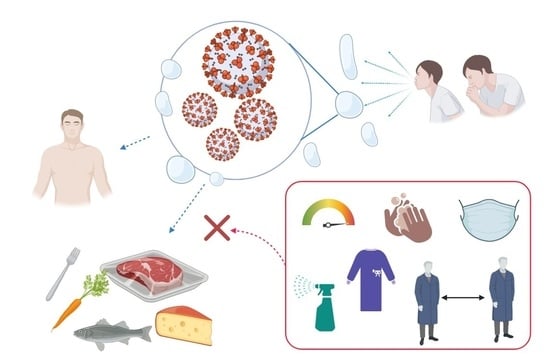
Food Safety Concerns in “COVID-19 Era”
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. SARS-CoV-2: A New Zoonosis
3. Can the Virus Be Transferred from the Food Surface to Humans?
Detection of the Virus on Different Environments and Surfaces
4. How to Manage the Risk of Food-Related COVID-19 Infection?
| Topic | Authorities | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Safety | COVID-19 and Food Safety: Guidance for competent authorities responsible for national food safety control systems Interim guidance, COVID-19: Animal-human interface and food safety | WHO | [67] |
| COVID-19 and Food Safety: Guidance for Food Businesses Interim guidance COVID-19: Animal-human interface and food safety | WHO | [60] | |
| WHO recommendations to reduce risk of transmission of emerging pathogens from animals to humans in live animal markets or animal product markets COVID-19: Animal-human interface and food safety | WHO | [64] | |
| Best Practices for Retail Food Stores, Restaurants, and Food Pick-Up/Delivery Services During the COVID-19 Pandemic | FDA | [65] | |
| COVID-19 Information for Consumers—Shopping for Food | FDA | [68] | |
| Temporary Policy During the COVID-19 Public Health Emergency Regarding the Qualified Exemption from the Standards for the Growing, Harvesting, Packing, and Holding of Produce for Human Consumption | FDA | [69] | |
| Temporary Policy Regarding Packaging and Labelling of Shell Eggs Sold by Retail Food Establishments During the COVID-19 Public Health Emergency | FDA | [70] | |
| Temporary Policy Regarding Certain Food Labelling Requirements During the COVID-19 Public Health Emergency: Minor Formulation Changes and Vending Machines | FDA | [71] | |
| Temporary Policy Regarding Preventive Controls and FSVP Food Supplier Verification Onsite Audit Requirements During the COVID-19 Public Health Emergency | FDA | [72] | |
| Hand hygiene practice | Recommendations to Member States to improve hand hygiene practices to help prevent the transmission of the COVID-19 virus | WHO | [73] |
| Guide to local production: WHO recommended hand rub formulations | WHO | [74] | |
| Personal Protective Equipment (PPEs) | Proper Usage of Face Masks/Coverings to Protect Against COVID-19 | FDA | [75] |
| PPE guide for community and social care settings | Public Health England | [76] | |
| Advice on the use of masks in the context of COVID-19 | WHO | [77] | |
| Prevention | Water, sanitation, hygiene, and waste management for SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19 | WHO | [78] |
| Sinification | Cleaning and disinfection of environmental surfaces in the context of COVID-19 | WHO | [79] |
| Food and Agriculture: Considerations for Prioritization of PPE, Cloth Face Coverings, Disinfectants, and Sanitation Supplies During the COVID-19 Pandemic | FDA | [80] | |
| Work | Considerations for public health and social measures in the workplace in the context of COVID-19 | WHO | [81] |
| Getting your workplace ready for COVID-19: How COVID-19 spreads | WHO | [82] | |
| Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak: Rights, roles, and responsibilities of health workers, including key considerations for occupational safety and health | WHO | [83] | |
| Best Practices for Re-Opening Retail Food Establishments During the COVID-19 Pandemic-Food Safety Checklist | FDA | [84] | |
| Employee Health and Food Safety Checklist for Human and Animal Food Operations During the COVID-19 Pandemic | FDA OSHA | [85] | |
| Protecting Seafood Processing Workers from COVID-19 Seafood Processing Workers | CDC OSHA FDA | [86] | |
| Meat and Poultry Processing Workers and Employers | CDC OSHA | [87] | |
| Guidance on the Essential Critical Infrastructure Workforce: Ensuring Community and National Resilience in COVID-19 Response | CISA | [88] | |
| Implementing Safety Practices for Critical Infrastructure Workers Who May Have Had Exposure to a Person with Suspected or Confirmed COVID-19 | CDC | [89] | |
| Guidance on Returning to Work June 2020 | OSHA | [90] | |
| The six-step COVID-19 business continuity plan for SMEs April 2020 | ILO | [91] | |
| Diagnosis | Laboratory testing for coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in suspected human cases | WHO | [92] |
5. Potential Approaches to Reduce the Risk of SARS-CoV-2 Contamination
6. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Q.; Guan, X.; Wu, P.; Wang, X.; Zhou, L.; Tong, Y.; Ren, R.; Leung, K.S.M.; Lau, E.H.Y.; Wong, J.Y.; et al. Early Transmission Dynamics in Wuhan, China, of Novel Coronavirus–Infected Pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Director-General’s Opening Remarks at the Media Briefing on COVID-19—11 March 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-remarks-at-the-media-briefing-on-covid-19---11-march-2020 (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- Day, M. Covid-19: Identifying and isolating asymptomatic people helped eliminate virus in Italian village. BMJ 2020, 368, m1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batisse, D.; Benech, N.; Botelho-Nevers, E.; Bouiller, K.; Collarino, R.; Conrad, A.; Gallay, L.; Goehringer, F.; Gousseff, M.; Joseph, D.C.; et al. Clinical recurrences of COVID-19 symptoms after recovery: Viral relapse, reinfection or inflammatory rebound? J. Infect. 2020, 81, 816–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, A.T.; Tong, Y.X.; Zhang, S. False-negative of RT-PCR and prolonged nucleic acid conversion in COVID-19: Rather than recurrence. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 1755–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mattiuzzi, C.; Henry, B.M.; Sanchis-Gomar, F.; Lippi, G. Sars-cov-2 recurrent rna positivity after recovering from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A meta-analysis. Acta Biomed. 2020, 91, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Rong, L.; Nian, W.; He, Y. Review article: Gastrointestinal features in COVID-19 and the possibility of faecal transmission. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 51, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfefferle, S.; Reucher, S.; Nörz, D.; Lütgehetmann, M. Evaluation of a quantitative RT-PCR assay for the detection of the emerging coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 using a high throughput system. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- CDC Public Health Guidance for Potential COVID-19 Exposure Associated with Travel. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/php/risk-assessment.html (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- The RECOVERY Collaborative Group. Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19—Preliminary Report. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC Therapeutic Options for COVID-19 Patients | CDC. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/therapeutic-options.html (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- Dyal, J.W.; Grant, M.P.; Broadwater, K.; Bjork, A.; Waltenburg, M.A.; Gibbins, J.D.; Hale, C.; Silver, M.; Fischer, M.; Steinberg, J.; et al. COVID-19 Among Workers in Meat and Poultry Processing Facilities—19 States, April 2020. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waltenburg, M.A.; Victoroff, T.; Rose, C.E.; Butterfield, M.; Jervis, R.H.; Fedak, K.M.; Gabel, J.A.; Feldpausch, A.; Dunne, E.M.; Austin, C.; et al. Update: COVID-19 Among Workers in Meat and Poultry Processing Facilities—United States, April–May 2020. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middleton, J.; Reintjes, R.; Lopes, H. Meat plants—A new front line in the covid-19 pandemic. BMJ 2020, 370, m2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, A.W.H.; Chu, J.T.S.; Perera, M.R.A.; Hui, K.P.Y.; Yen, H.-L.; Chan, M.C.W.; Peiris, M.; Poon, L.L.M. Stability of SARS-CoV-2 in different environmental conditions. Lancet Microbe 2020, 1, e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Doremalen, N.; Bushmaker, T.; Morris, D.H.; Holbrook, M.G.; Gamble, A.; Williamson, B.N.; Tamin, A.; Harcourt, J.L.; Thornburg, N.J.; Gerber, S.I.; et al. Aerosol and surface stability of HCoV-19 (SARS-CoV-2) compared to SARS-CoV-1. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- FDA. Food Safety and Availability during the Coronavirus Pandemic. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/food-safety-and-availability-during-coronavirus-pandemic (accessed on 25 January 2021).
- EFSA; Hugas, M.; FDA. Coronavirus: No Evidence that Food Is a Source or Transmission Route. Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/news/coronavirus-no-evidence-food-source-or-transmission-route (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- Andersen, K.G.; Rambaut, A.; Lipkin, W.I.; Holmes, E.C.; Garry, R.F. The proximal origin of SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 450–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Q.; Guo, D. Emerging coronaviruses: Genome structure, replication, and pathogenesis. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kratzel, A.; Steiner, S.; Todt, D.; V’kovski, P.; Brueggemann, Y.; Steinmann, J.; Steinmann, E.; Thiel, V.; Pfaender, S. Temperature-dependent surface stability of SARS-CoV-2. J. Infect. 2020, 81, 452–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, W.; Wang, W.; Zhao, X.; Zai, J.; Li, X. Cross-species transmission of the newly identified coronavirus 2019-nCoV. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, S.; Posteraro, B.; Marchetti, S.; Tamburrini, E.; Carducci, B.; Lanzone, A.; Valentini, P.; Buonsenso, D.; Sanguinetti, M.; Vento, G.; et al. Excretion of SARS-CoV-2 in human breast milk. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 1430–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, T.T.Y.; Jia, N.; Zhang, Y.W.; Shum, M.H.H.; Jiang, J.F.; Zhu, H.C.; Tong, Y.G.; Shi, Y.X.; Ni, X.B.; Liao, Y.S.; et al. Identifying SARS-CoV-2-related coronaviruses in Malayan pangolins. Nature 2020, 583, 282–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Maio, F.; Lo Cascio, E.; Babini, G.; Sali, M.; Della Longa, S.; Tilocca, B.; Roncada, P.; Arcovito, A.; Sanguinetti, M.; Scambia, G.; et al. Improved binding of SARS-CoV-2 Envelope protein to tight junction-associated PALS1 could play a key role in COVID-19 pathogenesis. Microbes Infect. 2020, 22, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilocca, B.; Soggiu, A.; Sanguinetti, M.; Babini, G.; De Maio, F.; Britti, D.; Zecconi, A.; Bonizzi, L.; Urbani, A.; Roncada, P. Immunoinformatic analysis of the SARS-CoV-2 envelope protein as a strategy to assess cross-protection against COVID-19. Microbes Infect. 2020, 22, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilocca, B.; Soggiu, A.; Sanguinetti, M.; Musella, V.; Britti, D.; Bonizzi, L.; Urbani, A.; Roncada, P. Comparative computational analysis of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein epitopes in taxonomically related coronaviruses. Microbes Infect. 2020, 22, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, R.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Niu, P.; Yang, B.; Wu, H.; Wang, W.; Song, H.; Huang, B.; Zhu, N.; et al. Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: Implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet 2020, 395, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.-L.; Wang, X.-G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.-R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.-L.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, T.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, Z. Probable Pangolin Origin of SARS-CoV-2 Associated with the COVID-19 Outbreak. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, 1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilocca, B.; Britti, D.; Urbani, A.; Roncada, P. Computational Immune Proteomics Approach to Target COVID-19. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 4233–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilocca, B.; Soggiu, A.; Musella, V.; Britti, D.; Sanguinetti, M.; Urbani, A.; Roncada, P. Molecular basis of COVID-19 relationships in different species: A one health perspective. Microbes Infect. 2020, 22, 218–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, N.H.L.; Chu, D.K.W.; Shiu, E.Y.C.; Chan, K.H.; McDevitt, J.J.; Hau, B.J.P.; Yen, H.L.; Li, Y.; Ip, D.K.M.; Peiris, J.S.M.; et al. Respiratory virus shedding in exhaled breath and efficacy of face masks. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 676–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- CDC Interim Guidelines for Collecting, Handling, and Testing Clinical Specimens from Persons for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/lab/guidelines-clinical-specimens.html (accessed on 25 January 2021).
- IDFA. Emergency Prevention Measures to Achieve Physical (Social) Distancing in Food Manufacturing Facilities as Related to COVID-19. 2020. Available online: https://www.idfa.org/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/2020-03-31-Emergency-Preventions-Measures-for-Physical-Distancing-in-Food-Manufacturing-as-Related-to-COVID-19.pdf (accessed on 25 January 2021).
- WHO. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): How Is It Transmitted? Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/q-a-detail/q-a-how-is-covid-19-transmitted (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- Pang, X.; Ren, L.; Wu, S.; Ma, W.; Yang, J.; Di, L.; Li, J.; Xiao, Y.; Kang, L.; Du, S.; et al. Cold-chain food contamination as the possible origin of Covid-19 resurgence in Beijing. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 1861–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COVID-19 Virus Found in Imported Frozen Chicken Wings_Notices-Shenzhen Government. Available online: http://www.sz.gov.cn/en_szgov/news/notices/content/post_8000285.html (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- Han, J.; Zhang, X.; He, S.; Jia, P. Can the coronavirus disease be transmitted from food? A review of evidence, risks, policies and knowledge gaps. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, D.; Reilly, A.; Kang, A.; Zheng, E.; Cook, A.R.; Anderson, D.E. Seeding of outbreaks of COVID-19 by contaminated fresh and frozen food. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbourt, D.E.; Haddow, A.D.; Piper, A.E.; Bloomfield, H.; Kearney, B.J.; Fetterer, D.; Gibson, K.; Minogue, T. Modeling the Stability of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-1 2) on Skin, Currency, and Clothing 2 3. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondin-Brosseau, M.; Harlow, J.; Doctor, T.; Nasheri, N. Examining the Persistence of Human Coronaviruses on Fresh Produce. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pung, R.; Chiew, C.J.; Young, B.E.; Chin, S.; Chen, M.I.C.; Clapham, H.E.; Cook, A.R.; Maurer-Stroh, S.; Toh, M.P.H.S.; Poh, C.; et al. Investigation of three clusters of COVID-19 in Singapore: Implications for surveillance and response measures. Lancet 2020, 395, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizou, M.; Galanakis, I.M.; Aldawoud, T.M.S.; Galanakis, C.M. Safety of foods, food supply chain and environment within the COVID-19 pandemic. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 102, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, A.; Gkogka, E.; Le Guyader, F.S.; Loisy-Hamon, F.; Lee, A.; van Lieshout, L.; Marthi, B.; Myrmel, M.; Sansom, A.; Schultz, A.C.; et al. Foodborne viruses: Detection, risk assessment, and control options in food processing. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 285, 110–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederwerder, M.C.; Hesse, R.A. Swine enteric coronavirus disease: A review of 4 years with porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus and porcine deltacoronavirus in the United States and Canada. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 660–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Decaro, N.; Mari, V.; Campolo, M.; Lorusso, A.; Camero, M.; Elia, G.; Martella, V.; Cordioli, P.; Enjuanes, L.; Buonavoglia, C. Recombinant Canine Coronaviruses Related to Transmissible Gastroenteritis Virus of Swine Are Circulating in Dogs. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 1532–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasoksuz, M.; Alekseev, K.; Vlasova, A.; Zhang, X.; Spiro, D.; Halpin, R.; Wang, S.; Ghedin, E.; Saif, L.J. Biologic, Antigenic, and Full-Length Genomic Characterization of a Bovine-Like Coronavirus Isolated from a Giraffe. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 4981–4990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Doorn, A.S.; Meijer, B.; Frampton, C.M.A.; Barclay, M.L.; de Boer, N.K.H. Systematic review with meta-analysis: SARS-CoV-2 stool testing and the potential for faecal-oral transmission. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 52, 1276–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Guo, C.; Tang, L.; Hong, Z.; Zhou, J.; Dong, X.; Yin, H.; Xiao, Q.; Tang, Y.; Qu, X.; et al. Prolonged presence of SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA in faecal samples. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 434–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Shen, L.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, H. SARS-CoV-2 may persist in digestive tract longer than respiratory tract. Preprints 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hindson, J. COVID-19: Faecal–oral transmission? Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboubakr, H.A.; Sharafeldin, T.A.; Goyal, S.M. Stability of SARS-CoV-2 and other coronaviruses in the environment and on common touch surfaces and the influence of climatic conditions: A review. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fears, A.; Klimstra, W.; Duprex, P.; Hartman, A.; Weaver, S.; Plante, K.; Mirchandani, D.; Plante, J.; Aguilar, P.; Fernandez, D.; et al. Comparative dynamic aerosol efficiencies of three emergent coronaviruses and the unusual persistence of SARS-CoV-2 in aerosol suspensions. medRxiv Prepr. Serv. Health Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Z.D.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhang, S.F.; Li, X.; Li, L.; Li, C.; Cui, Y.; Fu, R.B.; Dong, Y.Z.; Chi, X.Y.; et al. Aerosol and Surface Distribution of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 in Hospital Wards, Wuhan, China, 2020. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1586–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddell, S.; Goldie, S.; Hill, A.; Eagles, D.; Drew, T.W. The effect of temperature on persistence of SARS-CoV-2 on common surfaces. Virol. J. 2020, 17, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastorino, B.; Touret, F.; Gilles, M.; de Lamballerie, X.; Charrel, R.N. Prolonged Infectivity of SARS-CoV-2 in Fomites. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 2256–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matson, M.J.; Yinda, C.K.; Seifert, S.N.; Bushmaker, T.; Fischer, R.J.; van Doremalen, N.; Lloyd-Smith, J.O.; Munster, V.J. Effect of Environmental Conditions on SARS-CoV-2 Stability in Human Nasal Mucus and Sputum. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 2276–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Global Surface Sampling of Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): A practical “How To” Protocol for Health Care and Public Health Professionals. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/surface-sampling-of-coronavirus-disease-(-covid-19)-a-practical-how-to-protocol-for-health-care-and-public-health-professionals (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- WHO. World Health Organization COVID-19 and Food Safety: Guidance for food Businesses: Interim Guidance. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/covid-19-and-food-safety-guidance-for-food-businesses (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- Nakat, Z.; Bou-Mitri, C. COVID-19 and the food industry: Readiness assessment. Food Control 2021, 121, 107661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety, Crisis Management in Food, Animals and Plants Food Hygiene. COVID-19 and Food Safety Questions and Answers. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/food/sites/food/files/safety/docs/biosafety_crisis_covid19_qandas_en.pdf (accessed on 25 January 2021).
- FDA. US Food and Drug Administration Food Safety and the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). U.S. Food Drug 2020, 2019, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. WHO Recommendations to Reduce Risk of Transmission of Emerging Pathogens from Animals to Humans in Live Animal Markets. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/coronavirus/who-recommendations-to-reduce-risk-of-transmission-of-emerging-pathogens-from-animals-to-humans-in-live-animal-markets (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- FDA. Best Practices for Retail Food Stores, Restaurants, and Food Pick-Up/Delivery Services during the COVID-19. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/food-safety-during-emergencies/best-practices-retail-food-stores-restaurants-and-food-pick-updelivery-services-during-covid-19#employeehealth (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- Pittet, D.; Allegranzi, B.; Boyce, J. The World Health Organization Guidelines on Hand Hygiene in Health Care and Their Consensus Recommendations. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2009, 30, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COVID-19 and Food Safety: Guidance for Competent Authorities Responsible for National Food Safety Control Systems. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/covid-19-and-food-safety-guidance-for-competent-authorities-responsible-for-national-food-safety-control-systems (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- FDA. Shopping for Food During the COVID-19 Pandemic—Information for Consumers. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/food-safety-during-emergencies/shopping-food-during-covid-19-pandemic-information-consumers (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- FDA. Temporary Policy During the COVID-19 Public Health Emergency Regarding the Qualified Exemption from the Standards for the Growing, Harvesting, Packing, and Holding of Produce for Human Consumption Guidance for Industry. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/temporary-policy-during-covid-19-public-health-emergency-regarding-qualified-exemption-standards (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- FDA. Temporary Policy Regarding Packaging and Labeling of Shell Eggs Sold by Retail Food Establishments During the COVID-19 Public Health Emergency Guidance for Industry Preface Public Comment. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/emergency-preparedness-and- (accessed on 26 January 2021).
- FDA Temporary Policy Regarding Certain Food Labeling Requirements during the COVID-19 Public Health Emergency: Minor Formulation Changes and Vending Machines. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/temporary-policy-regarding-certain-food-labeling-requirements-during-covid-19-public-health (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- FDA Temporary Policy Regarding Preventive Controls and FSVP Food Supplier Verification Onsite Audit Requirements During the COVID-19 Public Health Emergency. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/temporary-policy-regarding-preventive-controls-and-fsvp-food-supplier-verification-onsite-audit (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- WHO Recommendations to Member States to Improve Hand Hygiene Practices to Help Prevent the Transmission of the COVID-19 Virus. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/recommendations-to-member-states-to-improve-hand-hygiene-practices-to-help-prevent-the-transmission-of-the-covid-19-virus (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- World Health Organization (WHO) Guide to Local Production: WHO-Recommended Handrub Formulations Introduction. Available online: https://www.who.int/gpsc/5may/Guide_to_Local_Production.pdf (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- CDC Proper Usage of Face Masks/Coverings to Protect against COVID-19. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/cloth-face-cover.html. (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- GOV.UK. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Illustrated Guide for Community and Social Care Settings—GOV.UK. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/personal-protective-equipment-ppe-illustrated-guide-for-community-and-social-care-settings (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- WHO Advice on the Use of Masks in the Context of COVID-19: Interim Guidance-2. Available online: WHO/2019-nCoV/IPC_Masks/Children/2020.1 (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- WHO. Water, Sanitation, Hygiene, and Waste Management for SARS-CoV-2, the Virus that Causes COVID-19. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/water-sanitation-hygiene-and-waste-management-for-the-covid-19-virus-interim-guidance (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- WHO. Cleaning and Disinfection of Environmental Surfaces in the Context of COVID-19. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/cleaning-and-disinfection-of-environmental-surfaces-inthe-context-of-covid-19 (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- USDA; FDA. Food and Agriculture: Considerations for Prioritization of PPE, Cloth Face Coverings, Disinfectants, and Sanitation Supplies During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/food-safety-during-emergencies/food-and-agriculture-considerations-prioritization-ppe-cloth-face-coverings-disinfectants-and (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- WHO. Overview of Public Health and Social Measures in the Context of COVID-19. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/considerations-for-public-health-and-social-measures-in-the-workplace-in-the-context-of-covid-19 (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- WHO. Getting your Workplace Ready for COVID-19. Available online: www.WHO.int%0Awww.WHO.int. (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- WHO. Coronavirus Disease (Covid-19) Outbreak: Rights, Roles and Responsibilities of Health Workers, Including Key Considerations for Occupational Safety. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/coronavirus-disease-(covid-19)-outbreak-rights-roles-and-responsibilities-of-health-workers-including-key-considerations-for-occupational-safety-and-health (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- FDA Best Practices for Re-Opening Retail Food Establishments during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/food-safety-during-emergencies/best-practices-re-opening-retail-food-establishments-during-covid-19-pandemic (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). Employee Health and Food Safety Checklist for Human and Animal Food Operations During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/food-safety-during-emergencies/employee-health-and-food-safety-checklist-human-and-animal-food-operations-during-covid-19-pandemic (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- CDC; FDA. Protecting Seafood Processing Workers from COVID-19. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/community/guidance-seafood-processing.html (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- CDC Meat and Poultry Processing Workers and Employers. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/community/organizations/meat-poultry-processing-workers-employers.html (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA); Wales, B. Guidance on the Essential Critical Infrastructure Workforce: Ensuring Community and National Resilience in COVID-19 Response. Available online: https://www.cisa.gov/publication/guidance-essential-critical-infrastructure-workforce (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- CDC; FDA. Interim Guidance for Implementing Safety Practices for Critical Infrastructure Workers Who May Have Had Exposure to a Person with Suspected or Confirmed COVID-19. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/community/critical-workers/implementing-safety-practices.html (accessed on 25 January 2021).
- OSHA Guidance on Preparing Workplaces for COVID-19. Available online: https://www.osha.gov/Publications/OSHA3990.pdf (accessed on 25 January 2021).
- ILO (International Labor Organization). The Six-Step COVID-19 Business Continuity Plan for SMEs. Available online: https://www.ilo.org/wcmsp5/groups/public/---ed_dialogue/---act_emp/documents/publication/wcms_740375.pdf (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- WHO Laboratory Testing for 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in Suspected Human Cases. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/10665-331501 (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- Desai, A.N.; Aronoff, D.M. Food Safety and COVID-19. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2020, 323, 1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampf, G.; Voss, A.; Scheithauer, S. Inactivation of coronaviruses by heat. J. Hosp. Infect. 2020, 105, 348–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Getting Your Workplace Ready for COVID-19: How COVID-19 Spreads. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/getting-your-workplace-ready-for-covid-19-how-covid-19-spreads (accessed on 25 January 2021).
- Feldmann, F.; Shupert, W.L.; Haddock, E.; Twardoski, B.; Feldmann, H. Gamma irradiation as an effective method for inactivation of emerging viral pathogens. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019, 100, 1275–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heilingloh, C.S.; Aufderhorst, U.W.; Schipper, L.; Dittmer, U.; Witzke, O.; Yang, D.; Zheng, X.; Sutter, K.; Trilling, M.; Alt, M.; et al. Susceptibility of SARS-CoV-2 to UV Irradiation. Am. J. Infect. Control 2020, 48, 1273–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragan, I.; Hartson, L.; Pidcoke, H.; Bowen, R.; Goodrich, R. Pathogen reduction of SARS-CoV-2 virus in plasma and whole blood using riboflavin and UV light. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darnell, M.E.R.; Subbarao, K.; Feinstone, S.M.; Taylor, D.R. Inactivation of the coronavirus that induces severe acute respiratory syndrome, SARS-CoV. J. Virol. Methods 2004, 121, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.M.; Zhao, X.S.; Wen, R.F.; Huang, J.J.; Pi, G.H.; Zhang, S.X.; Han, J.; Bi, S.L.; Ruan, L.; Dong, X.P. Stability of SARS Coronavirus in Human Specimens and Environment and Its Sensitivity to Heating and UV Irradiation. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2003, 16, 246–255. [Google Scholar]
- Eickmann, M.; Gravemann, U.; Handke, W.; Tolksdorf, F.; Reichenberg, S.; Müller, T.H.; Seltsam, A. Inactivation of three emerging viruses—Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, Crimean–Congo haemorrhagic fever virus and Nipah virus—In platelet concentrates by ultraviolet C light and in plasma by methylene blue plus visible light. Vox Sang. 2020, 115, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ratnesar-Shumate, S.; Williams, G.; Green, B.; Krause, M.; Holland, B.; Wood, S.; Bohannon, J.; Boydston, J.; Freeburger, D.; Hooper, I.; et al. Simulated Sunlight Rapidly Inactivates SARS-CoV-2 on Surfaces. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 222, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Criscuolo, E.; Diotti, R.A.; Ferrarese, R.; Alippi, C.; Viscardi, G.; Signorelli, C.; Mancini, N.; Clementi, M.; Clementi, N. Fast inactivation of SARS-CoV-2 by UV-C and ozone exposure on different materials. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, Z.; Meral, R.; Cetinkaya, T. Relevance of SARS-CoV-2 in food safety and food hygiene: Potential preventive measures, suggestions and nanotechnological approaches. VirusDisease 2020, 31, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randazzo, W.; Fabra, M.J.; Falcó, I.; López-Rubio, A.; Sánchez, G. Polymers and Biopolymers with Antiviral Activity: Potential Applications for Improving Food Safety. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 754–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warnes, S.L.; Green, S.M.; Michels, H.T.; Keevil, C.W. Biocidal efficacy of copper alloys against pathogenic enterococci involves degradation of genomic and plasmid DNAs. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 5390–5401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talebian, S.; Wallace, G.G.; Schroeder, A.; Stellacci, F.; Conde, J. Nanotechnology-based disinfectants and sensors for SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 618–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balagna, C.; Perero, S.; Percivalle, E.; Nepita, E.V.; Ferraris, M. Virucidal effect against Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 of a silver nanocluster/silica composite sputtered coating. Open Ceram. 2020, 1, 100006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Cheng, C.; Zhao, T.; Chen, Y.; Ayaz Ahmed, M. Frozen food: Is it safe to eat during COVID-19 pandemic? Public Health 2020, 190, e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ma, M.; He, D.; Yi, H. Re-emergence of coronavirus disease in Chinese cities associated with chilled and frozen food products. J. Infect. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Yang, M.; Zhao, X.; Guo, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Lei, W.; Han, W.; Jiang, F.; Liu, W.J.; et al. Cold-chain transportation in the frozen food industry may have caused a recurrence of COVID-19 cases in destination: Successful isolation of SARS-CoV-2 virus from the imported frozen cod package surface. Biosaf. Health 2020, 2, 199–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Surface/Aereosol | Detection of Virus | Condition | Virus Load | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aerosol | 3 h | 21 to 23 °C Relative humidity 40% | 105.25 TCID50/L air | [16] |
| Plastic | 72 h | |||
| Copper | 4 h | |||
| Cardboard | 24 h | |||
| Stainless Steel | 72 h | |||
| Surgical mask (inner side) | 4 d | 22 °C Relative humidity: ∼65% | 107.8 TCID50/mL | [15] |
| Surgical mask (outside) | 7 d | |||
| Glass | 2 d | |||
| Banknote | 2 d | |||
| Paper | 30 min | |||
| Tissue paper | 30 min | |||
| Wood | 1 d | |||
| Stainless stell | 4 d | |||
| Plastic | 4 d | |||
| Aerosol | 16 h | Not displayed | 102/L aerosol | [54] |
| Stainless steel | 28 d/7/48 h | 20/30/40 °C Relative humidity: 50% | 4.97 × 107/mL diluted into a standard solution | [56] |
| Polymer note | 28 d/7/48 h | |||
| Paper note | 28 d/21/48 h | |||
| Glass | 28 d/7/48 h | |||
| Cotton | 14 d/3 h/not detected | |||
| Vinyl | 28 d/3/48 h | |||
| Skin samples (Sus scrofa) | 14 d/96/8 h | 4/22/37 °C | Vero 76 kidney cells at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 0.01 | [41] |
| Banknote | 96/8/4 h | |||
| Clothing | 96/4/4 h | |||
| Metal surface | 180 h | 4/30 °C Relative humidity of 30–40%, 1 h drying | 9.6 × 104 TCID50/mL | [21] |
| Glass Polystyrene plastic Aluminum | 96 h °C for 96 h | 45–55% relative humidity 19–21 °C | 106 TCID50/mL | [57] |
| Activities | Measures | References |
|---|---|---|
| Personnel management |
| [60] |
| Environment and common space management |
| [60,95] |
| Food retail |
| [9,81] |
| Food Preparation |
| [15,65] |
| Delivery or Receiving |
| [88,92] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ceniti, C.; Tilocca, B.; Britti, D.; Santoro, A.; Costanzo, N. Food Safety Concerns in “COVID-19 Era”. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 12, 53-68. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres12010006
Ceniti C, Tilocca B, Britti D, Santoro A, Costanzo N. Food Safety Concerns in “COVID-19 Era”. Microbiology Research. 2021; 12(1):53-68. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres12010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleCeniti, Carlotta, Bruno Tilocca, Domenico Britti, Adriano Santoro, and Nicola Costanzo. 2021. "Food Safety Concerns in “COVID-19 Era”" Microbiology Research 12, no. 1: 53-68. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres12010006
APA StyleCeniti, C., Tilocca, B., Britti, D., Santoro, A., & Costanzo, N. (2021). Food Safety Concerns in “COVID-19 Era”. Microbiology Research, 12(1), 53-68. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres12010006