Food Additives from Fruit and Vegetable By-Products and Bio-Residues: A Comprehensive Review Focused on Sustainability
Abstract
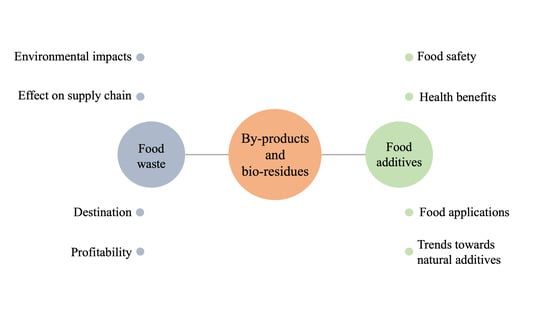
:1. Introduction
2. Generation of Fruit and Vegetable Waste
2.1. Food Waste Definition
2.2. Waste in the Food Supply Chain
2.3. Most-Representative Fruits and Vegetables Generating Waste
2.3.1. Fruit Waste and By-Products
2.3.2. Vegetable Waste and By-Products
2.4. Destination of the Generated By-Products/Biowaste
3. Valorization of By-Products/Biowaste
4. Food Additives—Their Role in Modern Diets
5. Trends towards Natural Additives
5.1. Antioxidants
5.2. Sweeteners
5.3. Antimicrobials
5.4. Colorants
5.5. Other Additives
6. Trends and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Augustin, M.A.; Sanguansri, L.; Fox, E.M.; Cobiac, L.; Cole, M.B. Recovery of wasted fruit and vegetables for improving sustainable diets. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 95, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Adhikari, B. Novel technologies applied for recovery and value addition of high value compounds from plant byproducts: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 3, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala-Zavala, J.F.; González-Aguilar, G.; Siddiqui, M.W. Plants Food By-Products: Industrial Relevance for Food Additives and Nutraceuticals. In Postharvest Biology and Technology; Apple Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018; p. 382. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. The State of Food and Agriculture. Moving forward on Food Loss and Waste Reduction. 2019. Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/ca6030en/ca6030en.pdf (accessed on 15 July 2020).
- Esparza, I.; Jim, N.; Bimbela, F.; Ancín-Azpilicueta, C.; Gandía, L.M. Fruit and vegetable waste management: Conventional and emerging approaches. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 265, 110510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. An EU Action Plan for the Circular Economy. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/resource.html?uri=cellar:8a8ef5e8-99a0-11e5-b3b7-01aa75ed71a1.0012.02/DOC_1&format=PDF (accessed on 13 July 2020).
- Laufenberg, G.; Kunz, B.; Nystroem, M. Transformation of vegetable waste into value added products: (A) the upgrading concept; (B) practical implementations. Bioresour. Technol. 2003, 87, 167–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilucia, F.; Lacivita, V.; Conte, A.; Nobile, M.A.D. Sustainable Use of Fruit and Vegetable By-Products to Enhance Food Packaging Performance. Foods 2020, 9, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority. Directive 2008/98/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32008L0098andfrom=EN (accessed on 15 July 2020).
- Bellemare, M.F.; Çakir, M.; Peterson, H.H.; Novak, L.; Rudi, J. On the Measurement of Food Waste. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2017, 99, 1148–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, L.; Schuster, M.; Torero, M. The Reality of Food Losses: A New Measurement Methodology. Int. Food Policy Res. Inst. 2017, 01686, 40. [Google Scholar]
- Ostergren, K.; Gustavsson, J.; Bos-Brouwers, H.; Timmermans, T.; Hansen, J.; Moller, H.; Anderson, G.; O’Connor, C.; Soethoudt, H.; Quested, T.; et al. FUSIONS Definitional Framework for Food Waste—Full Report. Available online: https://www.eu-fusions.org/phocadownload/Publications/FUSIONS%20Definitional%20Framework%20for%20Food%20Waste%202014.pdf (accessed on 15 July 2020).
- Espinosa-Alonso, L.G.; Valdez-Morales, M.; Aparicio-Fernandez, X.; Medina-Godoy, S.; Guevara-Lara, F. Chapter 8—Vegetables By-Products. In Food Wastes and By-Products; Campos-Vega, R., Oohmah, B.D., Vergara-Castañeda, H.A., Eds.; Wiley Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 223–266. [Google Scholar]
- Galanakis, C.M. Recovery of high components from food wastes: Conventional, emerging technologies and commercialized applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 26, 68–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schieber, A. Side Streams of Plant Food Processing as a Source of Valuable Compounds: Selected Examples. Annu. Rev. Sci. Technol. 2017, 8, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, P.; Gray, L.J.; Troughton, J.; Khunti, K.; Davies, M.J. Fruit and vegetable intake and incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2010, 341, c4229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Genkinger, J.M.; Plantz, E.A.; Hoffman, S.C.; Comstock, G.W.; Helzlsouer, K.J. Fruit, Vegetable, and Antioxidant Intake and All-Cause, Cancer, and Cardiovascular Disease Mortality in a Community-dwelling Population in Washington County, Maryland. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2004, 160, 1223–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djilas, S.; Jasna, C.; Cetkovic, G. By-products of fruits processing as a source of phytochemicals. Chem. Ind. Chem. Eng. Q. 2009, 15, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarty, I.; Mandavgane, S.A. Valorization of fruit and vegetable waste for biofertilizer and biogas. J. Food Process Eng. 2020, 44, e13512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-León, C.; Ramírez-Guzman, N.; Londoño-Hernandez, L.; Martinez-Medina, G.A.; Díaz-Herrera, R.; Navarro-Macias, V.; Alvarez-Pérez, O.B.; Picazo, B.; Fillarreal-Vázquez, M.; Ascacio-Valdes, J.; et al. Food Waste and Byproducts: An Opportunity to Minimize Malnutrition and Hunger in Developing Countries. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2018, 2, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Gaur, V.K.; Kim, S.H.; Pandey, A. Microbial strategies for bio-transforming food waste into resources. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 299, 122580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parfitt, J.; Barthel, M.; MacNaughton, S. Food waste within food supply chains: Quantification and potential for change to 2050. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 3065–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramos, M.; Jiménez, A.; Garrigós, M.C. Il-based advanced techniques for the extraction of value-added compounds from natural sources and food by-products. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 119, 115616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, H.; Czajkowska, K.; Cichowska, J.; Lenart, A. What’s new in biopotential of fruit and vegetable by-products applied in the food processing industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 67, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.L.; Malcata, X.; Revel, G. Volatile Contents of Grape Marcs in Portugal. J. Food Compos. Anal. 1996, 9, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyk, J.S.V.; Gama, R.; Morrison, D.; Swart, S.; Pletschke, B.I. Food processing waste: Problems, current management, and prospects for utilisation of the lignocellulose component through enzyme synergistic degradation. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 26, 521–531. [Google Scholar]
- Walia, M.; Rawat, K.; Bhushan, S.; Padwad, Y.S.; Singh, B. Fatty acid composition, physicochemical properties, antioxidant, and cytotoxic activity of apple seed oil obtained from apple pomace. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 929–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamma, D.; Christakopoulos, P. Biotransformation of Citrus By-Products into Value Added Products. Waste Biomass Valorization 2014, 5, 529–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledesma-Escobar, C.A.; De Castro, M.D.L. Towards a comprehensive exploitation of citrus. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 39, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, S.L.; Petropoulos, S.A.; Alexopoulos, A.; Heleno, S.A.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Potato peels as sources of functional compounds for the food industry: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 103, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matharu, A.S.; Melo, E.M.; Houghton, J.A. Opportunity for high value-added chemicals from food supply chain wastes. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 215, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowe, C. Review on Potential Use of Fruit and Vegetables By-Products as a Valuable Source of Natural Food Additives. Food Sci. Qual. Manag. 2015, 45, 47–61. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, A.N.; Paula, D.A.; Oliveira, E.B.; Saraiva, S.H.; Stringheta, P.C.; Ramos, A.M. Optimization of pectin extraction from Ubá mango peel through surface response methodology. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, A.; Farooq, U.; Akram, K.; Hayat, Z.; Sha, A.; Sarfraz, F.; Asim, M.; Sidhu, I.; Rehman, H. Therapeutic potentials of bioactive compounds from mango fruit wastes. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulos, S.A.; Ntatsi, G.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Long-term storage of onion and the factors that affect its quality: A critical review. Food Rev. Int. 2017, 33, 62–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, A.; Chakrabarty, D. Isolation of nanocellulose from waste sugarcane bagasse (SCB) and its characterization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 1291–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.W.; Hasanulbasori, M.A.; Chiat, P.F.; Lee, H.V. Pyrus pyrifolia fruit peel as sustainable source for spherical and porous network based nanocellulose synthesis via one-pot hydrolysis system. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 123, 1305–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, W.; Ma, Z.; Li, X.; Hu, X. Structural rearrangement of native and processed pea starches following simulated digestion in vitro and fermentation characteristics of their resistant starch residues using human fecal inoculum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 172, 490–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayesree, N.; Hang, P.K.; Priyangaa, A.; Krishnamurthy, N.P.; Ramanan, R.N.; Turki, M.S.A.; Charis, M.G.; Ooi, C.W. Valorisation of carrot peel waste by water-induced hydrocolloidal complexation for extraction of carotene and pectin. Chemosphere 2021, 272, 129919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papoutsis, K.; Edelenbos, M. Postharvest environmentally and human-friendly pre-treatments to minimize carrot waste in the supply chain caused by physiological disorders and fungi. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 112, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirabella, N.; Castellani, V.; Sala, S. Current options for the valorization of food manufacturing waste: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 65, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roda, A.; Marco, D.; Faveri, D.; Giacosa, S.; Dordoni, R.; Lambri, M. Effect of pre-treatments on the saccharification of pineapple waste as a potential source for vinegar production. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 4477–4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meghana, M.; Shastri, Y. Sustainable valorization of sugar industry waste: Status, opportunities, and challenges. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 303, 12292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, N.K.; Kumar, M.; Ghosh, P.; Kumar, S.S.; Singh, L.; Vijay, V.K.; Kumar, V. Anaerobic digestion of sugarcane bagasse for biogas production and digestate valorization. Chemosphere 2022, 295, 133893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolniak-Ostek, J. Chemical composition and antioxidant capacity of different anatomical parts of pear (Pyrus communis L.). Food Chem. 2016, 203, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogeropoulos, N.; Chiou, A.; Pyriochou, V.; Peristeraki, A.; Karathanos, V.T. Bioactive phytochemicals in industrial tomatoes and their processing byproducts. LWT–Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 49, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schieber, A.; Stintzing, F.C.; Carle, R. By-products of plant food processing as a source of functional compounds—Recent developments. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2001, 12, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shi, H.; He, Y.; Fei, X.; Peng, L. Preparation and characterization of carboxymethyl cellulose-based composite films reinforced by cellulose nanocrystals derived from pea hull waste for food packaging applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 4104–4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasta, H.F.B.; Lentz, L.; Rodrigues, L.G.G.; Mezzomo, N.; Vitali, L.; Ferreira, S.R.S. Pressurized liquid extraction applied for the recovery of phenolic compounds from beetroot waste. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 21, 101353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vulić, J.J.; Ćebović, T.N.; Čanadanović-Bruneta, J.M.; Ćetković, G.S.; Čanadanović, V.M.; Djilas, S.M.; Šaponjac, V.T.T. In vivo and in vitro antioxidant effects of beetroot pomace extracts. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 6, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florencia, V.; Lopez, O.V.; García, M.A. Exploitation of by-products from cassava and ahipa starch extraction as filler of thermoplastic corn starch. Compos. Part B 2020, 182, 107653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padi, R.K.; Chimphangoa, A.; Roskilly, A.P. Economic and environmental analysis of waste-based bioenergy integration into industrial cassava starch processes in Africa. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 31, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, C.B.; Jonathan, M.; Saad, S.M.I.; Schols, H.A.; Venema, K. Characterization and in vitro digestibility of by-products from Brazilian food industry Cassava bagasse, orange bagasse and passion fruit peel. Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fibre 2018, 16, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oghenejoboh, K.M.; Orugba, H.O.; Oghenejoboh, U.M.; Agarry, S.E. Value added cassava waste management and environmental sustainability in Nigeria: A review. Environ. Chall. 2021, 4, 100127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russ, W.; Meyer-Pittroff, R. Utilizing Waste Products from the Food Production and Processing Industries Utilizing Waste Products from the Food Production and Processing Industries. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2010, 44, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Moreno, N.; Esparza, I.; Bimbela, F.; Gandía, L.M.; Ancín-Azpilicueta, C. Valorization of selected fruit and vegetable wastes as bioactive compounds: Opportunities and challenges. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 50, 2061–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Valderrama, S.; Escamilla-Alvarado, C.; Rivas-García, P.; Magnin, J.P.; Alcalá-Rodríguez, M.; García-Reyes, R.B. Biorefinery concept comprising acid hydrolysis, dark fermentation, and anaerobic digestion for co-processing of fruit and vegetable wastes and corn stover. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 28585–28596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazgin, O.; Keskin-Gundogdu, T. Production of Biogas and Astaxanthin from Fruit and Vegetable Wastes Using an Integrated System. Int. J. Second. Metab. 2020, 7, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, M.A.; Lima, V.; Silva, A.S.; Vilarinho, F.; Castilho, M.C.; Khwaldia, K.; Ramos, F. Pomegranate and grape by-products and their active compounds: Are they a valuable source for food applications? Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 86, 68–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasaai, M.R.; Moosavi, A. Treatment of Kraft paper with citrus wastes for food packaging applications: Water and oxygen barrier properties improvement. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2017, 12, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, N.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Wastes and by-products: Upcoming sources of carotenoids for biotechnological purposes and health-related applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 62, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Señorans, F.J.; Ibáñez, E.; Cifuentes, A. New Trends in Food Processing. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2003, 43, 507–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; World Health Organization. Codex Alimentarius. General Standard for Food Additives. Codex Stan 192-1995. Available online: https://www.fao.org/fao-who-codexalimentarius/sh-proxy/en/?lnk=1&url=https%253A%252F%252Fworkspace.fao.org%252Fsites%252Fcodex%252FStandards%252FCXS%2B192-1995%252FCXS_192e.pdf (accessed on 30 March 2020).
- Bearth, A.; Cousin, M.; Siegrist, M. The consumer’s perception of artificial food additives: Influences on acceptance, risk, and benefit perceptions. Food Qual. Prefer. 2014, 38, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degreef, F. “What’s the deal with these strange substances in our food?” The representation of food additives by Belgian consumer organizations, 1960–1995. Food Foodways 2019, 27, 144–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltmarsh, M. Recent trends in the use of food additives in the United Kingdom. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 649–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asioli, D.; Aschemann-Witzel, J.; Caputo, C.; Vecchio, R.; Annunziata, A.; Naes, T.; Varela, P. Making sense of the “clean label” trends: A review of consumer food choice behavior and discussion of industry implications. Food Res. Int. 2017, 99, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carocho, M.; Barreiro, M.F.; Morales, P.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Adding Molecules to Food, Pros and Cons: A Review on Synthetic and Natural Food Additives. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 377–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Wang, X.; Sang, Y.; Liu, Q. Assessment of the Determination of Azodicarbonamide and Its Decomposition Product Semicarbazide: Investigation of Variation in Flour and Flour Products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 9313–9318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.K.; Naqshbandi, A.; Fareed, M.; Mahmood, R. Oral administration of a nephrotoxic dose of potassium bromate, a food additive, alters renal redox and metabolic status and inhibits brush border membrane enzymes in rats. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 980–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, N.; Fukushima, S.; Tsuda, H. Carcinogenity and modification of the carcinogenic response by BHA, BHT and other antioxidants. CRC Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2008, 15, 109–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritz, E.; Hahn, K.; Ketteler, M.; Kuhlmann, M.K.; Mann, J. Phosphate Additives in Food—A Health Risk. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2012, 109, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Dehghan, P.; Mohammadi, A.; Mohammadzadeh-Aghdash, H.; Dolatabadi, J.E.N. Pharmacokinetic and toxicological aspects of potassium sorbate food additive and its constituents. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 80, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, H.; Cho, Y.; Chung, M.; Kim, B.H. Preliminary data on sulphite intake from the Korean diet. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2007, 20, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Use of the Term Natural on Food Labeling. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/food-labeling-nutrition/use-term-natural-food-labeling (accessed on 2 April 2020).
- Kumar, Y.; Yadav, D.N.; Ahmad, T.; Narsaiah, K. Recent Trends in the Use of Natural Antioxidants for Meat and Meat Products. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2015, 14, 796–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baines, D. Defining the term “natural” in the context of food products. In Natural Food Additives, Ingredients, and Flavourings; Baines, D., Seal, R., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2012; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Gokoglu, N. Novel natural food preservatives and applications in seafood preservation: A review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 2068–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dávila-Aviña, J.E.; Zoellner, C.; Sólis-Soto; Rojas-Verde, G.; Garcia-Amezquita, L.E. Chapter 2: Economic and Environmental Benefits of Utilizing Plant Food By-Products. In Plant Food By-Products: Industrial Relevance for Food Additives and Nutraceutic; Ayala-Zavala, J.F., González-Aguilar, G., Siddiqui, M.W., Eds.; Apple Academic Press: Oakville, Australia, 2018; pp. 25–54. [Google Scholar]
- Faustino, M.; Veiga, M.; Sousa, P.; Costa, E.M.; Silva, S.; Pintado, M. Agro-Food Byproducts as a New Source of Natural Food Additives. Molecules 2019, 24, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chantaro, P.; Devahastin, S.; Chiewchan, N. Production of antioxidant high dietary fiber powder from carrot peels. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 41, 1987–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, B.; Shao, P.; Sun, P. Ultrasound-assisted emulsion electrosprayed particles for the stabilization of β-carotene and its nutritional supplement potential. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 102, 105634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Carranza, P.; Ávila-Sosa, R.; Guerrero-Beltrán, J.A.; Navarro-Cruz, A.R.; Corona-Jiménez, E.; Ochoa-Velasco, C.E. Optimization of antioxidant compounds extraction from fruit by-products: Apple pomace, orange, and banana peel. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2016, 40, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osuna, M.B.; Romero, C.A.; Romero, A.M.; Judis, M.A.; Bertola, N.C. Proximal composition, sensorial properties and effect of ascorbic acid and α-tocopherol on oxidative stability of bread made with whole flours and vegetable oils. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 98, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Górnás, P. Unique variability of tocopherol composition in various seed oils recovered from by-products of apple industry: Rapid and simple determination of all four homologues (α, β, γ and δ) by RP-HPLC/FLD. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, F.; Zhuang, H.; Chen, X.; Li, L.; Qiao, W.; Zhang, J. Effects of plant polyphenols and α-tocopherol on lipid oxidation, residual nitrites, biogenic amines, and N-nitrosamines formation during ripening and storage of dry-cured bacon. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 60, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okunowo, W.O.; Oyedeji, O.; Afolabi, L.O.; Matanmi, E. Essential Oil of Grape Fruit (Citrus paradisi) Peels and Its Antimicrobial Activities. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dussault, D.; Vu, K.D.; Lacroix, M. In vitro evaluation of antimicrobial activities of various commercial essential oils, oleoresin and pure compounds against food pathogens and application in ham. Meat Sci. 2014, 96, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mandalari, G.; Bennett, R.N.; Bisignano, G.; Trombetta, D.; Saija, A.; Faulds, C.B.; Gasson, M.J.; Narbad, A. Antimicrobial activity of flavonoids extracted from bergamot (Citrus bergamia Risso) peel, a byproduct of the essential oil industry. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 103, 2056–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Xiong, Q.; Wei, Y.; Shao, X. Antimicrobial action of flavonoids from Sedum aizoon L. against lactic acid bacteria in vitro and in refrigerated fresh pork meat. J. Func. Foods 2018, 40, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Carpena, J.G.; Morcuende, D.; Andrade, M.J.; Kylli, P.; Estévez, M. Avocado (Persea americana Mill.) Phenolics, In Vitro Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities, and Inhibition of Lipid and Protein Oxidation in Porcine Patties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 5625–5635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, R.C.; Rosa, S.R.; Weimer, P.; Moura, J.G.L.; Oliveira, V.R.; Castilhos, J. Assessment of compounds and cytotoxicity of Citrus deliciosa Tenore essential oils: From an underexploited by-product to a rich source of high-value bioactive compounds. Food Biosci. 2020, 38, 100779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Ding, D.; Shao, H.; Peng, Q.; Huang, Y. Antibacterial Activity and Physical Properties of Fish Gelatin-Chitosan Edible Films Supplemented with D-Limonene. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2017, 2017, 1837171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knoblich, M.; Anderson, B.; Latshaw, D. Analyses of tomato peel and seed byproducts and their use as a source of carotenoids. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2005, 85, 1166–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, D.M.; Minuceli, F.S.; Ribeiro, M.A.S.; Marques, D.R.; Testa, G.; Monteiro, A.R.G.; Moreira, J.N.; Clemente, E. Production Lycopene Dye São Caetano Melon (Momordica charantia L.) for Food Application. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2017, 57, 1951–1956. [Google Scholar]
- Crizel, T.M.; Hermes, V.S.; Rios, A.O.; Flôres, S.H. Evaluation of bioactive compounds, chemical and technological properties of fruits byproducts powder. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 4067–4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Backes, E.; Leichweis, M.G.; Pereira, C.; Carocho, M.; Barreira, J.C.M.; Genena, A.K.; Baraldi, I.J.; Barreiro, M.F.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Ficus carica L. and Prunus spinosa L. extracts as new anthocyanin-based food colorants: A thorough study in confectionery products. Food Chem. 2020, 333, 127457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrien, M.; Badr, A.; Gosselin, A.; Desjardins, Y.; Angers, P. Optimization of a green process for the extraction of lutein and chlorophyll from spinach by-products using response surface methodology (RSM). LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 79, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durmaz, Y.; Kilicli, M.; Toker, O.S.; Konar, N.; Palabiyik, I.; Tamturk, F. Using spray-dried microalgae in ice cream formulation as a natural colorant: Effect on physicochemical and functional properties. Algal Res. 2020, 47, 101811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S.; Nadeem, M.; Ahmad, F.; Mushtaq, Z. Biotechnological Production of Xylitol from Banana Peel and Its Impact on Physicochemical Properties of Rusks. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2013, 15, 747–756. [Google Scholar]
- Esfahlan, A.J.; Jamei, R.; Esfahlan, R.J. The importance of almond (Prunus amygdalus L.) and its by-products. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, R.V.; Santos, D.C.; Santana, A.C.A.; Filho, J.G.O.; Almeida, A.B.; Lima, T.M.; Silva, F.G.; Egea, M.B. Quality parameters and sensorial profile of clarified “Cerrado” cashew juice supplemented with Saccharomyces boulardii and different sweeteners. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 128, 109319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harini, K.; Ramya, K.; Sukumar, M. Extraction of nano celulose fibers from the banana peel and bract for production of acetyl and lauroyl cellulose. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 201, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Hou, Q.; Zhuang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, W. Effect of regenerated cellulose fiber on the physicochemical properties and sensory characteristics of fat-reduced emulsified sausage. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 97, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seixas, F.L.; Fukuda, D.L.; Turbiani, F.R.B.; Garcia, P.S.; Petkowics, C.L.O.; Jagadevan, S.; Gimenes, M.L. Extraction of pectin from passion fruit peel (Passiflora edulis f. flavicarpa) by microwave-induced heating. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 38, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, H.A.; Hameed, A.M.; Refaey, M.M.; Sayqal, A.; Aly, A.A. Rheological, physio-chemical, and organoleptic characteristics of ice cream enriched with Doum syrup and pomegranate peel. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 7346–7356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldán, E.; Sánchez-Moreno, C.; Ancos, B.; Cano, M.P. Characterization of onion (Allium cepa L.) by-products as food ingredients with antioxidant and antibrowning properties. Food Chem. 2008, 108, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorat, I.D.; Jagtap, D.D.; Mohapatra, D.; Joshi, D.C.; Sutar, R.F.; Kapdi, S.S. Antioxidants, their properties, uses in food products and their legal implications. Int. J. Food Stud. 2013, 2, 81–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Ghorat, F.; Ul-Haq, I.; Ur-Rehman, H.; Aslam, F.; Heydari, M.; Shariati, M.A.; Okuskhanova, E.; Yessimbekov, Z.; Thiruvengadam, M.; et al. Lycopene as a Natural Antioxidant Used to Prevent Human Health Disorders. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Xiong, Y.L. Natural antioxidants as food and feed additives to promote health benefits and quality of meat products: A review. Meat Sci. 2016, 120, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maestri, D.M.; Nepote, V.; Lamarque, A.; Zygaglo, J.A. Natural Products as Antioxidants. Available online: https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.621.3859&rep=rep1&type=pdf (accessed on 10 April 2022).
- Zhang, W.; Yu, S.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, B.; Mu, W. Recent advances in D-allulose: Physiological functionalities, applications, and biological production. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 54, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havelaar, A.H.; Brul, S.; Jong, A.; Jonge, R.; Zwietering, M.H.; Kuile, B.H. Future challenges to microbial food safety. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 139, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Juneja, V.K.; Dweivedi, H.P.; Yan, X. Novel Natural Food Antimicrobials. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 3, 381–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibane, L.B.; Degraeve, P.; Ferhout, H.; Bouajila, J.; Oulahal, N. Plant antimicrobial polyphenols as potential natural food preservatives. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 99, 1457–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quinto, E.J.; Caro, I.; Villalobos-Delgado, L.H.; Mateo, J.; De-Mateo-Silleras, B.; Redondo-Del-Rio, R. Food Safety through Natural Antimicrobials. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Francis, F.J. Quality as Influenced by Color. Food Qual. Prefer. 1995, 6, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Amaya, D.B. Natural food pigments and colorants. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2016, 7, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroux, J.; Langendorff, V.; Schick, G.; Vaishnav, V.; Mazoyer, J. Emulsion stabilizing properties of pectin. Food Hydrocoll. 2003, 17, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Amount of FV Produced (Million Tons) | Percentage of Waste and By-Product (%) | By-Products or Bio-Residues | Amount of By-Products or Nio-Residues (Million Tons) | Destination | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grape | 70 | 20–40 | Pomace | +10 | Animal feed, composting, seed oil extraction, alcoholic drink production | [15,25] |
| Apple | 69 | 25–35 | Pomace | 17–24 | Fertilizer, animal feed, pectin extraction, seed oil extraction | [15,26,27] |
| Citrus fruits | 110–115 | 50–65 | Peel | +15 | Deposition on land near the production site, animal feed, and burning | [28,29] |
| Potato | 368 | 15–40 | Peel | 48–140 | Landfill and animal feed | [15,26,30] |
| Tomato | 146 | 3–7 | Pomace | 4.3–10.2 | Animal feed | [15,26] |
| Banana | 102 | 30–40 | Peel | 9 | Incineration deposition in plantation areas, animal feed, biogas production | [15,20,31] |
| Mango | 39 | 15–60 | Peel | - | Untreated deposition, animal feed | [32,33,34] |
| Beet | 228 | - | Pulp | 80 | - | [26] |
| Onion | 85.8 | 5–50 | Peel | 0.5 | - | [32,35] |
| Olive | 20 | 20 | Olive endocarp | 3.7 | - | [26] |
| Pineapple | 19–25 | 10–60 | Pomace | 8.7 | [20,32] | |
| Sugarcane | 1949.3 | 30 | Bagasse | 584.8 | Fuel to power the sugar mill | [36] |
| Pear | 23 | 15–20 | Leaves and pomace | 3.5–4.6 | Animal feed, incineration, landfill | [37] |
| Pea | 13.5 | - | Pod/hull | - | Incineration | [38] |
| Carrot | 40 | 12% | Pomace and peel | 4.8 | - | [39,40] |
| Additive | Compound | GRAS Status/EU E Number | By-Product or Residue | Food Application | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antioxidants | β-carotene | GRAS/E160a | Carrot peel | Meal replacement bar | [81,82] |
| Ascorbic acid | GRAS/E300 | Apple pomace | Bread | [83,84] | |
| Tocopherol | GRAS/E306 | Apple seeds | Dry-cured bacon | [85,86] | |
| Antimicrobials | Essential oils | Not GRAS/No E number | Grapefruit peel | Ham | [87,88] |
| Flavonoids | GRAS/No E number | Bergamot peel | Fresh pork meat | [89,90] | |
| Catechins | Not GRAS/No E number | Avocado peel and seed | Pork patties | [91] | |
| Limonene | Not GRAS/No E number | Citrus deliciosa peel | Edible films | [92,93] | |
| Colorants | Lycopene | GRAS/E160d | Tomato peel | Dye beverages | [94,95] |
| Anthocyanins | Not GRAS/E163 | Blueberry pomace | Confectionery products | [96,97] | |
| Chlorophyll | Not GRAS/E140 | Spinach by-products | Ice cream | [98,99] | |
| Sweetener | Xylitol | GRAS/E967 | Banana peel Almond shell | Rusks Cashew juice | [100,101,102] |
| Emulsifier/stabilizer | Cellulose | GRAS/E460 | Banana bract (BB) and peel (BP) | Sausage | [103,104] |
| Pectin | GRAS/E440 | Passion fruit peel | Ice cream | [105,106] | |
| Antibrowning | Thiols | Not GRAS/No E number | Onion bagasse | Fresh-cut avocado | [107] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ueda, J.M.; Pedrosa, M.C.; Heleno, S.A.; Carocho, M.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Barros, L. Food Additives from Fruit and Vegetable By-Products and Bio-Residues: A Comprehensive Review Focused on Sustainability. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5212. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095212
Ueda JM, Pedrosa MC, Heleno SA, Carocho M, Ferreira ICFR, Barros L. Food Additives from Fruit and Vegetable By-Products and Bio-Residues: A Comprehensive Review Focused on Sustainability. Sustainability. 2022; 14(9):5212. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095212
Chicago/Turabian StyleUeda, Jonata M., Mariana C. Pedrosa, Sandrina A. Heleno, Márcio Carocho, Isabel C. F. R. Ferreira, and Lillian Barros. 2022. "Food Additives from Fruit and Vegetable By-Products and Bio-Residues: A Comprehensive Review Focused on Sustainability" Sustainability 14, no. 9: 5212. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095212
APA StyleUeda, J. M., Pedrosa, M. C., Heleno, S. A., Carocho, M., Ferreira, I. C. F. R., & Barros, L. (2022). Food Additives from Fruit and Vegetable By-Products and Bio-Residues: A Comprehensive Review Focused on Sustainability. Sustainability, 14(9), 5212. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095212