Processing Speed and Attentional Shift/Mental Flexibility in Patients with Stroke: A Comprehensive Review on the Trail Making Test in Stroke Studies
Abstract
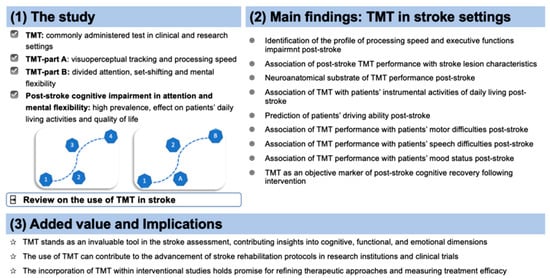
:1. Introduction
2. TMT in Stroke
2.1. TMT: Social and Demographic Factors Associated with the Increased Risk of Executive Dysfunction after Stroke
2.2. TMT and Clinical Features
2.3. TMT and Neuroanatomical Features
2.4. TMT and Speech Abilities
2.5. TMT and Mood Status
2.6. TMT and Driving Ability
2.7. TMT and Instrumental Activities of Daily Living
2.8. TMT and Gait Assessment
2.9. TMT in Interventional Studies
2.10. Limitations of TMT Performance in Stroke Settings
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carone, D.; Strauss, E.; Sherman, E.M.S.; Spreen, O. A Compendium of Neuropsychological Tests: Administration, Norms, and Commentary. Appl. Neuropsychol. 2007, 14, 62–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezak, M.D.; Howieson, D.B.; Bigler, E.D.; Tranel, D.; Lezak, M.D.; Howieson, D.B.; Bigler, E.D.; Tranel, D. Neuropsychological Assessment; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-0-19-539552-5. [Google Scholar]
- Arbuthnott, K.; Frank, J. Trail Making Test, Part B as a Measure of Executive Control: Validation Using a Set-Switching Paradigm. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2000, 22, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamberty, G.J.; Axelrod, B.N. Derived adult Trail Making Test indices. In The Quantified Process Approach to Neuropsychological Assessment; Studies on Neuropsychology, Neurology and Cognition; Taylor & Francis: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2006; pp. 161–171. ISBN 978-1-84169-456-6. [Google Scholar]
- Lamberty, G.; Putnam, S.; Chatel, D.; Bieliauskas, L.; Adams, K. Derived Trail Making Test indices: A preliminary report. Neuropsychiatry Neuropsychol. Behav. Neurol. 1994, 7, 230–234. [Google Scholar]
- Christidi, F.; Kararizou, E.; Triantafyllou, N.; Anagnostouli, M.; Zalonis, I. Derived Trail Making Test indices: Demographics and cognitive background variables across the adult life span. Neuropsychol. Dev. Cogn. B Aging Neuropsychol. Cogn. 2015, 22, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Cubillo, I.; Periáñez, J.A.; Adrover-Roig, D.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, J.M.; Ríos-Lago, M.; Tirapu, J.; Barceló, F. Construct validity of the Trail Making Test: Role of task-switching, working memory, inhibition/interference control, and visuomotor abilities. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2009, 15, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demakis, G.J. Frontal lobe damage and tests of executive processing: A meta-analysis of the category test, stroop test, and trail-making test. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2004, 26, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varjacic, A.; Mantini, D.; Demeyere, N.; Gillebert, C.R. Neural signatures of Trail Making Test performance: Evidence from lesion-mapping and neuroimaging studies. Neuropsychologia 2018, 115, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressler, S.L.; Menon, V. Large-scale brain networks in cognition: Emerging methods and principles. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2010, 14, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeley, W.W.; Menon, V.; Schatzberg, A.F.; Keller, J.; Glover, G.H.; Kenna, H.; Reiss, A.L.; Greicius, M.D. Dissociable intrinsic connectivity networks for salience processing and executive control. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 2349–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuriat, P.-A.; Cristofori, I.; Gordon, B.; Grafman, J. The shifting role of the cerebellum in executive, emotional and social processing across the lifespan. Behav. Brain Funct. 2022, 18, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellebaum, C.; Daum, I. Cerebellar involvement in executive control. Cerebellum 2007, 6, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turken, A.; Whitfield-Gabrieli, S.; Bammer, R.; Baldo, J.V.; Dronkers, N.F.; Gabrieli, J.D.E. Cognitive processing speed and the structure of white matter pathways: Convergent evidence from normal variation and lesion studies. Neuroimage 2008, 42, 1032–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filley, C.M. Cognitive Dysfunction in White Matter Disorders: New Perspectives in Treatment and Recovery. J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2021, 33, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filley, C.M.; Fields, R.D. White matter and cognition: Making the connection. J. Neurophysiol. 2016, 116, 2093–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaillard, A.; Naegele, B.; Trabucco-Miguel, S.; LeBas, J.F.; Hommel, M. Hidden dysfunctioning in subacute stroke. Stroke 2009, 40, 2473–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokinen, H.; Melkas, S.; Ylikoski, R.; Pohjasvaara, T.; Kaste, M.; Erkinjuntti, T.; Hietanen, M. Post-stroke cognitive impairment is common even after successful clinical recovery. Eur. J. Neurol. 2015, 22, 1288–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renjen, P.N.; Gauba, C.; Chaudhari, D. Cognitive Impairment After Stroke. Cureus 2015, 7, e335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolwyk, R.J.; Mihaljcic, T.; Wong, D.K.; Chapman, J.E.; Rogers, J.M. Poststroke Cognitive Impairment Negatively Impacts Activity and Participation Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Stroke 2021, 52, 748–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Kim, D.-Y.; Leigh, J.-H.; Kim, M.-W. Value of the Frontal Assessment Battery Tool for Assessing the Frontal Lobe Function in Stroke Patients. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2020, 44, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.-Y.; Wuang, Y.-P.; Lin, Y.-H.; Su, J.-H. The role of processing speed in post-stroke cognitive dysfunction. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2015, 30, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povroznik, J.M.; Ozga, J.E.; Vonder Haar, C.; Engler-Chiurazzi, E.B. Executive (dys)function after stroke: Special considerations for behavioral pharmacology. Behav. Pharmacol. 2018, 29, 638–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turunen, K.E.A.; Laari, S.P.K.; Kauranen, T.V.; Uimonen, J.; Mustanoja, S.; Tatlisumak, T.; Poutiainen, E. Domain-Specific Cognitive Recovery after First-Ever Stroke: A 2-Year Follow-Up. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2018, 24, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leśniak, M.; Bak, T.; Czepiel, W.; Seniów, J.; Członkowska, A. Frequency and prognostic value of cognitive disorders in stroke patients. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2008, 26, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Einstad, M.S.; Saltvedt, I.; Lydersen, S.; Ursin, M.H.; Munthe-Kaas, R.; Ihle-Hansen, H.; Knapskog, A.-B.; Askim, T.; Beyer, M.K.; Næss, H.; et al. Associations between post-stroke motor and cognitive function: A cross-sectional study. BMC Geriatr. 2021, 21, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, S.; Donnellan, C.; Stokes, E. Associations between executive function and physical function poststroke: A pilot study. Physiotherapy 2013, 99, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, S.; Donnellan, C.; Stokes, E. Executive dysfunction and balance function post-stroke: A cross-sectional study. Physiotherapy 2016, 102, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu-Ambrose, T.; Falck, R.S.; Dao, E.; Best, J.R.; Davis, J.C.; Bennett, K.; Hall, P.A.; Hsiung, G.-Y.R.; Middleton, L.E.; Goldsmith, C.H.; et al. Effect of Exercise Training or Complex Mental and Social Activities on Cognitive Function in Adults with Chronic Stroke: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, E2236510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, S.; Liu, C.; Dai, P.; Lan, Y.; Xu, G.; Zhang, H. Effect of Executive Dysfunction on Posture Control and Gait after Stroke. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 3051750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadley, V.G.; Bull, T.P.; Zhang, Y.; Barba, C.; Bryan, R.N.; Crowe, M.; Desiderio, L.; Deutsch, G.; Erus, G.; Geldmacher, D.S.; et al. Cognitive Processing Speed Is Strongly Related to Driving Skills, Financial Abilities, and Other Instrumental Activities of Daily Living in Persons With Mild Cognitive Impairment and Mild Dementia. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2021, 76, 1829–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaulieu-Bonneau, S.; Fortier-Brochu, É.; Ivers, H.; Morin, C.M. Attention following traumatic brain injury: Neuropsychological and driving simulator data, and association with sleep, sleepiness, and fatigue. Neuropsychol. Rehabil. 2017, 27, 216–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekiaris, E.; Amditis, A.; Panou, M. DRIVABILITY: A new concept for modelling driving performance. Cogn. Technol. Work. 2003, 5, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, K.; Lee, H.; Falkmer, T. Post-stroke driving: Examining the effect of executive dysfunction. J. Saf. Res. 2014, 49, e1–e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lee, Y.-N.; Jo, E.-M.; Lee, E.-Y. Reliability and Validity of Culturally Adapted Executive Function Performance Test for Koreans with Stroke. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2017, 26, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipskaya-Velikovsky, L.; Zeilig, G.; Weingarden, H.; Rozental-Iluz, C.; Rand, D. Executive functioning and daily living of individuals with chronic stroke: Measurement and implications. Int. J. Rehabil. Res. 2018, 41, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Sohn, M.K.; Jee, S.; Yang, S.S. The characteristics of cognitive impairment and their effects on functional outcome after inpatient rehabilitation in subacute stroke patients. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 41, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, M.; Tammasse, J.; Bintang, A.K.; Harahap, H.S. The frequency and determinants of executive dysfunction among patients with subacute phase of ischemic stroke in West Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia. Bali Med. J. 2023, 12, 249–254. [Google Scholar]
- Arsic, S.; Konstantinovic, L.; Eminovic, F.; Pavlovic, D.; Popovic, M.B.; Arsic, V. Correlation between the quality of attention and cognitive competence with motor action in stroke patients. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 823136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihle-Hansen, H.; Langhammer, B.; Lydersen, S.; Gunnes, M.; Indredavik, B.; Askim, T. A physical activity intervention to prevent cognitive decline after stroke: Secondary results from the life after stroke study, an 18-month randomized controlled trial. J. Rehabil. Med. 2019, 51, 646–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, G.; Halford, G.S.; Chappell, M.; Maujean, A.; Shum, D.H.K. Planning following stroke: A relational complexity approach using the Tower of London. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavin, S.J.; McCune-Richardson, L.; Moore, J.; Ecklund-Johnson, E.; Gronseth, G.S.; Akinwuntan, A. Cognitive Testing During Mild Acute Ischemic Stroke Predicts Long-Term Return to Work. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2022, 31, 106132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, C.O.; Branco, L.D.; Cotrena, C.; Fonseca, R.P. Correlational analysis of performance in executive function tasks after stroke. Psychol. Neurosci. 2015, 8, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laari, S.P.K.; Kauranen, T.V.; Turunen, K.E.A.; Mustanoja, S.M.; Tatlisumak, T.; Poutiainen, E.T. Executive Dysfunction Related to Binge Drinking in Ischemic Stroke. Cogn. Behav. Neurol. 2020, 33, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maaijwee, N.A.M.M.; Rutten-Jacobs, L.C.A.; Schaapsmeerders, P.; van Dijk, E.J.; de Leeuw, F.-E. Ischaemic stroke in young adults: Risk factors and long-term consequences. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2014, 10, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synhaeve, N.E.; Schaapsmeerders, P.; Arntz, R.M.; Maaijwee, N.A.M.; Rutten-Jacobs, L.C.A.; Schoonderwaldt, H.C.; Dorresteijn, L.D.A.; de Kort, P.L.M.; van Dijk, E.J.; Kessels, R.P.C.; et al. Cognitive performance and poor long-term functional outcome after young stroke. Neurology 2015, 85, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, M.V. Plasticity in the developing brain: Implications for rehabilitation. Dev. Disabil. Res. Rev. 2009, 15, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contador, I.; Alzola, P.; Stern, Y.; de la Torre-Luque, A.; Bermejo-Pareja, F.; Fernández-Calvo, B. Is cognitive reserve associated with the prevention of cognitive decline after stroke? A Systematic review and meta-analysis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2023, 84, 101814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhudy, L.M.; Wells-Pittman, J.; Flemming, K.D. Psychosocial Sequelae of Stroke in Working-Age Adults: A Pilot Study. J. Neurosci. Nurs. 2020, 52, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.; Wang, J.-C.; Sun, F.; Sun, Z.-Y.; Lin, Y.-J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, B.; Liu, L.; Luo, X.-G. Assessment of cerebrovascular reserve impairment using the breath-holding index in patients with leukoaraiosis. Neural Regen. Res. 2019, 14, 1412–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.Y.; Hwang, J.-W.; Pyun, S.-B. Relationship between cognitive function and dysphagia after stroke. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 41, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolin, M.; Van Patten, R.; Greif, T.; Fucetola, R. Predicting cognitive functioning, activities of daily living, and participation 6 months after mild to moderate stroke. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2018, 33, 562–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sörös, P.; Harnadek, M.; Blake, T.; Hachinski, V.; Chan, R. Executive dysfunction in patients with transient ischemic attack and minor stroke. J. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 354, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, A.; Stanne, T.M.; Redfors, P.; Viken, J.; Samuelsson, H.; Nilsson, S.; Jood, K.; Jern, C. Fibrinogen concentrations predict long-term cognitive outcome in young ischemic stroke patients. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 2, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lattanzi, S.; Coccia, M.; Pulcini, A.; Cagnetti, C.; Galli, F.L.; Villani, L.; Campa, S.; Dobran, M.; Polonara, G.; Ceravolo, M.G.; et al. Endovascular treatment and cognitive outcome after anterior circulation ischemic stroke. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harahap, H.S.; Akbar, M.; Bintang, A.K.; Tammasse, J.; Zainuddin, A.A. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) C677T polymorphism rather than homocysteine increase the risk of ischemic stroke-associated executive dysfunction. Bali Med. J. 2022, 11, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappellari, M.; Forlivesi, S.; Zucchella, C.; Valbusa, V.; Sajeva, G.; Musso, A.M.; Micheletti, N.; Tomelleri, G.; Bovi, T.; Bonetti, B.; et al. Factors influencing cognitive performance after 1-year treatment with direct oral anticoagulant in patients with atrial fibrillation and previous ischemic stroke: A pilot study. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2021, 51, 767–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, D.A.; Galecki, A.T.; Okullo, D.; Briceño, E.M.; Kabeto, M.U.; Morgenstern, L.B.; Langa, K.M.; Giordani, B.; Brook, R.; Sanchez, B.N.; et al. Association of Blood Pressure and Cognition after Stroke. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 29, 104754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaheen, H.A.; Daker, L.I.; Abbass, M.M.; Abd El Fattah, A.A. Post-stroke executive dysfunction and verbal fluency negatively correlated to IL8. Egypt. J. Neurol. Psychiatry Neurosurg. 2019, 55, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbaum Halevi, D.; Bursaw, A.W.; Karamchandani, R.R.; Alderman, S.E.; Breier, J.I.; Vahidy, F.S.; Aden, J.K.; Cai, C.; Zhang, X.; Savitz, S.I. Cognitive deficits in acute mild ischemic stroke and TIA and effects of rt-PA. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2019, 6, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmann, M.; Thommessen, B.; Rønning, O.M.; Benth, J.Š.; Reichenbach, A.S.; Fure, B. Middle Cerebral Artery Pulsatility Index is Associated with Cognitive Impairment in Lacunar Stroke. J. Neuroimaging 2016, 26, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Li, T.; Xu, B.; Fu, B. Fluoxetine May Enhance VEGF, BDNF and Cognition in Patients with Vascular Cognitive Impairment No Dementia: An Open-Label Randomized Clinical Study. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2021, 17, 3819–3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y.; De Guio, F.; Duering, M.; Jouvent, E.; Hervé, D.; Godin, O.; Dichgans, M.; Chabriat, H. Predictors and Clinical Impact of Incident Lacunes in Cerebral Autosomal Dominant Arteriopathy with Subcortical Infarcts and Leukoencephalopathy. Stroke 2017, 48, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotlęga, D.; Peda, B.; Palma, J.; Zembroń-łacny, A.; Gołab-Janowska, M.; Masztalewicz, M.; Nowacki, P.; Szczuko, M. Free fatty acids are associated with the cognitive functions in stroke survivors. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2021, 18, 6500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dacosta-Aguayo, R.; Graña, M.; Fernández-Andújar, M.; López-Cancio, E.; Cáceres, C.; Bargalló, N.; Barrios, M.; Clemente, I.; Monserrat, P.T.; Sas, M.A.; et al. Structural integrity of the contralesional hemisphere predicts cognitive impairment in ischemic stroke at three months. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Ye, L.; Lin, R.; Lin, H.; Tang, T.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L. Neuropsychological and neuroimaging assessments of early cognitive impairment in patients after mild ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2020, 19, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cipolotti, L.; Healy, C.; Chan, E.; Bolsover, F.; Lecce, F.; White, M.; Spanò, B.; Shallice, T.; Bozzali, M. The impact of different aetiologies on the cognitive performance of frontal patients. Neuropsychologia 2015, 68, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldsman, M.; Werden, E.; Egorova, N.; Khlif, M.S.; Brodtmann, A. Microstructural degeneration and cerebrovascular risk burden underlying executive dysfunction after stroke. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagberg, G.; Ihle-Hansen, H.; Fure, B.; Thommessen, B.; Ihle-Hansen, H.; Øksengård, A.R.; Beyer, M.K.; Wyller, T.B.; Müller, E.G.; Pendlebury, S.T.; et al. No evidence for amyloid pathology as a key mediator of neurodegeneration post-stroke—A seven-year follow-up study. BMC Neurol. 2020, 20, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Y.; Liu, C.; Zuo, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z. The relationship between altered degree centrality and cognitive function in mild subcortical stroke: A resting-state fMRI study. Brain Res. 2023, 1798, 148125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.; Fridriksson, J.; Perry, C.M.; Tryon, S.C.; Ross, A.; Fritz, S.; Herter, T.M. A novel computational model to probe visual search deficits during motor performance. J. Neurophysiol. 2017, 117, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varjačić, A.; Mantini, D.; Levenstein, J.; Slavkova, E.D.; Demeyere, N.; Gillebert, C.R. The role of left insula in executive set-switching: Lesion evidence from an acute stroke cohort. Cortex 2018, 107, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anziano, M.; Mouthon, M.; Thoeny, H.; Sperber, C.; Spierer, L. Mental flexibility depends on a largely distributed white matter network: Causal evidence from connectome-based lesion-symptom mapping. Cortex 2023, 165, 38–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, T.; Ridgeway, G.; Luchmee, D.; Jacob, J.; Kantak, S. Bimanual coordination during reach-to-grasp actions is sensitive to task goal with distinctions between left- and right-hemispheric stroke. Exp. Brain Res. 2022, 240, 2359–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankowska, A.M.; Klimkiewicz, R.; Kubsik, A.; Klimkiewicz, P.; Śmigielski, J.; Woldańska-Okońska, M. Location of the ischemic focus in rehabilitated stroke patients with impairment of executive functions. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2017, 26, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, M.A.; Park, O.T.; Shin, J.-H. Anatomical correlates of neuropsychological deficits among patients with the cerebellar stroke. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 41, 924–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferris, J.; Greeley, B.; Yeganeh, N.M.; Rinat, S.; Ramirez, J.; Black, S.; Boyd, L. Exploring biomarkers of processing speed and executive function: The role of the anterior thalamic radiations. NeuroImage Clin. 2022, 36, 103174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muir, R.T.; Lam, B.; Honjo, K.; Harry, R.D.; McNeely, A.A.; Gao, F.-Q.; Ramirez, J.; Scott, C.J.M.; Ganda, A.; Zhao, J.; et al. Trail making test elucidates neural substrates of specific poststroke executive dysfunctions. Stroke 2015, 46, 2755–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, A.; Sutoko, S.; Kiguchi, M.; Atsumori, H.; Obata, A.; Funane, T.; Kandori, A.; Mizuguchi, T.; Shimonaga, K.; Hama, S.; et al. Projection of Damaged Visual and Language Regions on Low Trail Making Test Part-B Performance in Stroke Patients. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 853942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, B.; Rösser, N.; Tabeling, S.; Stürenburg, H.J.; De Haan, B.; Karnath, H.-O.; Wessel, K. Errors on the trail making test are associated with right hemispheric frontal lobe damage in stroke patients. Behav. Neurol. 2015, 2015, 309235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godefroy, O.; Aarabi, A.; Dorchies, F.; Barbay, M.; Andriuta, D.; Diouf, M.; Thiebaut de Schotten, M.; Kassir, R.; Tasseel-Ponche, S.; Roussel, M.; et al. Functional architecture of executive processes: Evidence from verbal fluency and lesion mapping in stroke patients. Cortex 2023, 164, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajtar-Zembaty, A.; Zielińska, D.; Bober-Płonka, B.; Starowicz-Filip, A.; Rajtar-Zembaty, J.; Nowak, R.; Przewłocki, R. Application of the Trail Making Test in the assessment of cognitive flexibility in patients with speech disorders after ischaemic cerebral stroke. Aktual. Neurol. 2015, 2015, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonini, M.V.; Radanovic, M. Cognitive deficits in post-stroke aphasia. Arq. De. Neuro-Psiquiatr. 2015, 73, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niessen, E.; Ant, J.M.; Bode, S.; Saliger, J.; Karbe, H.; Fink, G.R.; Stahl, J.; Weiss, P.H. Preserved performance monitoring and error detection in left hemisphere stroke. NeuroImage Clin. 2020, 27, 102307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnellan, C.; Al Banna, M.; Redha, N.; Al Sharoqi, I.; Al-Jishi, A.; Bakhiet, M.; Taha, S.; Abdulla, F. Association Between Metacognition and Mood Symptoms Poststroke. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry Neurol. 2016, 29, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swardfager, W.; MacIntosh, B.J. Depression, Type 2 Diabetes, and Poststroke Cognitive Impairment. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair. 2017, 31, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, M.; Hoshiyama, M. Apathy and depression during the recovery stage after stroke. Int. J. Ther. Rehabil. 2020, 27, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslaksen, P.M.; Ørbo, M.; Elvestad, R.; Schäfer, C.; Anke, A. Prediction of on-road driving ability after traumatic brain injury and stroke. Eur. J. Neurol. 2013, 20, 1227–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.Y.; Lee, J.S.; Oh, Y.J. Cut-off point for the trail making test to predict unsafe driving after stroke. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2016, 28, 2110–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barco, P.P.; Wallendorf, M.J.; Snellgrove, C.A.; Ott, B.R.; Carr, D.B. Predicting road test performance in drivers with stroke. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 2014, 68, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hird, M.A.; Vesely, K.A.; Tasneem, T.; Saposnik, G.; Macdonald, R.L.; Schweizer, T.A. A case-control study investigating simulated driving errors in ischemic stroke and subarachnoid hemorrhage. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Omokute, Y.; Mitsuyama, A.; Takaoka, Y.; Takama, C.; Watanabe, Y. Predictors of track test performance in drivers with stroke. Turk. Neurosurg. 2017, 27, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiu, J.; Harmon, A.C.; Stowe, J.D.; Zwa, A.; Kinnear, M.; Dimitrov, L.; Nolte, T.; Carr, D.B. Feasibility and validity of a low-cost racing simulator in driving assessment after stroke. Geriatrics 2020, 5, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delis-Kaplan Executive Function System. Im Internet. Available online: https://www.pearsonassessments.com/store/usassessments/en/Store/Professional-Assessments/Cognition-%26-Neuro/Delis-Kaplan-Executive-Function-System/p/100000618.html (accessed on 18 January 2024).
- Al-Dughmi, M.; Al-Sharman, A.; Stevens, S.; Siengsukon, C.F. Executive function is associated with off-line motor learning in people with chronic stroke. J. Neurol. Phys. Ther. 2017, 41, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Lee, J.A.; Choi, H. Driving trail making test part B: A variant of the TMT-B. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2016, 28, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minor, M.; Jaywant, A.; Toglia, J.; Campo, M.; O’Dell, M.W. Discharge Rehabilitation Measures Predict Activity Limitations in Patients With Stroke 6 Months After Inpatient Rehabilitation. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2022, 101, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari, A.; Rostami, H.R.; Akbarfahimi, M. Predictors of Instrumental Activities of Daily Living Performance in Patients with Stroke. Occup. Ther. Int. 2021, 2021, 6675680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.; Perry, C.M.; Fritz, S.L.; Fridriksson, J.; Herter, T.M. Eye Movements Interfere With Limb Motor Control in Stroke Survivors. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair. 2018, 32, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamre, C.; Fure, B.; Helbostad, J.L.; Wyller, T.B.; Ihle-Hansen, H.; Vlachos, G.; Ursin, M.H.; Tangen, G.G. Impairments in spatial navigation during walking in patients 70 years or younger with mild stroke. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2020, 27, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.-O.; Lee, S.-H. Effects of cognitive-motor dual-Task training combined with auditory motor synchronization training on cognitive functioning in individuals with chronic stroke. Medicine 2018, 97, e10910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Yim, J. Effects of an exercise protocol for improving handgrip strength and walking speed on cognitive function in patients with chronic stroke. Med. Sci. Monit. 2017, 23, 5402–5409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.-O.; Lee, S.-H. Effect of a dual-task program with different cognitive tasks applied to stroke patients: A pilot randomized controlled trial. NeuroRehabilitation 2019, 44, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, K.; Hosoi, Y.; Harada, Y. Walking Ability Associated with Executive Dysfunction in Patients with Stroke: A Cross-Sectional Study. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uwa-Agbonikhena, I.F.; Gryb, V.A.; Gerasymchuk, V.R. Associations between the upper extremity function and cognition in post-stroke patients. Wiad. Lek. 2021, 74, 1917–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durcan, S.; Flavin, E.; Horgan, F. Factors associated with community ambulation in chronic stroke. Disabil. Rehabil. 2016, 38, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, C.Y.; Yoon, H.S.; Kim, H.D.; Kang, K.Y. The Effect of the Degree of Dual-Task Interference on Gait, Dual-Task Cost, Cognitive Ability, Balance, and Fall Efficacy in People with Stroke A Cross-Sectional Study. Medicine 2021, 100, E26275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanabe, J.; Amimoto, K.; Sakai, K.; Osaki, S.; Yoshihiro, N.; Kataoka, T. Effects and Adaptation of Visual-Motor Illusion Using Different Visual Stimuli on Improving Ankle Joint Paralysis of Stroke Survivors—A Randomized Crossover Controlled Trial. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teuschl, Y.; Ihle-Hansen, H.; Matz, K.; Dachenhausen, A.; Ratajczak, P.; Tuomilehto, J.; Ursin, M.H.; Hagberg, G.; Thommessen, B.; Øksengård, A.R.; et al. Multidomain Intervention for the Prevention of Cognitive Decline after Stroke—A Pooled Patient-Level Data Analysis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2018, 25, 1182–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, W.; Lei, M.; Tao, S.; Jie, L.T.; Qian, L.; Lin, F.Q.; Ping, W.X. Effects of combined intervention of physical exercise and cognitive training on cognitive function in stroke survivors with vascular cognitive impairment: A randomized controlled trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2019, 33, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haire, C.M.; Vuong, V.; Tremblay, L.; Patterson, K.K.; Chen, J.L.; Thaut, M.H. Effects of therapeutic instrumental music performance and motor imagery on chronic post-stroke cognition and affect: A randomized controlled trial. NeuroRehabilitation 2021, 48, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, T.; Abo, M.; Kakita, K.; Masuda, T.; Yamazaki, R. Does a combined intervention program of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation and intensive occupational therapy affect cognitive function in patients with post-stroke upper limb hemiparesis? Neural Regen. Res. 2016, 11, 1932–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, S.K.; Held, J.P.O.; de Bruin, E.D.; Knols, R.H. Personalized Motor-Cognitive Exergame Training in Chronic Stroke Patients—A Feasibility Study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 730801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-G.; Bae, S.-H.; Kim, K.-Y. Effects of dual-task training with different intensity of aerobic exercise on cognitive function and neurotrophic factors in chronic stroke patients. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2019, 12, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonkhoff, A.K.; Schirmer, M.D.; Bretzner, M.; Etherton, M.; Donahue, K.; Tuozzo, C.; Nardin, M.; Giese, A.; Wu, O.; Calhoun, V.D.; et al. Abnormal dynamic functional connectivity is linked to recovery after acute ischemic stroke. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2021, 42, 2278–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yin, M.; Luo, J.; Huang, L.; Zhang, S.; Pan, C.; Hu, X. Effects of transcranial magnetic stimulation on the performance of the activities of daily living and attention function after stroke: A randomized controlled trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2020, 34, 1465–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, M.K.L.; Johansson, B.; Carlsson, M.L.; Schuit, R.C.; Rönnbäck, L. Effect of the monoaminergic stabiliser (−)-OSU6162 on mental fatigue following stroke or traumatic brain injury. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2020, 32, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozental-Iluz, C.; Zeilig, G.; Weingarden, H.; Rand, D. Improving executive function deficits by playing interactive video-games: Secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial for individuals with chronic stroke. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2016, 52, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tanikaga, M.; Muzuno, J.; Tanaka, M.; Hoshiyama, M. Assessment of attention function recovery in patients after stroke using sequential desk-top tasks. Int. J. Ther. Rehabil. 2018, 25, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrisi, M.; Maresca, G.; De Cola, M.C.; Cannavò, A.; Sciarrone, F.; Silvestri, G.; Bramanti, A.; Luca, R.D.; Calabrò, R.S. Using telerehabilitation to improve cognitive function in post-stroke survivors: Is this the time for the continuity of care? Int. J. Rehabil. Res. 2019, 42, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ye, M.; Tong, Y.; Xiong, L.; Wu, X.; Geng, C.; Zhang, W.; Dai, Z.; Tian, W.; Rong, J. Effects of robot-assisted therapy on upper limb and cognitive function in patients with stroke: Study protocol of a randomized controlled study. Trials 2022, 23, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, T.J.; Polatajko, H.; Baum, C.; Rios, J.; Cirone, D.; Doherty, M.; McEwen, S. Combined Cognitive-Strategy and Task-Specific Training Affects Cognition and Upper-Extremity Function in Subacute Stroke: An Exploratory Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Occup. Ther. Off. Publ. Am. Occup. Ther. Assoc. 2016, 70, 7002290010p1–7002290010p10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-S.; Lim, J.-H.; Jeon, B.-H.; Song, C.-S. Non-immersive Virtual Reality Rehabilitation Applied to a Task-oriented Approach for Stroke Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2020, 38, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Ko, J.; Woo, Y. Effects of dual task training with visual restriction and an unstable base on the balance and attention of stroke patients. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2013, 25, 1579–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gjellesvik, T.I.; Becker, F.; Tjønna, A.E.; Indredavik, B.; Lundgaard, E.; Solbakken, H.; Brurok, B.; Tørhaug, T.; Lydersen, S.; Askim, T. Effects of High-Intensity Interval Training After Stroke (The HIIT Stroke Study) on Physical and Cognitive Function: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2021, 102, 1683–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.; Jeong, J.-G.; Cheong, Y.-S.; Nam, T.-W.; Kim, J.-H.; Park, C.-H.; Park, E.; Jung, T.-D. The effectiveness of computer-assisted cognitive rehabilitation and the degree of recovery in patients with traumatic brain injury and stroke. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; He, Z.; Yuan, J.; Lin, H.; Fu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, N.; Li, G.; Bu, J.; Chen, M.; et al. Application of Immersive Virtual-Reality-Based Puzzle Games in Elderly Patients with Post-Stroke Cognitive Impairment: A Pilot Study. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallesen, H.; Bjerk, M.; Pedersen, A.R.; Nielsen, J.F.; Evald, L. The Effects of High-Intensity Aerobic Exercise on Cognitive Performance After Stroke: A Pilot Randomised Controlled Trial. J. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Dis. 2019, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caliandro, P.; Molteni, F.; Simbolotti, C.; Guanziroli, E.; Iacovelli, C.; Reale, G.; Giovannini, S.; Padua, L. Exoskeleton-assisted gait in chronic stroke: An EMG and functional near-infrared spectroscopy study of muscle activation patterns and prefrontal cortex activity. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2020, 131, 1775–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelli, L.; Iacovelli, C.; Loreti, C.; Malizia, A.M.; Barone Ricciardelli, I.; Tomaino, A.; Fusco, A.; Biscotti, L.; Padua, L.; Giovannini, S. Robotic-assisted rehabilitation for balance in stroke patients (ROAR-S): Effects of cognitive, motor and functional outcomes. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 27, 8198–8211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biscetti, F.; Straface, G.; Giovannini, S.; Santoliquido, A.; Angelini, F.; Santoro, L.; Porreca, C.F.; Pecorini, G.; Ghirlanda, G.; Flex, A. Association between TNFRSF11B gene polymorphisms and history of ischemic stroke in Italian diabetic patients. Hum. Genet. 2013, 132, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsiakiri, A.; Christidi, F.; Tsiptsios, D.; Vlotinou, P.; Kitmeridou, S.; Bebeletsi, P.; Kokkotis, C.; Serdari, A.; Tsamakis, K.; Aggelousis, N.; et al. Processing Speed and Attentional Shift/Mental Flexibility in Patients with Stroke: A Comprehensive Review on the Trail Making Test in Stroke Studies. Neurol. Int. 2024, 16, 210-225. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16010014
Tsiakiri A, Christidi F, Tsiptsios D, Vlotinou P, Kitmeridou S, Bebeletsi P, Kokkotis C, Serdari A, Tsamakis K, Aggelousis N, et al. Processing Speed and Attentional Shift/Mental Flexibility in Patients with Stroke: A Comprehensive Review on the Trail Making Test in Stroke Studies. Neurology International. 2024; 16(1):210-225. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16010014
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsiakiri, Anna, Foteini Christidi, Dimitrios Tsiptsios, Pinelopi Vlotinou, Sofia Kitmeridou, Paschalina Bebeletsi, Christos Kokkotis, Aspasia Serdari, Konstantinos Tsamakis, Nikolaos Aggelousis, and et al. 2024. "Processing Speed and Attentional Shift/Mental Flexibility in Patients with Stroke: A Comprehensive Review on the Trail Making Test in Stroke Studies" Neurology International 16, no. 1: 210-225. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16010014
APA StyleTsiakiri, A., Christidi, F., Tsiptsios, D., Vlotinou, P., Kitmeridou, S., Bebeletsi, P., Kokkotis, C., Serdari, A., Tsamakis, K., Aggelousis, N., & Vadikolias, K. (2024). Processing Speed and Attentional Shift/Mental Flexibility in Patients with Stroke: A Comprehensive Review on the Trail Making Test in Stroke Studies. Neurology International, 16(1), 210-225. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint16010014