Altered Protein Expression of Cardiac CYP2J and Hepatic CYP2C, CYP4A, and CYP4F in a Mouse Model of Type II Diabetes—A Link in the Onset and Development of Cardiovascular Disease?
Abstract
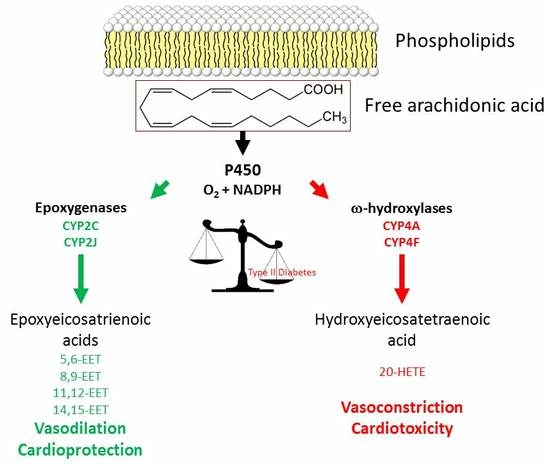
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Model
2.2. Western Blots of Liver Proteins
2.3. Western Blots of Cardiac Protein
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Limitation
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaspera, R.; Totah, R.A. Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids: Formation, metabolism and potential role in tissue physiology and pathophysiology. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2009, 5, 757–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seubert, J.M.; Zeldin, D.C.; Nithipatikom, K.; Gross, G.J. Role of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids in protecting the myocardium following ischemia/reperfusion injury. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2007, 82, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, C.M.; Cedars, A.; Gross, R.W. Eicosanoid signalling pathways in the heart. Cardiovasc. Res. 2009, 82, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, H.; Banthiya, S.; van Leyen, K. Mammalian lipoxygenases and their biological relevance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1851, 308–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.; Liu, B.; Zhou, Y. The endothelial cyclooxygenase pathway: Insights from mouse arteries. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 780, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, I. Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids, cell signaling and angiogenesis. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2007, 82, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamieson, K.L.; Endo, T.; Darwesh, A.M.; Samokhvalov, V.; Seubert, J.M. Cytochrome P450-derived eicosanoids and heart function. Pharmacol Ther. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huwiler, A.; Pfeilschifter, J. Lipids as targets for novel anti-inflammatory therapies. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 124, 96–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayajiki, K.; Okamura, T.; Fujioka, H.; Imaoka, S.; Funae, Y.; Toda, N. Involvement of CYP3A-derived arachidonic acid metabolite(s) in responses to endothelium-derived K+ channel opening substance in monkey lingual artery. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 128, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delozier, T.C.; Kissling, G.E.; Coulter, S.J.; Dai, D.; Foley, J.F.; Bradbury, J.A.; Murphy, E.; Steenbergen, C.; Zeldin, D.C.; Goldstein, J.A. Detection of human CYP2C8, CYP2C9, and CYP2J2 in cardiovascular tissues. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2007, 35, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klose, T.S.; Blaisdell, J.A.; Goldstein, J.A. Gene structure of CYP2C8 and extrahepatic distribution of the human CYP2Cs. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 1999, 13, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.A.; Neul, D.; Clouser-Roche, A.; Dalvie, D.; Wester, M.R.; Jiang, Y.; Jones, J.P.; Friewald, S.; Zientek, M.; Totah, R.A. Identification of novel substrates for human cytochrome P450 2J2. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2010, 38, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Moomaw, C.R.; Tomer, K.B.; Falck, J.R.; Zeldin, D.C. Molecular cloning and expression of CYP2J2, a human cytochrome P450 arachidonic acid epoxygenase highly expressed in heart. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 3460–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeldin, D.C.; Foley, J.; Goldsworthy, S.M.; Cook, M.E.; Boyle, J.E.; Ma, J.; Moomaw, C.R.; Tomer, K.B.; Steenbergen, C.; Wu, S. CYP2J subfamily cytochrome P450s in the gastrointestinal tract: Expression, localization, and potential functional significance. Mol. Pharmacol. 1997, 51, 931–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeldin, D.C.; Foley, J.; Ma, J.; Boyle, J.E.; Pascual, J.M.; Moomaw, C.R.; Tomer, K.B.; Steenbergen, C.; Wu, S. CYP2J subfamily P450s in the lung: Expression, localization, and potential functional significance. Mol. Pharmacol. 1996, 50, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zeldin, D.C.; Foley, J.; Boyle, J.E.; Moomaw, C.R.; Tomer, K.B.; Parker, C.; Steenbergen, C.; Wu, S. Predominant expression of an arachidonate epoxygenase in islets of Langerhans cells in human and rat pancreas. Endocrinology 1997, 138, 1338–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borlak, J.; Walles, M.; Levsen, K.; Thum, T. Verapamil: metabolism in cultures of primary human coronary arterial endothelial cells. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2003, 31, 888–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, R.A.; Goodwin, B.; Merrihew, R.V.; Krol, W.L.; Lecluyse, E.L. Cloning, tissue expression, and regulation of beagle dog CYP4A genes. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 92, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Xie, X.; Chen, Y.; Hammock, B.D.; Kong, W.; Zhu, Y. Homocysteine upregulates soluble epoxide hydrolase in vascular endothelium in vitro and in vivo. Circ Res. 2012, 110, 808–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, B.B.; Thompson, D.A.; Howard, L.L.; Morisseau, C.; Hammock, B.D.; Weiss, R.H. Inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase attenuate vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 2222–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbekai, R.H.; El-Kadi, A.O. Cytochrome P450 enzymes: Central players in cardiovascular health and disease. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 112, 564–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman, R.J.; Maier, K.G.; Sun, C.W.; Harder, D.R.; Alonso-Galicia, M. Renal and cardiovascular actions of 20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid and epoxyeicosatrienoic acids. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2000, 27, 855–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul-Ghani, M.; DeFronzo, R.A.; Del Prato, S.; Chilton, R.; Singh, R.; Ryder, R.E.J. Cardiovascular Disease and Type 2 Diabetes: Has the Dawn of a New Era Arrived? Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuck, R.N.; Theken, K.N.; Edin, M.L.; Caughey, M.; Bass, A.; Ellis, K.; Tran, B.; Steele, S.; Simmons, B.P.; Lih, F.B.; et al. Cytochrome P450-derived eicosanoids and vascular dysfunction in coronary artery disease patients. Atherosclerosis 2013, 227, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Su, W.; Allen, S.; Pang, H.; Daugherty, A.; Smart, E.; Gong, M.C. COX-2 Up-regulation and vascular smooth muscle contractile hyperreactivity in spontaneous diabetic db/db mice. Cardiovasc. Res. 2005, 67, 723–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatley, M.E.; Srinivasan, S.; Reilly, K.B.; Bolick, D.T. Increased Production of 12/15 Lipoxygenase Eicosanoids Accelerates Monocyte/Endothelial Interactions in Diabetic db/db Mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 25369–25375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patoine, D.; Levac, X.; Pilote, S.; Drolet, B.; Simard, C. Decreased CYP3A expression and activity in guinea pig models of diet-induced metabolic syndrome: Is fatty liver infiltration involved? Drug Metab. Dispos. 2013, 41, 952–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilote, S.; Virgili, J.; Patoine, D.; Drolet, B.; Simard, C. Altered hepatic protein expression of CYP4F in mouse models of Type I and Type II diabetes. In Proceedings of the 5th ICCR Congress on Chronic Societal Cardiometabolic Diseases, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 8–12 July 2015; Volume 7, p. 28. [Google Scholar]
- Patoine, D.; Petit, M.; Pilote, S.; Picard, F.; Drolet, B.; Simard, C. Modulation of CYP3a expression and activity in mice models of Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2014, 2, e00082:1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingma, J.; Simard, D.; Patoine, D.; Pilote, S.; Drolet, B.; Rouleau, J.; Simard, C. Chronic kidney disease augments cardiovascular risk: Modulation of myocardial blood flow regulation and CYP450 arachidonic acid metabolites. International Academy of Cardiology Annual Scientific Sessions 2014. In Proceedings of the 19th World Congress on Heart Disease, Boston, MA, USA, 25–28 July 2014. Cardiology 2014, 128 (Suppl. 1), 115. [Google Scholar]
- Imig, J.D. Eicosanoids and renal damage in cardiometabolic syndrome. Exp. Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2008, 4, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimojo, N.; Ishizaki, T.; Imaoka, S.; Funae, Y.; Fujii, S.; Okuda, K. Changes in amounts of cytochrome P450 isozymes and levels of catalytic activities in hepatic and renal microsomes of rats with streptozocin-induced diabetes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1993, 46, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousif, M.H.; Benter, I.F.; Roman, R.J. Cytochrome P450 metabolites of arachidonic acid play a role in the enhanced cardiac dysfunction in diabetic rats following ischaemic reperfusion injury. Auton. Autacoid. Pharmacol. 2009, 29, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enriquez, A.; Leclercq, I.; Farrell, G.C.; Robertson, G. Altered expression of hepatic CYP2E1 and CYP4A in obese, diabetic ob/ob mice, and fa/fa Zucker rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 255, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Dey, A.; Romanko, O.P.; Stepp, D.W.; Wang, M.H.; Zhou, Y.; Jin, L.; Pollock, J.S.; Clinton Webb, R.; Imig, J.D. Decreased epoxygenase and increased epoxide hydrolase expression in the mesenteric artery of obese Zucker rats. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2005, 288, R188–R196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Quigley, J.E.; Yuan, J.; Wang, M.H.; Zhou, Y.; Imig, J.D. PPAR-alpha activator fenofibrate increases renal CYP-derived eicosanoid synthesis and improves endothelial dilator function in obese Zucker rats. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2006, 290, H2187–H2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theken, K.N.; Deng, Y.; Schuck, R.N.; Oni-Orisan, A.; Miller, T.M.; Kannon, M.A.; Poloyac, S.M.; Lee, C.R. Enalapril reverses high-fat diet-induced alterations in cytochrome P450-mediated eicosanoid metabolism. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 302, E500–E509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akasaka, T.; Sueta, D.; Arima, Y.; Tabata, N.; Takashio, S.; Izumiya, Y.; Yamamoto, E.; Tsujita, K.; Kojima, S.; Kaikita, K.; et al. CYP2C19 variants and epoxyeicosatrienoic acids in patients with microvascular angina. IJC Heart Vasc. 2017, 15, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theken, K.N.; Schuck, R.N.; Edin, M.L.; Tran, B.; Ellis, K.; Bass, A.; Lih, F.B.; Tomer, K.B.; Poloyac, S.M.; Wu, M.C.; et al. Evaluation of cytochrome P450-derived eicosanoids in humans with stable atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Atherosclerosis 2012, 222, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsaad, A.M.; Zordoky, B.N.; Tse, M.M.; El-Kadi, A.O. Role of cytochrome P450-mediated arachidonic acid metabolites in the pathogenesis of cardiac hypertrophy. Drug Metab. Rev. 2013, 45, 173–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tacconelli, S.; Patrignani, P. Inside epoxyeicosatrienoic acids and cardiovascular disease. Front Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, P.K.; Wolf, I.; Jin, R.; Lasker, J.M. Metabolism of arachidonic acid to 20-hydroxy-5,8,11, 14-eicosatetraenoic acid by P450 enzymes in human liver: Involvement of CYP4F2 and CYP4A11. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1998, 285, 1327–1336. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roman, R.J. P-450 metabolites of arachidonic acid in the control of cardiovascular function. Physiol. Rev. 2002, 82, 131–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Measures at Sacrifice (Week 12) | Control Mice (n = 17) | BKS.Cg-m +/+ Leprdb/J Mice (db/db: T2D) (n = 20) |
|---|---|---|
| Weight (g) | 23.5 ± 0.5 | 41.3 ± 0.9 *** |
| Glycemia (mM) | 8.2 ± 0.7 | 31.3 ± 0.6 *** |
| Insulinemia (ng/mL) | 0.67 ± 0.06 | 3.90 ± 0.50 *** |
| HDL-C (mM) | 2.10 ± 0.05 | 3.18 ± 0.13 *** |
| Triglyceridemia (mM) | 1.67 ± 0.07 | 2.33 ± 0.22 ** |
| Cholesterolemia (mM) | 2.32 ± 0.17 | 3.77 ± 0.11 *** |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Drolet, B.; Pilote, S.; Gélinas, C.; Kamaliza, A.-D.; Blais-Boilard, A.; Virgili, J.; Patoine, D.; Simard, C. Altered Protein Expression of Cardiac CYP2J and Hepatic CYP2C, CYP4A, and CYP4F in a Mouse Model of Type II Diabetes—A Link in the Onset and Development of Cardiovascular Disease? Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics9040044
Drolet B, Pilote S, Gélinas C, Kamaliza A-D, Blais-Boilard A, Virgili J, Patoine D, Simard C. Altered Protein Expression of Cardiac CYP2J and Hepatic CYP2C, CYP4A, and CYP4F in a Mouse Model of Type II Diabetes—A Link in the Onset and Development of Cardiovascular Disease? Pharmaceutics. 2017; 9(4):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics9040044
Chicago/Turabian StyleDrolet, Benoit, Sylvie Pilote, Carolanne Gélinas, Alida-Douce Kamaliza, Audrey Blais-Boilard, Jessica Virgili, Dany Patoine, and Chantale Simard. 2017. "Altered Protein Expression of Cardiac CYP2J and Hepatic CYP2C, CYP4A, and CYP4F in a Mouse Model of Type II Diabetes—A Link in the Onset and Development of Cardiovascular Disease?" Pharmaceutics 9, no. 4: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics9040044
APA StyleDrolet, B., Pilote, S., Gélinas, C., Kamaliza, A. -D., Blais-Boilard, A., Virgili, J., Patoine, D., & Simard, C. (2017). Altered Protein Expression of Cardiac CYP2J and Hepatic CYP2C, CYP4A, and CYP4F in a Mouse Model of Type II Diabetes—A Link in the Onset and Development of Cardiovascular Disease? Pharmaceutics, 9(4), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics9040044