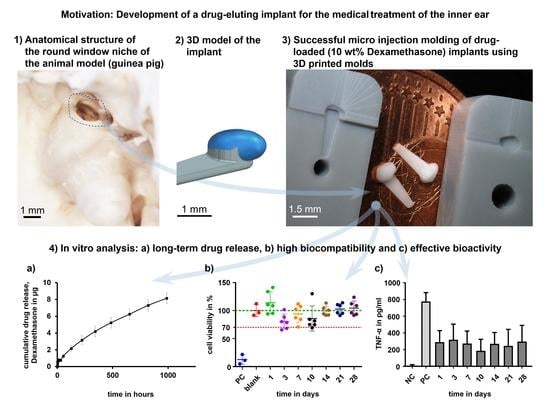
Micro Injection Molding of Drug-Loaded Round Window Niche Implants for an Animal Model Using 3D-Printed Molds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Three-Dimensional Models of Guinea Pig Round Window Niche and Mold
2.2. Rapid Tooling of Molds via Digital Light Processing
2.3. Micro Injection Molding of Drug-Loaded Implants
2.4. Drug Release
2.5. Biocompatibility
2.6. Bioefficacy
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Rapid Tooling of Molds via Digital Light Processing
3.2. Micro Injection Molding of Implant Prototypes
3.3. Drug Release
3.4. Biocompatibility and Bioefficacy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| TNF-α in pg/mL (Mean ± Standard Deviation) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 290 ± 138 | 318 ± 186 | 275 ± 148 | 188 ± 136 | 270 ± 134 | 246 ± 196 | 298 ± 192 | |
| Time point of sampling in days | 1 | 3 | 7 | 10 | 14 | 21 | 28 |
| 1 | - | ns | ns | *** | ns | ns | ns |
| 3 | - | - | ns | *** | ns | * | ns |
| 7 | - | - | - | ** | ns | ns | ns |
| 10 | - | - | - | - | * | ns | *** |
| 14 | - | - | - | - | - | ns | ns |
| 21 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ns |
| 28 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
References
- Nyberg, S.; Abbott, N.J.; Shi, X.; Steyger, P.S.; Alain, D. Delivery of therapeutics to the inner ear: The challenge of the blood-labyrinth barrier. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaao0935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borden, R.C.; Saunders, J.E.; Berryhill, W.E.; Krempl, G.A.; Thompson, D.M.; Queimado, L. Hyaluronic acid hydrogel sustains the delivery of dexamethasone across the round window membrane. Audiol. Neurootol. 2011, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulson, D.P.; Abuzeid, W.; Jiang, H.; Oe, T.; O’Malley, B.W.; Li, D. A novel controlled local drug delivery system for inner ear disease. Laryngoscope 2008, 118, 706–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matin, F.; Gao, Z.; Repp, F.; John, S.; Lenarz, T.; Scheper, V. Determination of the Round Window Niche Anatomy Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography Imaging as Preparatory Work for Individualized Drug-Releasing Implants. J. Imaging 2021, 7, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mau, R.; Schick, P.; Matin-Mann, F.; Gao, Z.; Alcacer Labrador, D.; John, S.; Repp, F.; Lenarz, T.; Weitschies, W.; Scheper, V.; et al. Digital light processing and drug stability of Dexamethasone-loaded implant prototypes for medical treatment of the inner ear. Trans. Addit. Manuf. Meets Med. Trans. AMMM 2022, 4, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plontke, S.K.; Löwenheim, H.; Mertens, J.; Engel, C.; Meisner, C.; Weidner, A.; Zimmermann, R.; Preyer, S.; Koitschev, A.; Zenner, H.-P. Randomized, double blind, placebo controlled trial on the safety and efficacy of continuous intratympanic dexamethasone delivered via a round window catheter for severe to profound sudden idiopathic sensorineural hearing loss after failure of systemic therapy. Laryngoscope 2009, 119, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdur, O.; Kayhan, F.T.; Cirik, A.A. Effectiveness of intratympanic dexamethasone for refractory sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2014, 271, 1431–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, W.-J.; Xu, J.; Yi, H.-J.; Ye, J.-Y. Clinical Analysis of Intratympanic Injection of Dexamethasone for Treating Sudden Deafness. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021, 14, 2575–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berjis, N.; Soheilipour, S.; Musavi, A.; Hashemi, S.M. Intratympanic dexamethasone injection vs methylprednisolone for the treatment of refractory sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2016, 5, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albu, S.; Nagy, A.; Doros, C.; Marceanu, L.; Cozma, S.; Musat, G.; Trabalzini, F. Treatment of Meniere’s disease with intratympanic dexamethazone plus high dosage of betahistine. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2016, 37, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atrache Al Attrache, N.; Krstulovic, C.; Pérez Guillen, V.; Morera Pérez, C.; Pérez Garrigues, H. Response Over Time of Vertigo Spells to Intratympanic Dexamethasone Treatment in Meniere’s Disease Patients. J. Int. Adv. Otol. 2016, 12, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverstein, H.; Isaacson, J.E.; Olds, M.J.; Rowan, P.T.; Rosenberg, S. Dexamethasone inner ear perfusion for the treatment of Meniere’s disease: A prospective, randomized, double-blind, crossover trial. Am. J. Otol. 1998, 19, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takeda, T.; Takeda, S.; Kakigi, A. Effects of Glucocorticoids on the Inner Ear. Front. Surg. 2020, 7, 596383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzayat, S.; El-Sherif, H.; Hegazy, H.; Gabr, T.; El-Tahan, A.-R. Tinnitus: Evaluation of Intratympanic Injection of Combined Lidocaine and Corticosteroids. ORL J. Otorhinolaryngol. Relat. Spec. 2016, 78, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bas, E.; Bohorquez, J.; Goncalves, S.; Perez, E.; Dinh, C.T.; Garnham, C.; Hessler, R.; Eshraghi, A.A.; van de Water, T.R. Electrode array-eluted dexamethasone protects against electrode insertion trauma induced hearing and hair cell losses, damage to neural elements, increases in impedance and fibrosis: A dose response study. Hear. Res. 2016, 337, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Schwieger, J.; Matin-Mann, F.; Behrens, P.; Lenarz, T.; Scheper, V. Dexamethasone for Inner Ear Therapy: Biocompatibility and Bio-Efficacy of Different Dexamethasone Formulations In Vitro. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Fernandez, C.S.; Xu, L.; Velliou, E.; Homer-Vanniasinkam, S.; Tiwari, M.K. High-resolution 3D printing for healthcare. In 3D Printing in Medicine; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 225–271. ISBN 9780323898317. [Google Scholar]
- Bahati, D.; Bricha, M.; El Mabrouk, K. Vat Photopolymerization Additive Manufacturing Technology for Bone Tissue Engineering Applications. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2023, 25, 2200859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Weng, S.; Hamel, C.M.; Montgomery, S.M.; Wu, J.; Kuang, X.; Zhou, K.; Qi, H.J. Design for the reduction of volume shrinkage-induced distortion in digital light processing 3D printing. Extrem. Mech. Lett. 2021, 48, 101403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttridge, C.; Shannon, A.; O’Sullivan, A.; O’Sullivan, K.J.; O’Sullivan, L.W. Biocompatible 3D printing resins for medical applications: A review of marketed intended use, biocompatibility certification, and post-processing guidance. Ann. 3d Print. Med. 2022, 5, 100044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.L.; Lee, J.M.; Zhou, M.; Chen, Y.-W.; Lee, K.-X.A.; Yeong, W.Y.; Shen, Y.-F. Vat polymerization-based bioprinting-process, materials, applications and regulatory challenges. Biofabrication 2020, 12, 22001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Paunović, N.; Leroux, J.-C. Challenges and Opportunities in 3D Printing of Biodegradable Medical Devices by Emerging Photopolymerization Techniques. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2109864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Xu, H.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Kormakov, S.; Wu, D.; Sun, J. Overview of Injection Molding Technology for Processing Polymers and Their Composites. ES Mater. Manuf. 2020, 8, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan-Manshadi, A.; Yu, P.; Dargusch, M.; StJohn, D.; Qian, M. Metal injection moulding of surgical tools, biomaterials and medical devices: A review. Powder Technol. 2020, 364, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giboz, J.; Copponnex, T.; Mélé, P. Microinjection molding of thermoplastic polymers: A review. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2007, 17, R96–R109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amellal, K.; Tzoganakis, C.; Penlidis, A.; Rempel, G.L. Injection molding of medical plastics: A review. Adv. Polym. Technol. 1994, 13, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Melo, L.P.; Salmoria, G.V.; Fancello, E.A.; Roesler, C.R.d.M. Effect of Injection Molding Melt Temperatures on PLGA Craniofacial Plate Properties during In Vitro Degradation. Int. J. Biomater. 2017, 2017, 1256537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zema, L.; Loreti, G.; Melocchi, A.; Maroni, A.; Gazzaniga, A. Injection Molding and its application to drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2012, 159, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dormann, B.; Decker, C.; Juettner, G. High prescision micro molding injection of 2 component liquid silicone. In Proceedings of the Annual Technical Conference-ANTEC, Conference Proceedings, Orlando, FL, USA, 2–4 April 2012; pp. 1843–1846, ISBN 9781622760831. [Google Scholar]
- Calaon, M.; Baruffi, F.; Fantoni, G.; Cirri, I.; Santochi, M.; Hansen, H.N.; Tosello, G. Functional Analysis Validation of Micro and Conventional Injection Molding Machines Performances Based on Process Precision and Accuracy for Micro Manufacturing. Micromachines 2020, 11, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Weng, C.; Deng, Z.; Sun, H.; Jiang, B. Fabrication and performance of nickel-based composite mold inserts for micro-injection molding. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 615, 156417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, A.B.; Álvarez, S.H.; Isaza, C.V.; Montealegre-Rubio, W. Analysis and Advances in Additive Manufacturing as a New Technology to Make Polymer Injection Molds for World-Class Production Systems. Polymers 2022, 14, 1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, E.; ter Horst, J.H.; Markl, D. Development of 3D printed rapid tooling for micro-injection moulding. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2021, 235, 116498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempsey, D.; McDonald, S.; Masato, D.; Barry, C. Characterization of Stereolithography Printed Soft Tooling for Micro Injection Molding. Micromachines 2020, 11, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 3D Slicer Image Computing Platform. Available online: https://www.slicer.org/ (accessed on 20 May 2023).
- Fedorov, A.; Beichel, R.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Finet, J.; Fillion-Robin, J.-C.; Pujol, S.; Bauer, C.; Jennings, D.; Fennessy, F.; Sonka, M.; et al. 3D Slicer as an image computing platform for the Quantitative Imaging Network. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 30, 1323–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LithoLabs GmbH. Product Information “Asiga PlasGRAY V2”. Available online: https://litholabs.one/en/dental/resin/model/61/asiga-plasgray-v2 (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- Avantor Inc., NuSil Technology LLM. MED-4244: Low Consistency Silicone Elastomer. Available online: https://www.avantorsciences.com/assetsvc/asset/en_US/id/29019092/contents/en_us_tds_nusimed-4244.pdf (accessed on 8 February 2023).
- Bohl, A.; Rohm, H.W.; Ceschi, P.; Paasche, G.; Hahn, A.; Barcikowski, S.; Lenarz, T.; Stöver, T.; Pau, H.-W.; Schmitz, K.-P.; et al. Development of a specially tailored local drug delivery system for the prevention of fibrosis after insertion of cochlear implants into the inner ear. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2012, 23, 2151–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matin-Mann, F.; Gao, Z.; Schwieger, J.; Ulbricht, M.; Domsta, V.; Senekowitsch, S.; Weitschies, W.; Seidlitz, A.; Doll, K.; Stiesch, M.; et al. Individualized, Additively Manufactured Drug-Releasing External Ear Canal Implant for Prevention of Postoperative Restenosis: Development, In Vitro Testing, and Proof of Concept in an Individual Curative Trial. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zink, B.; Kovács, N.K.; Kovács, J.G. Thermal analysis based method development for novel rapid tooling applications. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 108, 104297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinho, P.G.; Pouzada, A.S. Alternative materials in moulding elements of hybrid moulds: Structural integrity and tribological aspects. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 113, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, M.S.; Ashtankar, K.M.; Kuthe, A.M.; Dahake, S.W.; Mawale, M.B. Direct rapid manufacturing of molds with conformal cooling channels. RPJ 2018, 24, 1347–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mau, R.; Jüttner, G.; Gao, Z.; Matin, F.; Alcacer Labrador, D.; Repp, F.; John, S.; Scheper, V.; Lenarz, T.; Seitz, H. Micro injection molding of individualised implants using 3D printed molds manufactured via digital light processing. Curr. Dir. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 7, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mau, R.; Nazir, J.; Gao, Z.; Alcacer Labrador, D.; Repp, F.; John, S.; Lenarz, T.; Scheper, V.; Seitz, H.; Matin-Mann, F. Digital Light Processing of Round Window Niche Implant Prototypes for Implantation Studies. Curr. Dir. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 8, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, N.A.; Narasimhan, B. Mathematical models in drug delivery: How modeling has shaped the way we design new drug delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2014, 190, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, R.S.; Peppas, N.A. Present and future applications of biomaterials in controlled drug delivery systems. Biomaterials 1981, 2, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salt, A.N.; Plontke, S.K. Pharmacokinetic principles in the inner ear: Influence of drug properties on intratympanic applications. Hear. Res. 2018, 368, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; François, F.; Bourien, J.; Eybalin, M.; Lloyd, R.V.; van de Water, T.R.; Puel, J.-L.; Venail, F. Prevention of trauma-induced cochlear fibrosis using intracochlear application of anti-inflammatory and antiproliferative drugs. Neuroscience 2016, 316, 261–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domsta, V.; Seidlitz, A. 3D-Printing of Drug-Eluting Implants: An Overview of the Current Developments Described in the Literature. Molecules 2021, 26, 4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farto-Vaamonde, X.; Auriemma, G.; Aquino, R.P.; Concheiro, A.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C. Post-manufacture loading of filaments and 3D printed PLA scaffolds with prednisolone and dexamethasone for tissue regeneration applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 141, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Guo, G.; Fan, R.; Liang, J.; Deng, X.; Luo, F.; Qian, Z. PLA/F68/dexamethasone implants prepared by hot-melt extrusion for controlled release of anti-inflammatory drug to implantable medical devices: I. Preparation, characterization and hydrolytic degradation study. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 441, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés Fuentes, I.A.; Videhult Pierre, P.; Engmér Berglin, C. Improving Clinical Outcomes in Cochlear Implantation Using Glucocorticoid Therapy: A Review. Ear. Hear. 2020, 41, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledeți, I.; Bengescu, C.; Cîrcioban, D.; Vlase, G.; Vlase, T.; Tomoroga, C.; Buda, V.; Ledeți, A.; Dragomirescu, A.; Murariu, M. Solid-state stability and kinetic study of three glucocorticoid hormones: Prednisolone, prednisone and cortisone. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 141, 1053–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyoubi, S.; van Kampen, E.E.M.; Kocabas, L.I.; Parulski, C.; Lechanteur, A.; Evrard, B.; de Jager, K.; Muller, E.; Wilms, E.W.; Meulenhoff, P.W.C.; et al. 3D printed, personalized sustained release cortisol for patients with adrenal insufficiency. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 630, 122466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsen, A.J.; Cruickshanks, K.J.; Pinto, A.; Schubert, C.R.; Dalton, D.S.; Fischer, M.E.; Klein, B.E.K.; Klein, R.; Tsai, M.Y.; Tweed, T.S. Neuroprotective factors and incident hearing impairment in the epidemiology of hearing loss study. Laryngoscope 2019, 129, 2178–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, T.H.; Harris, J.P.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Vorasubin, N. Dose Effect of Intratympanic Dexamethasone for Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: 24 mg/mL Is Superior to 10 mg/mL. Otol. Neurotol. 2015, 36, 1321–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hütten, M.; Dhanasingh, A.; Hessler, R.; Stöver, T.; Esser, K.-H.; Möller, M.; Lenarz, T.; Jolly, C.; Groll, J.; Scheper, V. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of a hydrogel reservoir as a continuous drug delivery system for inner ear treatment. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connolly, T.M.; Eastwood, H.; Kel, G.; Lisnichuk, H.; Richardson, R.; O’Leary, S. Pre-operative intravenous dexamethasone prevents auditory threshold shift in a guinea pig model of cochlear implantation. Audiol. Neurootol. 2011, 16, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











| Sample of GP-RNIs | Mass in Mg |
|---|---|
| 1 | 0.92 |
| 2 | 0.83 |
| 3 | 0.83 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mau, R.; Eickner, T.; Jüttner, G.; Gao, Z.; Wei, C.; Fiedler, N.; Senz, V.; Lenarz, T.; Grabow, N.; Scheper, V.; et al. Micro Injection Molding of Drug-Loaded Round Window Niche Implants for an Animal Model Using 3D-Printed Molds. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1584. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061584
Mau R, Eickner T, Jüttner G, Gao Z, Wei C, Fiedler N, Senz V, Lenarz T, Grabow N, Scheper V, et al. Micro Injection Molding of Drug-Loaded Round Window Niche Implants for an Animal Model Using 3D-Printed Molds. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(6):1584. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061584
Chicago/Turabian StyleMau, Robert, Thomas Eickner, Gábor Jüttner, Ziwen Gao, Chunjiang Wei, Nicklas Fiedler, Volkmar Senz, Thomas Lenarz, Niels Grabow, Verena Scheper, and et al. 2023. "Micro Injection Molding of Drug-Loaded Round Window Niche Implants for an Animal Model Using 3D-Printed Molds" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 6: 1584. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061584
APA StyleMau, R., Eickner, T., Jüttner, G., Gao, Z., Wei, C., Fiedler, N., Senz, V., Lenarz, T., Grabow, N., Scheper, V., & Seitz, H. (2023). Micro Injection Molding of Drug-Loaded Round Window Niche Implants for an Animal Model Using 3D-Printed Molds. Pharmaceutics, 15(6), 1584. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061584