Author Contributions
Data curation, Z.C. (Zining Chen); Formal analysis, J.Y.; Investigation, Z.C. (Zining Chen); Methodology, J.Y.; Project administration, J.Y., Z.C. (Zhiguo Chen) and D.F.; Resources, Z.C. (Zhiguo Chen); Supervision, D.F.; Writing—original draft, Z.C. (Zining Chen); Writing—review & editing, Z.C. (Zining Chen) and J.Y.
Figure 4.
Equipment used for the separation of the rind and pith of corn stalks.
Figure 4.
Equipment used for the separation of the rind and pith of corn stalks.
Figure 5.
Corn stalk rind: (a) exterior and (b) interior.
Figure 5.
Corn stalk rind: (a) exterior and (b) interior.
Figure 6.
WKF-250 crusher.
Figure 6.
WKF-250 crusher.
Figure 7.
High-speed multi-functional crusher.
Figure 7.
High-speed multi-functional crusher.
Figure 8.
Constant-temperature magnetic stirrer.
Figure 8.
Constant-temperature magnetic stirrer.
Figure 9.
Chemical reagent.
Figure 9.
Chemical reagent.
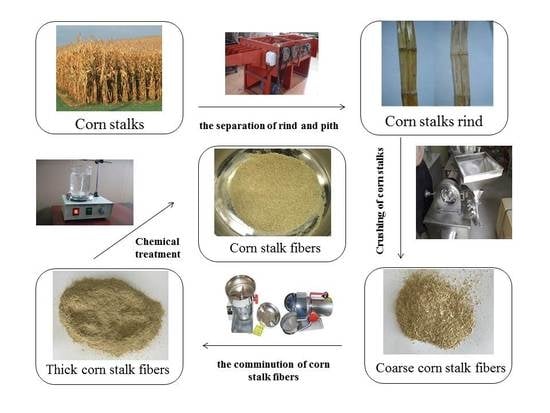
Figure 10.
The physical and chemical processing of corn stalk fiber.
Figure 10.
The physical and chemical processing of corn stalk fiber.
Figure 11.
Effect of pretreatment of corn stalk fibers on their oil absorption property: (a) effect of comminution time (reaction temperature 80 °C; mass fraction of solution 0.5%; reaction time 30 min); (b) effect of reaction temperature (comminution time 3.5 min; mass fraction of solution 0.5%; reaction time 30 min); (c) effect of mass fraction of solution (comminution time 3.5 min; reaction temperature 80 °C; reaction time 30 min); and (d) effect of reaction time (comminution time 3.5 min; reaction temperature 80 °C; mass fraction of solution 0.5%).
Figure 11.
Effect of pretreatment of corn stalk fibers on their oil absorption property: (a) effect of comminution time (reaction temperature 80 °C; mass fraction of solution 0.5%; reaction time 30 min); (b) effect of reaction temperature (comminution time 3.5 min; mass fraction of solution 0.5%; reaction time 30 min); (c) effect of mass fraction of solution (comminution time 3.5 min; reaction temperature 80 °C; reaction time 30 min); and (d) effect of reaction time (comminution time 3.5 min; reaction temperature 80 °C; mass fraction of solution 0.5%).
Figure 12.
Fiber size distribution curve.
Figure 12.
Fiber size distribution curve.
Figure 13.
Corn stalk fibers without chemical treatment.
Figure 13.
Corn stalk fibers without chemical treatment.
Figure 14.
Corn stalk fibers after chemical treatment.
Figure 14.
Corn stalk fibers after chemical treatment.
Figure 15.
Lignin fibers.
Figure 15.
Lignin fibers.
Figure 16.
Basalt fibers.
Figure 16.
Basalt fibers.
Figure 17.
Percentage mass loss of the fibers.
Figure 17.
Percentage mass loss of the fibers.
Figure 18.
Corn stalk fibers without chemical treatment. (a) before heating, (b) after heating.
Figure 18.
Corn stalk fibers without chemical treatment. (a) before heating, (b) after heating.
Figure 19.
Corn stalk fibers after chemical treatment. (a) before heating, (b) after heating.
Figure 19.
Corn stalk fibers after chemical treatment. (a) before heating, (b) after heating.
Figure 20.
Lignin fibers. (a) before heating, (b) after heating.
Figure 20.
Lignin fibers. (a) before heating, (b) after heating.
Figure 21.
Basalt fibers. (a) before heating, (b) after heating.
Figure 21.
Basalt fibers. (a) before heating, (b) after heating.
Figure 22.
Thermogravimetric analysis (TG) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) curves for corn stalk fibers without chemical treatment.
Figure 22.
Thermogravimetric analysis (TG) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) curves for corn stalk fibers without chemical treatment.
Figure 23.
TG and DSC curves for corn stalk fibers after chemical treatment.
Figure 23.
TG and DSC curves for corn stalk fibers after chemical treatment.
Table 1.
Physical properties of lignin fiber.
Table 1.
Physical properties of lignin fiber.
| Tested Property | Unit | Value | testing Base |
|---|
| Fiber length | mm | <5 | JT/T 533-2004 |
| Ash content | % | 18.9 | JT/T 533-2004 |
| PH | — | 7.8 | JT/T 533-2004 |
| Oil absorption rate | multiple | 5.3 | JT/T 533-2004 |
| Mositure content | % | 2.9 | JT/T 533-2004 |
| Density | g/cm3 | 0.536 | JT/T 533-2004 |
Table 2.
Physical properties of basalt fiber.
Table 2.
Physical properties of basalt fiber.
| Tested Property | Unit | Value | testing Base |
|---|
| Fiber diameter | μm | 15.72 | JT/T 776.1-2010 |
| Fiber length | mm | 7 | JT/T 776.1-2010 |
| Oil absorption rate | multiple | 2.4 | JT/T766.1-2010 |
| Mositure content | % | 0.2 | JT/T766.1-2010 |
| Breaking strength | MPa | 1612 | JT/T 776.1-2010 |
| Elongation at break | % | 2.2 | JT/T 776.1-2010 |
| Density | g/cm3 | 2.63 | JT/T 776.1-2010 |
| Elastic Modulus | MPa | 102.9 × 103 | JT/T 776.1-2010 |
| Heat resistance, fracture strength retention | % | 96.1 | JT/T 776.1-2010 |
Table 3.
Physical properties of asphalts.
Table 3.
Physical properties of asphalts.
| Asphalt Type | AH-90 Asphalt | SBS-Modified Asphalt |
|---|
| Tested Property | Unit | Value | Value |
|---|
| Penetration (25 °C) | 0.1mm | 83.0 | 63.0 |
| Softening point | °C | 44.0 | 72.5 |
| Ductility | cm | >100(10 °C) | 55(5 °C) |
| Ductility (15 °C) | cm | >100 | —— |
| Wax content | % | 2.0 | —— |
| Flash point | °C | 276 | 245 |
| Burning point | °C | 285 | —— |
| Solubility | % | 99.8 | 99.5 |
| Density (15 °C) | g/cm3 | 1.007 | 1.015 |
| Dynamic viscosity | Pa.s | 211(60 °C) | 2.4(135 °C) |
Table 4.
Percentage of mass passing through each mesh of SMA-13 asphalt mixture.
Table 4.
Percentage of mass passing through each mesh of SMA-13 asphalt mixture.
| Screen Size (mm) | 16 | 13.2 | 9.5 | 4.75 | 2.36 | 1.18 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.15 | 0.075 |
|---|
| Design level (%) | 100 | 91 | 67.4 | 30.7 | 23.5 | 20.2 | 16.8 | 15 | 13.9 | 10.3 |
| Normative median (%) | 100 | 95 | 62.5 | 27 | 20.5 | 19 | 16 | 13 | 12 | 10 |
| Specification range (%) | 100 | 90~100 | 50~75 | 20~34 | 15~26 | 14~24 | 12~20 | 10~16 | 9~15 | 8~12 |
Table 5.
Specific values of different levels of different parameters.
Table 5.
Specific values of different levels of different parameters.
| Level | Parameter A | Parameter B | Parameter C | Parameter D |
|---|
| | Final comminution time (min) | Mass of the sodium hydroxide reagent (g) | Reaction temperature (°C) | Reaction time (min) |
| 1 | 3 | 2.5 | 60 | 15 |
| 2 | 3.5 | 5 | 70 | 30 |
| 3 | 4 | 10 | 80 | 45 |
| 4 | | 20 | 90 | 60 |
Table 6.
Experimental plan.
Table 6.
Experimental plan.
| Experiment No. | Levels | | | |
|---|
| | Parameter A | Parameter B | Parameter C | Parameter D |
| 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 |
| 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 |
| 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 |
| 4 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 2 |
| 5 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 |
| 6 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 2 |
| 7 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| 8 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 9 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2 |
| 10 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| 11 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| 12 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
Table 7.
Mass ratios of the three kinds of fibers.
Table 7.
Mass ratios of the three kinds of fibers.
| No. | Fiber Type | Mass Ratio in Asphalt (%) |
|---|
| 1 | Corn stalk fiber | 2 |
| 2 | Corn stalk fiber | 4 |
| 3 | Corn stalk fiber | 6 |
| 4 | Corn stalk fiber | 8 |
| 5 | Corn stalk fiber | 10 |
| 6 | Lignin fiber | 1 |
| 7 | Lignin fiber | 1.5 |
| 8 | Lignin fiber | 2 |
| 9 | Basalt fiber | 1 |
| 10 | Basalt fiber | 1.5 |
| 11 | Basalt fiber | 2 |
| 12 | Basalt fiber | 2.5 |
Table 8.
Percentages of fibers in different screening size ranges.
Table 8.
Percentages of fibers in different screening size ranges.
| Screening Size Range (μm) | Fiber Type |
|---|
| Corn Stalk Fibers |
|---|
| | No comminution (%) | Comminution
(%) | Comminution and
chemical treatment (%) |
| 0.875–0.425 | 26.2 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.425–0.180 | 61.0 | 40.3 | 46.7 |
| 0.180–0.106 | 6.5 | 20.1 | 24.7 |
| >0.106 | 6.3 | 39.6 | 28.6 |
Table 9.
Hygroscopicity of fibers.
Table 9.
Hygroscopicity of fibers.
| Fiber Type | Water Content (%) | Moisture Absorption Rate (%) |
|---|
| Corn stalk fiber | 3.6 | 24.4 |
| Lignin fiber | 3.8 | 17.8 |
| Basalt fiber | 0.1 | 1.6 |
Table 10.
General performance index of fibers.
Table 10.
General performance index of fibers.
| Technical Indicator | Fiber Type | | |
|---|
| | Corn stalk fibers | Lignin fibers | Basalt fibers |
| Fiber length (mm) | <3 | <2 | 6 |
| Fiber diameter (μm) | 50–425 | — | 15.72 |
| Relative density (g/cm3) | 1.04 | 0.56 | 2.63 |
| Color | Golden | Gray | Gold-green |
| Melting temperature (°C) | >240 | >200 | 1250 |
Table 11.
Rutting factors of different fiber asphalts.
Table 11.
Rutting factors of different fiber asphalts.
| Type no. | Fiber Type | | Rutting Factor (kPa) | |
|---|
| | | | Temperature (°C) | |
| | | 64 | 70 | 76 |
| 1 | Corn stalk fiber | 1.238 | 0.616 | |
| 2 | 1.706 | 0.861 | |
| 3 | 1.889 | 0.967 | |
| 4 | 2.089 | 1.047 | 0.57 |
| 5 | 2.419 | 1.188 | 0.637 |
| 6 | Lignin fiber | 1.5 | 0.753 | |
| 7 | 2.205 | 1.197 | 0.676 |
| 8 | 2.034 | 1.16 | 0.659 |
| 9 | Basalt fiber | 1.351 | 0.694 | |
| 10 | 1.32 | 0.696 | |
| 11 | 1.496 | 0.751 | |
| 12 | 1.585 | 0.811 | |
Table 12.
The Marshall test results of SMA-13 asphalt mixture.
Table 12.
The Marshall test results of SMA-13 asphalt mixture.
| Mixture Type | Fiber Content (%) | Asphalt Stone Ratio (%) | Gross Volume Density (g/cm3) | VV (%) | VMA (%) | VFA (%) | Stability (kN) | Flow Value (0.1mm) |
|---|
| No blending | 0 | 5.6 | 2.406 | 3.33 | 20.1 | 82.4 | 8.78 | 27.5 |
| Adding lignin fiber | 0.3 | 5.8 | 2.367 | 3.56 | 21.4 | 81.7 | 9.71 | 31.4 |
| Adding corn stalk fiber | 0.3 | 5.8 | 2.371 | 3.60 | 21.9 | 80.5 | 9.68 | 33.5 |
| Adding corn stalk fiber | 0.6 | 6.0 | 2.358 | 3.62 | 22.1 | 80.7 | 9.87 | 26.5 |
| Adding corn stalk fiber | 0.9 | 6.2 | 2.361 | 3.66 | 20.9 | 82.3 | 11.10 | 38.3 |
| Specification | — | — | —— | 3~4 | ≥17 | 75~85 | ≥6 | — |
Table 13.
The Spitting and immersion Marshall test results of SMA-13 asphalt mixture.
Table 13.
The Spitting and immersion Marshall test results of SMA-13 asphalt mixture.
| Mixture Type | Spitting Strength (kN) | Residual Stability (%) |
|---|
| No blending | 11.3 | 83.4 |
| Adding 0.3% lignin fiber | 13.5 | 87.3 |
| Adding 0.3% corn stalk fiber | 15.6 | 86.9 |
| Adding 0.6% corn stalk fiber | 14.6 | 87.7 |
| Adding 0.9% corn stalk fiber | 12.3 | 88.2 |
| Specification | — | ≥80 |
Table 14.
Market prices of the experimental materials from a local dealer.
Table 14.
Market prices of the experimental materials from a local dealer.
| Material | Market Price (RMB/tonne) |
|---|
| Sodium hydroxide | 4000 |
| Corn stalks | 130 |
| Water | 5.6 |
Table 15.
Economic analysis of the preparation of corn stalk fibers.
Table 15.
Economic analysis of the preparation of corn stalk fibers.
| Product | Price (RMB) |
|---|
| Sodium hydroxide particles (96 g, fiber: sodium hydroxide = 4.8:1) | 0.08 |
| Water (4000 g, sodium hydroxide: water = 1:200) | 0.0224 |
| Corn stalks (320 g, corn stalks: fiber = 100:30) | 0.0416 |
| Unit cost of produced corn stalk fibers = 1500 RMB/tonne |
Table 16.
Market prices of the fibers for asphalt pavement applications.
Table 16.
Market prices of the fibers for asphalt pavement applications.
| Fiber Type | Price (RMB/tonne) |
|---|
| Corn stalk fiber | 1500 |
| Lignin fiber | 4300 |
| Basalt fiber | 16000 |