People’s Tendency Toward Norm-Interventions to Tackle Waste Disposal in Public Open Spaces in Phnom Penh, Cambodia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Design of Statements
2.3. Questionnaire Design
2.4. Questionnaire Survey
2.5. Analytical Method
3. Results
3.1. Sample Distribution
3.2. Score Weight of Each Statement
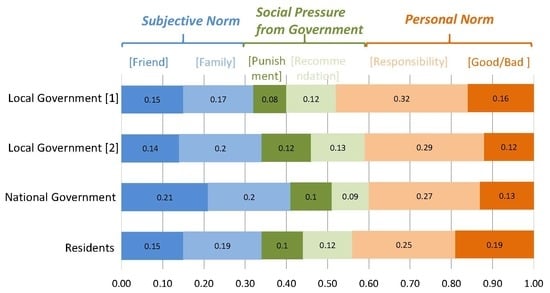
3.3. Opinion from the Central and Local Governments on Proposed Interventions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoornweg, D.; Bhada-Tata, P. What a Waste: A Global Review of Solid Waste Management; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Srun, P.; Kurisu, K. Internal and External Influential Factors on Waste Disposal Behavior in Public Open Spaces in Phnom Penh, Cambodia. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kum, V.; Sharp, A.; Harnpornchai, N. Improving the solid waste management in Phnom Penh city: A strategic approach. Waste Manag. 2005, 25, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seng, B.; Kaneko, H.; Hirayama, K.; Katayama-Hirayama, K. Municipal solid waste management in Phnom Penh, capital city of Cambodia. Waste Manag. Res. 2010, 29, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojedokun, O. Attitude towards littering as a mediator of the relationship between personality attributes and responsible environmental behavior. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 2601–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miliute-Plepiene, J.; Hage, O.; Plepys, A.; Reipas, A. What motivates households recycling behaviour in recycling schemes of different maturity? Lessons from Lithuania and Sweden. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2016, 113, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boadi, K.O.; Kuitunen, M. Municipal solid waste management in the Accra Metropolitan Area, Ghana. Environmentalist 2003, 23, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeva, K.; Alriksson, S. Influence of recycling programmes on waste separation behaviour. Waste Manag. 2017, 68, 732–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Ling, M.; Lu, Y.; Shen, M. External influences on forming residents’ waste separation behaviour: Evidence from households in Hangzhou, China. Habitat Int. 2017, 63, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oskamp, S.; Harrington, M.J.; Edwards, T.C.; Sherwood, D.L.; Okuda, S.M.; Swanson, D.C. Factors influencing household recycling behavior. Environ. Behav. 1991, 23, 494–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopper, J.R.; Nielsen, J.M. Recycling as altruistic behavior: Normative and behavioral strategies to expand participation in a community recycling program. Environ. Behav. 1991, 23, 195–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, G. Altruistic, egoistic, and normative effects on curbside recycling. Environ. Behav. 2001, 33, 733–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.; Foxall, G.R.; Pallister, J. Beyond the intention–behaviour mythology: An integrated model of recycling. Mark. Theory 2002, 2, 29–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabernero, C.; Hernández, B.; Cuadrado, E.; Luque, B.; Pereira, C.R. A multilevel perspective to explain recycling behaviour in communities. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 159, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botetzagias, I.; Dima, A.F.; Malesios, C. Extending the theory of planned behavior in the context of recycling: The role of moral norms and of demographic predictors. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 95, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strydom, W. Applying the theory of planned behavior to recycling behavior in South Africa. Recycling 2018, 3, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornik, J.; Cherian, J.; Madansky, M.; Narayana, C. Determinants of recycling behavior: A synthesis of research results. J. Socio Econ. 1995, 24, 105–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, S. Strategies for sustainability: Citizens and responsible environmental behaviour. Area 2003, 35, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstad, A. Household food waste separation behavior and the importance of convenience. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 1317–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehair, K.J.; Shanklin, C.W.; Brannon, L.A. Written messages improve edible food waste behaviors in a university dining facility. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2013, 113, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallbekken, S.; Sælen, H. ‘Nudging’ hotel guests to reduce food waste as a win–win environmental measure. Econ. Lett. 2013, 119, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreland, J.; Melsop, S. Design Interventions to Encourage Pro-Environmental Behavior. Available online: http://www.plea2014.in/wp-content/uploads/2014/12/Paper_6E_2672_PR.pdf (accessed on 18 June 2019).
- Farrow, K.; Grolleau, G.; Ibanez, L. Social norms and pro-environmental behavior: A review of the evidence. Ecol. Econ. 2017, 140, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöckli, S.; Niklaus, E.; Dorn, M. Call for testing interventions to prevent consumer food waste. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 136, 445–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, M.P.; Rice, R. Misperceiving the college drinking norm and related problems: A nationwide study of exposure to prevention information, perceived norms and student alcohol misuse. J. Stud. Alcohol 2005, 66, 470–478. [Google Scholar]
- Cialdini, R.B.; Reno, R.R.; Kallgren, C.A. A focus theory of normative conduct: Recycling the concept of norms to reduce littering in public places. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1990, 58, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, N.J.; Cialdini, R.B.; Griskevicius, V. A room with a viewpoint: Using social norms to motivate environmental conservation in hotels. J. Consum. Res. 2008, 35, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grodzińska-Jurczak, M.; Tomal, P.; Tarabuła-Fiertak, M.; Nieszporek, K.; Read, A.D. Effects of an educational campaign on public environmental attitudes and behaviour in Poland. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2006, 46, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagkaloglou, S.; Kasser, T. Increasing collaborative, pro-environmental activism: The roles of Motivational Interviewing, self-determined motivation, and self-efficacy. J. Environ. Psychol. 2018, 58, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khatib, I.A.; Arafat, H.A.; Daoud, R.; Shwahneh, H. Enhanced solid waste management by understanding the effects of gender, income, marital status, and religious convictions on attitudes and practices related to street littering in Nablus—Palestinian territory. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, P.W.; Bator, R.J.; Large, L.B.; Bruni, C.M.; Tabanico, J.J. Littering in context: Personal and environmental predictors of littering behavior. Environ. Behav. 2013, 45, 35–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cintri. Waste Collection Reports for Khan Dongkor, Khan Prampir Meakkakra, Khan Chbar Amporv, Khan Chhroy Chongva, Khan Chomkar Mom, Khan Duon Penh, Khan Mean Chey, Khan Pousenchey, Khan Prek Pnov, Khan Reussey Keo District, Khan Sensok, and Khan Tuol Kork. 2016. Available online: http://www.cintri.com.kh/view.aspx?LID=KH&mID=H11 (accessed on 10 March 2019). (In Khmer).
- National Institute of Statistics of Cambodia (NIS). General Population Census of Cambodia 2008; National Institute of Statistics, Ministry of Planning: Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, S.H. Normative influences on altruism. In Advances in Experimental Social Psychology; Berkowitz, L., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1977; pp. 221–279. [Google Scholar]
- Yamane, T. Statistics: An Introductory Analysis, 2nd ed.; Harper and Row: New York, NY, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Saaty, T.L. Fundamentals of Decision Making and Priority Theory, with The Analytic Hierarchy Process; RWS Publications: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 1994; Volume 6, pp. 69–92. [Google Scholar]
- Dodd, F.J.; Donegan, H.A.; McMaster, T.B.M. Inverse Inconsistency in Analytic Hierarchies. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1995, 80, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, S.L.; Tang, S.L. A Comparison of the Saaty’s AHP and Modified AHP for Right and Left Eigenvector Inconsistency. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1998, 106, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortoleto, A.P.; Kurisu, K.H.; Hanaki, K. Model development for household waste prevention behaviour. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 2195–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bamberg, S.; Mӧser, G. Twenty years after Hines, Hungerford, and Tomera: A new meta-analysis of psycho-social determinants of pro-environmental behavior. J. Environ. Psychol. 2007, 27, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, N.; Goodwin, J.; Jones, P.; Weaver, N. Sustaining recycling: Identification and application of limiting factors in kerbside recycling areas. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 1998, 5, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chase, N.; Dominick, G.; Trepal, A.; Bailey, L.; Friedman, D. “This Is Public Health: Recycling Counts!” description of a pilot health communications campaign. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2009, 6, 2980–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cotterill, S.; John, P.; Liu, H.; Nomura, H. Mobilizing citizen effort to enhance environmental outcomes: A randomized controlled trial of a door-to-door recycling campaign. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 91, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddox, P.; Doran, C.; Williams, I.D.; Kus, M. The role of intergenerational influence in waste education programmes: The THAW project. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 2590–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Commune | Collection Frequency (times/week) | Population Density (persons/km2) | Streets Surveyed | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HH | Phsar Dermkor | High | 7 | High | 31,065 | St. 223, 230, 234, 231, 239 |
| LH | Toek Thlar | Low | 3 | High | 9186 | St. 1019, 2004, 598 |
| HL | Tonle Basak | High | 7 | Low | 6499 | St. 21, 73, 93, 442, 462 |
| LL | Dangkao | Low | 3 | Low | 1141 | St. 217, 1,5,9,11 st. prey sa |
| No. | Abbrev. | Target Factor | Targeting Points | Statements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | Sb (fr) | Subjective norms (Sb) | Friends’ expectations | “Let’s cooperate with your friends and try not to dispose of waste in public!” |
| (2) | Sb (fm) | Family’s expectations | “Let’s cooperate with your beloved family and try not to dispose of waste in public!” | |
| (3) | Sp_g (pun) | Social pressure from the government (Sp_g) | Strict pressure | “You will be punished by the government if you dispose of waste in public!” |
| (4) | Sp_g (rec) | Soft pressure | “Government recommends you not to dispose of waste in public!” | |
| (5) | Pn (res) | Personal norms (Pn) | Responsibility | “This is your responsibility not to dispose of waste in public!” |
| (6) | Pn (G/B) | Good or bad | “Disposing of waste in public is bad thing, so do not dispose of waste in public!” |
| Category | Questions | Contents | Answer Type | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | Socio-demographics | I_1 | Age | Written |
| I_2 | Gender | SA * from 2 items | ||
| I_3 | Address (district) | Written | ||
| I_4 | Family income | SA from 4 items | ||
| I_7 | Education level | SA from 5 items | ||
| I_8 | Family sizes | Written | ||
| I_9 | House type | SA from 6 items | ||
| II | About current waste collection services | II_4, 9 | Collection and disposal frequency | SA from 5 items |
| II_6 | Usual number of waste bags disposed | SA from 4 items | ||
| II_7, 10 | Disposal location | SA from 8 (6) items | ||
| II_11 | Satisfaction with current services | 6-point scale | ||
| II_12 | Past experiences of disposing wastes in public open spaces | 5-point scale | ||
| II_13 | Reason for II_12 | SA from 5 items | ||
| II_15 | Free opinions on current waste collection services | Open question | ||
| III | Statement comparison | III_1–15 | 15 pair-wise comparisons among six statements | 5-point scale |
| Category | No. | Date | Position |
|---|---|---|---|
| Local government | LG1 | 14 March 2019 | Chief Officer of Environment in Prampi Makkara district |
| LG2 | 19 March 2019 | Chief Officer of Environment in Tuol Kork district | |
| National government | NG | 20 March 2019 | Deputy Director of Waste Management Department of the MoE |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Srun, P.; Kurisu, K. People’s Tendency Toward Norm-Interventions to Tackle Waste Disposal in Public Open Spaces in Phnom Penh, Cambodia. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6603. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11236603
Srun P, Kurisu K. People’s Tendency Toward Norm-Interventions to Tackle Waste Disposal in Public Open Spaces in Phnom Penh, Cambodia. Sustainability. 2019; 11(23):6603. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11236603
Chicago/Turabian StyleSrun, Pagnarith, and Kiyo Kurisu. 2019. "People’s Tendency Toward Norm-Interventions to Tackle Waste Disposal in Public Open Spaces in Phnom Penh, Cambodia" Sustainability 11, no. 23: 6603. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11236603
APA StyleSrun, P., & Kurisu, K. (2019). People’s Tendency Toward Norm-Interventions to Tackle Waste Disposal in Public Open Spaces in Phnom Penh, Cambodia. Sustainability, 11(23), 6603. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11236603