Absorption Behavior of Graphene Nanoplates toward Oils and Organic Solvents in Contaminated Water
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of GNPs
2.3. Absorption of Oils and Organic Solvents
2.4. Absorption Kinetics
2.5. Effect of Temperature
2.6. Effect of Aging Conditions
2.7. Recyclability and Recoverability
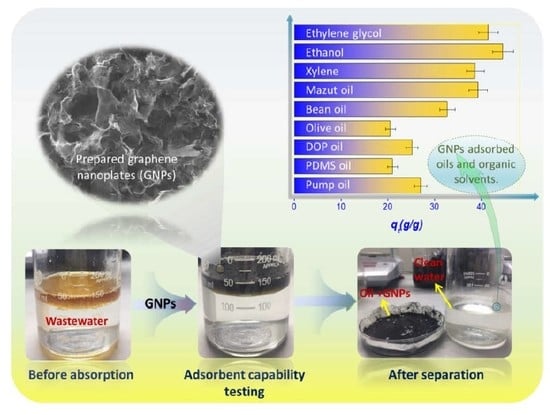
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crini, G. Non-conventional low-cost adsorbents for dye removal: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1061–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, J. Effects and risk evaluation of oil spillage in the sea areas of Changxing island. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 8491–8507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olasanmi, I.O.; Thring, R.W. The role of biosurfactants in the continued drive for environmental sustainability. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calcagnile, P.; Fragouli, D.; Bayer, I.S.; Anyfantis, G.C.; Martiradonna, L.; Cozzoli, P.D.; Cingolani, R.; Athanassiou, A. Magnetically driven floating foams for the removal of oil contaminants from water. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 5413–5419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, A.; Xu, F.; Zhang, X. Fabrication of biomass-derived carbon aerogels with high adsorption of oils and organic solvents: Effect of hydrothermal and post-pyrolysis processes. Materials 2016, 9, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adebajo, M.O.; Frost, R.L.; Kloprogge, J.T.; Carmody, O.; Kokot, S. Porous materials for oil spill cleanup: A review of synthesis and absorbing properties. J. Porous Mater. 2003, 10, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bayat, A.; Aghamiri, S.F.; Moheb, A.; Vakili-Nezhaad, G.R. Oil spill cleanup from sea water by sorbent materials. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2005, 28, 1525–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahed, M.A.; Aziz, H.A.; Isa, M.H.; Mohajeri, L.; Mohajeri, S. Optimal conditions for bioremediation of oily seawater. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 9455–9460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buist, I.; Potter, S.; Nedwed, T.; Mullin, J. Herding surfactants to contract and thicken oil spills in pack ice for in situ burning. J. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2011, 67, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Chen, M.; Zhang, L.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; Yan, J.; Wang, W.; Gao, J. Three-dimensional graphene-based aerogels prepared by a self-assembly process and its excellent catalytic and absorbing performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 7612–7621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.Y.; Li, C.; Liang, H.W.; Chen, J.F.; Yu, S.H. Ultralight, flexible, and fire-resistant carbon nanofiber aerogels from bacterial cellulose. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 125, 2997–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.Y.; Mubarak, N.M.; Abdullah, E.C.; Nizamuddin, S.; Khalid, M.; Inamuddin. Recent trends in the synthesis of graphene and graphene oxide based nanomaterials for removal of heavy metals—A review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 66, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsnelson, M.I. Graphene: Carbon in two dimensions. Mater. Today 2007, 10, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopelevich, Y.; Esquinazi, P. Graphene physics in graphite. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 4559–4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.-H.; Lu, J.-S.; Chen, Y.-C. Sustainable recovery of CO2 by using visible-light-responsive crystal cuprous oxide/reduced graphene oxide. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Yu, X.; Liu, X. Obtaining a sustainable competitive advantage from patent information: A patent analysis of the graphene industry. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rehman, S.K.U.; Ibrahim, Z.; Memon, S.A.; Javed, M.F.; Khushnood, R.A. A sustainable graphene based cement composite. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morozov, S.; Novoselov, K.; Katsnelson, M.; Schedin, F.; Elias, D.; Jaszczak, J.; Geim, A. Giant intrinsic carrier mobilities in graphene and its bilayer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 016602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Becerril, H.A.; Mao, J.; Liu, Z.; Stoltenberg, R.M.; Bao, Z.; Chen, Y. Evaluation of solution-processed reduced graphene oxide films as transparent conductors. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, D.; Wu, L.; Wei, T.; Liu, L.; Lv, Y.; Yu, F.; Chen, L.; Shi, Y. N, S Dual-doped carbon derived from dye sludge by using polymeric flocculant as soft template. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kashif Ur Rehman, S.; Ibrahim, Z.; Memon, S.A.; Aunkor, M.T.H.; Faisal Javed, M.; Mehmood, K.; Shah, S.M.A. Influence of graphene nanosheets on rheology, microstructure, strength development and self-sensing properties of cement based composites. Sustainability 2018, 10, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Shafai, N.M.; El-Khouly, M.E.; El-Kemary, M.; Ramadan, M.S.; Derbalah, A.S.; Masoud, M.S. Fabrication and characterization of graphene oxide-titanium dioxide nanocomposite for degradation of some toxic insecticides. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 69, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, P.; Ravirajan, A.; Umasankaran, A.; Prakash, D.G.; Kumar, P.S. Theoretical and experimental investigation on the removal of oil spill by selective sorbents. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 63, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.; Satish Babu, K.K.C.; Torati, S.R.; Eom, Y.J.; Trung, T.Q.; Lee, N.-E.; Kim, C. Scalable production of water-dispersible reduced graphene oxide and its integration in a field effect transistor. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 63, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Fu, Z.; Chou, S.Y. Graphene transistors fabricated via transfer-printing in device active-areas on large wafer. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 3840–3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, H.-P.; Ren, X.-C.; Wang, P.; Yu, S.-H. Macroscopic multifunctional graphene-based hydrogels and aerogels by a metal ion induced self-assembly process. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 2693–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Jiang, H.; Li, G.; Zhi, C. Large scale fabrication of graphene for oil and organic solvent absorption. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2016, 26, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, R.; Chen, C.; Li, J.; Xu, L.; Xiao, G.; Yan, D. A facile approach to superhydrophobic and superoleophilic graphene/polymer aerogels. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 3057–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La, M.; Duc, D.; Bhargava, S.; Bhosale, S.V. Improved and a simple approach for mass production of graphene nanoplatelets material. Chem. Select 2016, 1, 949–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaković-Ognjanović, V.; Aleksić, G.; Rajaković, L. Governing factors for motor oil removal from water with different sorption materials. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 154, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geim, A.K.; Novoselov, K.S. The rise of graphene. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husseien, M.; Amer, A.; El-Maghraby, A.; Hamedallah, N. A comprehensive characterization of corn stalk and study of carbonized corn stalk in dye and gas oil sorption. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2009, 86, 360–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, D.; Dogu, S.; Karacik, B.; Yakan, S.D.; Okay, O.S.; Okay, O. Evaluation of butyl rubber as sorbent material for the removal of oil and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from seawater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3846–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Chu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, N.; Lin, L.; Liu, F.; Pan, Q. Robust superhydrophobic polyurethane sponge as a highly reusable oil-absorption material. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2013, 1, 5386–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.B.; Ha, W.; Jiang, K.; Chen, J.; Yang, J.L.; Shi, Y.P. Efficient synthesis of camptothecin propargylamine derivatives in water catalyzed by macroporous adsorption resin-supported gold nanoparticles. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 1399–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Kinetic Parameters | Mazut Oil | Ethylene Glycol (EG) |
|---|---|---|
| qe (g/g) | 61.358 ± 5.046 | 50.356 ± 1.433 |
| K (h−1) | 0.001 ± 5.574 × 10−4 | 0.017 ± 0.004 |
| Reduced Chi-Sqr | 31.214 | 7.412 |
| R-Square (R2) | 0.912 | 0.868 |
| Adj. R2 | 0.894 | 0.842 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
La, D.D.; Nguyen, T.A.; Nguyen, T.T.; Ninh, H.D.; Thi, H.P.N.; Nguyen, T.T.; Nguyen, D.A.; Dang, T.D.; Rene, E.R.; Chang, S.W.; et al. Absorption Behavior of Graphene Nanoplates toward Oils and Organic Solvents in Contaminated Water. Sustainability 2019, 11, 7228. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11247228
La DD, Nguyen TA, Nguyen TT, Ninh HD, Thi HPN, Nguyen TT, Nguyen DA, Dang TD, Rene ER, Chang SW, et al. Absorption Behavior of Graphene Nanoplates toward Oils and Organic Solvents in Contaminated Water. Sustainability. 2019; 11(24):7228. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11247228
Chicago/Turabian StyleLa, Duong Duc, Tuan Anh Nguyen, Thanh Tung Nguyen, Ha Duc Ninh, Hoai Phuong Nguyen Thi, Tham Thi Nguyen, Duy Anh Nguyen, Trung Dung Dang, Eldon R. Rene, Soon Woong Chang, and et al. 2019. "Absorption Behavior of Graphene Nanoplates toward Oils and Organic Solvents in Contaminated Water" Sustainability 11, no. 24: 7228. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11247228
APA StyleLa, D. D., Nguyen, T. A., Nguyen, T. T., Ninh, H. D., Thi, H. P. N., Nguyen, T. T., Nguyen, D. A., Dang, T. D., Rene, E. R., Chang, S. W., Thi, H. T., & Nguyen, D. D. (2019). Absorption Behavior of Graphene Nanoplates toward Oils and Organic Solvents in Contaminated Water. Sustainability, 11(24), 7228. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11247228