INGAP-Peptide Variants as a Novel Therapy for Type 1 Diabetes: Effect on Human Islet Insulin Secretion and Gene Expression
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. INGAP-P Variant Peptide Synthesis
2.2. Study Subjects
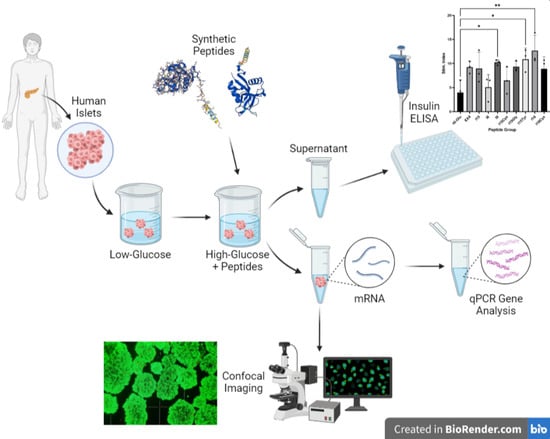
2.3. Human Islet Handling and Stimulation
2.4. Live Cell Viability Imaging
2.5. RT-qPCR Quantification of Islet Gene Expression
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. INGAP-P Variant Synthesis and Characterization
3.2. Islet Culture and Peptide-Stimulated Insulin Secretion
3.3. RT-qPCR Analysis of Islet Nuclear mRNA
3.4. Challenges and Limitations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rickels, M.R.; Norris, A.W.; Hull, R.L. A tale of two pancreases: Exocrine pathology and endocrine dysfunction. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 2030–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huan, C.; Stanek, A.; Mueller, C.; Ou, P.; Dong, S.; Zhang, J.; Abdel-Naby, R.; Gruessner, R. Loss of Reg proteins’ protection of islet β cells in chronic pancreatitis: A potential mechanism for the pathogenesis of type 3c diabetes. Curr. Opin. Endocr. Metab. Res. 2019, 5, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.L.; Peakman, M. Peptide Immunotherapy for Type 1 Diabetes-Clinical Advances. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arutyunyan, I.V.; Fatkhudinov, T.K.; Makarov, A.V.; Elchaninov, A.V.; Sukhikh, G.T. Regenerative medicine of pancreatic islets. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 2948–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Kuwabara, R.; Navarro Chica, C.E.; Smink, A.M.; Koster, T.; Medina, J.D.; de Haan, B.J.; Beukema, M.; Lakey, J.R.T.; Garcia, A.J.; et al. Toll-like receptor 2-modulating pectin-polymers in alginate-based microcapsules attenuate immune responses and support islet-xenograft survival. Biomaterials 2021, 266, 120460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakhneny, L.; Epshtein, A.; Landsman, L. Pericytes contribute to the islet basement membranes to promote beta-cell gene expression. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalbach, L.; Roma, L.P.; Schmitt, B.M.; Becker, V.; Korbel, C.; Wrublewsky, S.; Pack, M.; Spater, T.; Metzger, W.; Menger, M.M.; et al. Improvement of islet transplantation by the fusion of islet cells with functional blood vessels. EMBO Mol. Med. 2021, 13, e12616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, L. The Fate of Allogeneic Pancreatic Islets following Intraportal Transplantation: Challenges and Solutions. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 2424586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramswig, N.C.; Everett, L.J.; Schug, J.; Dorrell, C.; Liu, C.; Luo, Y.; Streeter, P.R.; Naji, A.; Grompe, M.; Kaestner, K.H. Epigenomic plasticity enables human pancreatic alpha to beta cell reprogramming. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, S.; Loganathan, G.; Hussain, A.; Williams, S.K.; Balamurugan, A.N. Ductal cell reprograming to insulin-producing cells as a potential beta cell replacement source for islet auto-transplant recipients. In Transplantation, Bioengineering, and Regeneration of the Endocrine Pancreas; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Docherty, F.M.; Sussel, L. Islet Regeneration: Endogenous and Exogenous Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanday, N.; Irwin, N.; Moffett, R.C.; Flatt, P.R.; O’Harte, F.P.M. Beneficial actions of a long-acting apelin analogue in diabetes are related to positive effects on islet cell turnover and transdifferentiation. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 2468–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muttenthaler, M.; King, G.F.; Adams, D.J.; Alewood, P.F. Trends in peptide drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nachnani, J.S.; Bulchandani, D.G.; Nookala, A.; Herndon, B.; Molteni, A.; Pandya, P.; Taylor, R.; Quinn, T.; Weide, L.; Alba, L.M. Biochemical and histological effects of exendin-4 (exenatide) on the rat pancreas. Diabetologia 2010, 53, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nano, E.; Petropavlovskaia, M.; Rosenberg, L. Islet neogenesis associated protein (INGAP) protects pancreatic beta cells from IL-1beta and IFNgamma-induced apoptosis. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynn, S.; Ricardo Espinosa Silva, Y.; Diambra, L.; McCarthy, A.N.; Liping, L.; Ru, B.; Roman, C.L.; Maiztegui, B.; Flores, L.E.; Gagliardino, J.J. A new analogue of islet neogenesis associated protein with higher structural and plasma stability. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 39, 766–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nano, E. Protecting Pancreatic B Cells against Cytokines Novel Function of Islet Neogenesis Associated Protein INGAP and Combinatorial Treatment with NFkB Inhibitor and SCA B1 NBD. Ph.D. Thesis, McGill University, Montréal, QC, Canada, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, I. Structure Modification of the Pentadecapeptide Fragment of Islet Neogenesis Associated Protein and Its Effects on Beta Cell Proliferation. Master’s Thesis, Northeastern Illinois University, Chicago, IL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, J.E.; Newgard, C.B. Mechanisms controlling pancreatic islet cell function in insulin secretion. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, L. Modified INGAP Peptides for Treating Diabetes. U.S. Patent 14,768,452, 7 January 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Petropavlovskaia, M.; Daoud, J.; Zhu, J.; Moosavi, M.; Ding, J.; Makhlin, J.; Assouline-Thomas, B.; Rosenberg, L. Mechanisms of action of islet neogenesis-associated protein: Comparison of the full-length recombinant protein and a bioactive peptide. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 303, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, H.; Bordin, S.; Stoppiglia, L.; Silva, K.; Borelli, M.; Del Zotto, H.; Gagliardino, J.; Boschero, A. Islet Neogenesis Associated Protein (INGAP) modulates gene expression in cultured neonatal rat islets. Regul. Pept. 2006, 136, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, J.M.; Guerassimoff, L.; Castiello, F.R.; Tabrizian, M. Synthesis and Screening of Novel Peptides on Human Pancreatic Islets for Type 1 Diabetes Therapies. In Proceedings of the 2020 42nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Gunton, J.E. Beta-cell function and human islet transplantation: Can we improve? J. Endocrinol. 2021, 248, R99–R112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josephine, M.; Egan, A.R.C.; Elahi, D. The insulinotropic effect of acute exendin-4 administered to humans: Comparison of nondiabetic state to T2D. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 1282–1290. [Google Scholar]
- Bruning, D.; Reckers, K.; Drain, P.; Rustenbeck, I. Glucose but not KCl diminishes submembrane granule turnover in mouse beta-cells. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2017, 59, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Stoffers, D.A.; Habener, J.F.; Bonner-Weir, S. Exendin 4 Stimulates both B-cell replication and neogenesis resulting in increased B-cell mass and improved glucose tolerance in diabetic rats. Diabetes 1999, 48, 2270–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, D.Y.; Kim, Y.S.; Ahn, I.S.; Kim, D.S.; Kang, S.; Hong, S.M.; Park, S. Exendin-4 potentiates insulinotropic action partly via increasing beta-cell proliferation and neogenesis and decreasing apoptosis in association with the attenuation of endoplasmic reticulum stress in islets of diabetic rats. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 111, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozera, B.; Rapacz, M. Reference genes in real-time PCR. J. Appl. Genet. 2013, 54, 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szkudelski, T.; Szkudelska, K. The relevance of AMP-activated protein kinase in insulin-secreting beta cells: A potential target for improving beta cell function? J. Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 75, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, N.J.; Powers, A.C. Use of human islets to understand islet biology and diabetes: Progress, challenges and suggestions. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, S.; Madec, A.M.; Mesnier, A.; Armanet, M.; Chikh, K.; Berney, T.; Thivolet, C. Glucose inhibits angiogenesis of isolated human pancreatic islets. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2010, 45, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marty, N.; Dallaporta, M.; Foretz, M.; Emery, M.; Tarussio, D.; Bady, I.; Binnert, C.; Beermann, F.; Thorens, B. Regulation of glucagon secretion by glucose transporter type 2 (glut2) and astrocyte-dependent glucose sensors. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 3545–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briant, L.; Salehi, A.; Vergari, E.; Zhang, Q.; Rorsman, P. Glucagon secretion from pancreatic alpha-cells. Upsala J. Med. Sci. 2016, 121, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacos, K.; Gillberg, L.; Volkov, P.; Olsson, A.H.; Hansen, T.; Pedersen, O.; Gjesing, A.P.; Eiberg, H.; Tuomi, T.; Almgren, P.; et al. Blood-based biomarkers of age-associated epigenetic changes in human islets associate with insulin secretion and diabetes. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Januszewski, A.S.; Cho, Y.H.; Joglekar, M.V.; Farr, R.J.; Scott, E.S.; Wong, W.K.M.; Carroll, L.M.; Loh, Y.W.; Benitez-Aguirre, P.Z.; Keech, A.C.; et al. Insulin micro-secretion in Type 1 diabetes and related microRNA profiles. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.-L.; Kaddour, N.; Xega, V.; Gao, Z.-H. Endocrine Regulation of the Pancreas by Insulin-like Growth Factors. In Cellular Endocrinology in Health and Disease; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihm, S.H.; Matsumoto, I.; Sawada, T.; Nakano, M.; Zhang, H.J.; Ansite, J.D.; Sutherland, D.E.; Hering, B.J. Effect of donor age on function of isolated human islets. Diabetes 2006, 55, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






| Donor | Islet Donor Information | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | Islet Size Index | Purity (%) | Islet Viability (%) | HbA1c (%) | BMI | Cause of Death | Height (in) | Weight (lbs) | Gender | |
| 1 | 59 | 0.93 | 90–95 | 95 | 5.0 | 24.5 | Stroke | 68 | 161 | Female |
| 2 | 55 | 0.79 | 90–95 | 95 | 5.6 | 28.4 | Stroke | 68 | 187 | Male |
| 3 | 37 | 1.25 | 90 | 95 | 5.8 | 23.9 | Head Trauma | 76 | 198 | Male |
| 4 | 26 | 1.18 | 95 | 95 | 5.9 | 30.3 | Head Trauma | 70 | 209 | Male |
| 5 | 19 | 1.17 | 90 | 95 | 5.8 | 23.1 | Head Trauma | 71 | 157 | Male |
| Gene | Function | Forward Primer Sequence | Reverse Primer Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Insulin | Encodes preproinsulin | GAA-CGA-GGC-TTC-TTC-TAC-AC | ACA-ATG-CCA-CGC-TTC-TG |
| Glucagon | Encodes preproglucagon | ACC-AGA-AGA-CAG-CAG-AAA-TG | GAA-TGT-GCC-CTG-TGA-ATG |
| SUR1 | Membrane protein; target of antidiabetic drugs | CGA-TGC-CAT-CAT CAC-AGA-AG | CTG-AGC-AGC-TTC-TCT-GGC-TT |
| GLUT2 | Transmembrane carrier protein | CTC-TCC-TTG-CTC-CTC-CTC-CT | TTG-GGA-GTC-CTG-TCA-ATT-CC |
| PDX1 | Insulin promoter factor 1 | ATG-GAT-GAA-GTC-TAC-CAA-AGC | CGT-GAG-ATG-TAC-TTG-TTG-AAT-AG |
| GAPDH | Catalyzes glycolysis, can activate transcription | CAC-CCA-CTC-CTC-CAC-CTT-TG | CCA-CCA-CCC-TGT-TGC-TGT-AG |
| Peptide ID | Variant | Sequence | Interest |
|---|---|---|---|
| I15 | INGAP-P | N’-Ile-Gly-Leu-His-Asp-Pro-Ser-His-Gly-Thr-Leu-Pro-Asn-Gly-Ser-C’ | INGAP’s bioactive region (already proven) |
| I6 | INGAP-P conserved motif | N’-Ile-Gly-Leu-His-Asp-Pro-C | Synergistic effect with I9 conserved motif |
| I9 | INGAP-P specific motif | N’-Ser-His-Gly-Thr-Leu-Pro-Asn-Gly-Ser-C’ | Synergistic effect with I6 specific motif |
| I15Cys | Cyclic INGAP-P | N’-Ile-Gly-Leu-His-Asp-Pro-Ser-His-Gly-Thr-Leu-Pro-Asn-Gly-Ser-Cys-C’ | Efficiency of the cyclization method (with cysteines) |
| I15Gly | Modified INGAP-P (C-terminal) | N’-Ile-Gly-Leu-His-Asp-Pro-Ser-His-Gly-Thr-Leu-Pro-Asn-Gly-Ser-Gly-C’ | Effect of glycine at the C-terminal amino acid on the ligand/receptor mechanism |
| I15Tyr | Modified INGAP-P (C-terminal) | N’-Ile-Gly-Leu-His-Asp-Pro-Ser-His-Gly-Thr-Leu-Pro-Asn-Gly-Ser-Tyr-C’ | Effect of tyrosine at the C-terminal amino acid on the ligand/receptor mechanism |
| I19 | Modified INGAP-P | N’-Cys-Cys-Ile_Gly-Leu-His-Asp-Pro-Ser-His-Gly-Thr-Leu-Pro-Asn-Gly-Ser—Cys-Cys-C’ | Effect of making a longer peptide with hydrophobic amino acids |
| I19Cys | Cyclic modified INGAP-P, longer peptide | N’-Cys-Cys-Ile-Gly-Leu-His-Asp-Pro-Ser-His-Gly-Thr-Leu-Pro-Asn-Gly-Ser—Cys-Cys-C’ | Efficiency of the cyclization method, combination of longer peptide (19) and cyclization |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Porter, J.M.; Guerassimoff, L.; Castiello, F.R.; Charette, A.; Tabrizian, M. INGAP-Peptide Variants as a Novel Therapy for Type 1 Diabetes: Effect on Human Islet Insulin Secretion and Gene Expression. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1833. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091833
Porter JM, Guerassimoff L, Castiello FR, Charette A, Tabrizian M. INGAP-Peptide Variants as a Novel Therapy for Type 1 Diabetes: Effect on Human Islet Insulin Secretion and Gene Expression. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(9):1833. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091833
Chicago/Turabian StylePorter, James M., Léa Guerassimoff, Francisco Rafael Castiello, André Charette, and Maryam Tabrizian. 2022. "INGAP-Peptide Variants as a Novel Therapy for Type 1 Diabetes: Effect on Human Islet Insulin Secretion and Gene Expression" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 9: 1833. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091833
APA StylePorter, J. M., Guerassimoff, L., Castiello, F. R., Charette, A., & Tabrizian, M. (2022). INGAP-Peptide Variants as a Novel Therapy for Type 1 Diabetes: Effect on Human Islet Insulin Secretion and Gene Expression. Pharmaceutics, 14(9), 1833. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091833