Affordability, Accessibility, and Awareness in the Adoption of Liquefied Petroleum Gas: A Case-Control Study in Rural India
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Research Questions and Hypothesis
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Operationalization of Variables
2.2. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Model Comparison
3.2. Demographic Predictors and LPG Adoption
3.3. Affordability and LPG Adoption
3.4. Accessibility and LPG Adoption
3.5. Awareness and LPG Adoption
4. Discussion
4.1. Caste and LPG Adoption
4.2. Affordability and LPG Adoption
4.3. Accessibility and LPG Adoption
4.4. Awareness and LPG Adoption
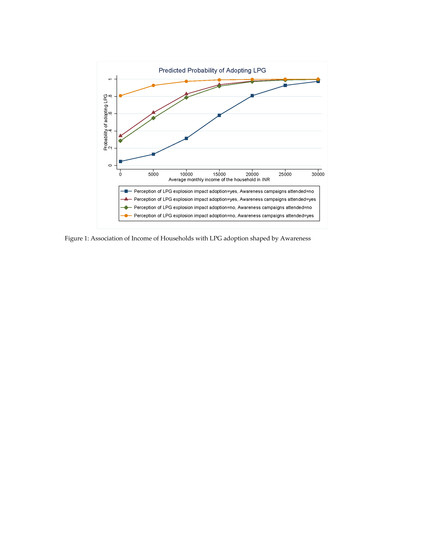
4.5. Marginal Effects on LPG Adoption
5. Limitations of the Manuscript
- Analyses for this study were based on a retrospective design. The retrospective nature of the study for LPG adopters might have led to decreased response validity due to issues of memory retention. Recall bias may further limit the accuracy of participants’ responses.
- The findings are from a case-control study and based on cross-sectional data. Thus, this one single study has limited implications on generalizability. Typical of a case-control study, findings also do not establish a causal relationship between independent and dependent variables. However, this study could be foundational for undertaking a larger longitudinal study on LPG adoption in energy-poor communities.
- Both adoption and sustained use of LPG could be a function of affordability, accessibility, and awareness of BPL rural communities, and are necessary to address challenges of HAP. The present study focused on the adoption component and analyzed only one of the aims of the larger study. Results for sustained use and its determinants will be published separately.
- Implementation studies on adoption and sustained use of evidence based interventions merit analyses at multiple levels [38,39]. Both individual and community level determinants could be associated with LPG adoption. This study accounted for individual level factors and explored 35 habitations. Statistical power was low for a multilevel examination.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scarpellini, S.; Sanz Hernández, M.A.; Llera-Sastresa, E.; Aranda, J.A.; López Rodríguez, M.E. The mediating role of social workers in the implementation of regional policies targeting energy poverty. Energy Policy 2017, 106, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, K.; McCauley, D.; Heffron, R.; Stephan, H.; Rehner, R. Energy justice: A conceptual review. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2016, 11, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rao, N.D.; Pachauri, S. Energy access and living standards: Some observations on recent trends. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, N.G.; Aunan, K.; Rehfuess, E.A. Liquefied Petroleum Gas as a Clean Cooking Fuel for Developing Countries: Implications for Climate, Forests, and Affordability; KfW Entwicklungsbank: Frankfurt, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- GACC. How do We Define and Measure Adoption? Available online: http://cleancookstoves.org/about/news/02-18-2016-how-do-we-define-and-measure-adoption.html (accessed on 8 December 2019).
- GACC. Defining and Measuring ‘Adoption’ of Clean Cookstoves and Fuels. Available online: http://cleancookstoves.org/about/news/05-22-2015-defining-and-measuring-adoption-of-clean-cookstoves-and-fuels.html (accessed on 8 December 2019).
- Kumar, P.; Mehta, S. Poverty, gender, and empowerment in sustained adoption of cleaner cooking systems: Making the case for refined measurement. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2016, 19, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Chalise, N.; Yadama, G.N. Dynamics of sustained use and abandonment of clean cooking systems: Study protocol for community-based system dynamics modeling. Int. J. Equity Health 2016, 15, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenthal, J.; Balakrishnan, K.; Bruce, N.; Chambers, D.; Graham, J.; Jack, D.; Kline, L.; Masera, O.; Mehta, S.; Mercado, I.R.; et al. Implementation Science to Accelerate Clean Cooking for Public Health. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, A3–A7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishesh, C.; Praveen, K.; Pratiti, P.; Gautam, N.Y. Dynamics of sustained use and abandonment of clean cooking systems: Lessons from rural India. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 035010. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Igdalsky, L. Sustained uptake of clean cooking practices in poor communities: Role of social networks. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2019, 48, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Kaushalendra Rao, R.; Reddy, N.H. Sustained uptake of LPG as cleaner cooking fuel in rural India: Role of affordability, accessibility, and awareness. World Dev. Perspect. 2016, 4, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Agrawal, S.; Ganesan, K. Rationalising Subsidies, Reaching the Underserved; Council on Energy, Environment and Water: New Delhi, India, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sehjpal, R.; Ramji, A.; Soni, A.; Kumar, A. Going beyond incomes: Dimensions of cooking energy transitions in rural India. Energy 2014, 68, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoop, T.D.; Brody, C.; Tripathi, S.; Vojtkova, M.; Warnock, R. Economic Self-Help Group Programmes for Improving Women’s Empowerment, 3ie Systematic Review Summary 11; International Initiative for Impact Evaluation (3ie): London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, J.J.; Pattanayak, S.K. Who adopts improved fuels and cookstoves? A systematic review. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollada, J.; Williams, K.N.; Miele, C.H.; Danz, D.; Harvey, S.A.; Checkley, W. Perceptions of Improved Biomass and Liquefied Petroleum Gas Stoves in Puno, Peru: Implications for Promoting Sustained and Exclusive Adoption of Clean Cooking Technologies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2017, 14, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, P.; Dhand, A.; Tabak, R.G.; Brownson, R.C.; Yadama, G.N. Adoption and sustained use of cleaner cooking fuels in rural India: A case control study protocol to understand household, network, and organizational drivers. Arch. Public Health 2017, 75, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srinivasan, S.; Carattini, S. Adding fuel to fire? Social spillovers in the adoption of LPG in India. Ecol. Econ. 2020, 167, 106398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.J.; Bhojvaid, V.; Brooks, N.; Das, I.; Jeuland, M.A.; Patange, O.; Pattanayak, S.K. Piloting Improved Cookstoves in India. J. Health Commun. 2015, 20, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yadama, G.N. Fires, Fuel, and the Fate of 3 Billion: The State of the Energy Impoverished; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, I. Inequality and the imperative for inclusive growth in Asia. Asian Dev. Rev. 2007, 24, 1. [Google Scholar]
- El Tayeb Muneer, S.; Mukhtar Mohamed, E.W. Adoption of biomass improved cookstoves in a patriarchal society: An example from Sudan. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 307, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pine, K.; Edwards, R.; Masera, O.; Schilmann, A.; Marrón-Mares, A.; Riojas-Rodríguez, H. Adoption and use of improved biomass stoves in Rural Mexico. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2011, 15, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geremew, K.; Gedefaw, M.; Dagnew, Z.; Jara, D. Current Level and Correlates of Traditional Cooking Energy Sources Utilization in Urban Settings in the Context of Climate Change and Health, Northwest Ethiopia: A Case of Debre Markos Town. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 572473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, C.F.; Urpelainen, J. LPG as a clean cooking fuel: Adoption, use, and impact in rural India. Energy Policy 2018, 122, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecelski, E. The Role of Women in Sustainable Energy Development; NREL/SR-550-26889; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.; Parikh, J.; Singh, C. Transition to LPG for cooking: A case study from two states of India. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2019, 51, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachauri, S.; Rao, N.D. Gender impacts and determinants of energy poverty: Are we asking the right questions? Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2013, 5, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, A.; Pachauri, S.; Bailis, R.; Zerriffi, H. Using sales data to assess cooking gas adoption and the impact of India’s Ujjwala programme in rural Karnataka. Nat. Energy 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Negotiating Access: The Social Process of Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) Cookstove Dissemination Intervention in Himachal Pradesh, India. Trop. Resour. Bull. 2014, 32–33, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, A.; Tawale, N.; Raynes-Greenow, C. Household air pollution intervention implications: Findings from qualitative studies and a field trial of clean cookstoves in two rural villages in India. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakar, Y. Studying household decision-making context and cooking fuel transition in rural India. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2018, 43, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schunder, T.; Bagchi-Sen, S. Understanding the household cooking fuel transition. Geogr. Compass 2019, e12469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puzzolo, E.; Pope, D.; Stanistreet, D.; Rehfuess, E.A.; Bruce, N.G. Clean fuels for resource-poor settings: A systematic review of barriers and enablers to adoption and sustained use. Environ. Res. 2016, 146, 218–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, A.K.; Bruce, N.; Puzzolo, E.; Dickinson, K.; Sturke, R.; Jack, D.W.; Mehta, S.; Shankar, A.; Sherr, K.; Rosenthal, J.P. An analysis of efforts to scale up clean household energy for cooking around the world. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2018, 46, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GOI. Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana. 2019. Available online: https://pmuy.gov.in/ (accessed on 10 November 2019).
- Acemoglu, D.; Ozdaglar, A.; Yildiz, E. Diffusion of innovations in social networks. In Proceedings of the 2011 50th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control and European Control Conference (CDC-ECC 2011), Orlando, FL, USA, 12–15 December 2011; pp. 2329–2334. [Google Scholar]
- Glasgow, R.E.; Vogt, T.M.; Boles, S.M. Evaluating the public health impact of health promotion interventions: The RE-AIM framework. Am. J. Public Health 1999, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- World LPG Association. LPG and the Global Energy Transition: A study on behalf of the World LPG Association; World LPG Association: Paris, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Rao, S.; Yamada, G.N. Energy Poverty in India; NASW Press: Washington, DC, USA; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Outcome Variable | Codes |
|---|---|
| LPG Adoption | 1 = Yes/0 = No |
| Demographic predictors | Codes |
| Age | Years |
| Marital status | 1 = Married/2 = Unmarried (ref)/3 = Divorced/4 = Widow |
| Literacy: Highest level of education completed | 0 = None (ref)/1 = Below or up to class 4/2 = Class 5 to class 8/3 = Class 9 to class 10/4 = Class 11 to class 12/5 = College |
| Caste | 0 = General (Ref)/1 = Other backward castes (OBC)/2 = Scheduled castes/scheduled tribes (SC/ST)/3 = Other religious minorities |
| Key predictors | |
| Affordability | Codes |
| Membership of self-help groups (SHGs) | 1 = Yes/0 = No |
| Monthly income of the household | Indian national rupee (INR), squared root transformed for normality |
| Accessibility | Codes |
| Nearest paved road from the household | Kilometers (km), square root transformed for normality |
| Availability of free biomass near the household | 1 = Yes/0 = No |
| Distance of the biomass source | Kilometers (km), square root transformed for normality |
| Preference for smaller LPG cylinders | 1 = Yes/2 = No (ref)/3 = Can’t say |
| Decision making capacity to purchase new stove | 1 = Respondent (ref)/2 = Spouse of respondent/3 = Respondent and spouse of the respondent/4 = Respondent, spouse of the respondent, and others/5 = Respondent and other but not the spouse/6 = Others but not the respondent or the spouse of the respondent |
| Awareness | Codes |
| Perception of LPG explosion (LPG safety) | 1 = Yes/0 = No |
| Campaigns attended | 1 = Yes/0 = No |
| Variables | Mean (Standard Deviation) | Percent of Response (Frequency) |
|---|---|---|
| Outcome variable | ||
| LPG Adoption | ||
| Yes | 50% (255) | |
| No | 50% (255) | |
| Independent variables | Mean (Standard Deviation) | Percent of Response (Frequency) |
| Demographic | ||
| Age | 40.34 (13.32) | |
| Marital Status | ||
| Married | 87.25% (445) | |
| Unmarried | 0.58% (3) | |
| Widow | 12.16% (62) | |
| Literacy: Highest level of education completed | ||
| None | 65.88% (336) | |
| Below or up to class 4 | 6.67% (34) | |
| Class 5 to class 8 | 13.53% (69) | |
| Class 9 to class 10 | 10.39% (53) | |
| Class 11 to class 12 | 1.96% (10) | |
| College | 1.57% (8) | |
| Caste | ||
| General | 14.51% (74) | |
| OBC | 48.63% (248) | |
| SC/ST | 35.88% (183) | |
| Other Religious Minorities | 0.98% (5) | |
| Affordability | ||
| Membership of SHG | ||
| Yes | 66.86% (341) | |
| No | 33.14% (169) | |
| Monthly income of the household (INR) | 2912.69 (2270.64) | |
| Accessibility | ||
| Nearest paved road from the household (km) | 0.67 (0.98) | |
| Availability of free biomass near the household | ||
| Yes | 12.75% (65) | |
| No | 87.25% (445) | |
| Distance of biomass source (Km) | 2.36 (1.37) | |
| Preference for smaller LPG cylinders | ||
| Yes | 1.37% (7) | |
| No | 92.16% (470) | |
| Can’t say | 6.47% (33) | |
| Decision making capacity to purchase new stove | ||
| Respondent | 28.82% (147) | |
| Spouse of respondent | 46.27% (236) | |
| Respondent and spouse of the respondent | 20.20% (103) | |
| Respondent, spouse of the respondent, and others | 0.98% (5) | |
| Respondent and others but not the spouse | 1.96% (10) | |
| Others but not the respondent or the spouse of the respondent | 1.76% (9) | |
| Awareness | ||
| Perception of LPG explosion (LPG safety) | ||
| Yes | 8.82% (45) | |
| No | 91.18% (465) | |
| Campaigns Attended | ||
| Yes | 7.84% (40) | |
| No | 92.16% (470) |
| Model 1 | Model 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | OR (95% CI) | |
| Demographic predictors | ||
| Age (years) | 0.98 (0.96–0.99) ** | 0.99 (0.97–1.01) |
| Marital status (Reference: unmarried) | ||
| Married | 1.96 (0.40–10.70) | 10.97 (1.81–66.65) ** |
| Widow | 1.91 (0.28–12.78) | 10.01(1.37–74.08) ** |
| Literacy: Highest education of the respondent (Reference: No education) | ||
| Below or up to class 4: | 0.60 (0.25–1.42) | 0.54 (0.17–1.67) |
| Class 5 to class 8: | 0.84 (0.55–1.27) | 0.79 (0.51–1.26) |
| Class 9 to class10: | 1.43 (0.71–2.88) | 1.08 (0.53–2.23) |
| Class 11 to class 12: | 2.10 (0.79–5.57) | 3.67 (0.34–40.09) |
| College: | 1.01 (0.21–4.92) | 0.74 (0.04–14.93) |
| Caste (Reference: General) | ||
| OBC | 0.64 (0.28–1.47) | 0.60 (0.27–1.31) |
| SC/ST | 0.11 (0.04–0.29) *** | 0.08 (0.28–0.30) *** |
| Other religious minorities | 0.34 (0.04–3.13) | 0.16 (0.02–1.22) * |
| Affordability | ||
| Membership with SHG (Reference: No) | ||
| Yes | 1.37 (0.76–2.47) | |
| Square root of Income of the household | ||
| INR | 1.0003 (1.00008–1.0005) * | |
| Accessibility | ||
| Nearest paved from the household (square root) | ||
| km | 0.76 (0.52–1.11) | |
| Preference for Smaller LPG cylinders (Reference: Yes) | ||
| No | 2.00 (0.06–65.94) | |
| Can’t say | 0.49 (0.02–15.08) | |
| Availability of free biomass near the household (Reference: No) | ||
| Yes | 0.01 (0.001–0.13) *** | |
| Distance of the biomass source (square root) | ||
| km | 1.16 (0.89–1.54) | |
| Decision making capacity to purchase new stove (Reference: Respondent) | ||
| Spouse of respondent | 0.59 (0.39–0.92) * | |
| Respondent and spouse of the respondent | 0.79 (0.43–1.45) | |
| Respondent, spouse of the respondent, and others | 1.27 (0.08–20.52) | |
| Respondent and others but not the spouse | 1.68 (0.45–6.25) | |
| Others but not the respondent or the spouse of the respondent | 1.05 (0.25–4.38) | |
| Awareness | ||
| Perception of LPG explosion (LPG safety) (Reference: No) | ||
| Yes | 0.125(0.06–0.39) *** | |
| Campaigns attended (Reference: No) | ||
| Yes | 11.68 (2.27–59.84) ** | |
| Goodness of fit | ||
| AIC | 630.31 | 404.35 |
| BIC | 681.12 | 500.51 |
| Pseudo R2 | 0.14 | 0.37 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumar, P.; Dover, R.E.; Díaz-Valdés Iriarte, A.; Rao, S.; Garakani, R.; Hadingham, S.; Dhand, A.; Tabak, R.G.; Brownson, R.C.; Yadama, G.N. Affordability, Accessibility, and Awareness in the Adoption of Liquefied Petroleum Gas: A Case-Control Study in Rural India. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4790. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12114790
Kumar P, Dover RE, Díaz-Valdés Iriarte A, Rao S, Garakani R, Hadingham S, Dhand A, Tabak RG, Brownson RC, Yadama GN. Affordability, Accessibility, and Awareness in the Adoption of Liquefied Petroleum Gas: A Case-Control Study in Rural India. Sustainability. 2020; 12(11):4790. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12114790
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumar, Praveen, Robert Ethan Dover, Antonia Díaz-Valdés Iriarte, Smitha Rao, Romina Garakani, Sophia Hadingham, Amar Dhand, Rachel G. Tabak, Ross C. Brownson, and Gautam N. Yadama. 2020. "Affordability, Accessibility, and Awareness in the Adoption of Liquefied Petroleum Gas: A Case-Control Study in Rural India" Sustainability 12, no. 11: 4790. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12114790
APA StyleKumar, P., Dover, R. E., Díaz-Valdés Iriarte, A., Rao, S., Garakani, R., Hadingham, S., Dhand, A., Tabak, R. G., Brownson, R. C., & Yadama, G. N. (2020). Affordability, Accessibility, and Awareness in the Adoption of Liquefied Petroleum Gas: A Case-Control Study in Rural India. Sustainability, 12(11), 4790. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12114790