Sustainable Agriculture and Its Implementation Gap—Overcoming Obstacles to Implementation
Abstract
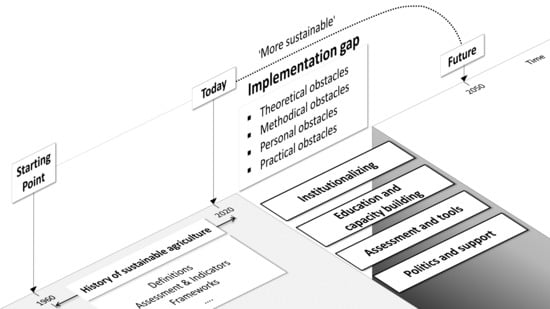
:1. Introduction
2. A Look Back at Sustainable Agriculture and Research Themes
3. Obstacles to Implementation
3.1. Theoretical Obstacles
3.1.1. Ambiguous Definition and Its Implications
3.1.2. Implementation Scale—A Possible Definition for the Term “Practice”
3.1.3. The Relationship Between Theory and Practice
3.2. Methodological Obstacles and Sustainability Assessments
- (a)
- Mean-oriented sustainability requires that the criteria (standards, measures, or rules) specifying sustainable agriculture are well defined and communicated (declaration of standards). The specifications can be adapted to a certain extent, for example, to take farm characteristics (e.g., animal husbandry yes/no) into account. Compliance with these criteria has to be checked (e.g., external audits, self-declaration, checklists, farm visits). If standards are not complied with, the farmer needs information about the necessary adjustments and modifications. Once the changes have been implemented, a new check can be performed. When all standards are met, full implementation is reached. In general, this is a relatively quick process and can be conducted in a single year.
- (b)
- Goal-oriented methods require more complex procedures. In principle, the different goals, resource use, potential adverse effects (e.g., to the environment) and the system’s stability have to be assessed and evaluated. An appropriate method would therefore have to record and analyze the specific system very precisely. In the next step, interactions and conflicts of interests between the different goals (e.g., improving farm income and outputs, reducing adverse environmental effects and costs, better conditions for employees) have to be identified and highlighted (synergies and trade-offs). Based on this analysis, possibilities for improvements in the system as a whole should be evaluated. The potential effects of adaptions could be modeled as scenarios during the decision-making process (by the farmer). The most suitable and most promising solution could be adopted as a goal for business development. A further assessment should be performed when all required adaptations have been realized. A comparison of the two evaluations should show better overall goal achievement. If this is the case, the farm is developing sustainably. The overall procedure takes much longer (several years), requires more data and information, and is more demanding. This could therefore be combined in a farm development and planning process.
3.2.1. Conflicting Aims of Assessment Methods
3.2.2. Suboptimal Method Development Process
3.2.3. Requirements and Functionalities That Have Not yet Been Taken into Account
Adaptability of Assessment Methods
Complexity and System Approach in the Assessment
Simplification
3.2.4. Difficulties in Applying Assessment Methods and Their Recommendations
Data and Data Requests
Assessment Results and Convenience
3.3. Personal Obstacles
3.3.1. Knowledge and Its Role in Implementation
3.3.2. Behavior and Decisions—The Farmer as the Central Actor in Decision-Making
3.4. Practical Obstacles
4. Suggestions for Overcoming Obstacles and Recommendations
4.1. Institutionalization (Creating Structures, Organizations, or Facilities)
4.2. Education, Capacity Building, and Sustainability Consulting
4.3. Assessment of Sustainable Agriculture and Tools
4.4. Politics, Support, and Appreciation
- Establishment and promotion of comprehensive farm sustainability advisory services and the promotion of the development and operation of appropriate advisory tools (for sustainability assessment);
- Training and qualification of sustainability advisors, improving the education of farmers, and improving university courses and other training programs;
- Supporting programs, funding, and subsidies for individualized methods (appropriate for each farm) to help farms become more sustainable and put in place the required changes;
- Funding and support for the establishment of an appropriate institution.
5. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trabelsi, M.; Mandart, E.; Le Grusse, P.; Bord, J.-P. How to measure the agroecological performance of farming in order to assist with the transition process. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 139–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Olde, E.M.; Oudshoorn, F.W.; Sørensen, C.A.G.; Bokkers, E.A.M.; De Boer, I.J.M. Assessing sustainability at farm-level: Lessons learned from a comparison of tools in practice. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 66, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.W. Is agricultural sustainability a useful concept? Agric. Syst. 1996, 50, 117–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.S.; McDonald, G.T. Assessing the sustainability of agriculture at the planning stage. J. Environ. Manag. 1998, 52, 15–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Velten, S.; Leventon, J.; Jager, N.; Newig, J. What Is Sustainable Agriculture? A Systematic Review. Sustainability 2015, 7, 7833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ikerd, J.E. The need for a systems approach to sustainable agriculture. In Agriculture and the Environment: Papers presented at the International Conference, 10–13 November 1991; Edwards, C.A., Wali, M.K., Horn, D.J., Miller, F., Eds.; Elsevier Science: Burlington, VT, USA, 1993; pp. 147–160. ISBN 9780444898005. [Google Scholar]
- Pretty, J. Agricultural sustainability: Concepts, principles and evidence. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2008, 363, 447–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Horrigan, L.; Lawrence, R.S.; Walker, P. How sustainable agriculture can address the environmental and human health harms of industrial agriculture. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slätmo, E.; Fischer, K.; Röös, E. The Framing of Sustainability in Sustainability Assessment Frameworks for Agriculture. Sociol. Rural. 2017, 57, 378–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, C.R.; Feola, G. Normative, Systemic and Procedural Aspects: A Review of Indicator-Based Sustainability Assessments in Agriculture. In Methods and Procedures for Building Sustainable Farming Systems; Marta-Costa, A.A., Soares da Silva, E.L.D.G., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 33–46. ISBN 978-94-007-5002-9. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, E.; Marta-Costa, A.A. The Needs for Building Sustainable Farming Systems: Issues and Scope. In Methods and Procedures for Building Sustainable Farming Systems; Marta-Costa, A.A., Soares da Silva, E.L.D.G., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 1–5. ISBN 978-94-007-5002-9. [Google Scholar]
- Deytieux, V.; Munier-Jolain, N.; Caneill, J. Assessing the sustainability of cropping systems in single- and multi-site studies. A review of methods. Eur. J. Agron. 2016, 72, 107–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Directive 2009/28/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 April 2009 on the promotion of the use of energy from renewable sources and amending and subsequently repealing Directives 2001/77/EC and 2003/30/EC (Text with EEA relevance). Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/ALL/?uri=CELEX%3A32009L0028 (accessed on 12 February 2020).
- Farrell, A.; Hart, M. What Does Sustainability Really Mean? The Search for Useful Indicators. Environment 1998, 40, 4–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council. Toward Sustainable Agricultural Systems in the 21st Century; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-0-309-14896-2. [Google Scholar]
- Kropff, M.J.; Bouma, J.; Jones, J.W. Systems approaches for the design of sustainable agro-ecosystems. Agric. Syst. 2001, 70, 369–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, M.V. (Ed.) Sustainable Agriculture: Definitions and Terms. In Sustainable Agriculture and Food Supply; Apple Academic Press: Waretown, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dahlberg, K.A. Sustainable Agriculture: Fad or Harbinger? BioScience 1991, 41, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, C.A.; Youngberg, G. Sustainable Agriculture-An Overview. In Sustainable Agriculture in Temperate Zones; Francis, C.A., Flora, C.B., King, L.D., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 1–23. ISBN 0471622273. [Google Scholar]
- Paracchini, M.L.; Bulgheroni, C.; Borreani, G.; Tabacco, E.; Banterle, A.; Bertoni, D.; Rossi, G.; Parolo, G.; Origgi, R.; De Paola, C. A diagnostic system to assess sustainability at a farm level: The SOSTARE model. Agric. Syst. 2015, 133, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunlong, C.; Smit, B. Sustainability in agriculture: A general review. Agric. Environ. 1994, 49, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darnhofer, I.; Bellon, S.; Dedieu, B.; Milestad, R. Adaptiveness to enhance the sustainability of farming systems. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 30, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gafsi, M.; Favreau, J.L. Appropriate method to assess the sustainability of organic farming systems. ID-20133409862. Building sustainable rural futures: The added value of systems approaches in times of change and uncertainty. In Proceedings of the 9th European IFSA Symposium, Vienna, Austria, 4–7 July 2010; pp. 912–921. [Google Scholar]
- Tilman, D.; Cassman, K.G.; Matson, P.A.; Naylor, R.; Polasky, S. Agricultural sustainability and intensive production practices. Nature 2002, 418, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.; Dumanski, J. FESLM: An International Framework for Evaluating Sustainable Land Management. World Soil Resources Report No. 73; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, S.B.; MacRae, R.J. Conceptual Framework for the Transition from Conventional to Sustainable Agriculture. J. Sustain. Agric. 1996, 7, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cauwenbergh, N.; Biala, K.; Bielders, C.; Brouckaert, V.; Franchois, L.; Garcia Cidad, V.; Hermy, M.; Mathijs, E.; Muys, B.; Reijnders, J.; et al. SAFE—A hierarchical framework for assessing the sustainability of agricultural systems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 120, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gal, P.-Y.; Merot, A.; Moulin, C.-H.; Navarrete, M.; Wery, J. A modelling framework to support farmers in designing agricultural production systems. Environ. Model. Softw. 2010, 25, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization. Sustainability assessment of food and agriculture systems. In SAFA, Guidelines, Version 3.0; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2014; ISBN 978-92-5-108485-4. [Google Scholar]
- Therond, O.; Duru, M.; Roger-Estrade, J.; Richard, G. A new analytical framework of farming system and agriculture model diversities. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2017, 37, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacon, C.M.; Getz, C.; Kraus, S.; Montenegro, M.; Holland, K. The Social Dimensions of Sustainability and Change in Diversified Farming Systems. Ecol. Soc. 2012, 17, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maleksaeidi, H.; Karami, E. Social-Ecological Resilience and Sustainable Agriculture Under Water Scarcity. Agroecol. Sustain. Food Syst. 2013, 37, 262–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poláková, J. Sustainability-Risk-Resilience: How Does the Case of the Good Agricultural and Environmental Conditions Measure up? Sustainability 2018, 10, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paracchini, M.L.; Pacini, C.; Calvo, S.; Vogt, J. Weighting and aggregation of indicators for sustainability impact assessment in the SENSOR context. In Sustainability Impact Assessment of Land Use Changes; Helming, K., Pérez-Soba, M., Tabbush, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; pp. 349–372. ISBN 9783540786474. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Limón, J.A.; Sanchez-Fernandez, G. Empirical evaluation of agricultural sustainability using composite indicators. Ecol. Econ. 2010, 69, 1062–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Alba, I.; Van der Werf, H. The Use of Reference Values in Indicator-Based Methods for the Environmental Assessment of Agricultural Systems. Sustainability 2011, 3, 424–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bezlepkina, I.; Reidsma, P.; Sieber, S.; Helming, K. Integrated assessment of sustainability of agricultural systems and land use: Methods, tools and applications. Agric. Syst. 2011, 104, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bélanger, V.; Vanasse, A.; Parent, D.; Allard, G.; Pellerin, D. Development of agri-environmental indicators to assess dairy farm sustainability in Quebec, Eastern Canada. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 23, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Passel, S.; Meul, M. Multilevel and multi-user sustainability assessment of farming systems. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2012, 32, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carof, M.; Colomb, B.; Aveline, A. A guide for choosing the most appropriate method for multi-criteria assessment of agricultural systems according to decision-makers’ expectations. Agric. Syst. 2013, 115, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebacq, T.; Baret, P.V.; Stilmant, D. Sustainability indicators for livestock farming. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2013, 33, 311–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schader, C.; Grenz, J.; Meier, M.S.; Stolze, M. Scope and precision of sustainability assessment approaches to food systems. Ecol. Soc. 2014, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Olde, E.M.; Moller, H.; Marchand, F.; McDowell, R.W.; MacLeod, C.J.; Sautier, M.; Halloy, S.; Barber, A.; Benge, J.; Bockstaller, C.; et al. When experts disagree: The need to rethink indicator selection for assessing sustainability of agriculture. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2017, 19, 1327–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Häni, F.; Braga, F.; Stämpfli, A.; Keller, T.; Fischer, M.; Porsche, H. RISE, a Tool for Holistic Sustainability Assessment at the Farm Level. Int. Food Agribus. Manag. Rev. 2003, 6, 78–90. [Google Scholar]
- Meul, M.; Passel, S.; Nevens, F.; Dessein, J.; Rogge, E.; Mulier, A.; Hauwermeiren, A. MOTIFS: A monitoring tool for integrated farm sustainability. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2008, 28, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schader, C.; Baumgart, L.; Landert, J.; Muller, A.; Ssebunya, B.; Blockeel, J.; Weisshaidinger, R.; Petrasek, R.; Mészáros, D.; Padel, S.; et al. Using the Sustainability Monitoring and Assessment Routine (SMART) for the Systematic Analysis of Trade-Offs and Synergies between Sustainability Dimensions and Themes at Farm Level. Sustainability 2016, 8, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bockstaller, C.; Guichard, L.; Keichinger, O.; Girardin, P.; Galan, M.-B.; Gaillard, G. Comparison of methods to assess the sustainability of agricultural systems. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2009, 29, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sadok, W.; Angevin, F.; Bergez, J.-É.; Bockstaller, C.; Colomb, B.; Guichard, L.; Reau, R.; Doré, T. Ex ante assessment of the sustainability of alternative cropping systems: Implications for using multi-criteria decision-aid methods. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2008, 28, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ness, B.; Urbel-Piirsalu, E.; Anderberg, S.; Olsson, L. Categorising tools for sustainability assessment. Ecol. Econ. 2007, 60, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumagalli, M.; Acutis, M.; Mazzetto, F.; Vidotto, F.; Sali, G.; Bechini, L. An analysis of agricultural sustainability of cropping systems in arable and dairy farms in an intensively cultivated plain. Eur. J. Agron. 2011, 34, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasso, V.; Oudshoorn, F.W.; De Olde, E.; Sørensen, C.A.G. Generic sustainability assessment themes and the role of context: The case of Danish maize for German biogas. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 49, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago-Brown, I.; Metcalfe, A.; Jerram, C.; Collins, C. Sustainability Assessment in Wine-Grape Growing in the New World: Economic, Environmental, and Social Indicators for Agricultural Businesses. Sustainability 2015, 7, 8178–8204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kassam, A.; Friedrich, T.; Shaxson, F.; Reeves, T.; Pretty, J.; De Moraes Sá, J.C. Production Systems for Sustainable Intensification Integrating Productivity with Ecosystem Services. TATuP 2011, 20, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schiefer, J.; Lair, G.J.; Blum, W.E.H. Indicators for the definition of land quality as a basis for the sustainable intensification of agricultural production. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2015, 3, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Struik, P.C.; Kuyper, T.W. Sustainable intensification in agriculture: The richer shade of green. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2017, 37, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfray, H.C.J.; Beddington, J.R.; Crute, I.R.; Haddad, L.; Lawrence, D.; Muir, J.F.; Pretty, J.; Robinson, S.; Thomas, S.M.; Toulmin, C. Food security: The challenge of feeding 9 billion people. Science 2010, 327, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bommarco, R.; Kleijn, D.; Potts, S.G. Ecological intensification: Harnessing ecosystem services for food security. Trends Ecol. Evol. (Amst) 2013, 28, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, C.A.; Eviner, V.T.; Gaudin, A.C.M. Ways forward for resilience research in agroecosystems. Agric. Syst. 2018, 162, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tilman, D.; Fargione, J.; Wolff, B.; D´Antonio, C.; Dobson, A.; Howarth, R.; Schindler, D.; Schlesinger, W.H.; Simberloff, D.; Swackhamer, D. Forecasting Agriculturally Driven Global Environmental Change. Science 2001, 292, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahon, N.; Crute, I.; Simmons, E.; Islam, M.M. Sustainable intensification – “oxymoron” or “third-way”? A systematic review. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 74, 73–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grassini, P.; Pittelkow, C.M.; Cassman, K.G.; Yang, H.S.; Archontoulis, S.; Licht, M.; Lamkey, K.R.; Ciampitti, I.A.; Coulter, J.A.; Brouder, S.M.; et al. Robust spatial frameworks for leveraging research on sustainable crop intensification. Glob. Food Secur. 2017, 14, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigby, D.; Woodhouse, P.; Young, T.; Burton, M. Constructing a farm level indicator of sustainable agricultural practice. Ecol. Econ. 2001, 39, 463–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repar, N.; Jan, P.; Dux, D.; Nemecek, T.; Doluschitz, R. Implementing farm-level environmental sustainability in environmental performance indicators: A combined global-local approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 140, 692–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darnhofer, I.; Fairweather, J.; Moller, H. Assessing a farm’s sustainability: Insights from resilience thinking. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 2010, 8, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darnhofer, I. Resilience and why it matters for farm management. Science 2014, 41, 461–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, H. Resilience for Whom? The Problem Structuring Process of the Resilience Analysis. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lélé, S.M. Sustainable development: A critical review. World Dev. 1991, 19, 607–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gal, P.-Y.; Dugué, P.; Faure, G.; Novak, S. How does research address the design of innovative agricultural production systems at the farm level? A review. Agric. Syst. 2011, 104, 714–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, P.S.; Vejre, H.; Dalgaard, T.; Brandt, J. An indicator-based method for quantifying farm multifunctionality. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 25, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchand, F.; Debruyne, L.; Triste, L.; Gerrard, C.; Padel, S.; Lauwers, L. Key characteristics for tool choice in indicator-based sustainability assessment at farm level. Ecol. Soc 2014, 19, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, J.; Tichit, M.; Poulot, M.; Darly, S.; Li, S.; Petit, C.; Aubry, C. Comparative review of multifunctionality and ecosystem services in sustainable agriculture. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 149, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabiha, N.-E.; Salim, R.; Rahman, S.; Rola-Rubzen, M.F. Measuring environmental sustainability in agriculture: A composite environmental impact index approach. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 166, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vellema, S. Transformation and sustainability in agriculture: Connecting practice with social theory. In Transformation and Sustainability in Agriculture: Connecting Practice with Social Theory; Vellema, S., Ed.; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 13–19. ISBN 978-90-8686-717-2. [Google Scholar]
- Pretty, J.; Sutherland, W.J.; Ashby, J.; Auburn, J.; Baulcombe, D.; Bell, M.; Bentley, J.; Bickersteth, S.; Brown, K.; Burke, J.; et al. The top 100 questions of importance to the future of global agriculture. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 2010, 8, 219–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanein, N.; Kloppenburg, J.R. Where the Grass Grows Again: Knowledge Exchange in the Sustainable Agriculture Movement1. Rural. Sociol. 1995, 60, 721–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cash, D.W.; Clark, W.C.; Alcock, F.; Dickson, N.M.; Eckley, N.; Guston, D.H.; Jäger, J.; Mitchell, R.B. Knowledge systems for sustainable development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 8086–8091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plummer, J.D. Researcher to Researcher—Mind the Gap. JAWWA 2017, 109, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, J.P.; Tushman, M.L.; Kimberly, J.R.; Starbuck, B.; Ashford, S. On the Relationship Between Research and Practice. J. Manag. Inq. 2007, 16, 128–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duxbury, N.; Bakas, F.E.; De Pato Carvalho, C. Why is research–practice collaboration so challenging to achieve? A creative tourism experiment. Tour. Geogr. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lynch, E.A.; Chesworth, B.M.; Connell, L.A. Implementation—The Missing Link in the Research Translation Pipeline: Is It Any Wonder No One Ever Implements Evidence-Based Practice? Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2018, 32, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- White, M.A. Sustainability: I know it when I see it. Ecol. Econ. 2013, 86, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Werf, H.M.G.; Petit, J. Evaluation of the environmental impact of agriculture at the farm level: A comparison and analysis of 12 indicator-based methods. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 93, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halberg, N.; Verschuur, G.; Goodlass, G. Farm level environmental indicators; are they useful? An overview of green accounting systems for European farms. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 105, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Payraudeau, S.; Van der Werf, H.M.G. Environmental impact assessment for a farming region: A review of methods. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ 2005, 107, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Werf, H.M.G.; Tzilivakis, J.; Lewis, K.; Basset-Mens, C. Environmental impacts of farm scenarios according to five assessment methods. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 118, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantsis, T.; Douma, C.; Giourga, C.; Loumou, A.; Polychronaki, E.A. A methodological approach to assess and compare the sustainability level of agricultural plant production systems. Ecological Indicators-ECOL INDIC 2010, 10, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triste, L.; Marchand, F.; Debruyne, L.; Meul, M.; Lauwers, L. Reflection on the development process of a sustainability assessment tool: Learning from a Flemish case. Ecol. Soc. 2014, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Olde, E.M.; Sautier, M.; Whitehead, J. Comprehensiveness or implementation: Challenges in translating farm-level sustainability assessments into action for sustainable development. Ecological Indicators - ECOL INDIC 2018, 85, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.S.; McDonald, G.T.; Thwaites, R.N. TIM: Assessing the sustainability of agricultural land management. J. Environ. Manag. 2000, 60, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparatos, A. Embedded value systems in sustainability assessment tools and their implications. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 1613–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Grady, M.J.; O’Hare, G.M.P. Modelling the smart farm. Inf. Process. Agric. 2017, 4, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.-K.; Park, D.-H.; Park, H.; Kim, S.-H. Smart Livestock Farms Using Digital Twin: Feasibility Study. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC), Jeju, Korea, 17–19 October 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1461–1463, ISBN 978-1-5386-5041-7. [Google Scholar]
- Seghezzo, L. The five dimensions of sustainability. Environ. Politics 2009, 18, 539–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sutherland, L.-A.; Darnhofer, I.; Wilson, G.; Zagata, L. Transition Pathways Towards Sustainability in Agriculture: Case Studies from Europe; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Craheix, D.; Angevin, F.; Doré, T.; De Tourdonnet, S. Using a multicriteria assessment model to evaluate the sustainability of conservation agriculture at the cropping system level in France. Eur. J. Agron. 2016, 76, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoletti, M.G.; Gomiero, T.; Pimentel, D. Introduction to the Special Issue: Towards A More Sustainable Agriculture. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2011, 30, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, C.G.; Fountas, S.; Nash, E.; Pesonen, L.; Bochtis, D.; Pedersen, S.M.; Basso, B.; Blackmore, S.B. Conceptual model of a future farm management information system. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2010, 72, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papajorgji, P.; Pinet, F.; Miralles, A.; Jallas, E.; Pardalos, P.M. Modeling: A Central Activity for Flexible Information Systems Development in Agriculture and Environment. Int. J. Agric. Environ. Inf. Syst. 2010, 1, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, C.R.; Feola, G.; Steinberger, J.K. Considering the normative, systemic and procedural dimensions in indicator-based sustainability assessments in agriculture. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2010, 30, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peano, C.; Tecco, N.; Dansero, E.; Girgenti, V.; Sottile, F. Evaluating the Sustainability in Complex Agri-Food Systems: The SAEMETH Framework. Sustainability 2015, 7, 6721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janssen, S.J.C.; Porter, C.H.; Moore, A.D.; Athanasiadis, I.N.; Foster, I.; Jones, J.W.; Antle, J.M. Towards a new generation of agricultural system data, models and knowledge products: Information and communication technology. Agric. Syst. 2017, 155, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfert, S.; Ge, L.; Verdouw, C.; Bogaardt, M.-J. Big Data in Smart Farming—A review. Agric. Syst. 2017, 153, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thivierge, M.-N.; Parent, D.; Bélanger, V.; Angers, D.A.; Allard, G.; Pellerin, D.; Vanasse, A. Environmental sustainability indicators for cash-crop farms in Quebec, Canada: A participatory approach. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 45, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, I.D.; Logan, J.; Harrison, M.B.; Straus, S.E.; Tetroe, J.; Caswell, W.; Robinson, N. Lost in knowledge translation: Time for a map? J. Contin. Educ. Health Prof. 2006, 26, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drolet, B.C.; Lorenzi, N.M. Translational research: Understanding the continuum from bench to bedside. Transl. Res. 2011, 157, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, D.H.; Adam, T.; Alonge, O.; Agyepong, I.A.; Tran, N. Implementation research: What it is and how to do it. BMJ 2013, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougherty, D.; Conway, P.H. The “3T’s” Road Map to Transform US Health Care: The “How” of High-Quality Care. JAMA 2008, 299, 2319–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, L.A.; Seifert, C.M. Translation of research into practice: Why we can’t “just do it”. J. Am. Board Fam. Pract. 2005, 18, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Titler, M.G. Translation research in practice: An introduction. Online J. Issues Nurs. 2018, 23, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliardi, A.R.; Kothari, A.; Graham, I.D. Research agenda for integrated knowledge translation (IKT) in healthcare: What we know and do not yet know. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2017, 71, 105–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ingram, J. Agronomist–farmer knowledge encounters: An analysis of knowledge exchange in the context of best management practices in England. Agric. Hum. Values 2008, 25, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazeer, S.; Fuggate, P. Sustainability framework for farm level cotton supply chain management. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management, Bangkok, Thailand, 5–7 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fountas, S.; Wulfsohn, D.; Blackmore, B.S.; Jacobsen, H.L.; Pedersen, S.M. A model of decision-making and information flows for information-intensive agriculture. Agric. Syst. 2006, 87, 192–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, G.S.; Rodrigues, I.A.; De Buschinelli, C.C.A.; De Barros, I. Integrated farm sustainability assessment for the environmental management of rural activities. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2010, 30, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michie, S.; Van Stralen, M.M.; West, R. The behavior change wheel: A new method for characterising and designing behavior change interventions. Implement. Sci. 2011, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steindl, C.; Jonas, E.; Sittenthaler, S.; Traut-Mattausch, E.; Greenberg, J. Understanding Psychological Reactance: New Developments and Findings. Z. Psychol. 2015, 223, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olbrich, R.; Quaas, M.F.; Baumgärtner, S. Personal norms of sustainability and farm management behavior. Sustainability 2014, 6, 4990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Firbank, L.G.; Elliott, J.; Drake, B.; Cao, Y.; Gooday, R. Evidence of sustainable intensification among British farms. Agric. Environ. 2013, 173, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tait, J.; Morris, D. Sustainable development of agricultural systems: Competing objectives and critical limits. Futures 2000, 32, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhardiman, D.; Giordano, M.; Leebouapao, L.; Keovilignavong, O. Farmers’ strategies as building block for rethinking sustainable intensification. Agric. Hum. Values 2016, 33, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaller, N. The concept of agricultural sustainability. Agric. Environ. 1993, 46, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, R.; Steinfeld, H.; Falcon, W.; Galloway, J.; Smil, V.; Bradford, E.; Alder, J.; Mooney, H. Agriculture. Losing the links between livestock and land. Science 2005, 310, 1621–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Godfray, H.C.J.; Garnett, T. Food security and sustainable intensification. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20120273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Huylenbroeck, G.; Vandermeulen, V.; Mettepenningen, E.; Verspecht, A. Multifunctionality of Agriculture: A Review of Definitions, Evidence and Instruments. Living Rev. Landsc. Res. 2007, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinton, S.M.; Lupi, F.; Robertson, P.G.; Hamilton, S.K. Ecosystem services and agriculture: Cultivating agricultural ecosystes for diverse benefits. Ecol. Econ. 2007, 64, 245–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunarathne, A.D.N.; Navaratne, D.G.; Pakianathan, A.E.; Perera, N.Y.T. Sustainable Food Supply Chain Management: An Integrated Framework and Practical Perspectives. In Innovative Solutions for Sustainable Supply Chains; Qudrat-Ullah, H., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 289–315. ISBN 978-3-319-94321-3. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Chu, F.; Dolgui, A.; Chu, C.; Zhou, W.; Piramuthu, S. Recent advances and opportunities in sustainable food supply chain: A model-oriented review. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2018, 56, 5700–5722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamprecht, J.; Corsten, D.; Noll, M.; Meier, E. Controlling the sustainability of food supply chains. Supp. Chain. Manag. 2005, 10, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.G. Developing sustainable food supply chains. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2008, 363, 849–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nielsen Company. The Sustainability Imperative. New Insights on Consumer Expectations, 2015. Available online: https://www.nielsen.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/3/2019/04/Nielsen20Global20Sustainability20Report202015.pdf (accessed on 12 February 2020).
- Komarek, A.M. Conservation agriculture in western China increases productivity and profits without decreasing resilience. Food Sec. 2018, 10, 1251–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.; Snapp, S.; Chikowo, R.; Thorne, P.; Bekunda, M.; Glover, J. Measuring sustainable intensification in smallholder agroecosystems: A review. Glob. Food Secur. 2017, 12, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kruize, J.W.; Robbemond, R.M.; Scholten, H.; Wolfert, J.; Beulens, A.J.M. Improving arable farm enterprise integration—Review of existing technologies and practices from a farmer’s perspective. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2013, 96, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallant, A.; Lee, H.-S. Teaching sustainability through system dynamics: Exploring stocks and flows embedded in dynamic computer models of an agricultural land management system. J. Geosci. Educ. 2017, 65, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knierim, A.; Thomas, A.; Schmitt, S. Agrarberatung im Wandel. B B Agrar 2017, 2017, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- COM/2018/392. Proposal for a regulation of the european parliament and of the council establishing rules on support for strategic plans to be drawn up by Member States under the Common agricultural policy (CAP Strategic Plans) and financed by the European Agricultural Guarantee Fund (EAGF) and by the European Agricultural Fund for Rural Development (EAFRD) and repealing Regulation (EU) No 1305/2013 of the European Parliament and of the Council and Regulation (EU) No 1307/2013 of the European Parliament and of the Council, 2018. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/ALL/?uri=CELEX:52018PC0392 (accessed on 23 February 2020).
- Dicks, L.; Bardgett, R.; Bell, J.; Benton, T.; Booth, A.; Bouwman, J.; Brown, C.; Bruce, A.; Burgess, P.; Butler, S.; et al. What do we need to know to Enhance the Environmental Sustainability of Agricultural Production? A Prioritisation of Knowledge Needs for the UK Food System. Sustainability 2013, 5, 3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrera, B.; Gerster-Bentaya, M.; Tzouramani, I.; Knierim, A. Advisory services and farm-level sustainability profiles: An exploration in nine European countries. J. Agric. Educ. Ext. 2019, 25, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrettle, S.; Hinz, A.; Scherrer-Rathje, M.; Friedli, T. Turning sustainability into action: Explaining firms’ sustainability efforts and their impact on firm performance. Sustain. Dev. Manuf. Serv. 2014, 147, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Term Used | Issues Mentioned | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Problems | Multi-functionality, scale, selected indicators, linkage of indicators, application of results | Silva et al. [11] |
| Limitations | Neglected impacts (e.g., biodiversity, soil quality, economic, and social effects), applicability to farm scale, transparency of methods | Schader et al. [42] |
| Shortcomings | Missing multi-functionality, no balance between the sustainability dimensions, missing focus on usability/implementation, neglecting interactions and conflicting goals | Binder et al. [10] |
| Shortcomings | Missing multi-functionality, not suitable for all forms of farming (e.g., organic) | Trabelsi et al. [1] |
| Factors (hindering tool adoption) | The complexity of sustainability, development process (integrated factors that influence the tools) | Triste et al. [87] |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Siebrecht, N. Sustainable Agriculture and Its Implementation Gap—Overcoming Obstacles to Implementation. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3853. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12093853
Siebrecht N. Sustainable Agriculture and Its Implementation Gap—Overcoming Obstacles to Implementation. Sustainability. 2020; 12(9):3853. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12093853
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiebrecht, Norman. 2020. "Sustainable Agriculture and Its Implementation Gap—Overcoming Obstacles to Implementation" Sustainability 12, no. 9: 3853. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12093853
APA StyleSiebrecht, N. (2020). Sustainable Agriculture and Its Implementation Gap—Overcoming Obstacles to Implementation. Sustainability, 12(9), 3853. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12093853