Landscape Management through Change Processes Monitoring in Iran
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of Study Methodology
2.2. Study Area
2.3. LULC Mapping and Detection
2.4. LULC Change Analysis
2.5. LULC Transition Potential Modeling
2.6. LULC Change Prediction
2.7. Selection of Study Intervals
2.8. LULC Modeling Validation
2.9. Calculation and Extraction of Landscape Metrics and Landscape Change Processes
3. Results
3.1. LULC Map Preparation and Validation
3.2. Change Analysis of LULC Maps
3.3. Transition Potential Modeling
3.4. LULC Change Prediction
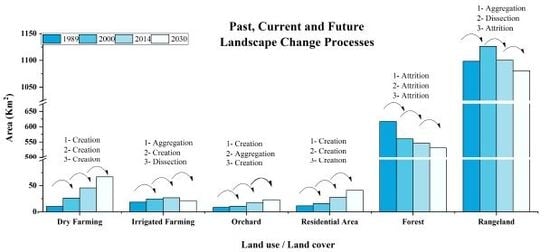
3.5. Investigation of Landscape Metrics and Change Processes
4. Discussion
4.1. LULC Changes
4.2. Transition Potential Modeling
4.3. LULC Change Prediction
4.4. Investigation of Landscape Metrics and Change Processes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Period | LU | Change Process | NP | PA | PP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1989–2000 | Dry Farming | Creation | 19 | 56 | 11,283 | 29,280 | 2264 | 7682 |
| Forest | Attrition | 618 | 475 | 685,319 | 622,508 | 77,290 | 75,312 | |
| Irrigated Farming | Aggregation | 229 | 240 | 20,491 | 27,345 | 11,458 | 15,076 | |
| Orchard | Creation | 41 | 74 | 9487 | 11,634 | 3240 | 4640 | |
| Rangeland | Aggregation | 694 | 582 | 1,220,938 | 1,251,890 | 91,710 | 91,686 | |
| Residential Area | Creation | 216 | 228 | 12,615 | 17,476 | 7460 | 9278 | |
| 2000–2014 | Dry Farming | Creation | 56 | 134 | 29,280 | 50,854 | 7682 | 15,882 |
| Forest | Attrition | 475 | 258 | 622,508 | 606,383 | 75,312 | 67,966 | |
| Irrigated Farming | Creation | 240 | 323 | 27,345 | 29,908 | 15,076 | 17,392 | |
| Orchard | Aggregation | 74 | 47 | 11,634 | 19,114 | 4640 | 6348 | |
| Rangeland | Dissection | 582 | 620 | 1,251,890 | 1,223,183 | 91,686 | 83,870 | |
| Residential Area | Creation | 228 | 243 | 17,476 | 30,691 | 9278 | 15,512 | |
| 2014–2030 | Dry Farming | Creation | 134 | 537 | 50,854 | 74,205 | 15,882 | 29,866 |
| Forest | Attrition | 258 | 202 | 606,383 | 590,322 | 67,966 | 61,062 | |
| Irrigated Farming | Dissection | 323 | 342 | 29,908 | 23,543 | 17,392 | 13,718 | |
| Orchard | Creation | 47 | 350 | 19,114 | 25,446 | 6348 | 11,602 | |
| Rangeland | Attrition | 620 | 545 | 1,223,183 | 1,200,879 | 83,870 | 78,664 | |
| Residential Area | Creation | 243 | 710 | 30,691 | 45,688 | 15,512 | 28,958 | |
References
- Chen, L.; Fu, B.; Xu, J.; Gong, J. Location-weighted landscape contrast index: A scale independent approach for landscape pattern evaluation based on source-sink ecological processes. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2003, 23, 2406–2413. [Google Scholar]
- Girvetz, E.H.; Thorne, J.H.; Berry, A.M.; Jaeger, J.A.G. Integration of landscape fragmentation analysis into regional planning: A statewide multi-scale case study from California, USA. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2008, 86, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zheng, X. Simulation of land-use scenarios for Beijing using CLUE-S and Markov composite models. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2013, 23, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleemann, J.; Baysal, G.; Bulley, H.N.N.; Fürst, C. Assessing driving forces of land use and land cover change by a mixed-method approach in north-eastern Ghana, West Africa. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 196, 411–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, L.; Shi, Z.H.; Yin, W.; Huang, X. Spatial and seasonal patterns in stream water contamination across mountainous watersheds: Linkage with landscape characteristics. J. Hydrol. 2015, 523, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xystrakis, F.; Psarras, T.; Koutsias, N. A process-based land use/land cover change assessment on a mountainous area of Greece during 1945–2009: Signs of socio-economic drivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 587–588, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inkoom, J.N.; Frank, S.; Greve, K.; Walz, U.; Fürst, C. Suitability of different landscape metrics for the assessments of patchy landscapes in West Africa. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 85, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nor, A.N.M.; Corstanje, R.; Harris, J.A.; Brewer, T. Impact of rapid urban expansion on green space structure. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 81, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shooshtari, S.J.; Gholamalifard, M. Scenario-based land cover change modeling and its implications for landscape pattern analysis in the Neka Watershed, Iran. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2015, 1, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajewski, P.; Solecka, I.; Mrozik, K. Forest landscape change and preliminary study on its driving forces in ślȩza landscape park (Southwestern Poland) in 1883–2013. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mayer, A.L.; Buma, B.; Davis, A.D.; GagnCrossed, D.; Sign, S.A.; Louise Loudermilk, E.; Scheller, R.M.; Schmiegelow, F.K.A.; Wiersma, Y.F.; Franklin, J. How Landscape Ecology Informs Global Land-Change Science and Policy. Bioscience 2016, 66, 458–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Potschin, M.B.; Haines-Young, R.H. Landscapes and sustainability. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2006, 3, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lausch, A.; Herzog, F. Applicability of landscape metrics for the monitoring of landscape change: Issues of scale, resolution and interpretability. Ecol. Indic. 2002, 2, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitao, A.B.; Ahern, J. Applying landscape ecological concepts and metrics in sustainable landscape planning. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2002, 59, 65–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Hwang, S.J.; Lee, S.B.; Hwang, H.S.; Sung, H.C. Landscape ecological approach to the relationships of land use patterns in watersheds to water quality characteristics. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2009, 92, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gergel, S.E.; Turner, M.G.; Miller, J.R.; Melack, J.M.; Stanley, E.H. Landscape indicators of human impacts to riverine systems. Aquat. Sci. 2002, 64, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uuemaa, E.; Antrop, M.; Marja, R.; Roosaare, J.; Mander, Ü. Landscape Metrics and Indices: An Overview of Their Use in Landscape Research Imprint / Terms of Use. Living Rev. Landsc. Res. 2009, 3, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, S.; Yuan, F. Assessing landscape changes and dynamics using patch analysis and GIS modeling. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2012, 16, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motevalli, A.; Vafakhah, M. Flood hazard mapping using synthesis hydraulic and geomorphic properties at watershed scale. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2016, 30, 1889–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neel, M.C.; McGarigal, K.; Cushman, S.A. Behavior of class-level landscape metrics across gradients of class aggregation and area. Landsc. Ecol. 2004, 19, 435–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchin, S.; Richert, E.; Heilmeier, H.; Merta, M.; Seidler, C. Landscape metrics as a tool for evaluating scenarios for flood prevention and nature conservation. Landsc. Online 2011, 25, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toutakhane, A.; Mofareh, M. Investigation and Evaluation of Spatial Patterns in Tabriz Parks Using Landscape Metrics. J. Urban Environ. Eng. 2016, 10, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghsood, F.F.; Moradi, H.; Bavani, A.R.M.; Panahi, M.; Berndtsson, R.; Hashemi, H. Climate change impact on flood frequency and source area in northern Iran under CMIP5 scenarios. Water (Switz.) 2019, 11, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shooshtari, S.J.; Shayesteh, K.; Gholamalifard, M.; Azari, M.; López-Moreno, J.I.; Interactions, H.A.; Dei, C.D.A. Land cover change modelling in Hyrcanian forests, northern Iran: A landscape pattern and transformation analysis perspective. Cuad. Investig. Geogr. 2018, 44, 743–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poorzady, M.; Bakhtiari, F. Spatial and temporal changes of Hyrcanian forest in Iran. iForest-Biogeosciences For. 2009, 2, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozenstein, O.; Karnieli, A. Comparison of methods for land-use classification incorporating remote sensing and GIS inputs. Appl. Geogr. 2011, 31, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, S.; Khatami, R.; Mountrakis, G.; Mirzaee, S.; Pourghasemi, H.R.; Tazeh, M. Accuracy assessment of land cover/land use classifiers in dry and humid areas of Iran. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congalton, R.G. A review of assessing the accuracy of classifications of remotely sensed data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1991, 37, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakr, N.; Weindorf, D.C.; Bahnassy, M.H.; Marei, S.M.; El-Badawi, M.M. Monitoring land cover changes in a newly reclaimed area of Egypt using multi-temporal Landsat data. Appl. Geogr. 2010, 30, 592–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastman, J.R. TerrSet manual. Access. TerrSet Version 2015, 18, 1–390. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Radhakrishnan, N.; Mathew, S. Land use change modelling using a Markov model and remote sensing. Geom. Nat. Hazards Risk 2014, 5, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistocchi, A.; Luzi, L.; Napolitano, P. The use of predictive modeling techniques for optimal exploitation of spatial databases: A case study in landslide hazard mapping with expert system-like methods. Environ. Geol. 2002, 41, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mountrakis, G.; Im, J.; Ogole, C. Support vector machines in remote sensing: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.; Rai, P.; Mohan, K. Prediction of land use changes based on land change modeler (LCM) using remote sensing: A case study of Muzaffarpur (Bihar), India. J. Geogr. Inst. Jovan Cvijic SASA 2014, 64, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdy, O.; Zhao, S.A.; Salheen, M.; Eid, Y.Y. Analyses the Driving Forces for Urban Growth by Using IDRISI®Selva Models Abouelreesh—Aswan as a Case Study. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2017, 9, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romano, G.; Abdelwahab, O.M.M.; Gentile, F. Modeling land use changes and their impact on sediment load in a Mediterranean watershed. Catena 2018, 163, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Pontius, R.G. Diagnostic tools to evaluate a spatial land change projection along a gradient of an explanatory variable. Landsc. Ecol. 2010, 25, 1319–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Yang, X. Monitoring land changes in an urban area using satellite imagery, GIS and landscape metrics. Appl. Geogr. 2015, 56, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadoushan, M.A.; Soffianian, A.; Alebrahim, A. Predicting urban expansion in arak metropolitan area using two land change models. World Appl. Sci. J. 2012, 18, 1124–1132. [Google Scholar]
- Kavian, A.; Golshan, M.; Abdollahi, Z. Flow discharge simulation based on land use change predictions. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plexida, S.G.; Sfougaris, A.I.; Ispikoudis, I.P.; Papanastasis, V.P. Selecting landscape metrics as indicators of spatial heterogeneity—A comparison among Greek landscapes. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 26, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarigal, K.; Cushman, S.A.; Neel, M.C.; Ene, E. FRAGSTATS: Spatial Pattern Analysis Program for Categorical Maps. Available online: https://www.umass.edu/landeco/research/fragstats/downloads/fragstats_downloads.html (accessed on 22 February 2020).
- Dezhkam, S.; Jabbarian, A.B.; Darvishsefat, A.A.; Sakieh, Y. Performance evaluation of land change simulation models using landscape metrics. Geocarto Int. 2017, 32, 655–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, S.; Fürst, C.; Lorz, C.; Koschke, L.; Abiy, M.; Makeschin, F. Chances and limits of using landscape metrics within the interactive planning tool Pimp Your Landscape. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Integrative Landscape Modelling, Montpellier, France, 3–5 February 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, M.G.; Gardner, R.H.; O’neill, R.V. Landscape Ecology in Theory and Practice; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bogaert, J.; Ceulemans, R.; Salvador-Van Eysenrode, D. Decision Tree Algorithm for Detection of Spatial Processes in Landscape Transformation. Environ. Manag. 2004, 33, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brink, A.B.; Eva, H.D. Monitoring 25 years of land cover change dynamics in Africa: A sample based remote sensing approach. Appl. Geogr. 2009, 29, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statuto, D.; Cillis, G.; Picuno, P. Analysis of the effects of agricultural land use change on rural environment and landscape through historical cartography and GIS tools. J. Agric. Eng. 2016, 47, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geist, H.J.; Lambin, E.F. Proximate Causes and Underlying Driving Forces of Tropical Deforestation. Bioscience 2002, 52, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuelaish, B.; Olmedo, M.T.C. Scenario of land use and land cover change in the Gaza Strip using remote sensing and GIS models. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 274, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Megahed, Y.; Cabral, P.; Silva, J.; Caetano, M. Land Cover Mapping Analysis and Urban Growth Modelling Using Remote Sensing Techniques in Greater Cairo Region-Egypt. ISPRS Int. J. Geo Inform. 2015, 4, 1750–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camacho Olmedo, M.T.; Paegelow, M.; Mas, J.F. Interest in intermediate soft-classified maps in land change model validation: Suitability versus transition potential. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2013, 27, 2343–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, N.; Armenteras, D.; Retana, J. Land use and land cover change in the Colombian Andes: Dynamics and future scenarios. J. Land Use Sci. 2012, 8, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenczowski, G. Iran under the Pahlavis; Hoover Institution Press: Stanford, CA, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; He, H.S.; Bu, R.; Wen, Q.; Chang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Li, Y. The adequacy of different landscape metrics for various landscape patterns. Pattern Recognit. 2005, 38, 2626–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargis, C.; Bissonette, J.; David, J. The behavior of landscape metrics commonly used in the study of habitat fragmentation. Landsc. Ecol. 1998, 13, 167–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinar, A.; Campbell, M.B.; Zilberman, D. Adoption of improved irrigation and drainage reduction technologies under limiting environmental conditions. Environ. Resour. Econ. 1992, 2, 373–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhira, H.S.; Ramachandra, T.V.; Jagadish, K.S. Urban sprawl: Metrics, dynamics and modelling using GIS. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2004, 5, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| No. | Change Process | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Deformation | The shape is changing |
| 2 | Shift | The position is changing |
| 3 | Perforation | The number of patches is constant, but the area is decreasing |
| 4 | Shrinkage | The area and perimeter are decreasing, but the number of patches is constant |
| 5 | Enlargement | The number of patches is constant, but the area is increasing |
| 6 | Attrition | The number of patches and area are decreasing |
| 7 | Aggregation | The number of patches is decreasing, but area is constant or increasing |
| 8 | Creation | The number of patches and area are increasing |
| 9 | Dissection | The number of patches is increasing and the area is decreasing |
| 10 | Fragmentation | The number of patches is increasing and the area is strongly decreasing |
| LU | 1989 | 2000 | 2014 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area | % | Area | % | Area | % | |
| Dry Farming | 10.17 | 0.58 | 26.33 | 1.49 | 45.79 | 2.60 |
| Forest | 617.12 | 34.98 | 560.60 | 31.78 | 546.10 | 30.96 |
| Irrigated Farming | 18.45 | 1.05 | 24.59 | 1.39 | 26.90 | 1.52 |
| Orchard | 8.63 | 0.49 | 10.60 | 0.60 | 17.17 | 0.97 |
| Rangeland | 1098.39 | 62.26 | 1126.26 | 63.84 | 1100.52 | 62.38 |
| Residential | 11.36 | 0.64 | 15.74 | 0.89 | 27.62 | 1.57 |
| Year | NP | LSI | IJI | ENN | ED | AWMSI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1989 | 1817 | 18.30 | 37.67 | 65.01 | 15.45 | 12.19 |
| 2000 | 1655 | 19.21 | 50.19 | 70.10 | 16.32 | 13.10 |
| 2014 | 1625 | 19.51 | 65.55 | 74.83 | 16.60 | 11.94 |
| 2030 | 2595 | 20.99 | 78.71 | 74.37 | 18.06 | 11.78 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zabihi, M.; Moradi, H.; Gholamalifard, M.; Khaledi Darvishan, A.; Fürst, C. Landscape Management through Change Processes Monitoring in Iran. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1753. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12051753
Zabihi M, Moradi H, Gholamalifard M, Khaledi Darvishan A, Fürst C. Landscape Management through Change Processes Monitoring in Iran. Sustainability. 2020; 12(5):1753. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12051753
Chicago/Turabian StyleZabihi, Mohsen, Hamidreza Moradi, Mehdi Gholamalifard, Abdulvahed Khaledi Darvishan, and Christine Fürst. 2020. "Landscape Management through Change Processes Monitoring in Iran" Sustainability 12, no. 5: 1753. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12051753
APA StyleZabihi, M., Moradi, H., Gholamalifard, M., Khaledi Darvishan, A., & Fürst, C. (2020). Landscape Management through Change Processes Monitoring in Iran. Sustainability, 12(5), 1753. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12051753