Relating Molecular Dynamics Simulations to Functional Activity for Gly-Rich Membranolytic Helical Kiadin Peptides
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Peptide Design and Synthesis
2.2. MD Simulations
2.3. Preparation of Liposomes
2.4. Circular Dichroism
2.5. Antimicrobial Activity
2.6. Toxicity Assays
2.7. Surface Plasmon Resonance
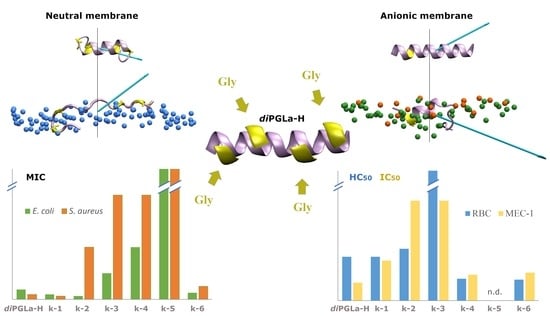
3. Results
3.1. Kiadin Peptides
3.2. Peptide–Membrane Interaction Simulations
3.3. Kiadin Structural Stability Determined by Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy
3.4. Binding to Neutral LUVs Determined Using Surface Plasmon Resonance
3.5. Antibacterial Activity
3.6. Toxicity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Zasloff, M. Antimicrobial Peptides of Multicellular Organisms. Nature 2002, 415, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasupuleti, M.; Schmidtchen, A.; Malmsten, M. Antimicrobial Peptides: Key Components of the Innate Immune System. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2012, 32, 143–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventola, C.L. The Antibiotic Resistance Crisis. Pharm. Ther. 2015, 40, 277–283. [Google Scholar]
- Rončević, T.; Puizina, J.; Tossi, A. Antimicrobial Peptides as Anti-Infective Agents in Pre-Post-Antibiotic Era? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, J.D.; Hancock, R.E. Alternative Mechanisms of Action of Cationic Antimicrobial Peptides on Bacteria. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2007, 5, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltzer, S.A.; Brown, M.H. Antimicrobial Peptides: Promising Alternatives to Conventional Antibiotics. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 20, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-C.; Park, Y.; Hahm, K.-S. The Role of Antimicrobial Peptides in Preventing Multidrug-Resistant Bacterial Infections and Biofilm Formation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 5971–5992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batoni, G.; Maisetta, G.; Esin, S. Antimicrobial Peptides and Their Interaction with Biofilms of Medically Relevant Bacteria. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Biomembr. 2016, 1858, 1044–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, S.; Ghimire, J.; Wu, E.; Wimley, W.C. Mechanistic Landscape of Membrane-Permeabilizing Peptides. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 6040–6085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, D.; Leontiadou, H.; Mark, A.E.; Marrink, S.-J. Toroidal Pores Formed by Antimicrobial Peptides Show Significant Disorder. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Biomembr. 2008, 1778, 2308–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeaman, M.R.; Yount, N.Y. Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Peptide Action and Resistance. Pharmacol. Rev. 2003, 55, 27–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brogden, K.A. Antimicrobial Peptides: Pore Formers or Metabolic Inhibitors in Bacteria? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amos, S.-B.T.A.; Vermeer, L.S.; Ferguson, P.M.; Kozlowska, J.; Davy, M.; Bui, T.T.; Drake, A.F.; Lorenz, C.D.; Mason, A.J. Antimicrobial Peptide Potency Is Facilitated by Greater Conformational Flexibility When Binding to Gram-Negative Bacterial Inner Membranes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelezetsky, I.; Tossi, A. Alpha-Helical Antimicrobial Peptides—Using a Sequence Template to Guide Structure–Activity Relationship Studies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Biomembr. 2006, 1758, 1436–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juretić, D.; Sonavane, Y.; Ilić, N.; Gajski, G.; Goić-Barišić, I.; Tonkić, M.; Kozic, M.; Maravić, A.; Pellay, F.-X.; Zoranić, L. Designed Peptide with a Flexible Central Motif from Ranatuerins Adapts Its Conformation to Bacterial Membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Biomembr. 2018, 1860, 2655–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevcsik, E.; Pabst, G.; Jilek, A.; Lohner, K. How Lipids Influence the Mode of Action of Membrane-Active Peptides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Biomembr. 2007, 1768, 2586–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malanovic, N.; Lohner, K. Antimicrobial Peptides Targeting Gram-Positive Bacteria. Pharmaceuticals 2016, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrink, S.J.; Corradi, V.; Souza, P.C.T.; Ingólfsson, H.I.; Tieleman, D.P.; Sansom, M.S.P. Computational Modeling of Realistic Cell Membranes. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 6184–6226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacor, S.; Guida, F.; Xhindoli, D.; Benincasa, M.; Gennaro, R.; Tossi, A. Effect of Targeted Minimal Sequence Variations on the Structure and Biological Activities of the Human Cathelicidin LL-37. Pept. Sci. 2018, 110, e24087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fjell, C.D.; Hiss, J.A.; Hancock, R.E.W.; Schneider, G. Designing Antimicrobial Peptides: Form Follows Function. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juretić, D.; Vukičević, D.; Ilić, N.; Antcheva, N.; Tossi, A. Computational Design of Highly Selective Antimicrobial Peptides. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2009, 49, 2873–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rončević, T.; Vukičević, D.; Krce, L.; Benincasa, M.; Aviani, I.; Maravić, A.; Tossi, A. Selection and Redesign for High Selectivity of Membrane-Active Antimicrobial Peptides from a Dedicated Sequence/Function Database. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Biomembr. 2019, 1861, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roncevic, T.; Vukicevic, D.; Ilic, N.; Krce, L.; Gajski, G.; Tonkic, M.; Goic-Barisic, I.; Zoranic, L.; Sonavane, Y.; Benincasa, M.; et al. Antibacterial Activity Affected by the Conformational Flexibility in Glycine-Lysine-Based Alpha-Helical Antimicrobial Peptides. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 2924–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roncevic, T.; Gajski, G.; Ilic, N.; Goic-Barisic, I.; Tonkic, M.; Zoranic, L.; Simunic, J.; Benincasa, M.; Mijakovic, M.; Tossi, A.; et al. PGLa-H Tandem-Repeat Peptides Active against Multidrug Resistant Clinical Bacterial Isolates. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2017, 1859, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sani, M.-A.; Saenger, C.; Juretic, D.; Separovic, F. Glycine Substitution Reduces Antimicrobial Activity and Helical Stretch of DiPGLa-H in Lipid Micelles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2017, 121, 4817–4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juretić, D.; Vukičević, D.; Petrov, D.; Novković, M.; Bojović, V.; Lučić, B.; Ilić, N.; Tossi, A. Knowledge-Based Computational Methods for Identifying or Designing Novel, Non-Homologous Antimicrobial Peptides. Eur. Biophys. J. 2011, 40, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamech, N.; Vukičević, D.; Ladram, A.; Piesse, C.; Vasseur, J.; Bojović, V.; Simunić, J.; Juretić, D. Improving the Selectivity of Antimicrobial Peptides from Anuran Skin. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 3341–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuipers, B.J.H.; Gruppen, H. Prediction of Molar Extinction Coefficients of Proteins and Peptides Using UV Absorption of the Constituent Amino Acids at 214 Nm To Enable Quantitative Reverse Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography−Mass Spectrometry Analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 5445–5451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhang, Y. Ab Initio Protein Structure Assembly Using Continuous Structure Fragments and Optimized Knowledge-Based Force Field. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2012, 80, 1715–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhang, Y. Toward Optimal Fragment Generations for Ab Initio Protein Structure Assembly. Proteins 2013, 81, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Páll, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS: High Performance Molecular Simulations through Multi-Level Parallelism from Laptops to Supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1–2, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oostenbrink, C.; Villa, A.; Mark, A.E.; Gunsteren, W.F.V. A Biomolecular Force Field Based on the Free Enthalpy of Hydration and Solvation: The GROMOS Force-Field Parameter Sets 53A5 and 53A6. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1656–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poger, D.; Gunsteren, W.F.V.; Mark, A.E. A New Force Field for Simulating Phosphatidylcholine Bilayers. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, N.; Eichenberger, A.P.; Choutko, A.; Riniker, S.; Winger, M.; Mark, A.E.; van Gunsteren, W.F. Definition and Testing of the GROMOS Force-Field Versions 54A7 and 54B7. Eur. Biophys. J. 2011, 40, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piggot, T.J.; Holdbrook, D.A.; Khalid, S. Electroporation of the E. Coli and S. Aureus Membranes: Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Complex Bacterial Membranes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 13381–13388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, I.; Kastenholz, M.; Lins, R.D.; Oostenbrink, C.; Schuler, L.D.; Tieleman, D.P.; van Gunsteren, W.F. A Consistent Potential Energy Parameter Set for Lipids: Dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine as a Benchmark of the GROMOS96 45A3 Force Field. Eur. Biophys. J. 2003, 32, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukol, A. Lipid Models for United-Atom Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Proteins. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2009, 5, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, H.J.C.; Postma, J.P.M.; van Gunsteren, W.F.; Hermans, J. Interaction Models for Water in Relation to Protein Hydration. In Intermolecular Forces; Pullman, B., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1981; Volume 14, pp. 331–342. ISBN 978-90-481-8368-5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Róg, T.; Gurtovenko, A.A.; Vattulainen, I.; Karttunen, M. Atomic-Scale Structure and Electrostatics of Anionic Palmitoyloleoylphosphatidylglycerol Lipid Bilayers with Na+ Counterions. Biophys. J. 2007, 92, 1114–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domański, J.; Stansfeld, P.J.; Sansom, M.S.P.; Beckstein, O. Lipidbook: A Public Repository for Force-Field Parameters Used in Membrane Simulations. J. Membr. Biol. 2010, 236, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, C.J.; Hub, J.S. MemGen: A General Web Server for the Setup of Lipid Membrane Simulation Systems. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2897–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrinello, M.; Rahman, A. Polymorphic Transitions in Single Crystals: A New Molecular Dynamics Method. J. Appl. Phys. 1981, 52, 7182–7190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, H.J.C.; Postma, J.P.M.; van Gunsteren, W.F.; DiNola, A.; Haak, J.R. Molecular Dynamics with Coupling to an External Bath. J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 81, 3684–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, B.; Bekker, H.; Berendsen, H.J.C.; Fraaije, J.G.E.M. LINCS: A Linear Constraint Solver for Molecular Simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 1997, 18, 1463–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essmann, U.; Perera, L.; Berkowitz, M.L.; Darden, T.; Lee, H.; Pedersen, L.G. A Smooth Particle Mesh Ewald Method. J. Chem. Phys. 1995, 103, 8577–8593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabsch, W.; Sander, C. Dictionary of Protein Secondary Structure: Pattern Recognition of Hydrogen-Bonded and Geometrical Features. Biopolymers 1983, 22, 2577–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautier, R.; Douguet, D.; Antonny, B.; Drin, G. HELIQUEST: A Web Server to Screen Sequences with Specific α-Helical Properties. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 2101–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reißer, S.; Strandberg, E.; Steinbrecher, T.; Ulrich, A.S. 3D Hydrophobic Moment Vectors as a Tool to Characterize the Surface Polarity of Amphiphilic Peptides. Biophys. J. 2014, 106, 2385–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual Molecular Dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgera, F.; Vaccari, L.; Antcheva, N.; Scaini, D.; Pacor, S.; Tossi, A. Primate Cathelicidin Orthologues Display Different Structures and Membrane Interactions. Biochem. J. 2009, 417, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tossi, A.; Sandri, L.; Giangaspero, A. Amphipathic, α-Helical Antimicrobial Peptides. Pept. Sci. 2000, 55, 4–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-H.; Yang, J.T.; Chau, K.H. Determination of the Helix and β Form of Proteins in Aqueous Solution by Circular Dichroism. Biochemistry 1974, 13, 3350–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters. Version 7.1. 2017. Available online: http://www.eucast.org (accessed on 23 October 2017).
- Stacchini, A.; Aragno, M.; Vallario, A.; Alfarano, A.; Circosta, P.; Gottardi, D.; Faldella, A.; Rege-Cambrin, G.; Thunberg, U.; Nilsson, K.; et al. MEC1 and MEC2: Two New Cell Lines Derived from B-Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia in Prolymphocytoid Transformation. Leuk. Res. 1999, 23, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dereani, S.; Macor, P.; D’Agaro, T.; Mezzaroba, N.; Dal-Bo, M.; Capolla, S.; Zucchetto, A.; Tissino, E.; Del Poeta, G.; Zorzet, S.; et al. Potential Therapeutic Role of AntagomiR17 for the Treatment of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2014, 7, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marson, D.; Guida, F.; Şologan, M.; Boccardo, S.; Pengo, P.; Perissinotto, F.; Iacuzzi, V.; Pellizzoni, E.; Polizzi, S.; Casalis, L.; et al. Mixed Fluorinated/Hydrogenated Self-Assembled Monolayer-Protected Gold Nanoparticles: In Silico and In Vitro Behavior. Small 2019, 15, 1900323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderluh, G.; Beseničar, M.; Kladnik, A.; Lakey, J.H.; Maček, P. Properties of Nonfused Liposomes Immobilized on an L1 Biacore Chip and Their Permeabilization by a Eukaryotic Pore-Forming Toxin. Anal. Biochem. 2005, 344, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulmschneider, J.P.; Ulmschneider, M.B. Molecular Dynamics Simulations Are Redefining Our View of Peptides Interacting with Biological Membranes. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 1106–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, T.; Wei, D.; Strandberg, E.; Ulrich, A.S.; Ulmschneider, J.P. How Reliable Are Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Membrane Active Antimicrobial Peptides? Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Biomembr. 2014, 1838, 2280–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelezetsky, I.; Pag, U.; Sahl, H.-G.; Tossi, A. Tuning the Biological Properties of Amphipathic α-Helical Antimicrobial Peptides: Rational Use of Minimal Amino Acid Substitutions. Peptides 2005, 26, 2368–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilić, N.; Novković, M.; Guida, F.; Xhindoli, D.; Benincasa, M.; Tossi, A.; Juretić, D. Selective Antimicrobial Activity and Mode of Action of Adepantins, Glycine-Rich Peptide Antibiotics Based on Anuran Antimicrobial Peptide Sequences. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Biomembr. 2013, 1828, 1004–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rončević, T.; Gerdol, M.; Mardirossian, M.; Maleš, M.; Cvjetan, S.; Benincasa, M.; Maravić, A.; Gajski, G.; Krce, L.; Aviani, I.; et al. Anisaxins, Helical Antimicrobial Peptides from Marine Parasites, Kill Resistant Bacteria by Lipid Extraction and Membrane Disruption. Acta Biomater. 2022, 146, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Melo, M.C.; Berglund, N.; Khan, A.; de la Fuente-Nunez, C.; Ulmschneider, J.P.; Ulmschneider, M.B. Understanding and Modelling the Interactions of Peptides with Membranes: From Partitioning to Self-Assembly. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2020, 61, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aronica, P.G.A.; Reid, L.M.; Desai, N.; Li, J.; Fox, S.J.; Yadahalli, S.; Essex, J.W.; Verma, C.S. Computational Methods and Tools in Antimicrobial Peptide Research. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 3172–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strandberg, E.; Bentz, D.; Wadhwani, P.; Bürck, J.; Ulrich, A.S. Terminal Charges Modulate the Pore Forming Activity of Cationic Amphipathic Helices. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Biomembr. 2020, 1862, 183243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Peptide | Sequence a | q b | H c | 2D-HM d | 3D-HM e (kTÅ/e) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simulation Time 0 ns | Simulation Time 300 ns | ||||||||
| H2O | DPLC | PE:PG | |||||||
| case1 | case2 | case1 | case2 | ||||||
| diPGLa-H | KIAKVALKALKIAKVALKAL-NH2 | +7 | 0.44 | 0.42 | 23.5 ± 0.5 | 13.7 | 68.7 | 42.7 | 41.1 |
| kiadin-1 | KIAKVALKALKIAKGALKAL-NH2 | +7 | 0.38 | 0.48 | 18.1 ± 0.7 | 27.4 | 18.1 | 12.4 | 69.5 |
| kiadin-2 | KIAKGALKALKIAKVALKAL-NH2 | +7 | 0.38 | 0.41 | 23.2 ± 0.9 | 37.0 | 52.7 | 46.2 | 67.1 |
| kiadin-3 | KIAKGALKALKIAKGALKAL-NH2 | +7 | 0.32 | 0.46 | 23.9 ± 0.9 | 38.2 | 37.9 | 44.6 | 39.8 |
| kiadin-4 | KIGKALGKALKALGKALGKA-NH2 | +7 | 0.21 | 0.65 | 20.2 ± 0.4 | 47.8 | 34.9 | 27.8 | 25.5 |
| kiadin-5 | KIAGKAGKIAKIAGKAGKIA-NH2 | +7 | 0.16 | 0.37 | 16.3 ± 0.8 | 20.7 | 22.0 | 64.3 | 27.1 |
| kiadin-6 | KIALKALKALKALGKALKAL-NH2 | +7 | 0.40 | 0.49 | 20.2 ± 0.7 | 26.0 | 20.3 | 65.2 | 49.9 |
| Peptide | E. coli | S. aureus | RBC | MEC-1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIC a | MBC b | MIC | MBC | HC50 c | IC50 d | |
| diPGLa-H | 1.5 | 1.5 | 0.75 | 1.5 | 22 ± 2 | 9 ± 3 |
| kiadin-1 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.5–1 | 1.5 | 22 ± 2 | 20 ± 3 |
| kiadin-2 | 0.25–0.5 | 0.5–1 | 8–16 | 8–16 | 26 ± 6 | >50 |
| kiadin-3 | 4 | 16 | 16–32 | 32 | 95 ± 10 | >50 |
| kiadin-4 | 8 | 16 | 16–32 | 32 | 11 ± 1 | 13 ± 1 |
| kiadin-5 | >64 | >64 | >64 | >64 | n.d | n.d. |
| kiadin-6 | 1–2 | 2–4 | 4 | 4 | 10.5 ± 0.5 | 14 ± 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rončević, T.; Maleš, M.; Sonavane, Y.; Guida, F.; Pacor, S.; Tossi, A.; Zoranić, L. Relating Molecular Dynamics Simulations to Functional Activity for Gly-Rich Membranolytic Helical Kiadin Peptides. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1433. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15051433
Rončević T, Maleš M, Sonavane Y, Guida F, Pacor S, Tossi A, Zoranić L. Relating Molecular Dynamics Simulations to Functional Activity for Gly-Rich Membranolytic Helical Kiadin Peptides. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(5):1433. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15051433
Chicago/Turabian StyleRončević, Tomislav, Matko Maleš, Yogesh Sonavane, Filomena Guida, Sabrina Pacor, Alessandro Tossi, and Larisa Zoranić. 2023. "Relating Molecular Dynamics Simulations to Functional Activity for Gly-Rich Membranolytic Helical Kiadin Peptides" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 5: 1433. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15051433
APA StyleRončević, T., Maleš, M., Sonavane, Y., Guida, F., Pacor, S., Tossi, A., & Zoranić, L. (2023). Relating Molecular Dynamics Simulations to Functional Activity for Gly-Rich Membranolytic Helical Kiadin Peptides. Pharmaceutics, 15(5), 1433. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15051433