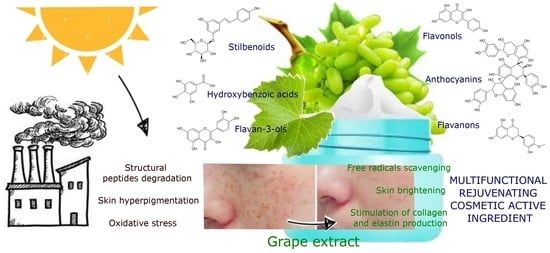
Vitis vinifera (Vine Grape) as a Valuable Cosmetic Raw Material
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. General Characteristics
2.1. Botanical Characteristic
2.2. Ecological Characteristic
2.3. Chemical Characteristic
3. Methods of Extraction and the Identification of Selected Groups of V. vinifera Metabolites
4. The Position of V. vinifera in the Official Documents
4.1. EMA–HMPC
4.2. EFSA
4.3. FDA
4.4. CosIng
5. V. vinifera as the Ingredient of the Cosmetic Formulation
6. Biological Activities of V. vinifera Confirmed by Scientific Reports with a Direct Application in Cosmetology
6.1. Anti-Aging and UV-Protection Activities
6.2. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
| Biological Activity | Tested Plant Material | Mechanism of Action | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-ageing activity | V. vinifera leaf extract | -the stimulation of SIRT 1 and HSP 4 genes | [23] |
| UV-protection activity | V. vinifera skin extract | -possessing skin-protecting activity against sun rays | [57] |
| Antioxidant activity | V. vinifera fruit extract V. vinifera skin extract V. vinifera leaf extract | -free oxygen radical scavenging | [21,59] [19] [59] |
| V.vinifera stem extract | [60] | ||
| V. vinifera pomace extract | -oxidation of human LDL lipoproteins -influence on lipid peroxidation | [61] | |
| Anti-inflammatory activity | V.vinifera leaf extract | -inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokines | [58] |
| Skin-whitening activity | V.vinifera leaf extract | -tyrosinase inhibition | [22] |
| V. vinifera cane extract | -tyrosinase inhibition | [50] |
6.3. Skin-Whitening Activity
7. Biological Activities Confirmed by Scientific Reports with a Potential Application in Cosmetology
7.1. Antioxidant Activity
7.2. Antimicrobial Activity
7.3. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
8. The Applications of V. vinifera In Vitro Cultures in Cosmetology
9. Safety of Use
9.1. Skin Irritation and Sensitisation
9.2. Eye Irritation
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kazmierski, L.; Roszkowski, S. Plant stem cells culture—A new tool for skin protection and regeneration. Med Res. J. 2019, 4, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoang, H.T.; Moon, J.-Y.; Lee, Y.-C. Natural Antioxidants from Plant Extracts in Skincare Cosmetics: Recent Applications, Challenges and Perspectives. Cosmetics 2021, 8, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faccio, G. Plant Complexity and Cosmetic Innovation. iScience 2020, 23, 101358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Organisation of Vine and Wine. Distribution of the World’s Grapevine Varieties. Available online: https://www.oiv.int (accessed on 19 March 2023).
- Goufo, P.; Singh, R.K.; Cortez, I. A Reference List of Phenolic Compounds (Including Stilbenes ) in Grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.). Antioxidants 2020, 9, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radulescu, C.; Buruleanu, L.C.; Nicolescu, C.M.; Olteanu, R.L.; Bumbac, M.; Holban, G.C.; Simal-Gandara, J. Phytochemical Profiles, Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activities of Grape (Vitis vinifera L.) Seeds and Skin from Organic and Conventional Vineyards. Plants 2020, 9, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo Di, C.; Sangiovanni, E.; Fumagalli, M.; Colombo, E.; Frigerio, G.; Colombo, F.; Peres de Sousa, L.; Altindişli, A.; Restani, P.; Dell’Agli, M. Evaluation of the Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Raisins (Vitis vinifera L.) in Human Gastric Epithelial Cells: A Comparative Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfahanian, Z.; Behbahani, M.; Shanehsaz, M.; Hessami, M.J.; Nejatian, M.A. Evaluation of Anticancer Activity of Fruit and Leave Extracts from Virus Infected and Healthy Cultivars of Vitis vinifera. Cell J. 2013, 15, 116–123. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.K.; Vasudeva, S.; Vasudeva, N. Hepatoprotective activity of Vitis vinifera root extract against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver damage in rats. Acta Pol. Pharm. Drug Res. 2012, 69, 933–937. [Google Scholar]
- Lakshmi, B.V.S.; Sudhakar, M.; Anisha, M. Neuroprotective role of hydroalcoholic extract of Vitis vinifera against aluminium-induced oxidative stress in rat brain. Neurotoxicology 2014, 41, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en (accessed on 19 March 2023).
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Available online: https://www.fda.gov (accessed on 19 March 2023).
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en (accessed on 19 March 2023).
- Leal, C.; Gouvinhas, I.; Santos, R.A.; Rosa, E.; Silva, A.M.; Saavedra, M.J.; Barros, A.I.R.N.A. Potential application of grape (Vitis vinifera L.) stem extracts in the cosmetic and pharmaceutical industries: Valorization of a by-product. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2020, 154, 112675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaduzzaman, A.K.M.; Chun, B.-S.; Kabir, S.R. Vitis vinifera Assisted Silver Nanoparticles with Antibacterial and Antiproliferative Activity against Ehrlich Ascites Carcinoma Cells. J. Nanoparticles 2016, 2016, 6898926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fiume, M.M.; Bergfeld, W.F.; Belsito, D.V.; Hill, R.A.; Klaassen, C.D.; Liebler, D.C.; Marks, J.G.; Shank, R.C.; Slaga, T.J.; Snyder, P.W.; et al. Safety Assessment of Vitis vinifera (Grape)-Derived Ingredients as Used in Cosmetics. Cosmet. Ingred. Rev. 2012, 33, 48S–83S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfukwa, T.M.; Fawole, O.A.; Manley, M.; Gouws, P.A.; Opara, U.L.; Mapiye, C. Food Preservative Capabilities of Grape (Vitis vinifera) and Clementine Mandarin (Citrus reticulata) By-products Extracts in South Africa. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, C.K.; Liu, X.; Ahmad, N. Resveratrol, in its natural combination in whole grape, for health promotion and disease management. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2015, 1348, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tzanova, M.; Atanassova, S.; Atanasov, V.; Grozeva, N. Content of Polyphenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Potential of Some Bulgarian Red Grape Varieties and Red Wines, Determined by HPLC, UV, and NIR Spectroscopy. Agriculture 2020, 10, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosmetic Ingredient Database (CosIng). Available online: www.ec.europa.eu (accessed on 19 March 2023).
- Zeghad, N.; Ahmed, E.; Belkhiri, A.; Heyden, Y.V.; Demeyer, K. Antioxidant activity of Vitis vinifera, Punica granatum, Citrus aurantium and Opuntia ficus indica fruits cultivated in Algeria. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.-S.; Chen, H.-J.; Huang, J.-P.; Lee, P.-C.; Tsai, C.-R.; Hsu, T.-F.; Huang, W.-Y. Kinetics of Tyrosinase Inhibitory Activity Using Vitis vinifera Leaf Extracts. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 5232680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Letsiou, S.; Kapazoglou, A.; Tsaftaris, A. Transcriptional and epigenetic effects of Vitis vinifera L. leaf extract on UV-stressed human dermal fibroblasts. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 48, 5763–5772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirtualny Atlas Roślin: Winorośl Właściwa. Available online: https://atlas.roslin.pl/plant/8227 (accessed on 19 March 2023).
- World Flora online (WFO): Vitis vinifera. Available online: http://www.efloras.org (accessed on 19 March 2023).
- Arroyo-García, R.; Ruiz-García, L.; Bolling, L.; Ocete, R.; López, M.A.; Arnold, C.; Ergul, A.; Söylemezoğlu, G.; Uzun, H.I.; Cabello, F.; et al. Multiple origins of cultivated grapevine (Vitis vinifera L. ssp. sativa) based on chloroplast DNA polymorphisms. Mol. Ecol. 2006, 15, 3707–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terral, J.-F.; Tabard, E.; Bouby, L.; Ivorra, S.; Pastor, T.; Figueiral, I.; Picq, S.; Chevance, J.-B.; Jung, C.; Fabre, L.; et al. Evolution and history of grapevine (Vitis vinifera) under domestication: New morphometric perspectives to understand seed domestication syndrome and reveal origins of ancient European cultivars. Ann. Bot. 2010, 105, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacilieri, R.; Lacombe, T.; Le Cunff, L.; Di Vecchi-Staraz, M.; Laucou, V.; Genna, B.; Péros, J.-P.; This, P.; Boursiquot, J.-M. Genetic structure in cultivated grapevines is linked to geography and human selection. BMC Plant Biol. 2013, 13, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rinaldo, A.R.; Cavallini, E.; Jia, Y.; Moss, S.M.A.; McDavid, D.A.J.; Hooper, L.C.; Robinson, S.P.; Tornielli, G.B.; Zenoni, S.; Ford, C.M.; et al. A grapevine anthocyanin acyltransferase, transcriptionally regulated by VvMYBA, can produce most acylated anthocyanins present in grape skins. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 1897–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evers, M.S.; Roullier-Gall, C.; Morge, C.; Sparrow, C.; Gobert, A.; Alexandre, H. Vitamins in wine: Which, what for, and how much? Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food. Saf. 2021, 20, 2991–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, M.; Kontoudakis, N.; Canals, J.M.; García-Romero, E.; Gómez-Alonso, S.; Zamora, F.; Hermosín-Gutiérrez, I. Improved method for the extraction and chromatographic analysis on a fused-core column of ellagitannins found in oak-aged wine. Food Chem. 2017, 226, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, B.; Narbonne, J.-F.; Ribera, D.; Badouard, C.; Ravanat, J.-L. Effect of dietary fat-soluble vitamins A and E and proanthocyanidin-rich extract from grape seeds on oxidative DNA damage in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidner, S.; Rybarczyk, A.; Karamać, M.; Król, A.; Mostek, A.; Grębosz, J.; Amarowicz, R. Differences in the Phenolic Composition and Antioxidant Properties between Vitis coignetiae and Vitis vinifera Seeds Extracts. Molecules 2013, 18, 3410–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, L.P.; Morais, D.R.; Souza, N.E.; Cottica, S.M.; Boroski, M.; Visentainer, J.V. Phenolic compounds and fatty acids in different parts of Vitis labrusca and V. vinifera grapes. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 1414–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handoussa, H.; Hanafi, R.S.; El-Khatib, A.H.; Linscheid, M.W.; Mahran, L.G.; Ayoub, N.A. Computer-assisted HPLC method development using DryLab for determination of major phenolic components in Corchorus olitorius and Vitis vinifera by using HPLC-PDA-ESI-TOF- MSn. Res. Rev. J. Bot. Sci. 2017, 6, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Pantelić, M.M.; Zagorac, D.Č.D.; Ćirić, I..; Pergal, M.V.; Relić, D.J.; Todić, S.R.; Natić, M.M. Phenolic profiles, antioxidant activity and minerals in leaves of different grapevine varieties grown in Serbia. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2017, 62, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anđelković, M.; Radovanović, B.; Anđelković, A.M.; Radovanovic, V. Phenolic Compounds and Bioactivity of Healthy and Infected Grapevine Leaf Extracts from Red Varieties Merlot and Vranac (Vitis vinifera L.). Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2015, 70, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewald, P.; Delker, U.; Winterhalter, P. Quantification of stilbenoids in grapevine canes and grape cluster stems with a focus on long-term storage effects on stilbenoid concentration in grapevine canes. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavelli, V.; Torri, L.; Zeppa, G.; Fiori, L.; Spigno, G. Recovery of Winemaking By-Products. It. J. Food Sci. 2016, 28, 542–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.E.; Grao-Cruces, E.; Millan-Linares, M.C.; Montserrat de la Paz, S. Grape (Vitis vinifera L.) Seed Oil: A Functional Food from the Winemaking Industry. Foods 2020, 9, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garavaglia, J.; Markoski, M.M.; Oliveira, A.; Marcadenti, A. Grape Seed Oil Compounds: Biological and Chemical Actions for Health. Nutr. Metab. Insights 2016, 9, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tzanova, M.; Atanasov, V.; Yaneva, Z.; Ivanova, D.; Dinev, T. Selectivity of Current Extraction Techniques for Flavonoids from Plant Materials. Processes 2020, 8, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shilpi, A.; Shivhare, U.S.; Basu, S. Supercritical CO2 Extraction of Compounds with Antioxidant Activity from Fruits and Vegetables Waste—A Review. Focus Mod. Food Ind. 2013, 2, 43–62. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, A.; Dubey, K.K.; Marathe, S.J.; Singhal, R. Supercritical fluid extraction of bioactives from fruit waste and its therapeutic potential. Food Biosci. 2023, 52, 102418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenli, Y.; Bo, S.; Yaping, Z. Supercritical CO2 extraction of resveratrol and its glycoside piceid from Chinese traditional medicinal herb Polygonum cuspidatum. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2005, 85, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passos, C.P.; Silva, R.M.; Da Silva, F.A.; Coimbra, M.A.; Silva, C.M. Supercritical fluid extraction of grape seed (Vitis vinifera L.) oil. Effect of the operating conditions upon oil composition and antioxidant capacity. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 160, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santagata, R.; Ripa, M.; Genovese, A.; Ulgiati, S. Food waste recovery pathways: Challenges and opportunities for an emerging bio-based circular economy. A systematic review and an assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 286, 125490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balmus, I.-M.; Copolovici, D.; Copolovici, L.; Ciobica, A.; Gorgan, D.L. Biomolecules from Plant Wastes Potentially Relevant in the Management of Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Co-Occurring Symptomatology. Molecules 2022, 27, 2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baroi, A.M.; Popitiu, M.; Fierascu, I.; Sărdărescu, I.-D.; Fierascu, R.C. Grapevine Wastes: A Rich Source of Antioxidants and Other Biologically Active Compounds. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malinowska, M.A.; Billet, K.; Drouet, S.; Munsch, T.; Unlubayir, M.; Tungmunnithum, D.; Giglioli-Guivarc’H, N.; Hano, C.; LaNoue, A. Grape Cane Extracts as Multifunctional Rejuvenating Cosmetic Ingredient: Evaluation of Sirtuin Activity, Tyrosinase Inhibition and Bioavailability Potential. Molecules 2020, 25, 2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, C.; Richard, T.; Renouf, E.; Bisson, J.; Waffo-Téguo, P.; Bordenave, L.; Ollat, N.; Mérillon, J.-M.; Cluzet, S. Comparative analyses of stilbenoids in canes of major Vitis vinifera L. cultivars. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 11392–11399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Waffo-Téguo, P.; Jourdes, M.; Li, H.; Teissedre, P.L. First evidence of epicatechin vanillate in grape seed and red wine. Food Chem. 2018, 259, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Waffo-Téguo, P.; Paissoni, M.A.; Jourdes, M.; Teissedre, P.L. New insight into the unresolved HPLC broad peak of Cabernet Sauvignon grape seed polymeric tannins by combining CPC and Q-ToF approaches. Food Chem. 2018, 249, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivas, N.; Nonier, M.F.; Vivas de Gaulejac, N.; Absalon, C.; Bertrand, A.; Mirabel, M. Differentiation of proanthocyanidin tannins from seeds, skins and stems of grapes (Vitis vinifera) and heartwood of Quebracho (Schinopsis balansae) by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry and thioacidolysis/liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 513, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souquet, J.-M.; Cheynier, V.; Brossaud, F.; Moutounet, M. Polymeric proanthocyanidins from grape skins. Phytochemistry 1996, 43, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, P.; Mbugua, D.M.; Pell, A.N. Analysis of condensed tannins: A review. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2001, 91, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cefali, L.C.; Ataide, J.A.; Sousa, I.M.O.; Figueiredo, M.C.; Ruiz, A.L.T.G.; Foglio, M.A.; Mazzola, P.G. In vitro solar protection factor, antioxidant activity, and stability of a topical formulation containing Benitaka grape (Vitis vinifera L.) peel extract. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 2677–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangiovanni, E.; Di Lorenzo, C.; Piazza, S.; Manzoni, Y.; Brunelli, C.; Fumagalli, M.; Magnavacca, A.; Martinelli, G.; Colombo, F.; Casiraghi, A.; et al. Vitis vinifera L. Leaf Extract Inhibits In Vitro Mediators of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress Involved in Inflammatory-Based Skin Diseases. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zielonka-Brzezicka, J.; Florkowska, K.; Nowak, A.; Muzykiewicz-Szymańska, A.; Klimowicz, A. The effect of thawing on the antioxidant activity of the leaves and fruit of the grapevine (Vitis vinifera). Pomer. J. Life Sci. 2021, 67, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llobera, A. Study on the Antioxidant Activity of Grape Stems (Vitis vinifera). A Preliminary Assessment of Crude Extracts. Food Nutr. Sci. 2012, 3, 500–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chidambara Murthy, K.N.; Singh, R.P.; Jayaprakasha, G.K. Antioxidant Activities of Grape (Vitis vinifera) Pomace Extracts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 5909–5914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, U.; Shafi, A.; Majeed, H.; Akram, K.; Liu, X.; Ye, J.; Luo, Y. Grape (Vitis vinifera L.) phytochemicals and their biochemical protective mechanisms against leading pathologies. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 134762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, D.A.; Salvador, A.A.; Smânia, A., Jr.; Smânia, E.F.A.; Maraschin, M.; Ferreira, S.R.S. Antimicrobial activity and composition profile of grape (Vitis vinifera) pomace extracts obtained by supercritical fluids. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 164, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filocamo, A.; Bisignano, C.; Mandalari, G.; Navarra, M. In VitroAntimicrobial Activity and Effect on Biofilm Production of a White Grape Juice (Vitis vinifera) Extract. Evid. -Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 856243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yadav, D.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, P.; Mishra, D. Antimicrobial properties of black grape (Vitis vinifera L.) peel extracts against antibiotic-resistant pathogenic bacteria and toxin producing molds. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2015, 47, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chopra, A.; Geetha, R.V. In vitro Anti-inflammatory Activity of Vitis vinifera Seed Extract Using Albumin Denaturation Assay. Plant Cell Biotechnol. Mol. Biol. 2020, 21, 33–37. [Google Scholar]
- PhytoCellTech™. Available online: https://www.phytocelltec.ch/en/ (accessed on 19 March 2023).
- Bonello, M.; Gašić, U.; Tešić, Ž.; Attard, E. Production of Stilbenes in Callus Cultures of the Maltese Indigenous Grapevine Variety, Ġellewża. Molecules 2019, 24, 2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mewis, I.; Smetanska, I.M.; Müller, C.T.; Ulrichs, C. Specific Polyphenolic Compounds in Cell Culture of Vitis vinifera L. cv. Gamay Fréaux. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2011, 164, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardid-Ruiz, A.; Harazin, A.; Barna, L.; Walter, F.R.; Bladé, C.; Suárez, M.; Deli, M.A.; Aragonès, G. The effects of Vitis vinifera L. phenolic compounds on a blood-brain barrier culture model: Expression of leptin receptors and protection against cytokine-induced damage. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 247, 112253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Plant Part | Compounds | References |
|---|---|---|
| Fruits | Anthocyanins: cyanidin 3-O-(6″-p-coumaroyl-glucoside), cyanidin 3-O-glucoside, delphinidin 3-O-(6″-acetyl-glucoside), delphinidin 3-O-glucoside, malvidin 3-O-(6″-acetyl-glucoside), malvidin 3-O-(6″-p-coumaroyl-glucoside), malvidin 3-O-glucoside, peonidin 3-O-(6″-p-coumaroyl-glucoside), peonidin 3-O-glucoside, petunidin 3-O-(6″-p-coumaroyl-glucoside), petunidin 3-O-glucoside Ellagitannins: castalagin, vescalagin, grandinin, roburin A, roburin B, roburin C, roburin D, roburin E, and acutissimins A and B Flavan-3-ols: procyanidin B1, procyanidin B2, procyanidin B3, procyanidin B4, procyanidin B1 3-O-gallate, procyanidin B2 3-O-gallate, procyanidin C1, procyanidin T2 Flavonols: quercetin 3-O-galactoside, quercetin 3-O-glucuronide, quercetin 3-O-rutinoside, isorhamnetin 3-O-glucoside, kaempferol 3-O-galactoside, kaempferol 3-O-glucoside Hydroxycinnamic acids: caffeoyl tartaric acid, cis-caffeoyl tartaric acid, trans-caffeoyl tartaric acid, p-coumaroyl tartaric acid, trans-p-coumaroyl tartaric acid Stilbenoids: monomeric (resveratrol, trans-resveratrol, resveratrol-3-O-glucoside, trans-resveratrol-3-O-glucoside, piceatannol) Vitamins and minerals: vitamin C, vitamin B1, vitamin B2, vitamin B3, vitamin B5, vitamin B6, vitamin B7, vitamin B9, myo-inositol; potassium (K), sulfur (S), copper (Cu), phosphorus (P), magnesium (Mg), iron (Fe), calcium (Ca), manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn), boron (B) | [5,16,29,30,31] |
| Skins | Anthocyanins: delphinidin-3,5-diglucoside, delphinidin-3-monoglucoside, malvidin-3,5-diglucoside, cyanidin-3-monoglucoside, petunidin-3-monoglucoside, pelargonidin-3-monoglucoside, peonidin-3-monoglucoside, malvidin-3-monoglucoside, delphinidin-3-(6-acetyl)-glucoside, cyanidin-3-(6-acetyl)-glucoside, petunidin-3-(6-acetyl)-glucoside, delphinidin-3-(6-caffeoyl)-glucoside, cyanidin-3-(6-caffeoyl)-glucoside, peonidin-3-(6-caffeoyl)-glucoside, malvidin-3-(6-acetyl)-glucoside, petunidin-3-(6-caffeoyl)-glucoside, delphinidin-3-(6-coumaroyl)-glucoside, peonidin-3-(6-caffeoyl)-glucoside, malvidin-3-(6-caffeoyl)-glucoside, cyanidin-3-(6-coumaroyl)-glucoside, petunidin-3-(6-coumaroyl)-glucoside, peonidin-3-(6-coumaroyl)-glucoside, malvidin-3-(6-coumaroyl)-glucoside Fatty acids: linoleic acid, palmitic acid, myristic acid, cis-7-hexadecenoic fatty acid, stearic acid, oleic acid, α-linolenic acid, arachidic acid, behenic acid, lignoceric acid, saturated fatty acids, monounsaturated fatty acids, polyunsaturated fatty acid Flavan-3-ols: procyanidin B1, procyanidin B2, procyanidin B3, procyanidin B4, procyanidin B1 3-O-gallate, procyanidin B2 3-O-gallate, procyanidin C1, procyanidin T2 Minerals: potassium (K), sulfur (S), copper (Cu), phosphorus (P), magnesium (Mg), iron (Fe), calcium (Ca), manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn), boron (B) | |
| Seeds | Carboxylic acids: primaric acid, p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid Fatty acids: myristic acid, palmitic acid, cis-7-hexadecenoic fatty acid, margaric acid, stearic acid, oleic acid, linoleic acid, α-linolenic acid, arachidic acid, behenic acid, saturated fatty acids, monounsaturated fatty acids, polyunsaturated fatty acid Flavan-3-ols: procyanidin B1, procyanidin B2, procyanidin B3, procyanidin B4, procyanidin B1 3-O-gallate, procyanidin B2 3-O-gallate, procyanidin C1, procyanidin C2, epicatechin, catechin Flavonols: quercetin, quercetin-3-β-D-glucoside, quercitrin, myricetin Hydroxybenzoic acids: gallic acid Hydroxycinnamic acids: caffeic acid, coumaric acid, ferulic acid, fertaric acid Stilbenoids: monomeric–trans-resveratrol, dimeric–trans-ε-viniferin Vitamins and minerals: vitamin A, vitamin E; potassium (K), sulfur (S), copper (Cu), phosphorus (P), magnesium (Mg), iron (Fe), calcium (Ca), manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn), boron (B) | [5,16,32,33,34] |
| Leaves | Anthocyanins: delphinidin-3-O-glucoside, cyanidin-3-O-glucoside, petunidin-3-O-glucoside, peonidin-3-O-glucoside, malvidin-3-O-glucoside, petunidin-3-(6-O-acetyl)glucoside, peonidin-3-(6-O-acetyl)glucoside, malvidin-3-(6-O-acetyl)glucoside, cyanidin-3-(6-O-coumaroyl)glucoside, petunidin-3-(6-O-coumaroyl)glucoside, peonidin-3-(6-O-coumaroyl)glucoside, malvidin-3-(6-O-coumaroyl)glucoside Coumarins: aesculin, fraxin, aesculutin, umbelliferone Flavan-3-ols: gallocatechin, catechin, procyanidin A1, procyanidin B1, procyanidin B2, procyanidin B3, procyanidin B4, epicatechin, epigallocatechin, epigallocatechin gallate, gallocatechin gallate, epicatechin gallate, catechin gallate Flavonols: quercetin, quercetin-3-O-glucoside, kaempferol, myricetin, myricetin-3-O-galactoside, myricetin-3-O-glucuronide, myricetin-3-O-glucoside, quercetin-3-O-rutinoside, quercetin-3-O-galactoside, quercetin-3-O-glucoside, quercetin-3-O-glucuronide, myricetin-3-O-rhamnoside, quercetin-3-O-rhamnoside, kaempferol-3-O-galactoside, kaempferol-3-O-rutinoside, kaempferol-3-O-glucuronide, quercetin-3-(6-O-acetyl)glucoside, quercetin-3-(3-O-arabinosyl)glucoside, quercetin-3-(7-O-glucosyl)glucuronide, kaempferol-3-O-glucoside, kaempferol-3-O-xyloside, kaempferol-3-O-rhamnoside, isorhamnetin-3-O-galactoside, isorhamnetin-3-O-glucoside, quercetin-3-(6-O-rhamnosyl)galactoside, isorhamnetin-3-O-arabinose, isorhamnetin-3-O-glucuronide, isorhamnetin-3-O-rutinoside, isorhamnetin-3-(4-O-rhamnosyl)rutinoside, kaempferol-3-(6-O-coumaroyl)glucoside, kaempferol-3(7-O-glucosyl)galactoside, diquercetin-3-(3-O-glucosyl)glucuronide Flavones: apigenin-7-O-glucoside, luteolin-7-O-glucoside Flavanones: taxifolin, naringenin, hesperetin, eriodictyol-7-O-glucoside, naringenin-7-O-glucoside Hydroxybenzoic acids: quinic acid, gallic acid, vanilic acid, syringic acid, protocatechuic acid, p-hydroxybenzoic acid, gentisic acid, γ-resorcylic acid, ellagic acid Hydroxycinnamic acids: caftaric acid, caffeic acid, fertaric acid, 1-O-sinapoyl-β-D-glucose, 1-O-(4-Coumaroyl)-glucose, 1-caffeoyl-β-D-glucose, ferulic acid pentose, coutaric acid, chlorogenic acid, p-coumaric acid, ferulic acid, sinapic acid, cinnamic acid Dihydrochalcones: phlorizin Stilbenoids: monomeric (trans-astringin, trans-resveratroloside, cis-resveratrol-O-glucoside, trans-piceid, cis-astringin, trans-piceatannol, cis-resveratroloside, cis-piceid, trans-isorhapontin, trans-resveratrol, 2,4,6-trihydroxyphenanthrene-2-O-glucoside, trans-isorhapontigenin, trans-pinostilbene-4-O-glucoside, cis-resveratrol, trans-pterostilbene, cis-pterostilbene, cis-isorhapontigenin, trans-rhaponticin, trans-pinostilbene, cis-pinostilbene, dimeric (restrytisol A, pallidol, ampelopsin D, quadrangularin A, (+)-cis-ε-viniferin, (+)-trans-ε-viniferin, trans-ω-viniferin, cis-ω-viniferin, trans-δ-viniferin, cis-δ-viniferin, trans-ε-viniferin derivative (dimethylated), trans-δ-viniferin derivative (dimethylated)), trimeric (ampelopsin B, trans-miyabenol C, cis-miyabenol C, davidiol A, α-viniferin), tetrameric (isohopeaphenol, ampelopsin H, vaticanol C-like isomer, hopeaphenol) | [5,35,36,37] |
| Stems/canes | Anthocyanins: malvidin-3-O-glucoside, malvidin-3-(6-O-caffeoyl) glucoside, malvidin-3-O-rutinoside Flavan-3-ols: gallocatechin, epicatechin, catechin, procyanidin B1, procyanidin B2, procyanidin B3, procyanidin B4, procyanidin B1 3-O-gallate, procyanidin B2 3-O-gallate, procyanidin A1, procyanidin C1, procyanidin T2, epigallocatechin, prodelphinidin A-type, procyanidin dimer gallate, epicatechin gallate, catechin gallate Flavonols: quercetin, quercetin-3-O-glucoside, kaempferol, quercetin-3-O-rutinoside, quercetin-3-O-galactoside, quercetin-3-O-glucuronide, quercetin-3-O-rhamnoside, kaempferol-3-O-rutinoside, quercetin-3-O-arabinose, kaempferol-3-O-glucoside, dihydrokaempferol-3-O-rhamnoside, isorhamnetin-3-(6-O-feruloyl) glucoside Flavanones: taxifolin-O-pentoside, taxifolin-3-O-glucoside, taxifolin-3-O-rhamnoside Hydroxybenzoic acids: gallic acid, syringic acid, protocatechuic acid, p-hydroxybenzoic acid, vanillic acid, ellagic acid Hydroxycinnamic acids: caftaric acid, caffeic acid, ferulic acid, 1-O-(4-coumaroyl)-glucose, 1-caffeoyl-β-D-glucose, ferulic acid pentose, chicoric acid, p-coumaric acid, coutaric acid, sinapic acid Stilbenoids: monomeric (trans-astringin, trans-resveratrol, trans-resveratroloside, trans-resveratrol-2-C-glucoside, trans-resveratrol-10-C-glucoside, trans-resveratrol-O-glucoside, cis-resveratrol-O-glucoside, trans-piceid, cis-piceid, trans-piceatannol, trans-isorhapontigenin, trans-pterostilbene, cis-pterostilbene) dimeric (leachianol G, leachianol F, restrytisol A, pallidol, caraphenol B, quadrangularin A, (+)-trans-ε-viniferin, viniferifuran, diptoindonesin A, trans-δ-viniferin, trans-ω-viniferin, trans-scirpusin A, maackin A, malibatol A, viniferal, vitisinol, C, vitisinol E, ampelopsin A, ampelopsin D, ampelopsin F), trimeric (trans-miyabenol C, cis-miyabenol C, davidiol A, α-viniferin, ampelopsin B, ampelopsin C, ampelopsin E, viniferol D), tetrameric (hopeaphenol, isohopeaphenol, ampelopsin H, vitisifuran A-B, vitisin A (r2-viniferin), vitisin B (r-viniferin), vitisin C, viniferol A, viniferol B, viniferol C), hexameric (viniphenol A) | [5,38] |
| Roots | Stilbenoids: monomeric (trans-resveratrol, trans-picaetannol, trans-piceid, cis-piceid), dimeric (vitisinol B, viniferether A-B, ampelopsin A, pallidol, (+)-trans-ε-viniferin, trans-ω-viniferin, trans-δ-viniferin), trimeric (trans-miyabenol C, ampelopsin C, ampelopsin E, viniferol D) tetrameric (vitisin A-B, hopeaphenol, isohopeaphenol, viniferol E, wilsonol C, heyneanol A, stenophellol C) | [5] |
| Compound Group/ Extracted Raw Material | Extraction Conditions/ Purification | Analysis Method | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ellagitannins (castalagin, vescalagin, grandinin, roburin A, roburin B, roburin C, roburin D, roburin E and acutissimins A and B)/oak-aged wine | Solid phase extraction (SPE)/a combined elution with methanol and ethyl acetate (1:1 v/v) | HPLC-DAD-ESI-MS/MS | [31] |
| Oligomeric tannins (epicatechin vanillate)/grape seed and wine | Lyophilisation/extraction with acetone/H2O (80:20 v/v)/evaporation/liquid-liquid crude fractionation: solubilisation in H2O, extraction with chloroform/extraction with ethyl acetate | UHPLC-HRMS system equipped with an ESI-Q-TOF MS | [52,53] |
| Proanthocyanidin tannins (catechin, epicatechin for procyanidins Tannins; gallocatechin, epigallocatechin for prodelphinidins tannins)/grape seeds, skins and stems | Lyophilisation and extraction with ethanol/acidified H2O (1:1; v/v) under nitrogen, then with chloroform or extraction with acetone/H2O (7:3, v/v) and lyophilisation | Bate–Smith reaction (total content of proanthocyanidins)/thioacidolysis/HPLC-ESI-MS/MALDI-ToF-MS | [54] |
| Condensed tannins/V. vinifera skins | Freezing, skin separation, extraction with acetone/H2O (3:2 v/v), concentration, dissolving in ethanol/H2O/trifluoroacetic acid (11:9:0.001) for analysis, the acidolysis of extracts: hydrolysis with 5% solution of toluene-alpha-thiol in methanol containing 0.2 M hydrochloric acid, 60 °C, 10 min. | LC-MS, NMR | [55,56] |
| Stilbenoids/grape canes | Extraction in acetone/H2O mixture (6:4) overnight at room temperature, and the dry extract suspension in methanol/H2O (1:1) | LC-MS, (A) H2O 0.1% formic acid and (B) acetonitrile 0.1% formic acid NMR | [51] |
| INCI Name | Indications |
|---|---|
| Vitis vinifera | Skin protecting, fragrance |
| Vitis vinifera bud extract | Skin conditioning |
| Vitis vinifera callus culture-conditioned media | Antioxidant, skin conditioning |
| Vitis vinifera callus extract | Skin protecting |
| Vitis vinifera callus powder | Skin conditioning |
| Vitis vinifera flower cell extract | Fragrance, skin protecting |
| Vitis vinifera flower extract | Fragrance, skin conditioning, emollient |
| Vitis vinifera fruit cell extract | Skin conditioning |
| Vitis vinifera fruit extract | Skin conditioning |
| Vitis vinifera fruit juice ferment less oil | Fragrance, perfuming |
| Vitis vinifera fruit meristem cell culture | Antioxidant, skin protecting |
| Vitis vinifera fruit powder | Antioxidant, skin conditioning |
| Vitis vinifera fruit water | Skin conditioning |
| Vitis vinifera juice | Antioxidant, skin conditioning |
| Vitis vinifera juice extract | Antioxidant, skin conditioning |
| Vitis vinifera leaf cera | Skin protecting |
| Vitis vinifera leaf extract | Skin conditioning |
| Vitis vinifera leaf oil | Fragrance |
| Vitis vinifera leaf water | Skin conditioning |
| Vitis vinifera leaf wax | Skin protecting |
| Vitis vinifera leaf/seed/skin extract | Antioxidant |
| Vitis vinifera root extract | Skin conditioning |
| Vitis vinifera seed | Skin conditioning |
| Vitis vinifera seed extract | Anti-seborrheic, antimicrobial, antioxidant, oral care, skin protecting, UV absorber |
| Vitis vinifera seed oil | Skin conditioning-emollient |
| Vitis vinifera seed powder | Skin conditioning-emollient |
| Vitis vinifera seed/skin/stem extract | Antioxidant |
| Vitis vinifera shoot extract | Antioxidant, skin conditioning |
| Vitis vinifera skin extract | Antioxidant |
| Vitis vinifera skin powder | Antioxidant, skin conditioning |
| Vitis vinifera stem extract | Skin conditioning, skin protecting |
| Vitis vinifera vine extract | Skin conditioning |
| Vitis vinifera vine sap | Skin conditioning |
| Manufacturer, Country | Trade Name, Form | INCI Name | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Panier des Sens (France) www.panierdessens.com | Active firming cream | Vitis vinifera (grape) seed oil, Vitis vinifera (grape) fruit extract, Vitis vinifera leaf extract | Moisturises, has firming properties, reduces the appearance of orange skin |
| Panier des Sens (France) www.panierdessens.com | Exfoliating Soap | Vitis vinifera (grape) seed oil, Vitis vinifera fruit extract, Vitis vinifera leaf extract, Vitis vinifera seed powder | Cleanses, exfoliates, smoothes skin |
| Caudalie (France) www.caudalie.com | Toner, Grape Water | Vitis vinifera (grape) fruit water, Vitis vinifera (grape) juice | Smoothes, refreshes, moisturises, prevents redness |
| Apivita (Greece) www.apivita.com | Face Mask Line Reducing with Grape | Vitis vinifera (Grape) seed oil | Regenerates, moisturises, reduces wrinkles, soothes irritations |
| Korres (Greece) www.korres.com | Red Grape Sheer Glow Daily Sunscreen Face Cream | Vitis vinifera fruit extract Korres Santorini grape fruit extract, Vitis vinifera grape fruit cell extract | Protects against photoaging, reduces the visibility of discolourations and wrinkles |
| FarmStay (South Korea) en.fscos.com | Grape stem cell whitening lifting essence | Vitis vinifera (grape) callus culture extract | Inhibits the process of ageing, brightens, regenerates, firms, protects against UV |
| Organique (Poland) www.organique.pl | Peeling Intense Anti-ageing/Grape | Vitis vinifera (Grape) Seed Oil, Grape Seed Powder (Vitis vinifera) | Protects the skin from ageing, exfoliates, stimulates microcirculation, stimulates the penetration of active ingredients |
| Josh Rosebrook (The United States) joshrosebrook.com | Nourish Shampoo | Grape Seed oil | Gently cleanses, removes sebum excess, moisturises, softens hair, stimulates blood circulation |
| Caudalie (Paris) www.caudalie.com | Vinosource-Hydra, Grape Water Gel Moisturiser | Vitis vinifera (Grape) Fruit Water, Vitis vinifera (Grape) Juice | Moisturises, soothes irritations, strengthens the skin’s protective barrier |
| Vinoperfect Instant Brightening Moisturiser | Palmitoyl Grapevine Shoot Extract | Moisturises, brightens, prevents discolourations | |
| Vinoperfect Glycolic Peel Mask | Vitis vinifera (Grape) Seed Oil, Palmitoyl Grapevine Shoot Extract | Gently exfoliates, brightens | |
| Resveratrol Lift Serum | Grape vine Shoot Extract | Moisturises, has firming properties, brightens | |
| Die Nikolai (Austria) www.dienikolai.at | Grapeseed Intensive Serum | Vitis vinifera (Grape) Seed Oil, Vitis vinifera (Grape) Seed Extract | Eliminates free radicals, regenerates and repairs skin damage |
| Organique (Poland) www.organique.pl | Body Butter Anti-ageing/Grape | Vitis vinifera Extract, Vitis vinifera (Grape) Seed Oil | Moisturises, smoothes, nourishes, regenerates and slows down the ageing process |
| Biological Activity | Tested Plant Material | Mechanism of Action | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antimicrobial | Pomace | Inhibition against: B. cereus, S. aureus, C. albicans, C. krusei | [63] |
| Fruit juice | Inhibition against: S. aureus, L. monocytogenes, S. epidermidis, E. hirae, S. pneumoniae, B. subtilis, S. pyogenes, E. durans, S. mutans, M. catarrhali | [64] | |
| Fruit skin | E. faecallis, S. aureus, E. aerogenes | [65] | |
| Anti-inflammatory | Dried fruit | -interleukin IL-8, (NF)-κB inhibition | [7] |
| Seed | - albumin denaturation assay | [66] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sharafan, M.; Malinowska, M.A.; Ekiert, H.; Kwaśniak, B.; Sikora, E.; Szopa, A. Vitis vinifera (Vine Grape) as a Valuable Cosmetic Raw Material. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1372. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15051372
Sharafan M, Malinowska MA, Ekiert H, Kwaśniak B, Sikora E, Szopa A. Vitis vinifera (Vine Grape) as a Valuable Cosmetic Raw Material. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(5):1372. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15051372
Chicago/Turabian StyleSharafan, Marta, Magdalena A. Malinowska, Halina Ekiert, Beata Kwaśniak, Elżbieta Sikora, and Agnieszka Szopa. 2023. "Vitis vinifera (Vine Grape) as a Valuable Cosmetic Raw Material" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 5: 1372. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15051372
APA StyleSharafan, M., Malinowska, M. A., Ekiert, H., Kwaśniak, B., Sikora, E., & Szopa, A. (2023). Vitis vinifera (Vine Grape) as a Valuable Cosmetic Raw Material. Pharmaceutics, 15(5), 1372. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15051372