Cytotoxicity and Apoptosis Induction of 6,7-Dehydroroyleanone from Taiwania cryptomerioides Bark Essential Oil in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Hydrodistillation of Bark Essential Oil
2.2. Column Chromatography, Thin Layer Chromatography, and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography
2.3. Identification and Quantification of Isolated Compound
2.4. Cell Culture and Cell Cytotoxicity Assay
2.5. Apoptosis Analysis Using Flow Cytometric Assay
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Cytotoxic Effect of T. cryptomerioides Bark Essential Oil and Its Fractions on Hep G2 Cells
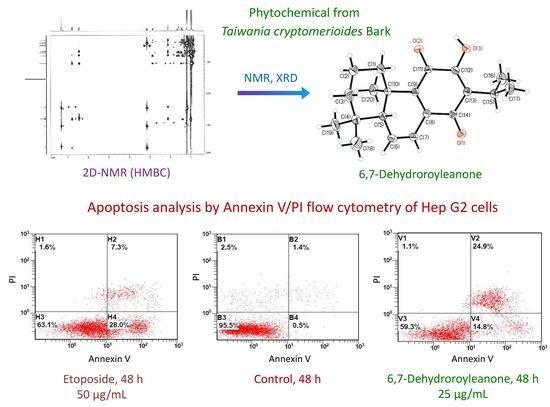
3.2. Identification of Chemical and Molecular Structures of 6,7-Dehydroroyleanone
3.3. Cytotoxic Effect of 6,7-Dehydroroyleanone on Hep G2 Cells
3.4. Apoptosis Effect of 6,7-Dehydroroyleanone on Hep G2 cells
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, S.T.; Wang, D.S.; Wu, C.L.; Shiah, S.G.; Kuo, Y.H.; Chang, C.J. Cytotoxicity of extractives from Taiwania cryptomerioides heartwood. Phytochemistry 2000, 55, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.I.; Chang, J.Y.; Kuo, C.C.; Pan, W.Y.; Kuo, Y.H. Four new 6-nor5(6 → 7)abeo-abietane type diterpenes and antitumoral cytotoxic diterpene constituents from the bark of Taiwania cryptomerioides. Planta Med. 2005, 71, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zeng, L.; Shi, G.; Zhao, G.X.; Kozlowski, J.F.; McLaughlin, J.L. Bioactive compounds from Taiwania cryptomerioides. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 38–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shyur, L.F.; Lee, S.H.; Chang, S.T.; Lo, C.P.; Kuo, Y.H.; Wang, S.Y. Taiwanin A inhibits MCF-7 cancer cell activity through induction of oxidative stress, upregulation of DNA damage checkpoint kinases, and activation of p53 and FasL/Fas signaling pathways. Phytomedicine 2010, 18, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.T.; Chen, P.F.; Wang, S.Y.; Wu, H.H. Antimite activity of essential oils and their constituents from Taiwania Cryptomerioides. J. Med. Entomol. 2001, 38, 455–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ho, P.J.; Chou, C.K.; Kuo, Y.H.; Tu, L.C.; Yeh, S.F. Taiwanin A induced cell cycle arrest and p53-dependent apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells. Life Sci. 2007, 80, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.T.; Cheng, S.S.; Wang, S.Y. Antitermitic activity of essential oils and components from Taiwania (Taiwania cryptomerioides). J. Chem. Ecol. 2001, 27, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.H.; Kuo, W.W.; Day, C.H.; Shibu, M.A.; Li, S.Y.; Chang, S.H.; Shih, H.N.; Chen, R.J.; Viswanadha, V.P.; Kuo, Y.H.; et al. Taiwanin E inhibits cell migration in human LoVo colon cancer cells by suppressing MMP-2/9 expression via p38 MAPK pathway. Environ. Toxicol. 2017, 32, 2021–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harn, H.J.; Chuang, H.M.; Chang, L.F.; Huang, A.Y.; Hsieh, S.T.; Lin, S.Z.; Chou, C.W.; Kuo, Y.H.; Chiou, T.W. Taiwanin A targets non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-activated gene-1 in human lung carcinoma. Fitoterapia 2014, 99, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viveiros, P.; Riaz, A.; Lewandowski, R.J.; Mahalingam, D. Current state of liver-directed therapies and combinatory approaches with systemic therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Cancers 2019, 11, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stolley, D.L.; Crouch, A.C.; Özkan, A.; Seeley, E.H.; Whitley, E.M.; Rylander, M.N.; Cressman, E.N.K. Combining chemistry and engineering for hepatocellular carcinoma: Nano-scale and smaller therapies. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.R.; Wang, Y.Y.; La, K.K.; Peng, L.; Song, X.H.; Shi, X.G.; Zhu, X.F.; Leung, P.C.; Ko, C.H.; Ye, C.X. Inhibitory effects of cocoa tea (Camellia ptilophylla) in human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 in vitro and in vivo through apoptosis. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2012, 23, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.Z.; Cheng, J.T.; Yiin, S.J.; Chen, C.Y.; Chen, C.H.; Wu, M.J.; Chern, C.L. Isoobtusilactone A induces both caspase-dependent and -independent apoptosis in Hep G2 cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagandeep, S.; Novikoff, P.M.; Ott, M.; Gupta, S. Paclitaxel shows cytotoxic activity in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Lett. 1999, 136, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; He, J.; Ye, X.; Zhu, J.; Hu, X.; Shen, M.; Ma, Y.; Mao, Z.; Song, H.; Chen, F. β-Thujaplicin induces autophagic cell death, apoptosis, and cell cycle arrest through ROS-mediated Akt and p38/ERK MAPK signaling in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mu, W.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Lv, Q.; Liu, G.; Zhang, J.; Li, X. Hinokiflavone induces apoptosis via activating mitochondrial ROS/JNK/caspase pathway and inhibiting NF-κB activity in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 8151–8165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.Y.; Yeh, T.F.; Hsu, F.L.; Lin, C.Y.; Chang, S.T.; Chang, H.T. Xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity and thermostability of cinnamaldehyde-chemotype leaf oil of Cinnamomum osmophloeum microencapsulated with β-cyclodextrin. Molecules 2018, 23, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Starek, M.; Plenis, A.; Zagrobelna, M.; Dabrowska, M. Assessment of lipophilicity descriptors of selected NSAIDS obtained at different TLC stationary phases. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, P.L.; Wu, C.L.; Chang, S.T.; Huang, S.L.; Chang, H.T. Antioxidative lignans from phytochemical extract of Calocedrus formosana Florin. BioResources 2012, 7, 4122–4131. [Google Scholar]
- Santonocito, D.; Granata, G.; Geraci, C.; Panico, A.; Siciliano, E.A.; Raciti, G.; Puglia, C. Carob seeds: Food waste or source of bioactive compounds? Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, A.; Marto, J.; Gonçalves, L.M.; Simões, S.; Félix, R.; Ascenso, A.; Lopes, F.; Ribeiro, H.M. Novel and modified neutrophil elastase inhibitor loaded in topical formulations for psoriasis management. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silvestre, G.F.G.; Lucena, R.P.; Oliveira, G.D.; Pereira, H.N.; Dias, J.A.B.; Souza, I.A.; Alves, H.S. Anti-tumor and anti-inflammatory activity in vivo of Apodanthera congestiflora Cogn. (Cucurbitaceae). Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.Y.; Liu, I.H.; Huang, X.Z.; Chen, H.J.; Chang, S.T.; Chang, M.L.; Ho, Y.T.; Chang, H.T. Antimelanogenesis effects of leaf extract and phytochemicals from ceylon olive (Elaeocarpus serratus) in zebrafish model. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, R.P. Identification of Essential Oil Components by Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry; Allured Publishing Corporation: Carol Stream, IL, USA, 2007; pp. 6–398. ISBN 978-1932633214. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H.T.; Lin, C.Y.; Hsu, L.S.; Chang, S.T. Thermal degradation of linalool-chemotype Cinnamomum osmophloeum leaf essential oil and its stabilization by microencapsulation with β-cyclodextrin. Molecules 2021, 26, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassallo, A.; Armentano, M.F.; Miglionico, R.; Caddeo, C.; Chirollo, C.; Gualtieri, M.J.; Ostuni, A.; Bisaccia, F.; Faraone, I.; Milella, L. Hura crepitans L. extract: Phytochemical characterization, antioxidant activity, and nanoformulation. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łapińska, Z.; Dębiński, M.; Szewczyk, A.; Choromańska, A.; Kulbacka, J.; Saczko, J. Electrochemotherapy with calcium chloride and 17β-estradiol modulated viability and apoptosis pathway in human ovarian cancer. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryczyk-Poprawa, A.; Zupkó, I.; Bérdi, P.; Żmudzki, P.; Piotrowska, J.; Pękala, E.; Berdys, A.; Muszyńska, B.; Opoka, W. Photodegradation of bexarotene and its implication for cytotoxicity. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietkiewicz, S.; Schmidt, J.H.; Lavrik, I.N. Quantification of apoptosis and necroptosis at the single cell level by a combination of imaging flow cytometry with classical Annexin V/propidium iodide staining. J. Immunol. Methods 2015, 423, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Ham, J.; Hong, T.; Song, G.; Lim, W. Fraxetin suppresses cell proliferation and induces apoptosis through mitochondria dysfunction in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines Huh7 and Hep3B. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myint, P.P.; Dao, T.T.P.; Kim, Y.S. Anticancer activity of Smallanthus sonchifolius methanol extract against human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Molecules 2019, 24, 3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edwards, O.E.; Feniak, G.; Los, M. Diterpenoid quinones of Inula royleana D. C. Can. J. Chem. 1962, 40, 1540–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michavila, A.; Fernández-Gadea, F.; Rodríguez, B. Abietane diterpenoids from the root of Salvia lavandulaefolia. Phytochemistry 1985, 25, 266–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, A.P.; Batista, O.; Simões, M.F.; Nascimento, J.; Duarte, A.; de la Torre, M.C.; Rodríguez, B. Abietane diterpenoids from Plectranthus grandidentatus. Phytochemistry 1997, 44, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kabouche, A.; Boutaghane, N.; Kabouche, Z.; Seguin, E.; Tillequin, F.; Benlabed, K. Components and antibacterial activity of the roots of Salvia jaminiana. Fitoterapia 2005, 76, 450–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusumoto, N.; Ashitani, T.; Hayasaka, Y.; Murayama, T.; Ogiyama, K.; Takahashi, K. Antitermitic activities of abietane-type diterpenes from Taxodium distichum cones. J. Chem. Ecol. 2009, 35, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazim, Z.C.; Rodrigues, F.; Amorin, A.C.L.; de Rezende, C.M.; Soković, M.; Tešević, V.; Vučković, I.; Krstić, G.; Cortez, L.E.R.; Colauto, N.B.; et al. New natural diterpene-type abietane from Tetradenia riparia essential oil with cytotoxic and antioxidant activities. Molecules 2014, 19, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demarchi, I.G.; Thomazella, M.V.; de Souza Terron, M.; Lopes, L.; Gazim, Z.C.; Cortez, D.A.; Donatti, L.; Aristides, S.M.; Silveira, T.G.; Lonardoni, M.V. Antileishmanial activity of essential oil and 6,7-dehydroroyleanone isolated from Tetradenia riparia. Exp. Parasitol. 2015, 157, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Ma, X.; Deng, S.; Yang, X.; Song, P. Crystal structure of 6,7-de-hydro-royleanone isolated from Taxodium distichum (L.) Rich. Acta Crystallogr. E. Crystallogr. Commun. 2018, 74, 62–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia, C.; Silva, C.O.; Monteiro, C.M.; Nicolai, M.; Viana, A.; Andrade, J.M.; Barasoain, I.; Stankovic, T.; Quintana, J.; Hernández, I.; et al. Anticancer properties of the abietane diterpene 6,7-dehydroroyleanone obtained by optimized extraction. Future Med. Chem. 2018, 10, 1177–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubínová, R.; Pŏrízková, R.; Navrátilová, A.; Farsa, O.; Hanáková, Z.; Băcinská, A.; Čížek, A.; Valentová, M.; Cížek, A.; Valentová, M. Antimicrobial and enzyme inhibitory activities of the constituents of Plectranthus madagascariensis (Pers.) Benth. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2014, 6366, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terron-Monich, M.S.; Demarchi, I.G.; da Silva, P.R.F.; Ramos-Milaré, Á.C.F.H.; Gazim, Z.C.; Silveira, T.G.V.; Lonardoni, M.V.C. 6,7-Dehydroroyleanone diterpene derived from Tetradenia riparia essential oil modulates IL-4/IL-12 release by macrophages that are infected with Leishmania amazonensis. Parasitol Res. 2019, 118, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldin, V.P.; Scodro, R.B.L.; Lopes-Ortiz, M.A.; de Almeida, A.L.; Gazim, Z.C.; Ferarrese, L.; Faiões, V.D.S.; Torres-Santos, E.C.; Pires, C.T.A. Caleffi-Ferracioli, K.R.; et al. Anti-Mycobacterium tuberculosis activity of essential oil and 6,7-dehydroroyleanone isolated from leaves of Tetradenia riparia (Hochst.) Codd (Lamiaceae). Phytomedicine 2018, 47, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isca, V.M.S.; Sencanski, M.; Filipovic, N.; Dos Santos, D.J.V.A.; Čipak Gašparović, A.; Saraíva, L.; Afonso, C.A.M.; Rijo, P.; García-Sosa, A.T. Activity to breast cancer cell lines of different malignancy and predicted interaction with protein kinase c isoforms of royleanones. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitarek, P.; Toma, M.; Ntungwe, E.; Kowalczyk, T.; Skała, E.; Wieczfinska, J.; Śliwiński, T.; Rijo, P. Insight the biological activities of selected abietane diterpenes isolated from Plectranthus spp. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amiri, F.; Zarnani, A.H.; Zand, H.; Koohdani, F.; Jeddi-Tehrani, M.; Vafa, M. Synergistic anti-proliferative effect of resveratrol and etoposide on human hepatocellular and colon cancer cell lines. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 718, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakherad, Z.; Safavi, M.; Fassihi, A.; Sadeghi-Aliabadi, H.; Bakherad, M.; Rastegar, H.; Saeedi, M.; Ghasemi, J.B.; Saghaie, L.; Mahdavi, M. Design and synthesis of novel cytotoxic indole-thiosemicarbazone derivatives: Biological evaluation and docking study. Chem. Biodivers. 2019, 16, e1800470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Specimen | Concentration (μg/mL) | Cytotoxicity * (%) | IC50 * (μg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bark oil | 12.5 | 10.23 ± 0.98 | 54.31 ± 0.60 a |
| 25 | 22.20 ± 0.10 | ||
| 50 | 49.47 ± 0.17 | ||
| 100 | 77.80 ± 0.17 | ||
| S2 fraction | 12.5 | 18.81 ± 0.90 | 32.22 ± 4.84 b |
| 25 | 26.43 ± 9.70 | ||
| 50 | 84.44 ± 1.75 | ||
| 100 | 90.62 ± 0.33 | ||
| S3 fraction | 12.5 | 44.37 ± 4.50 | 21.17 ± 1.09 c |
| 25 | 55.98 ± 3.57 | ||
| 50 | 82.61 ± 0.70 | ||
| 100 | 93.38 ± 0.23 |
| Time (h) | Specimen | IC50 (μg/mL) | IC50 (µM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 24 | Bark essential oil | 54.31 ± 0.60 b | - |
| 6,7-Dehydroroyleanone | 10.28 ± 0.18 d | 32.74 ± 0.57 C | |
| Etoposide * | 76.89 ± 0.34 a | 130.64 ± 0.58 A | |
| 48 | Bark essential oil | 30.27 ± 1.11 c | - |
| 6,7-Dehydroroyleanone | 5.22 ± 0.09 e | 16.62 ± 0.29 D | |
| Etoposide * | 29.68 ± 1.18 c | 50.43 ± 2.01 B |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, G.-R.; Chang, M.-L.; Chang, S.-T.; Ho, Y.-T.; Chang, H.-T. Cytotoxicity and Apoptosis Induction of 6,7-Dehydroroyleanone from Taiwania cryptomerioides Bark Essential Oil in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14020351
Chen G-R, Chang M-L, Chang S-T, Ho Y-T, Chang H-T. Cytotoxicity and Apoptosis Induction of 6,7-Dehydroroyleanone from Taiwania cryptomerioides Bark Essential Oil in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(2):351. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14020351
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Guan-Rong, Mei-Ling Chang, Shang-Tzen Chang, Yu-Tung Ho, and Hui-Ting Chang. 2022. "Cytotoxicity and Apoptosis Induction of 6,7-Dehydroroyleanone from Taiwania cryptomerioides Bark Essential Oil in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 2: 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14020351
APA StyleChen, G. -R., Chang, M. -L., Chang, S. -T., Ho, Y. -T., & Chang, H. -T. (2022). Cytotoxicity and Apoptosis Induction of 6,7-Dehydroroyleanone from Taiwania cryptomerioides Bark Essential Oil in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Pharmaceutics, 14(2), 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14020351