 |
| 02-04-C7 | Formulation on V & CL | 273.319 | −65.091 | 02-04-C1 | 13 |
| 02-04-C8 | Formulation on V & Ka | 331.262 | −7.148 | 02-04-C1 | 13 |
| 02-04-C9 | Formulation on V & CL & Ka | 246.629 | −26.690 | 02-04-C7 | 14 |
| 02-04-C10 | Formulation on V & CL & F | 259.065 | −14.254 | 02-04-C7 | 14 |
| 02-04-C11 * | Formulation on V & CL & Ka & F | 220.361 | −26.268 | 02-04-C9 | 15 |
| Parameters | Units | Estimate | SE | RSE (%) | Shrinkage (%) | IIV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tvV | L/kg | 18.832 | 0.065 | 0.348 | - | - |
| tvCL | L/h/kg | 9.167 | 0.252 | 2.739 | - | - |
| tvTlag | h | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.172 | - | - |
| tvKa | 1/h | 0.714 | 0.023 | 3.281 | - | - |
| tvF | - | 0.334 | 0.006 | 1.883 | - | - |
| dVdFormulation | - | −0.986 | 0.001 | 0.097 | - | - |
| dCLdFormulation | - | −0.990 | 0.001 | 0.054 | - | - |
| dKadFormulation | - | 1.552 | 0.004 | 0.264 | - | - |
| dFdFormulation | - | 0.193 | 0.000 | 0.114 | - | - |
| ω2V | - | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.201 | 0.238 |
| ω2CL | - | 0.008 | 0.000 | 1.317 | 0.085 | 9.199 |
| ω2Tlag | - | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.392 | 0.052 |
| ω2Ka | - | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.224 | 0.002 |
| ω2F | - | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.042 | 0.116 | 3.206 |
| σ | - | 0.552 | 0.005 | 0.967 | - | - |
| Parameters | Units | Final Model | Bootstrapping | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate | 95% Confidence Interval | Median | 95% Confidence Interval | ||
| tvV | L/kg | 18.832 | 18.827–18.835 | 18.832 | 18.826–18.836 |
| tvCL | L/h/kg | 9.167 | 9.166–9.175 | 9.168 | 9.165–9.176 |
| tvTlag | h | 0.000 | 0.000–0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000–0.000 |
| tvKa | 1/h | 0.714 | 0.714–0.714 | 0.714 | 0.713–0.715 |
| tvF | - | 0.334 | 0.334–0.334 | 0.334 | 0.334–0.334 |
| dVdFormulation | - | −0.986 | −0.988–−0.984 | −0.986 | −0.988–−0.984 |
| dCLdFormulation | - | −0.990 | −0.991–−0.989 | −0.990 | −0.991–−0.989 |
| dKadFormulation | - | 1.552 | 1.552–1.552 | 1.552 | 1.552–1.552 |
| dFdFormulation | - | 0.193 | 0.193–0.193 | 0.193 | 0.193–0.193 |
| ω2V | - | 0.000 | 0.000–0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000–0.000 |
| ω2CL | - | 0.008 | 0.008–0.009 | 0.008 | 0.007–0.009 |
| ω2Tlag | - | 0.000 | 0.000–0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000–0.000 |
| ω2Ka | - | 0.000 | 0.000–0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000–0.000 |
| ω2F | - | 0.001 | 0.001–0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001–0.001 |
| σ | - | 0.552 | 0.552–0.552 | 0.552 | 0.551–0.553 |
| 8 | Formulation | Size and Zeta Potential | Subjects | Pharmacokinetic Parameters | References | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1/2 | Tmax | Cmax | AUC0–∞ | CL/F | Vd | |||||
| Docetaxel | PLA-PLGA nanoparticles | 216 ± 1 nm −3.11 ± 0.28 mV | Mice (n = 3) 10 mg/kg intravenous | 6.6–7.4 (h) | -a | 19583–26753 (ng/mL) | 82743–95692 (h·ng/mL; AUC0~t) | 105–121 (mL/h/kg) | 943–1278 (L/kg) | Chu et al. (2013) [14] |
| PEG-PLGA nanoparticles | 186.7 ± 2.9 nm −25.9 ± 3.5 mV | Mice (n = 4) 5 mg/kg intravenous | 15.87 ± 1.66 (h) | -a | -a | 9221 ± 4709 (h·ng/mL) | 12.54 ± 4.53 (mL/h) | 290.41 ± 116.32 (mL) | Rafiei et al. (2017) [8] | |
| PLGA nanoparticles | 123.6 ± 9.5 nm −28.3 ± 1.2 mV | Mice (n = 4) 5 mg/kg intravenous | 6.05±0.78 (h) | -a | -a | 6601 ± 2,655 (h·μg/mL) | 17.23 ± 7.16 (L/h) | 150.81 ± 74.18 (L) | Rafiei et al. (2017) [8] | |
| Nanoemulsions | 120–140 nm −48–−29 mV | Mice (n = 3) 10 mg/kg intravenous | 6.1 ± 3.8 (h) | -a | 3660 ± 433 (ng/mL) | 2840 ± 55 (h·ng/L) | 3.5 ± 0.1 (L/h/kg) | 31 ± 19 (L/kg) | Patel et al. (2018) [4] | |
| SEDDS | 167.3 ± 2.30 | Rat (n = 6) 10 mg/kg oral | 34.83 ± 7.70 (h) | 0.17 (h) | 125.5 ± 2.50 (ng/mL) | 260.23 ± 51.8 (h·ng/mL) | 28.31 ± 3.33 (L/h/kg) | 1460.33 ± 484.28 (L/kg) | Valicherla et al. (2016) [9] | |
| Tacrolimus | SEDDS | 43.4 ± 3.58 nm −41.26 ± 1.94 mV | Rat (n = 6) 5 mg/kg oral | -a | 2.3 ± 0.5 (h) | 205.8 ± 32.8 (ng/mL) | 1745.2 ± 132.3 (h·ng/mL) | -a | -a | Cho et al. (2015) [13] |
| PLGA nanoparticles | 218 ± 51 nm −28.2 ± 4.3 mV | Rat (n = 6) 1 mg/kg intravenous | 3.157 ± 1.274 (h) | -a | -a | 566.187 ± 235.008 (h·ng/mL) | 10.29 ± 4.81 (mL/min) | -a | Shin et al. (2010) [16] | |
| PEG-PLGA nanoparticles | 220 ± 33 nm −24.5 ± 5.7 mV | Rat (n = 6) 1 mg/kg intravenous | 269.32 ± 136.16 (min) | -a | -a | 39526.18 ± 3411.35 (min·ng/mL) | 7.90 ± 0.62 (mL/min) | -a | Shin et al. (2010) [16] | |
| Paclitaxel | SEDDS | 18.4 ± 0.912 nm 12.5 ± 1.66 mV, | Rat (n = 5) 20 mg/kg oral | -a | 1.7 ± 0.2 (h) | 259.5 ± 7.5 (ng/mL) | 3308.5 ± 486.2 (h·ng/mL) | -a | -a | Cho et al. (2016) [12] |
| PEGylated nanoparticles | 178–180 nm −40.3–−39.5 mV | Rat (n = 6) 10 mg/kg oral | 6.2–9.3 (h) | 3.0–5.8 (h) | 1.9–2.1 (μg/mL) | 32–56 (h·μg/mL) | -a | -a | Zabaleta et al. (2012) [15] | |
| PLGA nanoparticles | 308.6 ± 6.22 nm −10.70 ± 0.21 mV | Rat (n = 3) 5 mg/kg intravenous | 28.48 ± 0.99 (h) | -a | 951.9 ± 47.5 (ng/mL) | 2915.46 ± 145.54 (h·ng/mL) | 0.80 ± 0.03 (L/h) | -a | Mandal et al. (2018) [5] | |
| 5-FU | Nanoemulsions | 20.3 ± 0.22 nm −4.65 ± 1.68 mV | Rat (n = 4) 20 mg/kg oral | 1.386 ± 0.146 (h) | 0.833 ± 0.289 (h) | 0.164 ± 0.044 (μg/mL) | 0.360 ± 0.091 (h·μg/mL) | -a | -a | Pangeni et al. (2016) [10] |
| PLA nanoparticles | 294 ± 5 nm | Rat (n = 5) 50 mg/kg oral | 3.46 ± 0.14 (h) | 6 (h) | 467.34 ± 0.75 (ng/mL) | 2200.53 ± 1.82 (h·ng/mL) | 2.4 ± 0.03 × 104 (L/h/kg) | 12.0 ± 0.02 × 104 (L/kg) | De Mattos et al. (2016) [11] | |
| PLA-PEG nanoparticles | 283 ± 10 nm | Rat (n = 5) 50 mg/kg oral | 3.01 ± 0.19 (h) | 6 (h) | 487.34 ± 1.79 (ng/mL) | 2281.1 ± 2.08 (h·ng/mL) | 2.4 ± 0.02 × 104 (L/h/kg) | 10.7 ± 0.02 × 104 (L/kg) | De Mattos et al. (2016) [11] | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, S.-H.; Jang, J.-H.; Lee, Y.-B. Pharmacokinetic Comparison between Methotrexate-Loaded Nanoparticles and Nanoemulsions as Hard- and Soft-Type Nanoformulations: A Population Pharmacokinetic Modeling Approach. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13071050
Jeong S-H, Jang J-H, Lee Y-B. Pharmacokinetic Comparison between Methotrexate-Loaded Nanoparticles and Nanoemulsions as Hard- and Soft-Type Nanoformulations: A Population Pharmacokinetic Modeling Approach. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(7):1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13071050
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Seung-Hyun, Ji-Hun Jang, and Yong-Bok Lee. 2021. "Pharmacokinetic Comparison between Methotrexate-Loaded Nanoparticles and Nanoemulsions as Hard- and Soft-Type Nanoformulations: A Population Pharmacokinetic Modeling Approach" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 7: 1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13071050
APA StyleJeong, S. -H., Jang, J. -H., & Lee, Y. -B. (2021). Pharmacokinetic Comparison between Methotrexate-Loaded Nanoparticles and Nanoemulsions as Hard- and Soft-Type Nanoformulations: A Population Pharmacokinetic Modeling Approach. Pharmaceutics, 13(7), 1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13071050