Improving the Bioactivity of Norfloxacin with Tablets Made from Paper
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Production and Characterization of Norfloxacin-Loaded smartFilms and smartFilm Granules
Particle Size
Pharmaceutical Characteristics
Crystalline State of Norfloxacin
2.2.2. Production and Characterization of Norfloxacin-Loaded smartFilm Tablets
Pharmaceutical Characteristics
2.2.3. Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity
In Vitro Antibacterial Activity
Ex Vivo Antibacterial Activity
2.2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Production and Characterization of Norfloxacin-Loaded smartFilm Granules
3.1.1. Particle Size
3.1.2. Pharmaceutical Characteristics
3.1.3. Crystalline State of Norfloxacin
3.2. Production and Characterization of Norfloxacin-Loaded smartFilm Tablets
3.2.1. Crystalline State of Norfloxacin
3.2.2. Pharmaceutical Characteristics
3.2.3. Dissolution Profile
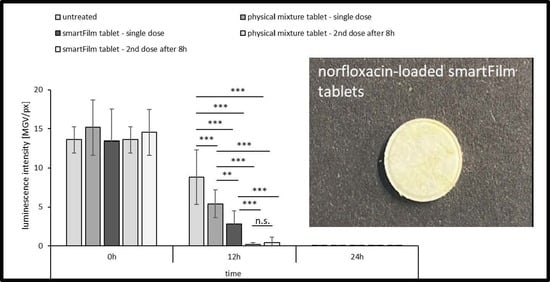
3.2.4. Determination of Antibacterial Activity
In Vitro Antibacterial Activity
Ex Vivo Antibacterial Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stegemann, S.; Leveiller, F.; Franchi, D.; de Jong, H.; Linden, H. When poor solubility becomes an issue: From early stage to proof of concept. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 31, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalepu, S.; Nekkanti, V. Insoluble drug delivery strategies: Review of recent advances and business prospects. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2015, 5, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Williams, R.O.; Watts, A.B.; Miller, D.A. Formulating Poorly Water Soluble Drugs, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; ISBN 9783030887193. [Google Scholar]
- Lemke, S.; Strätling, E.-J.; Welzel, H.-P.; Keck, C.M. Cellulose Fibre Based Support Matrices for Layered Products for Oral and Peroral Application and Their Preparation. European Patent Office EP3192499A1, 19 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lemke, S. Cellulosebasierte Filme (smartFilms®) als Alternative Orale Oder Perorale Applikationsform; Herstellung und Prüfung. Ph.D. Thesis, Freie Universität Berlin, Berlin, Germany. German Patent Application DE102016000541A1, 20 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Stumpf, F.; Keck, C.M. Tablets made from paper. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 548, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpf, F. Tabletten aus Papier—Tablets made from paper—Zur oralen Applikation schwerlöslicher Wirkstoffe. Ph.D. Thesis, Philipps-Universität Marburg, Marburg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Eckert, R.W.; Wiemann, S.; Keck, C.M. Improved Dermal and Transdermal Delivery of Curcumin with SmartFilms and Nanocrystals. Molecules 2021, 26, 1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkader, A.; Moos, C.; Pelloux, A.; Pfeiffer, M.; Alter, C.; Kolling, S.; Keck, C.M. Tablets Made from Paper—An Industrially Feasible Approach. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkader, A.; Preis, E.; Keck, C.M. smartFilm tablets for improved oral delivery of poorly soluble drugs. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breda, S.A.; Jimenez-Kairuz, A.F.; Manzo, R.H.; Olivera, M.E. Solubility behavior and biopharmaceutical classification of novel high-solubility ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin pharmaceutical derivatives. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 371, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padeĭskaia, E.N. Norfloksatsin: Bolee 20 let v klinicheskoĭ praktike, itogi i mesto v riadu ftorkhinolonov pri sovremennoĭ khimioterapii infektsiĭ. Antibiot. Khimioter. 2003, 48, 28–36. [Google Scholar]
- Pelikh, O.; Eckert, R.W.; Pinnapireddy, S.R.; Keck, C.M. Hair follicle targeting with curcumin nanocrystals: Influence of the formulation properties on the penetration efficacy. J. Control. Release 2020, 10, 598–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JASP Team. JASP, Version 0.13.1; Computer Software: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020.
- C.H. Beck. European Pharmacopoeia, 8th ed.; 2.09: Pharmaceutical Technical Procedures; C.H. Beck: Nördlingen, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Aslani, A.; Jahangiri, H. Formulation, characterization and physicochemical evaluation of ranitidine effervescent tablets. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 3, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyashiro, T.; Ruby, E.G. Shedding light on bioluminescence regulation in Vibrio fischeri. Mol. Microbiol. 2012, 84, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molnár, M.; Fenyvesi, É.; Berkl, Z.; Németh, I.; Fekete-Kertész, I.; Márton, R.; Vaszita, E.; Varga, E.; Ujj, D.; Szente, L. Cyclodextrin-mediated quorum quenching in the Aliivibrio fischeri bioluminescence model system—Modulation of bacterial communication. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 594, 120150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nallbati, L. A Bioluminescent Wound Microbiome Modification through Aliivibrio Fischeri and Effect of the Topical Application of Nor-floxacin Nanosuspension. Master’s Thesis, Philipps-Universität Marburg, Marburg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Fathi, H.A.; Abdelkader, A.; AbdelKarim, M.S.; Abdelaziz, A.A.; El-Mokhtar, M.A.; Allam, A.; Fetih, G.; El Badry, M.; Elsabahy, M. Electrospun vancomycin-loaded nanofibers for management of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus-induced skin infections. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 586, 119620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelikh, O.; Pinnapireddy, S.R.; Keck, C.M. Dermal penetration analysis of curcumin in an ex-vivo porcine ear model using epifluorescence microscopy and digital image processing. Ski. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2021, 34, 281–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keck, C.M.; Abdelkader, A.; Pelikh, O.; Wiemann, S.; Kaushik, V.; Specht, D.; Eckert, R.W.; Alnemari, R.M.; Dietrich, H.; Brüßler, J. Assessing the Dermal Penetration Efficacy of Chemical Compounds with the Ex-Vivo Porcine Ear Model. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, V.; Ganashalingam, Y.; Schesny, R.; Raab, C.; Sengupta, S.; Keck, C.M. Influence of Massage and Skin Hydration on Dermal Penetration Efficacy of Nile Red from Petroleum Jelly-An Unexpected Outcome. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, V.; Keck, C.M. Influence of mechanical skin treatment (massage, ultrasound, microdermabrasion, tape stripping and microneedling) on dermal penetration efficacy of chemical compounds. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2021, 169, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasband, W.S. ImageJ: Image Processing and Analysis in Java; Astrophysics Source Code Library: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; ascl: 1206.01. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinno, A. Nonparametric pairwise multiple comparisons in independent groups using Dunn’s test. Stata J. 2015, 15, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Taylor and Francis: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; ISBN 9781134742707. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer-Brandl, A.; Ritschel, W.A. Die Tablette: Handbuch der Entwicklung, Herstellung und Qualitätssicherung, 3rd ed.; vollständig überarb. und erw. Aufl.; ECV Editio Cantor Verl.: Aulendorf, Germany, 2012; ISBN 9783871934070. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, G.E. Review of the bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of oral norfloxacin. Am. J. Med. 1987, 82, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Kim, S.; Park, K. In vitro-in vivo correlation: Perspectives on model development. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 418, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Shrestha, N.; Préat, V.; Beloqui, A. An overview of in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo models for studying the transport of drugs across intestinal barriers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 175, 113795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Bulk Density (g/cm3) | Tapped Density (g/cm3) | Hausner Ratio | Carr Index | Angle of Repose | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paper granules * | 0.14 ± 0.00 * | 0.15 ± 0.00 * | 1.13 ± 0.04 * | 11.7 ± 3.6 * | 31° ± 0 * |
| smartFilm granules | 0.15 ± 0.00 | 0.18 ± 0.00 | 1.17 ± 0.00 | 14.9 ± 0.0 | 31° ± 0 |
| Thickness (mm) | Mass Uni-formity (%) | Content Uni-formity (%) | Friability (%) | Resistance to Crushing (N) | Disintegration | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paper tablets * | 1.7 ± 0.04 * | 1.8 ± 1.6 * | n.a. | 0.23 * | 112.8 ±18.6 * min.: 84.2 max.: 129.5 | All tablets disintegrated within 5 min * |
| smartFilm tablets | 2.3 ± 0.05 | 2.9 ± 1.8 | 97.5 ± 1.5 max: 99.3 | 0.07 | 110.7 ± 12.2 min.: 82.5 max.: 125.9 | All tablets disintegrated within 15 min |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdelkader, A.; Nallbati, L.; Keck, C.M. Improving the Bioactivity of Norfloxacin with Tablets Made from Paper. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15020375
Abdelkader A, Nallbati L, Keck CM. Improving the Bioactivity of Norfloxacin with Tablets Made from Paper. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(2):375. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15020375
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdelkader, Ayat, Laura Nallbati, and Cornelia M. Keck. 2023. "Improving the Bioactivity of Norfloxacin with Tablets Made from Paper" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 2: 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15020375
APA StyleAbdelkader, A., Nallbati, L., & Keck, C. M. (2023). Improving the Bioactivity of Norfloxacin with Tablets Made from Paper. Pharmaceutics, 15(2), 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15020375