Assessment of Soil Erosion Using the RUSLE Model for the Epworth District of the Harare Metropolitan Province, Zimbabwe
Abstract
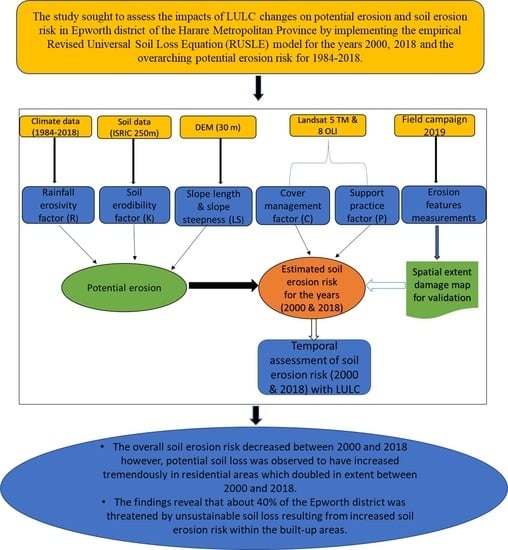
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Soil Erosion Modelling
2.2.1. Parameter Estimation for Soil Erosion Risk Assessment Using RUSLE
2.2.2. Data Integration for Soil Erosion Risk Assessment
Rainfall Erosivity Factor (R)
Soil Erodibility Factor (K)
Topographic Factor (LS)
Land Cover and Management Factor (C)
Support Practice Factor (P)
2.3. Mapping and Surveying Soil Erosion Dynamics
3. Results
3.1. Factors Controlling Soil Erosion
3.2. Potential Erosion Risk Analysis
3.3. Soil Erosion Risk
3.4. Magnitude of Soil Erosion in Epworth District
3.5. Land Use and Soil Loss Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alaci, D.S.A. Regulating Urbanisation in Sub-Saharan Africa through Cluster Settlements. Theor. Empirical Res. Urban Manag. 2019, 5, 16. [Google Scholar]
- African Development Bank Gender. Poverty and Environmental Indicators on African Countries; African Development Bank: Abidjan, Cote d’Ivoire, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Khosrokhani, M.; Pradhan, B. Spatio-temporal assessment of soil erosion at Kuala Lumpur metropolitan city using remote sensing data and GIS. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2014, 5, 252–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lambin, E.F.; Turner, B.L.; Geist, H.J.; Agbola, S.B.; Angelsen, A.; Bruce, J.W.; Coomes, O.T.; Dirzo, R.; Fischer, G.; Folke, C.; et al. The causes of land-use and land-cover change: Moving beyond the myths. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2001, 11, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshesha, D.T.; Tsunekawa, A.; Tsubo, M.; Ali, S.A.; Haregeweyn, N. Land-use change and its socio-environmental impact in Eastern Ethiopia’s highland. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2014, 14, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCool, D.K.; Brown, L.C.; Foster, G.R.; Mutchler, C.K.; Meyer, L.D. Revised Slope Steepness Factor for the Universal Soil Loss Equation. Trans. ASAE 1987, 30, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinren, R.N.; Yingkui, K.L. Approach to soil erosion assessment in terms of land-use structure changes. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2003, 58, 158–169. [Google Scholar]
- Chirisa, I.E.W.; Muhomba, K. Constraints to managing urban and housing land in the context of poverty: A case of Epworth settlement in Zimbabwe. Local Environ. 2013, 18, 950–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marondedze, A.K.; Schütt, B. Dynamics of Land Use and Land Cover Changes in Harare, Zimbabwe: A Case Study on the Linkage between Drivers and the Axis of Urban Expansion. Land 2019, 8, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chirisa, I. Building and urban planning in Zimbabwe with special reference to Harare: Putting needs, costs and sustainability in focus. Consilience 2014, 11, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Kamusoko, C.; Gamba, J.; Murakami, H. Monitoring Urban Spatial Growth in Harare Metropolitan Province, Zimbabwe. ARS 2013, 2, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karydas, C.G.; Sekuloska, T.; Silleos, G.N. Quantification and site-specification of the support practice factor when mapping soil erosion risk associated with olive plantations in the Mediterranean island of Crete. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 149, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McHugh, M.; Harrod, T.; Morgan, R. The extent of soil erosion in upland England and Wales. Earth Surf. Process. Landforms 2002, 27, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozsahin, E.; Duru, U.; Eroglu, I. Land Use and Land Cover Changes (LULCC), a Key to Understand Soil Erosion Intensities in the Maritsa Basin. Water 2018, 10, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borrelli, P.; Robinson, D.A.; Panagos, P.; Lugato, E.; Yang, J.E.; Alewell, C.; Wuepper, D.; Montanarella, L.; Ballabio, C. Land use and climate change impacts on global soil erosion by water (2015–2070). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 21994–22001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Soil degradation by erosion. Land Degrad. Dev. 2001, 12, 519–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahlaoi, H.; Rhinane, H.; Hilali, A.; Lahssini, S.; Khalile, L. Potential Erosion Risk Calculation Using Remote Sensing and GIS in Oued El Maleh Watershed, Morocco. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2015, 07, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pimentel, D.; Harvey, C.; Resosudarmo, P.; Sinclair, K.; Kurz, D.; McNair, M.; Crist, S.; Shpritz, L.; Fitton, L.; Saffouri, R.; et al. Environmental and Economic Costs of Soil Erosion and Conservation Benefits. Science 1995, 267, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rahman, M.R.; Shi, Z.H.; Chongfa, C. Soil erosion hazard evaluation—An integrated use of remote sensing, GIS and statistical approaches with biophysical parameters towards management strategies. Ecol. Model. 2009, 220, 1724–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, I.D.; Burch, G.J. Physical Basis of the Length-slope Factor in the Universal Soil Loss Equation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1986, 50, 1294–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, T.R. Rainfall Erosivity in East Africa. Geogr. Ann. Ser. A Phys. Geogr. 1979, 61, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, V.; Panagopoulos, T. Seasonality of Soil Erosion under Mediterranean Conditions at the Alqueva Dam Watershed. Environ. Manag. 2014, 54, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shikangalah, R.; Paton, E.; Jetlsch, F.; Blaum, N. Quantification of areal extent of soil erosion in dryland urban areas: An example from Windhoek, Namibia. Cities Environ. (CATE) 2017, 10, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Chalise, D.; Kumar, L.; Kristiansen, P. Land Degradation by Soil Erosion in Nepal: A Review. Soil Syst. 2019, 3, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chalise, D.; Kumar, L. Land use change affects water erosion in the Nepal Himalayas. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atreya, K.; Sharma, S.; Bajracharya, R.M.; Rajbhandari, N.P. Applications of reduced tillage in hills of central Nepal. Soil Tillage Res. 2006, 88, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Roux, J.J.; Sumner, P.D. Factors controlling gully development: Comparing continuous and discontinuous gullies. Land Degrad. Dev. 2012, 23, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, W.; Wu, B. Assessment of soil erosion and sediment delivery ratio using remote sensing and GIS: A case study of upstream Chaobaihe River catchment, north China. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2008, 23, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, S.; Koloa, C.; Pal, D.K.; Palsamanta, B. Estimation of potential soil erosion rate using RUSLE and E30 model. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2016, 2, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opeyemi, O.A.; Abidemi, F.H.; Victor, O.K. Assessing the Impact of Soil Erosion on Residential Areas of Efon-Alaaye Ekiti, Ekiti-State, Nigeria. Int. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2019, 5, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- USDA. NRCS Soil Quality—Urban Technical Note No. 1: Erosion and Sedimentation on Construction Sites; Soil Quality Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bruijnzeel, L.A. Hydrology of Moist Tropical Forests and Effects of Conversion: A State of Knowledge Review; Free University: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Ashiagbor, G.; Forkuo, E.K.; Laari, P.; Aabeyir, R. Modeling soil erosion using RUSLE and GIS tools. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 2, 12. [Google Scholar]
- FAO and ITPS Status of the World’s Soil Resources (SWSR)—Main Report; FAO of the United Nations and Intergovernmental Technical Panel on Soils: Rome, Italy, 2015.
- Hurni, H. Degradation and Conservation of the Resources in the Ethiopian Highlands. Mt. Res. Dev. 1988, 8, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). Ethiopian Highlands Reclamation Study: Ethiopia; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1986; p. 354. [Google Scholar]
- Legesse, D.; Vallet-Coulomb, C.; Gasse, F. Analysis of the hydrological response of a tropical terminal lake, Lake Abiyata(Main Ethiopian Rift Valley) to changes in climate and human activities. Hydrol. Process. 2004, 18, 487–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabantu, M.T.; Tshimanga, R.M.; Kileshye, J.M.O.; Gumindoga, W.; Beya, J.T. A GIS-based estimation of soil erosion parameters for soil loss potential and erosion hazard in the city of Kinshasa, the Democratic Republic of Congo. Proc. IAHS 2018, 378, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nhapi, I. The water situation in Harare, Zimbabwe: A policy and management problem. Water Policy 2009, 11, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merritt, W.S.; Letcher, R.A.; Jakeman, A.J. A review of erosion and sediment transport models. Environ. Model. Softw. 2003, 18, 761–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranzi, R.; Le, T.H.; Rulli, M.C. A RUSLE approach to model suspended sediment load in the Lo river (Vietnam): Effects of reservoirs and land use changes. J. Hydrol. 2012, 422–423, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning; Department of Agriculture, Science and Education Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; McCool, D.K.; Yoder, D.C. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); United States Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, J.G.; Srinivasan, R.; Muttiah, R.S.; Williams, J.R. Large Area Hydrologic Modeling and Assessment Part I: Model Development. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1998, 34, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laflen, J.M.; Lane, L.J.; Foster, G.R. WEPP: A new generation of erosion prediction technology. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1991, 46, 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Gertner, G.; Fang, S.; Anderson, A.B. Mapping Multiple Variables for Predicting Soil Loss by Geostatistical Methods with TM Images and a Slope Map. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2003, 69, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Li, G.; Valladares, G.S.; Batistella, M. Mapping soil erosion risk in Rondônia, Brazilian Amazonia: Using RUSLE, remote sensing and GIS. Land Degrad. Dev. 2004, 15, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.S.; Wu, B.F.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J. Regional soil erosion risk assessment in Hai Basin. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 15, 372–387. [Google Scholar]
- Chalise, D.; Kumar, L.; Shriwastav, C.P.; Lamichhane, S. Spatial assessment of soil erosion in a hilly watershed of Western Nepal. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamshad, A.; Azhari, M.N.; Isa, M.H.; Hussin, W.M.A.W.; Parida, B.P. Development of an appropriate procedure for estimation of RUSLE EI30 index and preparation of erosivity maps for Pulau Penang in Peninsular Malaysia. Catena 2008, 72, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woldemariam, G.; Iguala, A.; Tekalign, S.; Reddy, R. Spatial Modeling of Soil Erosion Risk and Its Implication for Conservation Planning: The Case of the Gobele Watershed, East Hararghe Zone, Ethiopia. Land 2018, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Igbokwe, J.I.; Akinyede, J.O.; Dang, B.; Alaga, T.; Ono, M.N.; Nnodu, V.C.; Anike, L.O. Mapping and monitoring of the impact of gully erosion in Southeastern Nigeria with satellite remote sensing and Geographic Information System. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2008, 37, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Okereke, C.N.; Onu, N.N.; Akaolisa, C.Z.; Ikoro, D.O.; Ibeneme, S.I.; Ubechu, B.; Chinemelu, E.S.; Amadikwa, L.O. Mapping gully erosion using remote sensing technique: A case study of Okigwe area, southeastern Nigeria. Int. J. Eng. Res. Appl. (IJERA) 2012, 2, 1955–1967. [Google Scholar]
- Aiello, A.; Adamo, M.; Canora, F. Remote sensing and GIS to assess soil erosion with RUSLE3D and USPED at river basin scale in southern Italy. Catena 2015, 131, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerri, C.E.P.; Demattě, J.A.M.; Ballester, M.V.R.; Martinelli, L.A.; Victoria, R.L.; Roose, E. GIS erosion risk assessment of the Piracicaba river basin, southeastern Brazil. Mapp. Sci. Remote Sens. 2001, 38, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butcher, C. Low Income Housing in Zimbabwe: A Case Study of the Epworth Squatter Upgrading Programme. 1986. Available online: https://opendocs.ids.ac.uk/opendocs/handle/20.500.12413/10008 (accessed on 15 October 2020).
- ZimStats (Zimbabwe National Statistics Agency) Census 2012: Preliminary Report. Available online: http://www.zimstat.co.zw/publications/Population/Harare.pdf. (accessed on 14 October 2020).
- Hove, M.; Tirimboi, A. Assessment of Harare Water Service Delivery. J. Sustain. Dev. Africa 2011, 13, 61–84. [Google Scholar]
- Nyamapfene, K. Soils of Zimbabwe; Nehanda Publishers: Harare, Zimbabwe, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, J.G.; Purves, W.D. A Guide to the Soils of Rhodesia; Technical Handbook No. 3; Information Services, Department of Research and Specialist Services, Ministry of Agriculture: Harare, Zimbabwe, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, P.; Luukkanen, O.; Tokola, T.; Nieminen, J. Effect of vegetation cover on soil erosion in a mountainous watershed. Catena 2008, 75, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasannakumar, V.; Vijith, H.; Abinod, S.; Geetha, N. Estimation of soil erosion risk within a small mountainous sub-watershed in Kerala, India, using Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) and geo-information technology. Geosci. Front. 2012, 3, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Abadi, A.M.A.; Ghalib, H.B.; Al-Qurnawi, W.S. Estimation of soil erosion in Northern Kirkuk governorate, Iraq using RUSLE, Remote Sensing and GIS. Carpathian J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2016, 11, 153–166. [Google Scholar]
- Tundu, C.; Tumbare, M.J.; Kileshye Onema, J.-M. Sedimentation and Its Impacts/Effects on River System and Reservoir Water Quality: Case Study of Mazowe Catchment, Zimbabwe. Proc. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 2018, 377, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karamage, F.; Zhang, C.; Liu, T.; Maganda, A.; Isabwe, A. Soil Erosion Risk Assessment in Uganda. Forests 2017, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K. A New European Slope Length and Steepness Factor (LS-Factor) for Modeling Soil Erosion by Water. Geosciences 2015, 5, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Millward, A.A.; Mersey, J.E. Adapting the RUSLE to model soil erosion potential in a mountainous tropical watershed. Catena 1999, 38, 109–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mati, B.M.; Morgan, R.P.; Gichuki, F.N.; Quinton, J.N.; Brewer, T.R.; Liniger, H.P. Assessment of erosion hazard with the USLE and GIS: A case study of the Upper Ewaso Ng’iro North basin of Kenya. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2000, 2, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, Y.; Nawaiseh, S. Spatial assessment of soil erosion risk using RUSLE and GIS techniques. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 4649–4669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, L.; Fang, N.F.; Zhang, B.; Shi, Z.H. Broad area mapping of monthly soil erosion risk using fuzzy decision tree approach: Integration of multi-source data within GIS. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2013, 27, 1251–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGS (United States Geologic Service). Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) 1 Arc-Second Global Data. Available online: https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/SRTM1Arc (accessed on 19 September 2018).
- International Soil Reference and Information Centre (ISRIC-World Soil Information). Available online: https://soilgrids.org (accessed on 17 July 2019).
- Stocking, M.A.; Elwell, H.A. Rainfall Erosivity over Rhodesia. Trans. Inst. Br. Geogr. 1976, 1, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Soil Erosion in the Tropics: Principles and Management; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Alexakis, D.D.; Hadjimitsis, D.G.; Agapiou, A. Integrated use of remote sensing, GIS and precipitation data for the assessment of soil erosion rate in the catchment area of “Yialias” in Cyprus. Atmos. Res. 2013, 131, 108–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-L.; Zhang, G.-L. Water infiltration in urban soils and its effects on the quantity and quality of runoff. J. Soils Sediments 2011, 11, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, Y.; Zregat, D.; Farhan, I. Spatial Estimation of Soil Erosion Risk Using RUSLE Approach, RS, and GIS Techniques: A Case Study of Kufranja Watershed, Northern Jordan. J. Water Resour. Prot. JWARP 2013, 5, 1247–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hengl, T.; De Jesus, J.M.; Heuvelink, G.B.M.; Gonzalez, M.R.; Kilibarda, M.; Blagotić, A.; Shangguan, W.; Wright, M.N.; Geng, X.; Bauer-Marschallinger, B.; et al. SoilGrids250m: Global gridded soil information based on machine learning. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharpley, A.N.; Williams, J.R. EPIC-Erosion/Productivity Imappct Calculator: 1. Model. Documentation; U.S. Department of Agriculture Technical Bulletin: Washington, DC, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Desmet, P.J.J.; Govers, A. A GIS procedure for automatically calculating the USLE LS factor on topographically complex landscape units. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1996, 51, 427–433. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Liu, H. An efficient method for identifying and filling surface depressions in digital elevation models for hydrologic analysis and modelling. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2006, 20, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, T.G. Calculating catchment area with divergent flow based on a regular grid. Comput. Geosci. 1991, 17, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarboton, D.G. A new method for the determination of flow directions and upslope areas in grid digital elevation models. Water Resour. Res. 1997, 33, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S. Soil erosion assessment and its verification using the universal soil loss equation and geographic information system: A case study at Boun, Korea. Environ. Geol. 2004, 45, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheir, R.B.; Abdallah, C.; Khawlie, M. Assessing soil erosion in Mediterranean karst landscapes of Lebanon using remote sensing and GIS. Eng. Geol. 2008, 99, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiedu, J.K. Assessing the Threat of Erosion to Nature-Based Interventions for Stormwater Management and Flood Control in the Greater Accra Metropolitan Area, Ghana. J. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 19, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leh, M.; Bajwa, S.; Chaubey, I. Impact of land use change on erosion risk: An integrated Remote Sensing, Geographic Information System and modelling methodology: Impact of land use change on erosion risk. Land Degrad. Dev. 2013, 24, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Phadke, V.S. Assessing soil loss by water erosion in Jamni River Basin, Bundelkhand region, India, adopting universal soil loss equation using GIS. Curr. Sci. Assoc. 2006, 90, 1431–1435. [Google Scholar]
- Panagos, P.; Karydas, C.; Borrelli, P.; Ballabio, C.; Meusburger, K. Advances in Soil Erosion Modelling Through Remote Sensing Data Availability at European Scale. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Remote sensing and Geoinformation of the Environment, Paphos, Cyprus, 12 August 2014; Hadjimitsis, D.G., Themistocleous, K., Michaelides, S., Papadavid, G., Eds.; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Paphos, Cyprus, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Alena, J.; Miloslav, J.; Martin, T. Field Determination of the Specific Input Characteristics to Calculate the Value of C Factor of Time-variable Crops for the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE). Soil Water Res. 2013, 1, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ochoa-Cueva, P.; Fries, A.; Montesinos, P.; Rodríguez-Díaz, J.A.; Boll, J. Spatial Estimation of Soil Erosion Risk by Land-Cover Change in the Andes of Southern Ecuador: Soil Erosion Risk by Land-Cover Change in Southern Ecuador. Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 26, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adornado, H.A.; Yoshida, M.; Apolinares, H.A. Erosion Vulnerability Assessment in REINA, Quezon Province, Philippines with Raster-based Tool Built within GIS Environment. Agric. Inf. Res. 2009, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bewket, W.; Sterk, G. Assessment of soil erosion in cultivated fields using a survey methodology for rills in the Chemoga watershed, Ethiopia. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2003, 97, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poesen, J.; Nachtergaele, J.; Verstraeten, G.; Valentin, C. Gully erosion and environmental change: Importance and research needs. Catena 2003, 50, 91–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imeson, A.C.; Kwaad, F.J.P.M. Gully types and gully prediction. KNAG Geogr. Tijdschr. XIV 5 1980, 14, 430–441. [Google Scholar]
- Lufafa, A.; Tenywa, M.M.; Isabirye, M.; Majaliwa, M.J.G.; Woomer, P.L. Prediction of soil erosion in a Lake Victoria basin catchment using a GIS-based Universal Soil Loss model. Agric. Syst. 2003, 76, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamutaze, Y. Revisiting socio-ecological resilience and sustainability in the coupled mountain landscapes in Eastern Africa. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2015, 14, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.P.C. Soil Erosion and Conservation, 3rd ed.; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hudson, N.W. Soil Conservation, 2nd ed.; Batsford: London, UK, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulkareem, J.H.; Pradhan, B.; Sulaiman, W.N.A.; Jamil, N.R. Prediction of spatial soil loss impacted by long-term land-use/land-cover change in a tropical watershed. Geosci. Front. 2019, 10, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.J.; Le Bissonnais, Y.; Bazzoffi, P.; Diaz, J.S.; Düwel, O.; Loj, G.; Øygarden, L.; Prasuhn, V.; Rydell, B.; Strauss, P. Nature and extent of soil erosion in Europe. In Reports of the Technical Working Groups Established under the Thematic Strategy for Soil Protection; EUR 21319 EN/1, Office for the Official Publications of the European Commission: Luxembourg, 2013; pp. 145–185. [Google Scholar]
- Verheijen, F.G.A.; Jones, R.J.A.; Rickson, R.J.; Smith, C.J. Tolerable versus actual soil erosion rates in Europe. Earth Sci. Rev. 2009, 94, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Meyer, A.; Poesen, J.; Isabirye, M.; Deckers, J.; Raes, D. Soil erosion rates in tropical villages: A case study from Lake Victoria Basin, Uganda. Catena 2011, 84, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuster, W.D.; Bonta, J.; Thurston, H.; Warnemuende, E.; Smith, D.R. Impacts of impervious surface on watershed hydrology: A review. Urban Water J. 2005, 2, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantón, Y.; Solé-Benet, A.; de Vente, J.; Boix-Fayos, C.; Calvo-Cases, A.; Asensio, C.; Puigdefábregas, J. A review of runoff generation and soil erosion across scales in semiarid south-eastern Spain. J. Arid. Environ. 2011, 75, 1254–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phil-Eze, P.O. Variability of soil properties related to vegetation cover in a tropical rainforest landscape. J. Geogr. Plan. 2010, 3, 174–188. [Google Scholar]
- Dams, J.; Dujardin, J.; Reggers, R.; Bashir, I.; Canters, F.; Batelaan, O. Mapping impervious surface change from remote sensing for hydrological modeling. J. Hydrol. 2013, 485, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jim, C.Y. Soil Compaction as a Constraint to Tree Growth in Tropical & Subtropical Urban Habitats. Environ. Conserv. 1993, 20, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.W.; Xue, Y.; Ma, C.F.; Wang, Z.G. A data fusion approach for soil erosion monitoring in the Upper Yangtze River Basin of China based on Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE) model. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 4777–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrieling, A. Satellite remote sensing for water erosion assessment: A review. Catena 2006, 65, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Poesen, J.; Ballabio, C.; Lugato, E.; Meusburger, K.; Montanarella, L.; Alewell, C. The new assessment of soil loss by water erosion in Europe. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 54, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.; Liang, Z.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Rossel, R.A.V.; Chappell, A.; Yu, W.; Shi, Z. Current and future assessments of soil erosion by water on the Tibetan Plateau based on RUSLE and CMIP5 climate models. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giang, P.; Giang, L.; Toshiki, K. Spatial and Temporal Responses of Soil Erosion to Climate Change Impacts in a Transnational Watershed in Southeast Asia. Climate 2017, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.S.; Frye, W.W.; Varco, J.J. Legume Winter Cover Crops. In Advances in Soil Science; Stewart, B.A., Ed.; Advances in Soil Science; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1987; Volume 7, pp. 95–139. ISBN 978-1-4612-9157-2. [Google Scholar]
- Jakab, G.; Madarász, B.; Szabó, J.; Tóth, A.; Zacháry, D.; Szalai, Z.; Kertész, Á.; Dyson, J. Infiltration and Soil Loss Changes during the Growing Season under Ploughing and Conservation Tillage. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nyamangara, J.; Marondedze, A.; Masvaya, E.N.; Mawodza, T.; Nyawasha, R.; Nyengerai, K.; Tirivavi, R.; Nyamugafata, P.; Wuta, M. Influence of basin-based conservation agriculture on selected soil quality parameters under smallholder farming in Zimbabwe. Soil Use Manag. 2014, 30, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soil Erosion Processes and Landscape Sensitivity in the Ethiopian Highlands. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/252969343_Assessment_of_Erosion_and_Soil_Erosion_Processes_-_a_Case_Study_from_the_Northern_Ethiopian_Highland (accessed on 14 October 2020).
- McCool, D.K.; Foster, G.R.; Mutchler, C.K.; Meyer, L.D. Revised Slope Length Factor for the Universal Soil Loss Equation. Trans. ASAE 1989, 32, 1571–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumindoga, W.; Rientjes, T.; Shekede, M.; Rwasoka, D.; Nhapi, I.; Haile, A. Hydrological Impacts of Urbanization of Two Catchments in Harare, Zimbabwe. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 12544–12574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braud, I.; Breil, P.; Thollet, F.; Lagouy, M.; Branger, F.; Jacqueminet, C.; Kermadi, S.; Michel, K. Evidence of the impact of urbanization on the hydrological regime of a medium-sized periurban catchment in France. J. Hydrol. 2013, 485, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.; Pradhan, B. Probabilistic landslide hazards and risk mapping on Penang Island, Malaysia. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2006, 115, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, R. An alternative way to assess water erosion of cultivated land—Field-based measurements: And analysis of some results. Appl. Geogr. 2002, 22, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamuju, N. Spatial Identification and Classification of Soil Erosion Prone Zones Using Remote Sensing & Gis Integrated ‘Rusle’ Model and ‘Sateec Gis System’. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Res. Technol. 2016, 676–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assouline, S.; Ben-Hur, M. Effects of rainfall intensity and slope gradient on the dynamics of interrill erosion during soil surface sealing. Catena 2006, 66, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koirala, P.; Thakuri, S.; Joshi, S.; Chauhan, R. Estimation of Soil Erosion in Nepal Using a RUSLE Modeling and Geospatial Tool. Geosciences 2019, 9, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alewell, C.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K.; Panagos, P. Using the USLE: Chances, challenges and limitations of soil erosion modelling. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2019, 7, 203–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trirnble, S.W.; Crosson, P.U.S. Soil Erosion Rates-Myth and Reality. Science 2000, 289, 248–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Auerswald, K.; Kainz, M.; Fiener, P. Soil erosion potential of organic versus conventional farming evaluated by USLE modelling of cropping statistics for agricultural districts in Bavaria. Soil Use Manag. 2006, 19, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzari, M.; Gioia, D.; Piccarreta, M.; Danese, M.; Lanorte, A. Sediment yield and erosion rate estimation in the mountain catchments of the Camastra artificial reservoir (Southern Italy): A comparison between different empirical methods. Catena 2015, 127, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D.R. Soil erosion and agricultural sustainability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13268–13272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seutloali, K.E.; Dube, T.; Mutanga, O. Assessing and mapping the severity of soil erosion using the 30-m Landsat multispectral satellite data in the former South African homelands of Transkei. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2017, 100, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, R.W.; Srinivasan, M.S. Identifying critical source areas for water quality: 2. Validating the approach for phosphorus and sediment losses in grazed headwater catchments. J. Hydrol. 2009, 379, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dijk, P.M.; Auzet, A.-V.; Lemmel, M. Rapid assessment of field erosion and sediment transport pathways in cultivated catchments after heavy rainfall events. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2005, 30, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, J.; Schütt, B. Mapping Complex Patterns of Erosion and Stability in Dry Mediterranean Ecosystems. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 74, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickup, G.; Chewings, V.H. Forecasting patterns of soil erosion in arid lands from Landsat MSS data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1988, 9, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Data Type | Resolution | Source |
|---|---|---|
| K Factor | 250 m | Global Soil map and attributes in raster (TIF format) from ISRIC (International Soil Reference Information Centre)-World Soil Information “SoilGrids” [71] |
| R Factor | - | Average monthly rainfall data from the Zimbabwe Department of Meteorological Services (Harare) database. |
| LS Factor | 30 m | Digital Elevation Model (DEM) from the United States Geological Survey (USGS) website [72] |
| C Factor | 30 m | Obtained by assigning weighted C factor values to the LULC maps adopted from Marondedze and Schütt, 2019 |
| P Factor | 30 m | The value of 1 was assigned to all-over the study area. |
| Rain Stations | Coordinates | Mean Annual Precipitation (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1984–2000 | 2000–2018 | 1984–2018 | ||
| Belvedere | 17°50′ S, 31°01′ E | 880.2 | 851.1 | 865.7 |
| Airport | 17°55′ S, 31°06′ E | 834.3 | 774.2 | 804.3 |
| Kutsaga | 17°55′ S, 31°08′ E | 804.6 | 792.8 | 798.7 |
| Land Area (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land Use Class | Weighted C Factor Value | 1984 | 2000 | 2018 |
| CBD/Industrial areas | 0.017 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.5 |
| LMD (Less concentrated) | 0.066 | 2.8 | 15.5 | 31.5 |
| HD (Concentrated) | 0.083 | 16.6 | 38 | 52.6 |
| Irrigated cropland | 0.166 | 1 | 7 | 0.4 |
| Rainfed cropland | 0.239 | 17.9 | 17 | 9.1 |
| Green spaces | 0.03 | 61.5 | 22 | 5.9 |
| Water | 0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.04 |
| ID | Land Use and Land Cover Class | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | CBD/Industries | Industries and central business district defined with high fraction of impervious surfaces mainly buildings and little proportion of vegetation |
| 2 | LMD residential (less concentrated) | Leafy and well established low and medium density suburbs surrounded with high vegetation |
| 3 | HD residential (concentrated) | High density residential areas with low vegetation cover or clustered settlements with areas undergoing developments and bare exposed land |
| 4 | Irrigated cropland | Cultivated land under irrigation schemes |
| 5 | Rainfed cropland | Cultivated land or land with crop residues after harvesting |
| 6 | Green spaces | All wooded areas, shrubs and bushes, riverine vegetation and grass covered areas |
| 7 | Water | Areas occupied by water, rivers, wetlands, reservoirs and dams |
| Soil Erosion Risk | Soil Loss (t ha−1 yr−1) | 1984–2018 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Area (km2) | Area (%) | ||
| Low | 0–1 | 0.5 | 1.4 |
| Moderate | 1–2 | 2.3 | 6.6 |
| High | 2–5 | 0.4 | 1.1 |
| Very high | 5–10 | 11.3 | 32.3 |
| Extreme | >10 | 20.5 | 58.6 |
| Soil Loss (t ha−1 yr−1) | Soil Erosion Risk | 2000 | 2018 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area (km2) | Area (%) | Area (km2) | Area (%) | ||
| 0–1 | Low | 19.6 | 56.3 | 20.7 | 59.5 |
| 1–2 | Moderate | 9.0 | 25.9 | 10.2 | 29.3 |
| 2–5 | High | 5.2 | 15.0 | 3.5 | 10.0 |
| 5–10 | Very high | 0.9 | 2.5 | 0.4 | 1.1 |
| >10 | Extreme | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.04 | 0.1 |
| Spatial Eroded Area (m2) | |
|---|---|
| Number of mapped sites | 49 |
| Total extent of erosion | 765 |
| Mean | 31 |
| Standard Deviation | 10.5 |
| Standard Mean Error | 1.5 |
| LULC Class. | 2000 | 2018 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil Loss (tons) | Area (km2) | Percentage (%) | Soil Loss (tons) | Area (km2) | Percentage (%) | |
| CBD/Industrial area | 40 | 0.12 | 0.4 | 47 | 0.19 | 0.5 |
| LMD (less concentrated) | 6218 | 5.41 | 15.5 | 12,203 | 10.96 | 31.5 |
| HD (concentrated) | 14,018 | 13.17 | 38 | 19,858 | 18.32 | 52.6 |
| Irrigated cropland | 6970 | 2.45 | 7 | 733 | 0.13 | 0.38 |
| Rainfed cropland | 19,228 | 5.85 | 17 | 9239 | 3.16 | 9.1 |
| Green spaces | 3934 | 7.78 | 22 | 854 | 2.06 | 5.9 |
| Water | 0 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0 | 0.01 | 0.04 |
| Total | 50,408 | 34.83 | 100 | 42,934 | 34.83 | 100 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marondedze, A.K.; Schütt, B. Assessment of Soil Erosion Using the RUSLE Model for the Epworth District of the Harare Metropolitan Province, Zimbabwe. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8531. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12208531
Marondedze AK, Schütt B. Assessment of Soil Erosion Using the RUSLE Model for the Epworth District of the Harare Metropolitan Province, Zimbabwe. Sustainability. 2020; 12(20):8531. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12208531
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarondedze, Andrew K., and Brigitta Schütt. 2020. "Assessment of Soil Erosion Using the RUSLE Model for the Epworth District of the Harare Metropolitan Province, Zimbabwe" Sustainability 12, no. 20: 8531. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12208531
APA StyleMarondedze, A. K., & Schütt, B. (2020). Assessment of Soil Erosion Using the RUSLE Model for the Epworth District of the Harare Metropolitan Province, Zimbabwe. Sustainability, 12(20), 8531. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12208531