How Blockchain Facilitates the Transition toward Circular Economy in the Food Chain?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Challenges of Circular Economy in the Food Sector
3.1.1. Lack of Information on Product and Processes
3.1.2. Complex Supply Chains
3.1.3. Lack of Technological Competencies
3.1.4. Quality Assurance and Food Safety Concerns
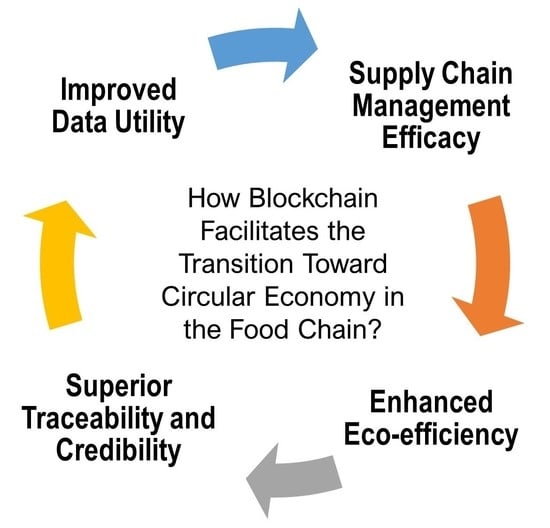
3.2. The Role of Blockchain in Circular Food Systems
3.2.1. Improved Data Utility
3.2.2. Supply Chain Management Efficacy
3.2.3. Enhanced Eco-Efficiency
3.2.4. Superior Traceability and Credibility
4. Discussion
4.1. Preventing Food Loss and Waste through Improved Data Utility, Eco-Efficiency, and Supply Chain Efficacy
4.2. Creating Trust Due to Enhanced Traceability and Monitoring
5. Perspectives
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Agri-food | Farming and food processing, food delivery and consumption |
| CE | Circular Economy |
| CPS | Cyber–Physical Systems |
| DPoS | Delegated PoS (Proof-of-Stake) |
| FAO | The Food and Agriculture Organization |
| FSC | Food Supply Chain |
| GPS | Global Positioning System |
| IBM | International Business Machines Corporation |
| ICT | Information and Communication Technology |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| PoC | Proof-of-Concept |
| PoS | Proof-of-Stake |
| PoW | Proof-of-Work |
| P2P | Peer-to-Peer |
| RFID | Radio-Frequency Identification |
| UAV | Unmanned Aerial Vehicles |
References
- FAO. The State of Food and Agriculture 2019. Moving Forward on Food Loss and Waste Reduction; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2019; ISBN 978-92-5-131789-1. Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/ca6030en/ca6030en.pdf (accessed on 29 November 2021).
- Farooque, M.; Zhang, A.; Liu, Y. Barriers to circular food supply chains in China. Supply Chain. Manag.: An. Int. J. 2019, 24, 677–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubeladze, D.; Pavliashvili, S. Linear economy and circular economy-current state assessment and future vision. Int. J. Innov. Technol. Econ. 2020, 5, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nižetić, S.; Šolić, P.; López-de-Ipiña González-de-Artaza, D.; Patrono, L. Internet of Things (IoT): Opportunities, issues and challenges towards a smart and sustainable future. J. Clean Prod. 2020, 274, 122877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moraga, G.; Huysveld, S.; Mathieux, F.; Blengini, G.A.; Alaerts, L.; Van Acker, K.; de Meester, S.; Dewulf, J. Circular economy indicators: What do they measure? Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 146, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foundation, E.M. Towards the Circular Economy: Economic and Business Rationale for an Accelerated Transition; Ellen MacArthur Foundation: Cowes, UK, 2019; pp. 21–34. Available online: https://www.ellenmacarthurfoundation.org/assets/downloads/publications/Ellen-MacArthur-Foundation-Towards-the-Circular-Economy-vol.1.pdf (accessed on 14 June 2020).
- Oliveira, M.M.; Lago, A.; Dal’ Magro, G.P. Food loss and waste in the context of the circular economy: A systematic review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 294, 126284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, S.; Bußler, S.; Schlüter, O.K. Food waste valorisation and circular economy concepts in insect production and processing. Waste Manag. 2020, 118, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alterå, O. Från värdekedja till värdecykel—Såfår Sverige en mer cirkulär ekonomi (From a value chain to a value circle—How Sweden will reach a more circular economy); Länsstyrelsen Västra Götalands län: Stockholm, Sweden, 2017; p. 22. [Google Scholar]
- FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations). Circular Economy: Waste-to-Resource & COVID-19; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy; Available online: http://www.fao.org/land-water/overview/covid19/circular/en/ (accessed on 21 August 2021).
- EMF. Towards the Circular Economy: Accelerating the Scale-up Across Global Supply Chains. Available online: https://reports.weforum.org/toward-the-circular-economy-accelerating-the-scale-up-across-global-supply-chains/ (accessed on 13 February 2018).
- Corona, B.; Shen, L.; Reike, D.; Rosales Carreón, J.; Worrell, E. Towards sustainable development through the circular economy—A review and critical assessment on current circularity metrics. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 151, 104498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Despoudi, S.; Dora, M. Circular food supply chains. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 34, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaCanne, C.E.; Lundgren, J.G. Regenerative agriculture: Merging farming and natural resource conservation profitably. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, S. Organizing alternative food futures in the peripheries of the industrial food system. J. Sustain. Educ. 2017, 14, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Duarte, L.O.; Kohan, L.; Pinheiro, L.; Fonseca Filho, H.; Baruque-Ramos, J. Textile natural fibers production regarding the agroforestry approach. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Newton, P.; Civita, N.; Frankel-Goldwater, L.; Bartel, K.; Johns, C. What is regenerative agriculture? A review of scholar and practitioner definitions based on processes and outcomes. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2020, 4, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, J.; Wang, X.; Kang, M.; Wang, H.; Wang, F.Y. Blockchain based provenance for agricultural products: A distributed platform with duplicated and shared bookkeeping. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Changshu, China, 26–30 June 2018; pp. 97–101. [Google Scholar]
- Banasik, A.; Kanellopoulos, A.; Claassen, G.D.H.; Bloemhof-Ruwaard, J.M.; van der Vorst, J.G.A.J. Assessing alternative production options for eco-efficient food supply chains using multi-objective optimization. Ann. Oper. Res. 2017, 250, 341–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ada, N.; Kazancoglu, Y.; Sezer, M.D.; Ede-Senturk, C.; Ozer, I.; Ram, M. Analyzing barriers of circular food supply chains and proposing industry 4.0 solutions. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Guo, S.; Xie, D.; Yan, Y. Blockchain: A new safeguard for agri-foods. Artif. Intell. Agric. 2020, 4, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamri, M.; Qasem, A.A.; Mohamed, A.A.; Hussain, S.; Ibraheem, M.A.; Shamlan, G.; Alqah, H.A.; Qasha, A.S. Food packaging’s materials: A food safety perspective. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 4490–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geueke, B.; Groh, K.; Muncke, J. Food packaging in the circular economy: Overview of chemical safety aspects for commonly used materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 193, 491–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toma, L.; Revoredo-Giha, C.; Costa-Font, M.; Thompson, B. Food Waste and Food Safety Linkagesalong the Supply Chain. EuroChoices 2020, 19, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wassenaer, L.; Verdouw, C.; Wolfert, S. What blockchain are we talking about? An analytical framework for understanding blockchain applications in agriculture and food. Front. Blockchain 2021, 4, 653128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrard, R.; Fielke, S. Blockchain for trustworthy provenances: A case study in the Australian aquaculture industry. Technol. Soc. 2020, 62, 101298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wamba, S.F.; Queiroz, M.M. Blockchain in the operations and supply chain management: Benefits, challenges and future research opportunities. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 52, 102064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettín-Díaz, R.; Rojas, A.E.; Mejía-Moncayo, C. Methodological approach to the definition of a Blockchain system for the food Industry supply chain traceability. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Science and Its Applications ICCSA, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 2–5 July 2018; Gervasi, O., Murgante, B., Misra, S., Stankova, E., Torre, C.M., Rocha, A.M.A.C., Taniar, D., Apduhan, B.O., Tarantino, E., Ryu, Y., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 19–33. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, F.J. An Agri-Food Supply Chain Traceability System For China Based On RFID & Blockchain Technology. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Service Systems and Service Management (ICSSSM), Kunming, China, 24–26 June 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, T. A Supply Chain Traceability System for food safety based on HACCP, Blockchain & Internet Of Things. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Service Systems and Service Management, Dalian, China, 16–18 June 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Galvez, J.F.; Mejuto, J.C.; Simal-Gandara, J. Future challenges on the use of blockchain for food traceability analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 107, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caro, M.P.; Ali, M.S.; Vecchio, M.; Giaffreda, R. Blockchain-based traceability in Agri-Food supply chain management: A practical implementation. In Proceedings of the IoT Vertical and Topical Summit on Agriculture, Tuscany, Italy, 8–9 May 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Nandi, S.; Sarkis, J.; Hervani, A.A.; Helms, M.M. Redesigning Supply Chains using Blockchain-Enabled Circular Economy and COVID-19 Experiences. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 27, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Li, M.; Yu, H.; Wang, M.; Xu, D.; Sun, C. A Trusted Blockchain-Based Traceability System for Fruit and Vegetable Agricultural Products. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 36282–36293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Dalhaus, T.; Wang, P.; Huang, J. Blockchain Technology for Agriculture. Appl. Ration. 2020, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Pendleton, M.; Njilla, L.; Xu, S. A Survey on Ethereum Systems Security: Vulnerabilities, Attacks, and Defenses. ACM Comput. Surv. 2021, 53, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, P.; Chen, T.; Luo, X.; Wen, Q. A survey on the security of blockchain systems. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020, 107, 841–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iansiti, M.; Lakhani, K.R. The Truth About Blockchain. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2017, 95, 118–127. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, D.; Donovan, J.; Topple, C. Achieving sustainability in food manufacturing operations and their supply chains: Key insights from a systematic literature review. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 28, 1491–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valoppi, F.; Agustin, M.; Abik, F.; Morais de Carvalho, D.; Sithole, J.; Bhattarai, M.; Varis, J.J.; Arzami, A.; Pulkkinen, E.E.; Mikkonen, K.S. Insight on current advances in food science and technology for feeding the world population. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 626227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejeb, A.; Rejeb, K.; Abdollahi, A.; Zailani, S.; Iranmanesh, M.; Ghobakhloo, M. Digitalization in food supply chains: A bibliometric review and key-route main path analysis. Sustainability 2021, 14, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Zhang, C.; Gong, Y.; Brown, S.; Li, Z. A content-analysis based literature review in blockchain adoption within food supply chain. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pandey, V.; Pant, M.; Snasel, V. Blockchain technology in food supply chains: Review and bibliometric analysis. Technol. Soc. 2022, 69, 101954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, N.; Ghadge, A.; Bourlakis, M. Blockchain adoption in food supply chains: A review and implementation framework. Prod. Plan. Control 2021, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, M.J.; Booth, A. A typology of reviews: An analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Inf. Libr. J. 2009, 26, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, B.N.; Johnson, C.D.; Adams, A. Writing narrative literature reviews for peer-reviewed journals: Secrets of the trade. J. Chiropr. Med. 2006, 5, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.D. The purpose, process and methods of writing a literature review: Editorial. Assoc. Oper. Room Nurses AORN J. 2016, 103, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, S.P.; Datta, S. Sustainable and green manufacturing—A narrative literature review. Mater. Today: Proc. 2020, 26, 2515–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente-Suárez, V.J.; Rodriguez-Besteiro, S.; Cabello-Eras, J.J.; Bustamante-Sanchez, A.; Navarro-Jiménez, E.; Donoso-Gonzalez, M.; Beltrán-Velasco, A.I.; Tornero-Aguilera, J.F. Sustainable Development Goals in the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Narrative Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acai, A.; Sonnadara, R.R.; O’Neill, T.A. Getting with the times: A narrative review of the literature on group decision making in virtual environments and implications for promotions committees. Perspect. Med. Educ. 2018, 7, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, M.; Singal, B. Blockchain technology in biomanufacturing: Current perspective and future challenges. In Blockchain Technology for Emerging Applications: A Comprehensive Approach; Islam, H., Pal, A.K., Samanta, D., Bhattacharyya, S., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2022; pp. 207–237. [Google Scholar]
- Sanka, A.I.; Cheung, R.C. A systematic review of blockchain scalability: Issues, solutions, analysis and future research. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2021, 195, 103232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Lee, J.-Y.; Gharehgozli, A. Blockchain in food supply chains: A literature review and synthesis analysis of platforms, benefits and challenges. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2021, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avraamidou, S.; Baratsas, S.G.; Tian, Y.; Pistikopoulos, E.N. Circular Economy—A challenge and an opportunity for Process Systems Engineering. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2020, 133, 106629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobson, K. Closing the loop or squaring the circle? Locating generative spaces for the circular economy. Prog. Hum. Geogr. 2015, 40, 88–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, B.; Upadhyay, A. Understanding barriers to circular economy: Cases from the manufacturing industry. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2020, 33, 729–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modgil, S.; Gupta, S.; Sivarajah, U.; Bhushan, B. Big data-enabled large-scale group decision making for circular economy: An emerging market context. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2021, 166, 120607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogetoft, P.; Olesen, H.B. Design of Production Contracts: Lessons from Theory and Agriculture; Copenhagen Business School Press DK: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2004; p. 208. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, C. Electronic agriculture, blockchain and digital agricultural democratization: Origin, theory and application. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 268, 122071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eijk, F.V. Barriers and Drivers towards a Circular Economy. Literature Review; Acceleratio B.V.: Naarden, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Han, Y.-Y.; Su, Z.-B.; Fang, J.-L.; Liu, Z.-Q.; Wang, K.-Y. A storage architecture for high-throughput crop breeding data based on improved blockchain technology. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 173, 105395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Huisman, W.; Hettinga, K.A.; Liu, N.; Heck, J.; Schrijver, G.H.; Gaiardoni, L.; van Ruth, S.M. Fraud vulnerability in the Dutch milk supply chain: Assessments of farmers, processors and retailers. Food Control. 2019, 95, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdousi, T.; Gruenbacher, D.; Scoglio, C.M. A Permissioned Distributed Ledger for the US Beef Cattle Supply Chain. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 154833–154847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, F.; Nicoletti, L.; Padovano, A. Estimating the Impact of Blockchain Adoption in the Food Processing Industry and Supply Chain. Int. J. Food Eng. 2020, 16, 20190109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Violino, S.; Pallottino, F.; Sperandio, G.; Figorilli, S.; Ortenzi, L.; Tocci, F.; Vasta, S.; Imperi, G.; Costa, C. A full technological traceability system for extra virgin olive oil. Foods 2020, 9, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, A.; Gligor, D.; Ngah, A. Applying Blockchain for Halal food traceability. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2020, 25, 947–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, K.; Bi, Y.; Jing, L.; Fu, H.-C.; Van Nieuwenhuyse, I. Research on agricultural supply chain system with double chain architecture based on blockchain technology. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 86, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Co, H.C.; Barro, F. Stakeholder theory and dynamics in supply chain collaboration. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2009, 29, 591–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, S.; Pizzol, M. Technology assessment of blockchain-based technologies in the food supply chain. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 269, 122193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, S.S.; Gunasekaran, A.; Sharma, R. Modeling the blockchain enabled traceability in agriculture supply chain. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 52, 101967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, K.; Nizamuddin, N.; Jayaraman, R.; Omar, M. Blockchain-based soybean traceability in agricultural supply chain. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 73295–73305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syromyatnikov, D.; Geiko, A.; Kuashbay, S.; Sadikbekova, A. Agile supply chain management in agricultural business. Int. J. Supply Chain. Manag. 2020, 9, 377–383. [Google Scholar]
- Tönnissen, S.; Teuteberg, F. Analysing the impact of blockchain-technology for operations and supply chain management: An explanatory model drawn from multiple case studies. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 52, 101953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, A.; Li, H. The Effect of Blockchain Technology on Supply Chain Sustainability Performances. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque, R.; Clark, J.H. Valorisation of food residues: Waste to wealth using green chemical technologies. Sustain. Chem. Processes 2013, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Gu, B.; Tian, G. Review of agricultural IoT technology. Artif. Intell. Agric. 2022, 2, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Wang, W.; Chen, B.; Zhang, X. Evaluation on Frozen Shellfish Quality by Blockchain Based Multi-Sensors Monitoring and SVM Algorithm during Cold Storage. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 54361–54370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, R.V.; Harsh, H.O.; Ray, P.; Babu, A.K. Food quality traceability prototype for restaurants using blockchain and food quality data index. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 240, 118021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berchicci, L.; Bodewes, W. Bridging environmental issues with new product development. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2005, 14, 272–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, R.; Butt, T.A. Safe farming as a service of blockchain-based supply chain management for improved transparency. Clust. Comput. 2020, 23, 2139–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antle, J.M. Economic analysis of food safety. Handb. Agric. Econ. 2001, 1, 1083–1136. [Google Scholar]
- Starbird, S.A.; Amanor-Boadu, V. Contract selectivity, food safety, and traceability. J. Agric. Food Ind. Organ. 2007, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronaghi, M.H. A blockchain maturity model in agricultural supply chain. Inf. Processing Agric. 2021, 8, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; Hao, Z.; Wang, F.; Li, H. Innovative Blockchain-Based Approach for Sustainable and Credible Environment in Food Trade: A Case Study in Shandong Province, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qlikchain Role of Blockchain to Prevent Information Asymmetry in Food Value Chains. Available online: https://www.qlikchain.com/qlikblogs/2019/10/24/role-of-blockchain-to-prevent-information-asymmetry-in-food-value-chains (accessed on 24 October 2019).
- Maaß, O.; Grundmann, P. Governing transactions and interdependences between linked value chains in a circular economy: The case of wastewater reuse in Braunschweig (Germany). Sustainability 2018, 10, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.R.; Zuhairi, M.F.; Saadat, M.N. Enhanced Blockchain Transaction: A Case of Food Supply Chain Management. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2020, 15, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.M.; Bode, C. An empirical investigation into supply chain vulnerability. J. Purch. Supply Manag. 2006, 12, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, A.Z.; Berger, P.D.; Gerstenfeld, A. Managing the supply-side risks in supply chains: Taxonomies, processes, and examples of decision-making modeling. In Applications of Supply Chain Management and E-Commerce Research; Geunes, J., Akçali, E., Pardalos, P.M., Romeijn, H.E., Shen, Z.-J.M., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2005; pp. 141–160. [Google Scholar]
- Monostori, J. Supply chains robustness: Challenges and opportunities. Procedia CIRP 2018, 67, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandon-Jones, E.; Squire, B.; Autry, C.W.; Petersen, K.J. A Contingent Resource-Based Perspective of Supply Chain Resilience and Robustness. J. Supply Chain. Manag. 2014, 50, 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Chen, H.; Hazen, B.T.; Kaur, S.; Santibañez Gonzalez, E.D.R. Circular economy and big data analytics: A stakeholder perspective. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2019, 144, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cillo, V.; Petruzzelli, A.M.; Ardito, L.; Del Giudice, M. Understanding sustainable innovation: A systematic literature review. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2019, 26, 1012–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschemann-Witzel, J.; Stangherlin, I.D.C. Upcycled by-product use in agri-food systems from a consumer perspective: A review of what we know, and what is missing. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2021, 168, 120749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmapalan, V.; O’Brien, W.J.; Morrice, D. Defining supply chain visibility for industrial construction projects. Front. Built Environ. 2021, 127, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, D.A.; McCutcheon, D.M.; Stuart, F.I.; Kerwood, H. Effects of supplier trust on performance of cooperative supplier relationships. J. Oper. Manag. 2004, 22, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G. The Impact of Supply Chain Relationship on Food Quality. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 131, 860–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monostori, L.; Kádár, B.; Bauernhansl, T.; Kondoh, S.; Kumara, S.; Reinhart, G.; Sauer, O.; Schuh, G.; Sihn, W.; Ueda, K. Cyber-physical systems in manufacturing. CIRP Ann. 2016, 65, 621–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.A.; Stranieri, A.; Gondal, I.; Balasubramanian, V. A survey on the adoption of blockchain in iot: Challenges and solutions. Blockchain: Res. Appl. 2021, 2, 100006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braungart, M.; McDonough, W.; Bollinger, A. Cradle-to-cradle design: Creating healthy emissions—A strategy for eco-effective product and system design. J. Clean. Prod. 2007, 15, 1337–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Blackshaw, K.; Cho, J.; Koolaji, N.; Yun, J.; Schindeler, A.; Valtchev, P.; Dehghani, F. Chapter4—Recovery of high-value compounds from food by-products. In Food Engineering Innovations Across the Food Supply Chain; Juliano, P., Buckow, R., Nguyen, M.H., Knoerzer, K., Sellahewa, J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 61–88. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.S.K.; Pfaltzgraff, L.A.; Herrero-Davila, L.; Mubofu, E.B.; Abderrahim, S.; Clark, J.H.; Koutinas, A.A.; Kopsahelis, N.; Stamatelatou, K.; Dickson, F.; et al. Food waste as a valuable resource for the production of chemicals, materials and fuels. Current situation and global perspective. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 426–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arancon, R.A.D.; Lin, C.S.K.; Chan, K.M.; Kwan, T.H.; Luque, R. Advances on waste valorization: New horizons for a more sustainable society. Energy Sci. Eng. 2013, 1, 53–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgens, B.; Powell, M.; Farmer, G.; Walsh, C.; Reed, E.; Royapoor, M.; Gosling, P.; Hall, J.; Heidrich, O. Creative upcycling: Reconnecting people, materials and place through making. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 189, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Wijewardena, K.P.; Karuppuswami, S.; Kriti, N.; Kumar, D.; Chahal, P. Blockchain inspired RFID-based information architecture for food supply chain. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 5803–5813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchherr, J.; Piscicelli, L.; Bour, R.; Kostense-Smit, E.; Muller, J.; Huibrechtse-Truijens, A.; Hekkert, M. Barriers to the Circular Economy: Evidence From the European Union (EU). Ecol. Econ. 2018, 150, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, J.; Han, Y. An Evidence of Distributed Trust in Blockchain-Based Sustainable Food Supply Chain. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, S.A.; Huang, N.-F.; Sofi, I.B.; Sultan, M. Agriculture-Food Supply Chain Management Based on Blockchain and IoT: A Narrative on Enterprise Blockchain Interoperability. Agriculture 2022, 12, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garaus, M.; Treiblmaier, H. The influence of blockchain-based food traceability on retailer choice: The mediating role of trust. Food Control 2021, 129, 108082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejeb, A.; Keogh, J.G.; Zailani, S.; Treiblmaier, H.; Rejeb, K. Blockchain Technology in the Food Industry: A Review of Potentials, Challenges and Future Research Directions. Logistics 2020, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Long, Y.; Song, H.-C.; He, Y.-D. Investment decision and coordination of green agri-food supply chain considering information service based on blockchain and big data. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 123646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guido, R.; Mirabelli, G.; Palermo, E.; Solina, V. A framework for food traceability: Case study – Italian extra-virgin olive oil supply chain. Int. J. Ind. Eng. Manag. 2020, 11, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Zhan, P.; Lei, M.; Zhou, F.; Wang, P. Food quality monitoring system based on smart contracts and evaluation models. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 12479–12490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, L.; Ullah, I.; Kim, D.-H. A secure fish farm platform based on blockchain for agriculture data integrity. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 170, 105251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jiong, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, B.; Chen, E. Development and assessment of blockchain-IoT-based traceability system for frozen aquatic product. J. Food Process. Eng. 2021, 44, e13669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, K.; Swanson, D. The supply chain has no clothes: Technology adoption of blockchain for supply chain transparency. Logistics 2018, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Powell, W.; Foth, M.; Natanelov, V.; Miller, T.; Dulleck, U. Strengthening consumer trust in beef supply chain traceability with a blockchain-based human-machine reconcile mechanism. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 180, 105886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeyratne, S.A.; Monfared, R.P. Blockchain ready manufacturing supply chain using distributed ledger. Int. J. Res. Eng. Technol. 2016, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Dobrovnik, M.; Herold, D.M.; Fürst, E.; Kummer, S. Blockchain for and in Logistics: What to Adopt and Where to Start. Logistics 2018, 2, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman Khan, S.A.; Yu, Z.; Sarwat, S.; Godil, D.I.; Amin, S.; Shujaat, S. The role of block chain technology in circular economy practices to improve organisational performance. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2022, 25, 605–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, R.S.; Sittón-Candanedo, I.; García, Ó.; Prieto, J.; Rodríguez-González, S. An intelligent Edge-IoT platform for monitoring livestock and crops in a dairy farming scenario. Ad Hoc Netw. 2020, 98, 102047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bumblauskas, D.; Mann, A.; Dugan, B.; Rittmer, J. A blockchain use case in food distribution: Do you know where your food has been? Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 52, 102008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.M.; Sung, J.; Park, T. Applications of blockchain to improve supply chain traceability. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 162, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grecuccio, J.; Giusto, E.; Fiori, F.; Rebaudengo, M. Combining blockchain and iot: Food-chain traceability and beyond. Energies 2020, 13, 3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogerson, M.; Parry, G.C. Blockchain: Case studies in food supply chain visibility. Supply Chain. Manag. 2020, 25, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malarvizhi, P. Interventions to scale-up palmpreneurship in Tamilnadu. Int. J. Recent Technol. Eng. 2019, 8, 1485–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, D.; Li, M. Convenience analysis of sustainable E-agriculture based on blockchain technology. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 271, 122503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.D.; Kumar, D.M.; Anandh, R. Block-chain Technology In Food Supply Chain Security. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2020, 9, 3446–3450. [Google Scholar]
- Kamath, R. Food Traceability on Blockchain: Walmart’s Pork and Mango Pilots with IBM. The JBBA 2018, 1, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, K.; Hao, M.; Yang, B. Food Safety Traceability Method Based on Blockchain Technology. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 2020, 1634, 012025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casino, F.; Kanakaris, V.; Dasaklis, T.K.; Moschuris, S.; Stachtiaris, S.; Pagoni, M.; Rachaniotis, N.P. Blockchain-based food supply chain traceability: A case study in the dairy sector. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2021, 59, 5758–5770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surasak, T.; Wattanavichean, N.; Preuksakarn, C.; Huang, S.C.H. Thai agriculture products traceability system using blockchain and Internet of Things. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2019, 10, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, J.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, A.; Chai, Y. Blockchain and IoT based food traceability for smart agriculture. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Crowd Science and Engineering, Association for Computing Machinery: Singapore, China, 28–31 July 2018. Article 3. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, D.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Hao, Z. Visual and User-Defined Smart Contract Designing System Based on Automatic Coding. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 73131–73143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Wang, K.; Cai, X.; Guo, S.; Guo, M.; Rong, C. A Comprehensive Survey of Blockchain: From Theory to IoT Applications and Beyond. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 8114–8154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Liu, S.; Lopez, C.; Lu, H.; Elgueta, S.; Chen, H.; Boshkoska, B.M. Blockchain technology in agri-food value chain management: A synthesis of applications, challenges and future research directions. Comput. Ind. 2019, 109, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, N.; Ormiston, J. Blockchain as a sustainability-oriented innovation?: Opportunities for and resistance to Blockchain technology as a driver of sustainability in global food supply chains. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2022, 175, 121403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.E. Satellite Remote Sensing in Agriculture and Food Security Assessment. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2015, 29, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaske, D.; Mvena, Z.S.K.; Sife, A.S. Mobile Phone Usage for Accessing Agricultural Information in Southern Ethiopia. J. Agric. Food Inf. 2018, 19, 284–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, M.R.; Razdari, A.M. Application of GIS and GPS in precision agriculture (a Review). Int. J. Adv. Biol. Biomed. Res. 2015, 3, 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, P.; Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Dong, Y. Blockchain-based safety management system for the grain supply chain. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 36398–36410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altay, A.; Learney, R.; Güder, F.; Dincer, C. Sensors in blockchain. Trends Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, A.S.; Tama, B.A.; Park, Y.; Rhee, K.-H. Advances in computer science and ubiquitous computing. In A Framework for Blockchain Based Secure Smart Green House Farming; Park, J.J., Loia, V., Yi, G., Sung, Y., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 1162–1167. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.P.; Petway, J.R.; Anthony, J.; Mukhtar, H.; Liao, S.W.; Chou, C.F.; Ho, Y.F. Blockchain: The evolutionary next step for ICT e-agriculture. Environments 2017, 4, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, V.N. Control of Salmonella in low-moisture foods. I. Minimizing entry of Salmonella into a processing facility. Food Prot. Trends 2009, 29, 342–353. [Google Scholar]
- Sokołowska, B.; Nasiłowska, J. Controlling spoilage and pathogenic microorganisms in beetroot (Beta vulgaris) juice by high hydrostatic pressure. In Safety Issues in Beverage Production; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 79–104. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J. Control of Salmonella in Low-Moisture Foods: Thermal Death Kinetics and Microbial Validation of Radio-Frequency Processes; Washington State University: Pullman, WA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gramoli, V. On the danger of private blockchains. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Distributed Cryptocurrencies and Consensus Ledgers (DCCL’16), Chicago, IL, USA, 25 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Esmaeilian, B.; Sarkis, J.; Lewis, K.; Behdad, S. Blockchain for the future of sustainable supply chain management in Industry 4.0. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 163, 105064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, M.W.; Bell, R.; Ferreira, C.M.; Gonzalez-Escalona, N.; Hoffmann, M.; Muruvanda, T.; Ottesen, A.; Ramachandran, P.; Reed, E.; Sharma, S.; et al. Genomics of foodborne pathogens for microbial food safety. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2018, 49, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bierbaum, R.; Leonard, S.A.; Rejeski, D.; Whaley, C.; Barra, R.O.; Libre, C. Novel entities and technologies: Environmental benefits and risks. Environ. Sci. Policy 2020, 105, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinnari, M.; Tapio, P. Future images of meat consumption in 2030. Futures 2009, 41, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dai, J.; Cui, L. The impact of digital technologies on economic and environmental performance in the context of industry 4.0: A moderated mediation model. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 229, 107777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, F.-Y. A Blockchain-based framework for collaborative production in distributed and social manufacturing. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Service Operations and Logistics, and Informatics (SOLI), Zhenghzhou, China, 6–8 November 2019; pp. 76–81. [Google Scholar]
- Yetis, H.; Karakose, M.; Baygin, N. Blockchain-based mass customization framework using optimized production management for industry 4.0 applications. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2022, 36, 101151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, A.; Ngan, P.T. A proposed framework model for dairy supply chain traceability. Sustain. Futures 2020, 2, 100034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, S.; Gunasekaran, A.; Arha, H. Understanding the Blockchain technology adoption in supply chains-Indian context. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2019, 57, 2009–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, M.M.; Fosso Wamba, S. Blockchain adoption challenges in supply chain: An empirical investigation of the main drivers in India and the USA. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2019, 46, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, M.; Singh, S.K.; Gupta, A.; Aggarwal, K.; Gupta, B.B.; Colace, F. Analysis and prognosis of sustainable development goals using big data-based approach during COVID-19 pandemic. Sustain. Technol. Entrep. 2022, 1, 100012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewa, T.; Ylianttila, M.; Liyanage, M. Survey on blockchain based smart contracts: Applications, opportunities and challenges. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2021, 177, 102857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Click, K.; Parizi, R.M.; Zhang, Q.; Dehghantanha, A.; Choo, K.-K.R. Sidechain technologies in blockchain networks: An examination and state-of-the-art review. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2020, 149, 102471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Chou, Y.-P.; Chou, Y.-C. An image authentication scheme using Merkle tree mechanisms. Future Internet 2019, 11, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altarawneh, A.; Herschberg, T.; Medury, S.; Kandah, F.; Skjellum, A. Buterin’s scalability trilemma viewed through a state-change-based classification for common consensus algorithms. In Proceedings of the IEEE 10th Annual Computing and Communication Workshop and Conference (CCWC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 6–8 January 2020; pp. 0727–0736. [Google Scholar]
- Karame, G. On the security and scalability of bitcoin’s blockchain. In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Vienna, Austria, 24–28 October 2016; pp. 1861–1862. [Google Scholar]


| Dimensions | Examples of Blockchain Impact on Agri-Food CE |
|---|---|
| Lack of Information on Products and Processes | |
| Complex Supply Chains | |
| Lack of Technological Competencies | |
| Quality Assurance and Food Safety Concerns |
| Dimensions | Examples of Blockchain Impact on Agri-Food CE |
|---|---|
| Improved Data Utility | |
| Supply Chain Management Efficacy | |
| Enhanced Eco-Efficiency | |
| Superior Traceability and Credibility |
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pakseresht, A.; Ahmadi Kaliji, S.; Xhakollari, V. How Blockchain Facilitates the Transition toward Circular Economy in the Food Chain? Sustainability 2022, 14, 11754. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141811754
Pakseresht A, Ahmadi Kaliji S, Xhakollari V. How Blockchain Facilitates the Transition toward Circular Economy in the Food Chain? Sustainability. 2022; 14(18):11754. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141811754
Chicago/Turabian StylePakseresht, Ashkan, Sina Ahmadi Kaliji, and Vilma Xhakollari. 2022. "How Blockchain Facilitates the Transition toward Circular Economy in the Food Chain?" Sustainability 14, no. 18: 11754. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141811754
APA StylePakseresht, A., Ahmadi Kaliji, S., & Xhakollari, V. (2022). How Blockchain Facilitates the Transition toward Circular Economy in the Food Chain? Sustainability, 14(18), 11754. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141811754