Pathogenic Intronic Splice-Affecting Variants in MYBPC3 in Three Patients with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Recruitment and Genetic Testing
2.2. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.3. Human K562 Cell Culture
2.4. In Vitro Splicing Minigene Assay
2.5. Reverse-Transcription PCR (RT-PCR)
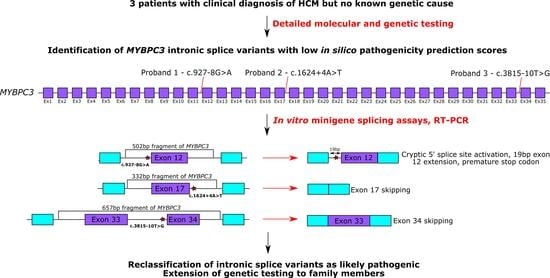
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics Associated with Three Intronic MYBPC3 Variants
3.2. In Vitro Minigene Assays to Assess the Impact of Intronic MYBPC3 Splice-Affecting Variants
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Towbin, J.A. Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2009, 32, S23–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hensley, N.; Dietrich, J.; Nyhan, D.; Mitter, N.; Yee, M.-S.; Brady, M. Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Anesthesia Analg. 2015, 120, 554–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marian, A.J.; Braunwald, E. Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Circ. Res. 2017, 121, 749–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, P.M.; Poloniecki, J.; Dickie, S.; Sharma, S.; Monserrat, L.; Varnava, A.; Mahon, N.G.; McKenna, W.J. Sudden death in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: Identification of high risk patients. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2000, 36, 2212–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenneaux, M.P.; Counihan, P.J.; Caforio, A.L.; Chikamori, T.; McKenna, W.J. Abnormal blood pressure response during exercise in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Circulation 1990, 82, 1995–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spirito, P.; Bellone, P.; Harris, K.M.; Bernabò, P.; Bruzzi, P.; Maron, B.J. Magnitude of Left Ventricular Hypertrophy and Risk of Sudden Death in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1778–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, W.J.; Franklin, R.C.; Nihoyannopoulos, P.; Robinson, K.C.; Deanfield, J.E.; Dickie, S.; Krikler, S.J. Arrhythmia and prognosis in infants, children and adolescents with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1988, 11, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greaves, S.C.; Roche, A.H.; Neutze, J.M.; Whitlock, R.M.; Veale, A.M. Inheritance of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: A cross sectional and M mode echocardiographic study of 50 families. Heart 1987, 58, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Branzi, A.; Romeo, G.; Specchia, S.; Lolli, C.; Binetti, G.; Devoto, M.; Bacchi, M.; Magnani, B. Genetic heterogeneity of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Int. J. Cardiol. 1985, 7, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmannova, H.; Kubanek, M.; Sramko, M.; Piherova, L.; Noskova, L.; Hodanova, K.; Stranecky, V.; Pristoupilova, A.; Sovova, J.; Marek, T.; et al. Isolated X-Linked Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Caused by a Novel Mutation of the Four-and-a-Half LIM Domain 1 Gene. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2013, 6, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marian, A.J. Modifier genes for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2002, 17, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Xie, J.; Zhu, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Xu, B. Next-generation sequencing identifies pathogenic and modifier mutations in a consanguineous Chinese family with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Medicine 2017, 96, e7010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, F.; Munkhsaikhan, U.; Boyle, C.; Borcky, T.; Zhao, W.; Purevjav, E.; Towbin, J.A.; Liao, F.; Williams, R.W.; et al. Identifying modifier genes for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2020, 144, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millat, G.; Bouvagnet, P.; Chevalier, P.; Dauphin, C.; Jouk, P.S.; Da Costa, A.; Prieur, F.; Bresson, J.-L.; Faivre, L.; Eicher, J.-C.; et al. Prevalence and spectrum of mutations in a cohort of 192 unrelated patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2010, 53, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaski, J.P.; Syrris, P.; Esteban, M.T.T.; Jenkins, S.; Pantazis, A.; Deanfield, J.; McKenna, W.J.; Elliott, P.M. Prevalence of Sarcomere Protein Gene Mutations in Preadolescent Children with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2009, 2, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erdmann, J.; Daehmlow, S.; Wischke, S.; Senyuva, M.; Werner, U.; Raible, J.; Tanis, N.; Dyachenko, S.; Hummel, M.; Hetzer, R.; et al. Mutation spectrum in a large cohort of unrelated consecutive patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Clin. Genet. 2003, 64, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, P.; Charron, P.; Carrier, L.; Ledeuil, C.; Cheav, T.; Pichereau, C.; Benaiche, A.; Isnard, R.; Dubourg, O.; Burban, M.; et al. Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Circulation 2003, 107, 2227–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigle, E.D.; Rakowski, H.; Kimball, B.P.; Williams, W.G. Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Circulation 1995, 92, 1680–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maron, B.J.; Maron, M.S. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Lancet 2013, 381, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colegrave, M.; Peckham, M. Structural Implications of β-Cardiac Myosin Heavy Chain Mutations in Human Disease. Anat. Rec. Adv. Integr. Anat. Evol. Biol. 2014, 297, 1670–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Previs, M.J.; Previs, S.B.; Gulick, J.; Robbins, J.; Warshaw, D.M. Molecular Mechanics of Cardiac Myosin-Binding Protein C in Native Thick Filaments. Science 2012, 337, 1215–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Previs, M.J.; Prosser, B.L.; Mun, J.Y.; Previs, S.B.; Gulick, J.; Lee, K.; Robbins, J.; Craig, R.; Lederer, W.J.; Warshaw, D.M. Myosin-binding protein C corrects an intrinsic inhomogeneity in cardiac excitation-contraction coupling. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1400205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Helms, A.S.; Thompson, A.D.; Glazier, A.A.; Hafeez, N.; Kabani, S.; Rodriguez, J.; Yob, J.M.; Woolcock, H.; Mazzarotto, F.; Lakdawala, N.K.; et al. Spatial and Functional Distribution of MYBPC3 Pathogenic Variants and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2020, 13, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marston, S.; Copeland, O.; Jacques, A.; Livesey, K.; Tsang, V.; McKenna, W.J.; Jalilzadeh, S.; Carballo, S.; Redwood, C.; Watkins, H. Evidence from Human Myectomy Samples That MYBPC3 Mutations Cause Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Through Haploinsufficiency. Circ. Res. 2009, 105, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Erdmann, J.; Raible, J.; Maki-Abadi, J.; Hammann, J.; Wollnik, B.; Frantz, E.; Fleck, E.; Regitz-Zagrosek, V.; Hummel, M.; Hetzer, R. Spectrum of clinical phenotypes and gene variants in cardiac myosin-binding protein C mutation carriers with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2001, 38, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Page, S.P.; Kounas, S.; Syrris, P.; Christiansen, M.; Frank-Hansen, R.; Andersen, P.S.; Elliott, P.M.; McKenna, W.J. Cardiac Myosin Binding Protein-C Mutations in Families with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2012, 5, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopes, L.R.; Barbosa, P.; Torrado, M.; Quinn, E.; Merino, A.; Ochoa, J.P.; Jager, J.; Futema, M.; Carmo-Fonseca, M.; Monserrat, L.; et al. Cryptic Splice-Altering Variants in MYBPC3 Are a Prevalent Cause of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2020, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, C.; Arscott, P.; Concannon, M.; Saberi, S.; Day, S.M.; Yashar, B.M.; Helms, A.S. Genetic testing impacts the utility of prospective familial screening in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy through identification of a nonfamilial subgroup. Genet. Med. 2017, 20, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marian, A.J. Challenges in the Diagnosis of Anderson-Fabry Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 1051–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelb, B.D.; Roberts, A.E.; Tartaglia, M. Cardiomyopathies in Noonan syndrome and the other RASopathies. Prog. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2015, 39, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elliott, P.; Baker, R.; Pasquale, F.; Quarta, G.; Ebrahim, H.; Mehta, A.B.; Hughes, D.; on Behalf of the ACES Study Group. Prevalence of Anderson-Fabry disease in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: The European Anderson-Fabry Disease Survey. Heart 2011, 97, 1957–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaranarayanan, R.; Fleming, E.J.; Garratt, C.J. Mimics of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy—Diagnostic Clues to Aid Early Identification of Phenocopies. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. Rev. 2013, 2, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ito, K.; Patel, P.N.; Gorham, J.M.; McDonough, B.; DePalma, S.R.; Adler, E.E.; Lam, L.; MacRae, C.A.; Mohiuddin, S.M.; Fatkin, D.; et al. Identification of pathogenic gene mutations in LMNA and MYBPC3 that alter RNA splicing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 7689–7694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bagnall, R.D.; Ingles, J.; Dinger, M.E.; Cowley, M.J.; Ross, S.B.; Minoche, A.E.; Lal, S.; Turner, C.; Colley, A.; Rajagopalan, S.; et al. Whole Genome Sequencing Improves Outcomes of Genetic Testing in Patients with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janin, A.; Chanavat, V.; Rollat-Farnier, P.; Bardel, C.; Nguyen, K.; Chevalier, P.; Eicher, J.; Faivre, L.; Piard, J.; Albert, E.; et al. Whole MYBPC3 NGS sequencing as a molecular strategy to improve the efficiency of molecular diagnosis of patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Hum. Mutat. 2019, 41, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank-Hansen, R.; Page, S.P.; Syrris, P.; McKenna, W.J.; Christiansen, M.; Andersen, P.S. Micro-exons of the cardiac myosin binding protein C gene: Flanking introns contain a disproportionately large number of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy mutations. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 16, 1062–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, E.S.; Ingles, J.; Semsarian, C.; Bagnall, R.D. Key Value of RNA Analysis of MYBPC3 Splice-Site Variants in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2019, 12, e002368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, M.; Orsborne, C.; Eden, J.; Wallace, A.; Church, H.J.; Tylee, K.; Deepak, S.; Cassidy, C.; Woolfson, P.; Miller, C.; et al. Mosaic Fabry Disease in a Male Presenting as Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Cardiogenetics 2020, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaganathan, K.; Panagiotopoulou, S.K.; McRae, J.F.; Darbandi, S.F.; Knowles, D.; Li, Y.I.; Kosmicki, J.A.; Arbelaez, J.; Cui, W.; Schwartz, G.B.; et al. Predicting Splicing from Primary Sequence with Deep Learning. Cell 2019, 176, 535–548.e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Desmet, F.O.; Hamroun, D.; Lalande, M.; Collod-Béroud, G.; Claustres, M.; Béroud, C. Human splicing finder: An online bioinformatics tool to predict splicing signals. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, e67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koch, L. Exploring human genomic diversity with gnomAD. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2020, 21, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishore, S.; Khanna, A.; Stamm, S. Rapid generation of splicing reporters with pSpliceExpress. Gene 2008, 427, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomas, H.B.; Wood, K.A.; Buczek, W.A.; Gordon, C.T.; Pingault, V.; Attié-Bitach, T.; Hentges, K.E.; Varghese, V.C.; Amiel, J.; Newman, W.G.; et al. EFTUD2 missense variants disrupt protein function and splicing in mandibulofacial dysostosis Guion-Almeida type. Hum. Mutat. 2020, 41, 1372–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-García, M.I.; Monserrat, L.; Ortiz, M.; Fernández, X.; Cazón, L.; Núñez, L.; Barriales-Villa, R.; Maneiro, E.; Veira, E.; Castro-Beiras, A.; et al. Screening mutations in myosin binding protein C3 gene in a cohort of patients with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. BMC Med. Genet. 2010, 11, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ellingford, J.M.; Thomas, H.B.; Rowlands, C.; Arno, G.; Beaman, G.; Gomes-Silva, B.; Campbell, C.; Gossan, N.; Hardcastle, C.; Webb, K.; et al. Functional and in-silico interrogation of rare genomic variants impacting RNA splicing for the diagnosis of genomic disorders. bioRxiv 2019, 781088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ingles, J.; Doolan, A.; Chiu, C.; Seidman, J.; Seidman, C.; Semsarian, C. Compound and double mutations in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: Implications for genetic testing and counselling. J. Med. Genet. 2005, 42, e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Helms, A.S.; Davis, F.M.; Coleman, D.; Bartolone, S.; Glazier, A.A.; Pagani, F.; Yob, J.M.; Sadayappan, S.; Pedersen, E.; Lyons, R.; et al. Sarcomere Mutation-Specific Expression Patterns in Human Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2014, 7, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carrier, L.; Bonne, G.; Bahrend, E.; Yu, B.; Richard, P.; Niel, F.; Hainque, B.; Cruaud, C.; Gary, F.; Labeit, S.; et al. Organization and Sequence of Human Cardiac Myosin Binding Protein C Gene (MYBPC3) and Identification of Mutations Predicted to Produce Truncated Proteins in Familial Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Circ. Res. 1997, 80, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flavigny, J.; Souchet, M.; Sébillon, P.; Berrebi-Bertrand, I.; Hainque, B.; Mallet, A.; Bril, A.; Schwartz, K.; Carrier, L. COOH-terminal truncated cardiac myosin-binding protein C mutants resulting from familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy mutations exhibit altered expression and/or incorporation in fetal rat cardiomyocytes. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 294, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanavy, D.M.; McNulty, S.M.; Jairath, M.K.; Brnich, S.E.; Bizon, C.; Powell, B.C.; Berg, J.S. Comparative analysis of functional assay evidence use by ClinGen Variant Curation Expert Panels. Genome Med. 2019, 11, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, C.L.; Fu, X.-D.; Gribskov, M. Characteristics and regulatory elements defining constitutive splicing and different modes of alternative splicing in human and mouse. RNA 2005, 11, 1777–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Huang, B.O.; Xu, Y.-M.; Huang, L.-F.; Lin, J.; Zhang, J.; Min, Q.-H.; Yang, W.-M.; Wang, X.-Z. Mechanism of alternative splicing and its regulation. Biomed. Rep. 2015, 3, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walsh, R.; Thomson, K.L.; Ware, J.S.; Funke, B.H.; Woodley, J.; McGuire, K.J.; Mazzarotto, F.; Blair, E.; Seller, A.; Exome Aggregation Consortium; et al. Reassessment of Mendelian gene pathogenicity using 7,855 cardiomyopathy cases and 60,706 reference samples. Genet. Med. 2017, 19, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poetter, K.; Jiang, H.; Hassanzadeh, S.; Master, S.R.; Chang, A.; Dalakas, M.C.; Rayment, I.; Sellers, J.R.; Fananapazir, L.; Epstein, N.D. Mutations in either the essential or regulatory light chains of myosin are associated with a rare myopathy in human heart and skeletal muscle. Nat. Genet. 1996, 13, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczesna, D.; Ghosh, D.; Li, Q.; Gomes, A.V.; Guzman, G.; Arana, C.; Zhi, G.; Stull, J.T.; Potter, J.D. Familial Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Mutations in the Regulatory Light Chains of Myosin Affect Their Structure, Ca2+ Binding, and Phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 7086–7092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaźmierczak, K.; Muthu, P.; Huang, W.; Jones, M.; Wang, Y.; Szczesna-Cordary, D. Myosin regulatory light chain mutation found in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy patients increases isometric force production in transgenic mice. Biochem. J. 2012, 442, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farman, G.P.; Muthu, P.; Kazmierczak, K.; Szczesna-Cordary, D.; Moore, J.R. Impact of familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy-linked mutations in the NH2 terminus of the RLC on β-myosin cross-bridge mechanics. J. Appl. Physiol. 2014, 117, 1471–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wood, K.A.; Ellingford, J.M.; Eden, J.; Thomas, H.B.; O’Keefe, R.T.; Hopton, C.; Newman, W.G. Pathogenic Intronic Splice-Affecting Variants in MYBPC3 in Three Patients with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Cardiogenetics 2021, 11, 73-83. https://doi.org/10.3390/cardiogenetics11020009
Wood KA, Ellingford JM, Eden J, Thomas HB, O’Keefe RT, Hopton C, Newman WG. Pathogenic Intronic Splice-Affecting Variants in MYBPC3 in Three Patients with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Cardiogenetics. 2021; 11(2):73-83. https://doi.org/10.3390/cardiogenetics11020009
Chicago/Turabian StyleWood, Katherine A., Jamie M. Ellingford, James Eden, Huw B. Thomas, Raymond T. O’Keefe, Claire Hopton, and William G. Newman. 2021. "Pathogenic Intronic Splice-Affecting Variants in MYBPC3 in Three Patients with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy" Cardiogenetics 11, no. 2: 73-83. https://doi.org/10.3390/cardiogenetics11020009
APA StyleWood, K. A., Ellingford, J. M., Eden, J., Thomas, H. B., O’Keefe, R. T., Hopton, C., & Newman, W. G. (2021). Pathogenic Intronic Splice-Affecting Variants in MYBPC3 in Three Patients with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Cardiogenetics, 11(2), 73-83. https://doi.org/10.3390/cardiogenetics11020009