What is Currently Driving the Growth of China’s Household Electricity Consumption? A Clustering and Decomposition Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Driving Factor Selection
2.2. Clustering and Decomposition Methods
3. Methods and Materials
3.1. RSR Clustering Method
3.2. LMDI Decomposition Algorithm
3.3. Rebound Effect
3.4. Data Selection
4. Results
4.1. RSR Clustering Result
4.2. Factor Decomposition Result
5. Discussion
5.1. Geographic Distribution Analysis
5.2. OutlierAanalysis
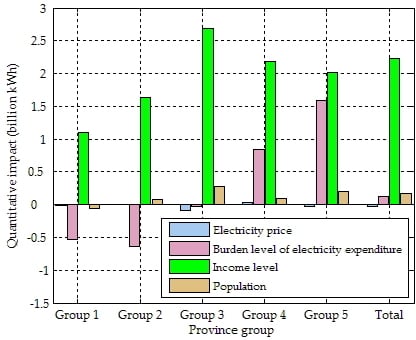
5.3. Driving Factor Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Bureau of Statistic of China. Statistical Bulletin on National Economic and Social Development 2018. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/zxfb/201902/t20190228_1651265.html (accessed on 28 May 2019). (In Chinese)
- Meng, M.; Mander, S.; Zhao, X.; Niu, D. Have market-oriented reforms improved the electricity generation efficiency of China’s thermal power industry? An empirical analysis. Energy 2014, 114, 734–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics. China Statistical Yearbook (2016–2018); China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2018.
- National Bureau of Statistics. China Statistical Yearbook on Environment (2016–2018); China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2018.
- IPCC. 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories. Available online: http://www.ipcc-nggip.iges.or.jp/public/2006gl/vol2.html (accessed on 29 May 2019).
- Li, C.; Zhang, X. Renminbi Internationalization in the New Normal: Progress, Determinants and Policy Discussions. China World Econ. 2017, 25, 22–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Energy Administration. Total Electricity Consumption Increased 8.5% in 2018. Available online: http://www.nea.gov.cn/2019-01/18/c_137754978.htm (accessed on 29 May 2019). (In Chinese)
- Meng, M.; Fu, Y.; Wang, X. Decoupling, decomposition and forecasting analysis of China’s fossil energy consumption from industrial output. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 177, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Energy Administration. Regulation Report on National Electricity Prices 2017. Available online: http://www.nea.gov.cn/2018-10/09/c_137519800.htm (accessed on 31 May 2019). (In Chinese)
- Ye, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; He, J. Research on the Inclining Block Tariffs Scheme for Solving Cross-subsidy under Demand Response—Based on the Perspective of Maximizing Social Welfare. Chin. J. Manag. Sci. 2019, 27, 149–159. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, X. Urbanization impact on residential energy consumption in China: The roles of income, urbanization level, and urban density. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 3542–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Chen, X.; Xue, B. Features, Driving Forces and Transition of the Household Energy Consumption in China: A Review. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcneil, M.A.; Letschert, V.E. Forecasting Electricity Demand in Developing Countries: A Study of Household Income and Appliance Ownership. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/228619092_Forecasting_Electricity_Demand_in_Developing_Countries_A_Study_of_Household_Income_and_Appliance_Ownership (accessed on 4 June 2019).
- He, X.; Reiner, D. Electricity demand and basic needs: Empirical evidence from China’s households. Energy Policy 2016, 90, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, K. Long-and short-run elasticities of residential electricity consumption in China: A partial adjustment model with panel data. Appl. Econ. 2015, 48, 2587–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, N.Z.; Guo, J.; Zheng, X. Effects of demand side management on Chinese household electricity consumption: Empirical findings from Chinese household survey. Energy Policy 2016, 95, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, M.; Wang, L.; Shang, W. Decomposition and forecasting analysis of China’s household electricity consumption using three-dimensional decomposition and hybrid trend extrapolation models. Energy 2018, 165, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhou, K.; Yang, S. A review of residential tiered electricity pricing in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 79, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Zeng, X.J.; Feng, P.; Cai, X. Clustering-based short-term load forecasting for residential electricity under the increasing-block pricing tariffs in China. Energy 2018, 165, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, X.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Y. China’s energy intensity target allocation needs improvement! Lessons from the convergence analysis of energy intensity across Chinese Provinces. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 223, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhau, S.P.; Moharil, R.M.; Adhau, P.G. K-Means clustering technique applied to availability of micro hydro power. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2014, 8, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, D.; Li, S.; Dai, S. Comprehensive Evaluation for Operating Efficiency of Electricity Retail Companies Based on the Improved TOPSIS Method and LSSVM Optimized by Modified Ant Colony Algorithm from the View of Sustainable Development. Sustainability 2018, 10, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Song, Y.; Fang, X.; Zuo, Y.; Weng, Y.; Pu, Y.; Bai, Y. Analysis of the Allocation of Nursing Human Resources in China Based on Rank Sum Ratio Method (In Chinese). Chin. Hosp. Manag. 2019, 39, 74–76. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.Y.; Ang, B.W. Analysing residential energy consumption using index decomposition analysis. Appl. Energy 2014, 113, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.; Kemp, R. Index decomposition analysis of residential energy consumption in China: 2002–2010. Appl. Energy 2014, 121, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Song, Y.; Li, P.; Li, H. Study on affecting factors of residential energy consumption in urban and rural Jiangsu. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 53, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, F.P.; Landajo, M.; Presno, M.J. Multilevel LMDI decomposition of changes in aggregate energy consumption. A cross country analysis in the EU-27. Energy Policy 2014, 68, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D. Evaluating the multi-period efficiency of East Asia airport companies. J. Air. Transp. Manag. 2017, 59, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Wu, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, J.; Song, M.; Hou, W. Determinants of changes in electricity generation intensity among different power sectors. Energy Policy 2019, 130, 389–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Ma, X. Uncovering CO2 Emissions Patterns from China-Oriented International Maritime Transport: Decomposition and Decoupling Analysis. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, B.W. Decomposition analysis for policymaking in energy: Which is the preferred method? Energy Policy 2004, 32, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Wang, L. Comprehensive Evaluation Method and Its Application in Medicine; People’s Medical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2014. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Berkhout, P.H.G.; Muskens, J.C.; Velthuijsen, J.W. Defining the rebound effect. Energy Policy 2000, 28, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lu, M.; Wang, J.C. Direct rebound effect on urban residential electricity use: An empirical study in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 30, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, F.; Ye, Z.; Yang, H.; Li, K. Exploring the rebound effect from the perspective of household: An analysis of China’s provincial level. Energy Econ. 2018, 75, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Province | Household Electricity Consumption | Population | Per Capita Disposable Income | Mean Electricity Price | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urban | Rural | Urban | Rural | |||||||||
| 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | |
| Beijing | 17.5 | 19.5 | 18.8 | 18.8 | 2.9 | 2.9 | 52.9 | 57.3 | 20.6 | 22.3 | 495.1 | 494.8 |
| Tianjin | 8.7 | 9.3 | 12.8 | 13 | 2.7 | 2.7 | 34.1 | 37.1 | 18.5 | 20.1 | 503.3 | 503.7 |
| Hebei | 37.2 | 39.5 | 38.1 | 39.8 | 36.1 | 34.9 | 26.2 | 28.3 | 11.1 | 11.9 | 510.7 | 510.2 |
| Shanxi | 16 | 17 | 20.2 | 20.7 | 16.5 | 16.1 | 25.8 | 27.4 | 9.5 | 10.1 | 493.2 | 491.9 |
| Inner Mongolia | 12.8 | 13.9 | 15.1 | 15.4 | 10 | 9.8 | 30.6 | 33 | 10.8 | 11.6 | 470.9 | 472.2 |
| Liaoning | 23 | 24.3 | 29.5 | 29.5 | 14.3 | 14.3 | 31.1 | 32.9 | 12.1 | 12.9 | 512.4 | 513.4 |
| Jilin | 10.7 | 11.2 | 15.2 | 15.3 | 12.3 | 12 | 24.9 | 26.5 | 11.3 | 12.1 | 534.8 | 531.9 |
| Heilongjiang | 16.8 | 17.3 | 22.4 | 22.5 | 15.7 | 15.5 | 24.2 | 25.7 | 11.1 | 11.8 | 521.2 | 521.6 |
| Shanghai | 18.6 | 21.8 | 21.2 | 21.3 | 3 | 2.9 | 53 | 57.7 | 23.2 | 25.5 | 571.3 | 572.9 |
| Jiangsu | 52.9 | 62 | 53.1 | 54.2 | 26.7 | 25.8 | 37.2 | 40.2 | 16.3 | 17.6 | 517.6 | 519.6 |
| Zhejiang | 44.3 | 51.7 | 36.5 | 37.5 | 18.9 | 18.5 | 43.7 | 47.2 | 21.1 | 22.9 | 556.1 | 558.9 |
| Anhui | 25.1 | 30.1 | 31 | 32.2 | 30.4 | 29.8 | 26.9 | 29.2 | 10.8 | 11.7 | 569.2 | 572.7 |
| Fujian | 34.5 | 38.1 | 24 | 24.6 | 14.4 | 14.1 | 33.3 | 36 | 13.8 | 15 | 551.5 | 557.2 |
| Jiangxi | 18.4 | 21 | 23.6 | 24.4 | 22.1 | 21.5 | 26.5 | 28.7 | 11.1 | 12.1 | 618.2 | 620.5 |
| Shandong | 50.3 | 55.4 | 56.1 | 58.7 | 42.3 | 40.8 | 31.6 | 34 | 12.9 | 14 | 536.7 | 538.6 |
| Henan | 41.4 | 42.5 | 44.4 | 46.2 | 50.4 | 49.1 | 25.6 | 27.2 | 10.9 | 11.7 | 563.2 | 563.7 |
| Hubei | 27.9 | 31.5 | 33.3 | 34.2 | 25.3 | 24.7 | 27.1 | 29.4 | 11.8 | 12.7 | 579.5 | 573.5 |
| Hunan | 32.9 | 38.7 | 34.5 | 35.6 | 33.3 | 32.2 | 28.8 | 31.3 | 11 | 11.9 | 607 | 607.8 |
| Guangdong | 84.6 | 90.4 | 74.5 | 76.1 | 34 | 33.9 | 34.8 | 37.7 | 13.4 | 14.5 | 645.6 | 648.2 |
| Guangxi | 25.1 | 27 | 22.6 | 23.3 | 25.4 | 25.1 | 26.4 | 28.3 | 9.5 | 10.4 | 562.9 | 557.7 |
| Hainan | 5 | 5.4 | 5 | 5.2 | 4.1 | 4 | 26.4 | 28.5 | 10.9 | 11.8 | 632.1 | 632.3 |
| Chongqing | 13.8 | 16.4 | 18.4 | 19.1 | 11.8 | 11.4 | 27.2 | 29.6 | 10.5 | 11.6 | 537.3 | 533.8 |
| Sichuan | 34.1 | 39.3 | 39.1 | 40.7 | 42.9 | 42 | 26.2 | 28.3 | 10.3 | 11.2 | 523.3 | 523.3 |
| Guizhou | 19.8 | 21.8 | 14.8 | 15.7 | 20.5 | 19.9 | 24.6 | 26.7 | 7.4 | 8.1 | 485.4 | 484.2 |
| Yunnan | 21.7 | 19.5 | 20.6 | 21.5 | 26.9 | 26.2 | 26.4 | 28.6 | 8.2 | 9 | 472 | 468 |
| Shaanxi | 18.8 | 21.1 | 20.5 | 21.1 | 17.5 | 17 | 26.4 | 28.4 | 8.7 | 9.4 | 507.1 | 506.3 |
| Gansu | 7.7 | 8.4 | 11.2 | 11.7 | 14.8 | 14.4 | 23.8 | 25.7 | 6.9 | 7.5 | 511.8 | 522.5 |
| Qinghai | 2.3 | 2.5 | 3 | 3.1 | 2.9 | 2.9 | 24.5 | 26.8 | 7.9 | 8.7 | 405.8 | 404 |
| Ningxia | 2.4 | 2.6 | 3.7 | 3.8 | 3 | 3 | 25.2 | 27.2 | 9.1 | 9.9 | 457.2 | 462.7 |
| Xinjiang | 8 | 8 | 11.2 | 11.6 | 12.5 | 12.4 | 26.3 | 28.5 | 9.4 | 10.2 | 533.6 | 530.9 |
| Province | Household Electricity Consumption | Population | Per Capita Disposable Income | Mean Electricity Price | RSR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urban | Rural | Urban | Rural | ||||
| Beijing | 20 | 8.8 | 22.8 | 16.9 | 15.9 | 16.4 | 0.559 |
| Tianjin | 7.5 | 10.8 | 20.8 | 18.6 | 16.6 | 15.4 | 0.498 |
| Hebei | 7.5 | 21.3 | 8.8 | 14.9 | 13.9 | 16.6 | 0.461 |
| Shanxi | 9 | 13.3 | 16.3 | 12.1 | 12.1 | 17.3 | 0.445 |
| Inner Mongolia | 14 | 11.3 | 17.8 | 13.8 | 13.4 | 14.4 | 0.47 |
| Liaoning | 6 | 8.3 | 22.3 | 11.9 | 12.4 | 14.6 | 0.419 |
| Jilin | 5 | 9.8 | 15.8 | 12.9 | 12.6 | 18.1 | 0.412 |
| Heilongjiang | 4 | 9.3 | 19.5 | 12.4 | 11.9 | 15.4 | 0.402 |
| Shanghai | 27 | 10.3 | 17.3 | 18.9 | 18.9 | 14.1 | 0.591 |
| Jiangsu | 26 | 11.8 | 9.3 | 14.6 | 15.4 | 13.4 | 0.502 |
| Zhejiang | 25 | 13.8 | 11.8 | 15.3 | 15.1 | 12.9 | 0.521 |
| Anhui | 30 | 18.3 | 16.8 | 16.4 | 15.6 | 12.6 | 0.609 |
| Fujian | 19 | 12.8 | 18.3 | 16.1 | 16.9 | 12.4 | 0.53 |
| Jiangxi | 23 | 17.3 | 13.3 | 15.9 | 17.1 | 13.6 | 0.556 |
| Shandong | 17 | 22.3 | 8.3 | 14.1 | 14.1 | 13.9 | 0.498 |
| Henan | 3 | 20.8 | 12.3 | 12.6 | 13.6 | 15.4 | 0.431 |
| Hubei | 22 | 14.3 | 14.3 | 17.9 | 13.1 | 19.1 | 0.559 |
| Hunan | 28 | 15.8 | 9.8 | 17.4 | 16.1 | 14.9 | 0.566 |
| Guangdong | 11 | 12.3 | 21.8 | 17.1 | 16.4 | 13.1 | 0.509 |
| Guangxi | 12 | 15.3 | 20.3 | 13.1 | 18.1 | 18.9 | 0.542 |
| Hainan | 16 | 17.8 | 10.8 | 14.4 | 17.4 | 15.9 | 0.512 |
| Chongqing | 29 | 18.8 | 10.3 | 18.1 | 19.1 | 18.4 | 0.631 |
| Sichuan | 24 | 19.8 | 15.3 | 15.6 | 17.9 | 16.1 | 0.604 |
| Guizhou | 18 | 22.8 | 11.3 | 18.4 | 18.5 | 17.3 | 0.59 |
| Yunnan | 1 | 21.8 | 13.8 | 17.6 | 18.5 | 18.6 | 0.507 |
| Shaanxi | 21 | 16.3 | 12.8 | 13.4 | 14.9 | 16.9 | 0.529 |
| Gansu | 15 | 19.3 | 14.8 | 15.3 | 12.9 | 11.9 | 0.494 |
| Qinghai | 13 | 16.8 | 18.8 | 19.1 | 17.6 | 17.6 | 0.572 |
| Ningxia | 10 | 14.8 | 19.5 | 13.8 | 14.6 | 12.1 | 0.471 |
| Xinjiang | 2 | 20.3 | 21.3 | 16.6 | 14.4 | 17.9 | 0.513 |
| Province | RSR | Accumulative Frequency | Quantile for Normal Distribution | Probit | Fitted RSR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heilongjiang | 0.402 | 3.3 | −1.8 | 3.2 | 0.401 |
| Jilin | 0.412 | 6.7 | −1.5 | 3.5 | 0.421 |
| Liaoning | 0.419 | 10 | −1.3 | 3.7 | 0.434 |
| Henan | 0.431 | 13.3 | −1.1 | 3.9 | 0.445 |
| Shanxi | 0.445 | 16.7 | −1 | 4 | 0.454 |
| Hebei | 0.461 | 20 | −0.8 | 4.2 | 0.461 |
| Inner Mongolia | 0.47 | 23.3 | −0.7 | 4.3 | 0.468 |
| Ningxia | 0.471 | 26.7 | −0.6 | 4.4 | 0.474 |
| Gansu | 0.494 | 30 | −0.5 | 4.5 | 0.48 |
| Tianjin, Shandong | 0.498 | 35 | −0.4 | 4.6 | 0.488 |
| Jiangsu | 0.502 | 40 | −0.3 | 4.8 | 0.496 |
| Yunnan | 0.507 | 43.3 | −0.2 | 4.8 | 0.501 |
| Guangdong | 0.509 | 46.7 | −0.1 | 4.9 | 0.507 |
| Hainan | 0.512 | 50 | 0 | 5 | 0.511 |
| Xinjiang | 0.513 | 53.3 | 0.1 | 5.1 | 0.516 |
| Zhejiang | 0.521 | 56.7 | 0.2 | 5.2 | 0.522 |
| Shaanxi | 0.529 | 60 | 0.3 | 5.3 | 0.526 |
| Fujian | 0.53 | 63.3 | 0.3 | 5.3 | 0.532 |
| Guangxi | 0.542 | 66.7 | 0.4 | 5.4 | 0.537 |
| Jiangxi | 0.556 | 70 | 0.5 | 5.5 | 0.543 |
| Beijing, Hubei | 0.559 | 75 | 0.7 | 5.7 | 0.552 |
| Hunan | 0.566 | 80 | 0.8 | 5.8 | 0.562 |
| Qinghai | 0.572 | 83.3 | 1 | 6 | 0.569 |
| Guizhou | 0.590 | 86.7 | 1.1 | 6.1 | 0.578 |
| Shanghai | 0.591 | 90 | 1.3 | 6.3 | 0.588 |
| Sichuan | 0.604 | 93.3 | 1.5 | 6.5 | 0.602 |
| Anhui | 0.609 | 96.7 | 1.8 | 6.8 | 0.621 |
| Chongqing | 0.631 | 99.2* | 2.4 | 7.4 | 0.656 |
| Group | Range of Probit | Range of Fitted RSR | Province |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | (−∞, 3.2) | <0.403 | Heilongjiang |
| 2 | [3.2, 4.4) | [0.403, 0.475) | Jilin, Liaoning, Henan, Shanxi, Hebei, Inner Mongolia, Ningxia |
| 3 | [4.4, 5.6) | [0.475, 0.548) | Gansu, Tianjin, Shandong, Jiangsu, Yunnan, Guangdong, Hainan, Xinjiang, Zhejiang, Shaanxi, Fujian, Guangxi, Jiangxi |
| 4 | [5.6, 6.8] | [0.548, 0.620] | Beijing, Hubei, Hunan, Qinghai, Guizhou, Shanghai, Sichuan |
| 5 | (6.8, +∞) | >0.620 | Anhui, Chongqing |
| Group | Province | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Heilongjiang | −14.4 | −524.1 | 1106.6 | −58.1 |
| 2 | Jilin | 59.4 | −188.2 | 758.8 | −79.9 |
| Liaoning | −46.1 | 35.7 | 1337.4 | −27 | |
| Henan | −32.8 | −2460.4 | 3363.6 | 229.5 | |
| Shanxi | 42.2 | −218.7 | 1145.5 | 80.9 | |
| Hebei | 40.9 | −1486.8 | 3554.3 | 231.6 | |
| Inner Mongolia | −35.7 | −72 | 1100.1 | 47.7 | |
| Ningxia | −29.4 | −45.7 | 209.3 | 25.7 | |
| 3 | Gansu | −165.5 | 75.7 | 749.1 | 30.7 |
| Tianjin | −7.3 | −302.8 | 773.3 | 86.9 | |
| Shandong | −185.8 | −49.3 | 4811.1 | 533.9 | |
| Jiangsu | −220 | 4165.2 | 4919.7 | 165 | |
| Yunnan | 173.5 | −4675.8 | 2116.8 | 125.5 | |
| Guangdong | −342.1 | −2436.7 | 7407.5 | 1201.3 | |
| Hainan | −2 | −42.3 | 480.1 | 34.2 | |
| Xinjiang | 39.7 | −914.5 | 716.9 | 127.9 | |
| Zhejiang | −244 | 3034.9 | 4090.1 | 439.1 | |
| Shaanxi | 30.3 | 395.3 | 1759.8 | 104.7 | |
| Fujian | −370.4 | 481.1 | 3170.1 | 329.2 | |
| Guangxi | 240.8 | −762.4 | 2214.5 | 227.1 | |
| Jiangxi | −73.5 | 710.4 | 1821.2 | 111.8 | |
| 4 | Beijing | 12.7 | 542.9 | 1487.4 | 17 |
| Hubei | 307.3 | 494.9 | 2660.9 | 166.9 | |
| Hunan | −46.4 | 2503.8 | 3407.9 | −5.3 | |
| Qinghai | 10.6 | −88 | 237.2 | 20.1 | |
| Guizhou | 54.4 | −463.6 | 2302.8 | 146.5 | |
| Shanghai | −58.7 | 1472.2 | 1764.9 | 41.6 | |
| Sichuan | −0.7 | 1468.1 | 3464.7 | 257.9 | |
| 5 | Anhui | −167.7 | 2337.9 | 2528 | 231.9 |
| Chongqing | 99.8 | 836.6 | 1494.2 | 159.4 |
| Province | Household Electricity Consumption | Population | Per Capita Disposable Income | Mean Electricity Price | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urban | Rural | Urban | Rural | |||||||||
| 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | |
| Beijing | 17.5 | 19.5 | 18.8 | 18.8 | 2.9 | 2.9 | 52.9 | 57.3 | 20.6 | 22.3 | 495.1 | 494.8 |
| Shanghai | 18.6 | 21.8 | 21.2 | 21.3 | 3 | 2.9 | 53 | 57.7 | 23.2 | 25.5 | 571.3 | 572.9 |
| Mean value of other provinces | 24.9 | 27.4 | 26.2 | 27 | 21 | 20.5 | 28.4 | 30.7 | 11.3 | 12.2 | 532.8 | 533.3 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, M.; Wu, S.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X. What is Currently Driving the Growth of China’s Household Electricity Consumption? A Clustering and Decomposition Analysis. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4648. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11174648
Meng M, Wu S, Zhou J, Wang X. What is Currently Driving the Growth of China’s Household Electricity Consumption? A Clustering and Decomposition Analysis. Sustainability. 2019; 11(17):4648. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11174648
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Ming, Shucheng Wu, Jin Zhou, and Xinfang Wang. 2019. "What is Currently Driving the Growth of China’s Household Electricity Consumption? A Clustering and Decomposition Analysis" Sustainability 11, no. 17: 4648. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11174648
APA StyleMeng, M., Wu, S., Zhou, J., & Wang, X. (2019). What is Currently Driving the Growth of China’s Household Electricity Consumption? A Clustering and Decomposition Analysis. Sustainability, 11(17), 4648. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11174648