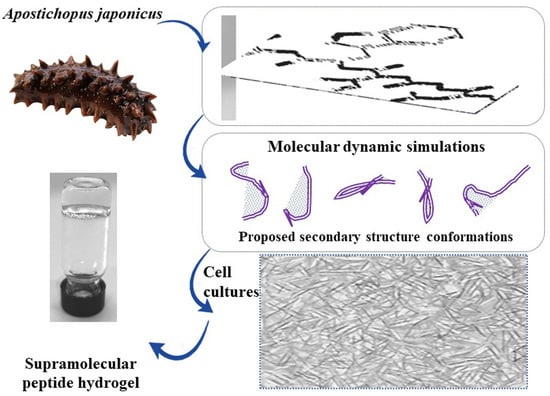
NGIWY-Amide: A Bioinspired Ultrashort Self-Assembled Peptide Gelator for Local Drug Delivery Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Peptide Synthesis
2.3. Characterization with Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectroscopy (LC-MS) and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)
2.4. Molecular Dynamics Simulations and Density Functional Theory Study
2.5. Molecular Docking Study
2.6. Peptide Supramolecular Hydrogel Formation and Characterization
2.7. Morphological Assessment
2.8. Confocal Laser-Scanning Microscopy (CLSM) and In Vitro Drug Release Studies and Kinetics
2.9. In Vitro Cell Viability and Cell Death Assays
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of the Self-Assembled Pentapeptide
3.2. NMR Studies
3.2.1. 1H NMR of the Peptide Hydrogel
3.2.2. NOESY NMR of the Peptide Hydrogel
3.2.3. Saturation Transfer Difference (STD) NMR
3.3. Molecular Modelling
3.3.1. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
3.3.2. DFT Study
3.3.3. Binding Free Energy Calculation
3.4. Pentapeptide Hydrogel Preparation and Characterization
3.4.1. Hydrogel Preparation and Rheological Studies
3.4.2. Optical Properties, Structural Conformation, and Crystallinity of the Pentapeptide Hydrogel
 π* transitions of the peptide bonds [39,40] and the carboxylic acid moieties in the peptide [41,42]. The absorption peak at 280 nm is attributed to the aromatic side chains of Trp, with a less intense π
π* transitions of the peptide bonds [39,40] and the carboxylic acid moieties in the peptide [41,42]. The absorption peak at 280 nm is attributed to the aromatic side chains of Trp, with a less intense π  π* transition identified as a shoulder at 292 nm. Even though less intense, the absorption of Tyr significantly overlapped with that of Trp in the same region. The fluorescence properties of the pentapeptide hydrogel were assessed after dilution of the hydrogel with Milli-Q water at a final concentration of 0.02% w/v. The intrinsic fluorescence of the pentapeptide derived from the excitation of Trp and Tyr, with Trp being significantly more fluorescent than Tyr [39]. As seen in Figure 7B, the pentapeptide exhibited a strong emission peak at 354 nm, due to the presence of the indolic ring of Trp. On the other hand, the fluorescence of tyrosine, due to the presence of its phenolic group, was observed as a shoulder at 295 nm [43], since its emission fluorescence was quenched by the presence of the adjacent tryptophan via resonance energy transfer and through ionization of its aromatic hydroxyl group.
π* transition identified as a shoulder at 292 nm. Even though less intense, the absorption of Tyr significantly overlapped with that of Trp in the same region. The fluorescence properties of the pentapeptide hydrogel were assessed after dilution of the hydrogel with Milli-Q water at a final concentration of 0.02% w/v. The intrinsic fluorescence of the pentapeptide derived from the excitation of Trp and Tyr, with Trp being significantly more fluorescent than Tyr [39]. As seen in Figure 7B, the pentapeptide exhibited a strong emission peak at 354 nm, due to the presence of the indolic ring of Trp. On the other hand, the fluorescence of tyrosine, due to the presence of its phenolic group, was observed as a shoulder at 295 nm [43], since its emission fluorescence was quenched by the presence of the adjacent tryptophan via resonance energy transfer and through ionization of its aromatic hydroxyl group.3.4.3. Morphological Evaluation of the Pentapeptide Hydrogel
3.5. Model Dye Localization in the Hydrogel Network and In Vitro Drug Release Studies
3.6. Cell Viability and Cell Death Assay
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hamley, I.W. Small Bioactive Peptides for Biomaterials Design and Therapeutics. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 14015–14041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kurbasic, M.; Parisi, E.; Garcia, A.M.; Marchesan, S. Self-Assembling, Ultrashort Peptide Gels as Antimicrobial Biomaterials. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 1300–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, M.; Zhuo, S. Applications of self-assembling ultrashort peptides in bionanotechnology. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 844–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia, A.M.; Melchionna, M.; Bellotto, O.; Kralj, S.; Semeraro, S.; Parisi, E.; Iglesias, D.; D’Andrea, P.; De Zorzi, R.; Vargiu, A.V.; et al. Nanoscale Assembly of Functional Peptides with Divergent Programming Elements. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 3015–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malonis, R.J.; Lai, J.R.; Vergnolle, O. Peptide-Based Vaccines: Current Progress and Future Challenges. Chem. Rev. 2019, 120, 3210–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tesauro, D.; Accardo, A.; Diaferia, C.; Milano, V.; Guillon, J.; Ronga, L.; Rossi, F. Peptide-Based Drug-Delivery Systems in Biotechnological Applications: Recent Advances and Perspectives. Molecules 2019, 24, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Wang, F.; Cui, H. Peptide-based supramolecular hydrogels for delivery of biologics. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2016, 1, 306–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Singh, I.; Sharma, A.K.; Kumar, P. Ultrashort Peptide Self-Assembly: Front-Runners to Transport Drug and Gene Cargos. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errante, F.; Ledwoń, P.; Latajka, R.; Rovero, P.; Papini, A.M. Cosmeceutical Peptides in the Framework of Sustainable Wellness Economy. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 572923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, R.; Gayakvad, B.; Shinde, S.D.; Rani, J.; Jain, A.; Sahu, B. Ultrashort Peptides—A Glimpse into the Structural Modifications and Their Applications as Biomaterials. ACS Appl. Biol. Mater. 2020, 3, 5474–5499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okesola, B.O.; Wu, Y.; Derkus, B.; Gani, S.; Wu, D.; Knani, D.; Smith, D.K.; Adams, D.J.; Mata, A. Supramolecular Self-Assembly To Control Structural and Biological Properties of Multicomponent Hydrogels. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 7883–7897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schnaider, L.; Shimonov, L.; Kreiser, T.; Zaguri, D.; Bychenko, D.; Brickner, I.; Kolusheva, S.; Lichtenstein, A.; Kost, J.; Gazit, E. Ultrashort Cell-Penetrating Peptides for Enhanced Sonophoresis-Mediated Transdermal Transport. ACS Appl. Biol. Mater. 2020, 3, 8395–8401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susapto, H.H.; Alhattab, D.; Abdelrahman, S.; Khan, Z.; Alshehri, S.; Kahin, K.; Ge, R.; Moretti, M.; Emwas, A.-H.; Hauser, C.A.E. Ultrashort Peptide Bioinks Support Automated Printing of Large-Scale Constructs Assuring Long-Term Survival of Printed Tissue Constructs. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 2719–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauf, S.; Susapto, H.H.; Kahin, K.; Alshehri, S.; Abdelrahman, S.; Lam, J.H.; Asad, S.; Jadhav, S.; Sundaramurthi, D.; Gao, X.; et al. Self-assembling tetrameric peptides allow in situ 3D bioprinting under physiological conditions. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 1069–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacPherson, D.; Bram, Y.; Park, J.; Schwartz, R.E. Peptide-based scaffolds for the culture and maintenance of primary human hepatocytes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seow, W.Y.; Hauser, C.A.E. Short to ultrashort peptide hydrogels for biomedical uses. Mater. Today 2014, 17, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peressotti, S.; Koehl, G.E.; Goding, J.A.; Green, R.A. Self-Assembling Hydrogel Structures for Neural Tissue Repair. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 4136–4163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, G.; Su, Z.; Reynolds, N.P.; Arosio, P.; Hamley, I.W.; Gazit, E.; Mezzenga, R. Self-assembling peptide and protein amyloids: From structure to tailored function in nanotechnology. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 4661–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, A.; Hakala, T.A.; Schnaider, L.; Bernardes, G.J.L.; Gazit, E.; Knowles, T.P.J. Biomimetic peptide self-assembly for functional materials. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2020, 4, 615–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, M.; Birenheide, R.; Koizumi, O.; Kobayakawa, Y.; Muneoka, Y.; Motokawa, T. Localization of the neuropeptide NGIWYamide in the holothurian nervous system and its effects on muscular contraction. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 1999, 266, 993–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kato, S.; Tsurumaru, S.; Taga, M.; Yamane, T.; Shibata, Y.; Ohno, K.; Fujiwara, A.; Yamano, K.; Yoshikuni, M. Neuronal peptides induce oocyte maturation and gamete spawning of sea cucumber, Apostichopus japonicus. Dev. Biol. 2009, 326, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siahaan, E.A.; Pangestuti, R.; Munandar, H.; Kim, S.K. Cosmeceuticals properties of sea cucumbers: Prospects and trends. Cosmetics 2017, 4, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chakraborty, P.; Gazit, E. Amino Acid Based Self-assembled Nanostructures: Complex Structures from Remarkably Simple Building Blocks. ChemNanoMat 2018, 4, 730–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vizirianakis, I.S.; Tsiftsoglou, A.S. Blockade of murine erythroleukemia cell differentiation by hypomethylating agents causes accumulation of discrete small poly(A)- RNAs hybridized to 3′-end flanking sequences of βmajor globin gene. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Cell Res. 2005, 1743, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamada, N.; Ariga, K.; Naito, M.; Matsubara, K.; Koyama, E. Regulation of beta-sheet structures within amyloid-like beta-sheet assemblage from tripeptide derivatives. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 12192–12199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalhete, S.M.; Nartowski, K.P.; Sarathchandra, N.; Foster, J.S.; Round, A.N.; Angulo, J.; Lloyd, G.O.; Khimyak, Y.Z. Supramolecular Amino Acid Based Hydrogels: Probing the Contribution of Additive Molecules using NMR Spectroscopy. Chem.-A Eur. J. 2017, 23, 8014–8024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ganesh, S.; Prakash, S.; Jayakumar, R. Spectroscopic investigation on gel-forming β-sheet assemblage of peptide derivatives. Biopolymers 2003, 70, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartels, C.; Widmer, A.; Ehrhardt, C. Absolute free energies of binding of peptide Analogs to the HIV-1 protease from molecular dynamics simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1294–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcelino, A.M.C.; Gierasch, L.M. Roles of β-turns in protein folding: From peptide models to protein engineering. Biopolymers 2008, 89, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, H.; Buckwalter, B.L.; Shieh, H.M.; Hecht, M.H. Periodicity of polar and nonpolar amino acids is the major determinant of secondary structure in self-assembling oligomeric peptides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 6349–6353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chowdhury, S.M.; Talukder, S.A.; Khan, A.M.; Afrin, N.; Ali, M.A.; Islam, R.; Parves, R.; Al Mamun, A.; Sufian, M.A.; Hossain, M.N.; et al. Antiviral Peptides as Promising Therapeutics against SARS-CoV-2. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 9785–9792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade-Ochoa, S.; García-Machorro, J.; Bello, M.; Rodríguez-Valdez, L.M.; Flores-Sandoval, C.A.; Correa-Basurto, J. QSAR, DFT and molecular modeling studies of peptides from HIV-1 to describe their recognition properties by MHC-I. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2018, 36, 2312–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horne, D.S. Casein structure, self-assembly and gelation. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 7, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghaee, E.; Ghasemi, J.B.; Manouchehri, F.; Balalaie, S. Combined docking, molecular dynamics simulations and spectroscopic studies for the rational design of a dipeptide ligand for affinity chromatography separation of human serum albumin. J. Mol. Model. 2014, 20, 2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivertsen, A.; Isaksson, J.; Leiros, H.K.S.; Svenson, J.; Svendsen, J.S.; Brandsdal, B.O. Synthetic cationic antimicrobial peptides bind with their hydrophobic parts to drug site II of human serum albumin. BMC Struct. Biol. 2014, 14, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maity, I.; Manna, M.K.; Rasale, D.B.; Das, A.K. Peptide-Nanofiber-Supported Palladium Nanoparticles as an Efficient Catalyst for the Removal of N-Terminus Protecting Groups. Chempluschem 2014, 79, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, C.; Pochan, D.J. Rheological properties of peptide-based hydrogels for biomedical and other applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 3528–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fleming, S.; Ulijn, R.V. Design of nanostructures based on aromatic peptide amphiphiles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 8150–8177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antosiewicz, J.M.; Shugar, D. UV–Vis spectroscopy of tyrosine side-groups in studies of protein structure. Part 2: Selected applications. Biophys. Rev. 2016, 8, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, B.; Asher, S.A. UV resonance Raman finds peptide bond-Arg side chain electronic interactions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 5659–5664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mcconnell, J.S.; Mcconnell, R.M.; Hossner, L.R. Ultraviolet Spectra of Acetic Acid, Glycine, and Glyphosate. J. Ark. Acad. Sci. 1993, 47, 73–76. [Google Scholar]
- Willard, M.; Cowan, W.M.; Vagelos, P.R. The polypeptide composition of intra-axonally transported proteins: Evidence for four transport velocities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1974, 71, 2183–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edelhoch, H.; Lippoldt, R.E. Structural studies on polypeptide hormones. I. Fluorescence. J. Biol. Chem. 1969, 244, 3876–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, A. Infrared spectroscopy of proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Bioenerg. 2007, 1767, 1073–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, J.D.; Mura, C.; Lampe, K.J. Stimuli-Responsive, Pentapeptide, Nanofiber Hydrogel for Tissue Engineering. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 4886–4899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pazderková, M.; Maloň, P.; Zíma, V.; Hofbauerová, K.; Kopecký, V., Jr.; Kočišová, E.; Pazderka, T.; Čeřovský, V.; Bednárová, L. Interaction of Halictine-Related Antimicrobial Peptides with Membrane Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, P.; Kaur, H.; Roy, S. Designing a Tenascin-C-Inspired Short Bioactive Peptide Scaffold to Direct and Control Cellular Behavior. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 6497–6510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, H.; Sharma, P.; Patel, N.; Pal, V.K.; Roy, S. Accessing Highly Tunable Nanostructured Hydrogels in a Short Ionic Complementary Peptide Sequence via pH Trigger. Langmuir 2020, 36, 12107–12120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignataro, M.F.; Herrera, M.G.; Dodero, V.I. Evaluation of Peptide/Protein Self-Assembly and Aggregation by Spectroscopic Methods. Molecules 2020, 25, 4854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiew, S.H.; Mohanram, H.; Ning, L.; Guo, J.; Sánchez-Ferrer, A.; Shi, X.; Pervushin, K.; Mu, Y.; Mezzenga, R.; Miserez, A. A Short Peptide Hydrogel with High Stiffness Induced by 310-Helices to β-Sheet Transition in Water. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1901173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karavasili, C.; Panteris, E.; Vizirianakis, I.S.; Koutsopoulos, S.; Fatouros, D.G. Chemotherapeutic Delivery from a Self-Assembling Peptide Nanofiber Hydrogel for the Management of Glioblastoma. Pharm. Res. 2018, 35, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulou, V.; Kosmidis, K.; Vlachou, M.; Macheras, P. On the use of the Weibull function for the discernment of drug release mechanisms. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 309, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosmidis, K.; Argyrakis, P.; Macheras, P. A Reappraisal of Drug Release Laws Using Monte Carlo Simulations: The Prevalence of the Weibull Function. Pharm. Res. 2003, 20, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krysmann, M.J.; Castelletto, V.; Kelarakis, A.; Hamley, I.W.; Hule, R.A.; Pochan, D.J. Self-assembly and hydrogelation of an amyloid peptide fragment. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 4597–4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, R.J.; Smith, A.M.; Collins, R.; Hodson, N.; Das, A.K.; Ulijn, R.V. Enzyme-assisted self-assembly under thermodynamic control. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigier-Carrière, C.; Boulmedais, F.; Schaaf, P.; Jierry, L. Surface-Assisted Self-Assembly Strategies Leading to Supramolecular Hydrogels. Angew. Chem. -Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 1448–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criado-Gonzalez, M.; Iqbal, M.H.; Carvalho, A.; Schmutz, M.; Jierry, L.; Schaaf, P.; Boulmedais, F. Surface Triggered Self-Assembly of Fmoc-Tripeptide as an Antibacterial Coating. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zou, X. Self-assemble peptide biomaterials and their biomedical applications. Bioact. Mater. 2019, 4, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Du, X.; Hashim, S.; Shy, A.; Xu, B. Aromatic-aromatic interactions enable α-helix to β-sheet transition of peptides to form supramolecular hydrogels. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaferia, C.; Rosa, E.; Accardo, A.; Morelli, G. Peptide-based hydrogels as delivery systems for doxorubicin. J. Pept. Sci. 2021, 28, e3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, E.; Diaferia, C.; Rosa, E.; Smaldone, G.; Morelli, G.; Accardo, A. Peptide-based hydrogels and nanogels for delivery of doxorubicin. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 1617–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Kang, C.; Liu, F.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, L.; Qiao, H. RGD Peptide-Based Target Drug Delivery of Doxorubicin Nanomedicine. Drug Dev. Res. 2017, 78, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thota, C.K.; Yadav, N.; Chauhan, V.S. A novel highly stable and injectable hydrogel based on a conformationally restricted ultrashort peptide. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alam, S.; Panda, J.J.; Mukherjee, T.K.; Chauhan, V.S. Short peptide based nanotubes capable of effective curcumin delivery for treating drug resistant malaria. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 14, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Altunbas, A.; Lee, S.J.; Rajasekaran, S.A.; Schneider, J.P.; Pochan, D.J. Encapsulation of curcumin in self-assembling peptide hydrogels as injectable drug delivery vehicles. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 5906–5914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baek, K.; Noblett, A.D.; Ren, P.; Suggs, L.J. Self-assembled nucleo-tripeptide hydrogels provide local and sustained doxorubicin release. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 3130–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Theodoroula, N.F.; Karavasili, C.; Vlasiou, M.C.; Primikyri, A.; Nicolaou, C.; Chatzikonstantinou, A.V.; Chatzitaki, A.-T.; Petrou, C.; Bouropoulos, N.; Zacharis, C.K.; et al. NGIWY-Amide: A Bioinspired Ultrashort Self-Assembled Peptide Gelator for Local Drug Delivery Applications. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14010133
Theodoroula NF, Karavasili C, Vlasiou MC, Primikyri A, Nicolaou C, Chatzikonstantinou AV, Chatzitaki A-T, Petrou C, Bouropoulos N, Zacharis CK, et al. NGIWY-Amide: A Bioinspired Ultrashort Self-Assembled Peptide Gelator for Local Drug Delivery Applications. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(1):133. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14010133
Chicago/Turabian StyleTheodoroula, Nikoleta F., Christina Karavasili, Manos C. Vlasiou, Alexandra Primikyri, Christia Nicolaou, Alexandra V. Chatzikonstantinou, Aikaterini-Theodora Chatzitaki, Christos Petrou, Nikolaos Bouropoulos, Constantinos K. Zacharis, and et al. 2022. "NGIWY-Amide: A Bioinspired Ultrashort Self-Assembled Peptide Gelator for Local Drug Delivery Applications" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 1: 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14010133
APA StyleTheodoroula, N. F., Karavasili, C., Vlasiou, M. C., Primikyri, A., Nicolaou, C., Chatzikonstantinou, A. V., Chatzitaki, A. -T., Petrou, C., Bouropoulos, N., Zacharis, C. K., Galatou, E., Sarigiannis, Y., Fatouros, D. G., & Vizirianakis, I. S. (2022). NGIWY-Amide: A Bioinspired Ultrashort Self-Assembled Peptide Gelator for Local Drug Delivery Applications. Pharmaceutics, 14(1), 133. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14010133