Spatiotemporal Analysis of Actual Evapotranspiration and Its Causes in the Hai Basin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Study Area
2.1. The Hai Basin
2.2. Data
3. Methods
3.1. ETWatch
3.2. Temporal Trend Analysis
3.3. Detrended Analysis
- (1)
- The significant linear trends in meteorological and RS parameters were removed. Specifically, the linear trend was calculated using least squares regression:where is a time series over and are coefficients in the least squares regression, is the prediction result and is the detrended stationary time series.
- (2)
- ET was derived from ETWatch using one detrended parameter and original data for other parameters.
- (3)
- The ET recalculated using detrended parameters was compared with the original ET, and the difference was considered the contribution of the parameter.
4. Results
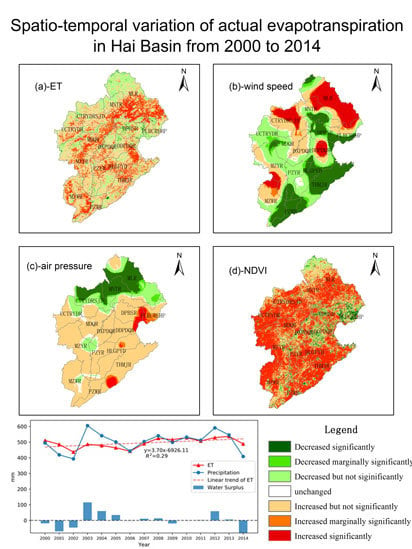
4.1. The Spatial Distributions of ET and Land Cover
4.2. The Temporal Change in ET
4.3. Quantitative Analysis of the Effects on ET
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, G.; Jia, L.; Menenti, M. Comparison of MOD16 and LSA-SAF MSG evapotranspiration products over europe for 2011. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 510–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Wang, K.; Liu, X.; Liu, C. Water storage in reservoirs built from 1997 to 2014 significantly altered the calculated evapotranspiration trends over China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 10097–10112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheffield, J.; Wood, E.F.; Munoz-Arriola, F. Long-term regional estimates of evapotranspiration for mexico based on downscaled isccp data. J. Hydrometeorol. 2010, 11, 253–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, R.; Caselles, V. A simplified equation to estimate spatial reference evaporation from remote sensing-based surface temperature and local meteorological data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 93, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Randerson, J.T.; Goulden, M.L. Continental-scale net radiation and evapotranspiration estimated using modis satellite observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2302–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, A.; Reichel, E. The World Water Balance: Mean Annual Global, Continental and Maritime Precipitation and Run-Off; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1975; p. 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Yang, H.-B.; Liu, F.-D.; An, S.-Q.; Cui, J.; Wang, Z.-S.; Liu, S.-R. Partitioning evapotranspiration flux components in a subalpine shrubland based on stable isotopic measurements. Bot. Stud. 2008, 49, 351–361. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop evapotranspiration-guidelines for computing crop water requirements-fao irrigation and drainage paper 56. FAO Rome 1998, 300, D05109. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B.; Jiang, L.; Yan, N.; Perry, C.; Zeng, H. Basin-wide evapotranspiration management: Concept and practical application in Hai Basin, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 145, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.; Wu, B.; Perry, C.; Zeng, H. Assessing potential water savings in agriculture on the Hai Basin plain, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 154, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yang, Z. Quantitative estimation of the impact of climate change on actual evapotranspiration in the Yellow River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2010, 395, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, D.; Nordblom, T.; Wu, B.; Yan, N. Regional water balance based on remotely sensed evapotranspiration and irrigation: An assessment of the Haihe plain, China. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 2514–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Dickinson, R. A review of global terrestrial evapotranspiration: Observation, modeling, climatology, and climatic variability. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosugi, Y.; Katsuyama, M. Evapotranspiration over a japanese cypress forest. Ii. Comparison of the eddy covariance and water budget methods. J. Hydrol. 2007, 334, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, K.B.; Hanson, P.J.; Mulholland, P.J.; Baldocchi, D.D.; Wullschleger, S.D. A comparison of methods for determining forest evapotranspiration and its components: Sap-flow, soil water budget, eddy covariance and catchment water balance. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2001, 106, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y. Determination of daily evaporation and evapotranspiration of winter wheat and maize by large-scale weighing lysimeter and micro-lysimeter. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2002, 111, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagler, P.L.; Scott, R.L.; Westenburg, C.; Cleverly, J.R.; Glenn, E.P.; Huete, A.R. Evapotranspiration on western us rivers estimated using the enhanced vegetation index from modis and data from eddy covariance and bowen ratio flux towers. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 97, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Yan, N.; Xiong, J.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Zhu, W.; Stein, A. Validation of etwatch using field measurements at diverse landscapes: A case study in Hai Basin of China. J. Hydrol. 2012, 436–437, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Menenti, M.; Feddes, R.A.; Holtslag, A.A.M. A remote sensing surface energy balance algorithm for land (SEBAL). 1. Formulation. J. Hydrol. 1998, 212–213, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleugh, H.A.; Leuning, R.; Mu, Q.; Running, S.W. Regional evaporation estimates from flux tower and modis satellite data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 106, 285–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z. The surface energy balance system (SEBS) for estimation of turbulent heat fluxes. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2002, 6, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Xiong, J.; Yan, N.; Yang, L. Etwatch: An Operational et Monitoring System with Remote Sensing. In Proceedings of the 2008 ISPRS Workshop on Geo-Information and Decision Support Systems, Tehran, Iran, 6–7 January 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Pelgrum, H.; Wang, J.; Ma, Y.; Moreno, J.F.; Roerink, G.J.; van der Wal, T. A remote sensing surface energy balance algorithm for land (SEBAL): Part 2: Validation. J. Hydrol. 1998, 212–213, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Improvements to a MODIS global terrestrial evapotranspiration algorithm. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1781–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteith, J. Evaporation and environment. Symp. Soc. Exp. Biol. 1965, 19, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Gemmer, M.; Zhai, J.; Liu, X.; Su, B.; Wang, Y. Spatio-temporal variation of actual evapotranspiration in the haihe river basin of the past 50 years. Quat. Int. 2013, 304, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Wu, B.; Wei, Y.; Yan, N.; Wang, H.; Guo, S. Quantifying impacts of climate variability and human activities on the hydrological system of the Haihe River Basin, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 1491–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Tian, H.; Chen, G.; Ren, W.; Zhang, C.; Liu, J. Effects of land-use and land-cover change on evapotranspiration and water yield in China during 1900–2000. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2008, 44, 1193–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Moiwo, J.P.; Yang, Y.; Han, S.; Yang, Y. Agricultural water-saving and sustainable groundwater management in Shijiazhuang Irrigation District, North China Plain. J. Hydrol. 2010, 393, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.-Y.; Gong, L.; Jiang, T.; Chen, D.; Singh, V.P. Analysis of spatial distribution and temporal trend of reference evapotranspiration and pan evaporation in Changjiang (Yangtze River) catchment. J. Hydrol. 2006, 327, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.-K. Quantifying fractal dynamics of groundwater systems with detrended fluctuation analysis. J. Hydrol. 2007, 336, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.D.; Yu, Z. Multifractal detrended fluctuation analysis of streamflow series of the Yangtze River Basin, China. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 4997–5003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Singh, V.P.; Chen, Y.D. Comparison of detrending methods for fluctuation analysis in hydrology. J. Hydrol. 2011, 400, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegos, A.; Malamos, N.; Efstratiadis, A.; Tsoukalas, I.; Karanasios, A.; Koutsoyiannis, D. Parametric modelling of potential evapotranspiration: A global survey. Water 2017, 9, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Cheng, W.; Liu, Q.; Wang, N. Spatiotemporal measurement of urbanization levels based on multiscale units: A case study of the Bohai Rim Region in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 531–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, W.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, D.; Xiang, B. Spatiotemporal dynamics of impervious surface areas across china during the early 21st century. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 1691–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Yuan, Q.; Yan, C.; Wang, Z.; Yu, X.; Li, A.; Ma, R.H.; Huang, J.L.; Chen, J.S.; Chang, C. Land cover changes of China from 2000 to 2010. Quat. Sci. 2014, 34, 723–731. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Shen, Y. Quantifying water and energy budgets and the impacts of climatic and human factors in the Haihe River Basin, China: 2. Trends and implications to water resources. J. Hydrol. 2015, 527, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changming, L.; Jingjie, Y.; Kendy, E. Groundwater exploitation and its impact on the environment in the North China Plain. Water Int. 2001, 26, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laads Web: Level-1 and Atmosphere Archive & Distribution System. Available online: https://ladsweb.modaps.eosdis.nasa.gov/search/ (accessed on 24 August 2017).
- LAADS DAAC. Mod021km-Level 1b Calibrated Radiances-1km. Available online: https://ladsweb.modaps.eosdis.nasa.gov/api/v1/productPage/product=MOD021KM (accessed on 12 December 2017).
- Vermote, E.F.; Tanré, D.; Deuze, J.L.; Herman, M.; Morcette, J.J. Second simulation of the satellite signal in the solar spectrum, 6s: An overview. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-L.; Tang, B.-H.; Wu, H.; Ren, H.; Yan, G.; Wan, Z.; Trigo, I.F.; Sobrino, J.A. Satellite-derived land surface temperature: Current status and perspectives. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 131, 14–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, K.; Qin, Z.; Shi, J.; Gong, P. A practical split-window algorithm for retrieving land-surface temperature from modis data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 3181–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Q.; Wu, B.; Xiong, J. Interpolation system for generating meteorological surfaces using to compute evapotranspiration in Haihe River Basin. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Seoul, Korea, 29 July 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, N.; Zhu, W.; Feng, X.; Chang, S. Spatial-temporal change analysis of evapotranspiration in the Heihe River Basin. In Proceedings of the 2014 Third International Workshop on Earth Observation and Remote Sensing Applications (EORSA), Changsha, China, 11–14 June 2014; pp. 38–41. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Yuan, Q.; Liu, Y. Object-based approach to national land cover mapping using HJ satellite imagery. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2014, 8, 083686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birsan, M.-V.; Molnar, P.; Burlando, P.; Pfaundler, M. Streamflow trends in Switzerland. J. Hydrol. 2005, 314, 312–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprent, P.; Smeeton, N.C. Applied Nonparametric Statistical Methods; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Box, J.F. Guinness, gosset, fisher, and small samples. Stat. Sci. 1987, 2, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. A new measure of rank correlation. Biometrika 1938, 30, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, J.D.; Chakraborti, S. Nonparametric Statistical Inference; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- De la Casa, A.C.; Ovando, G.G. Variation of reference evapotranspiration in the central region of Argentina between 1941 and 2010. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2016, 5, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, E.M.; Vogel, R.M.; Kroll, C.N. Trends in floods and low flows in the United States: Impact of spatial correlation. J. Hydrol. 2000, 240, 90–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, G.; Fu, G.; He, R.; Yan, X.; Jin, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, A. Attribution for decreasing streamflow of the Haihe River Basin, Northern China: Climate variability or human activities? J. Hydrol. 2012, 460, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estes, A.B.; Kuemmerle, T.; Kushnir, H.; Radeloff, V.C.; Shugart, H.H. Land-cover change and human population trends in the greater serengeti ecosystem from 1984–2003. Biol. Conserv. 2012, 147, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Xie, Z.H.; Liu, Q.; Xia, J. Simulating hydrologic changes with climate change scenarios in the haihe river basin. Pedosphere 2005, 15, 595–600. [Google Scholar]
- Duo, A.; Zhao, W.; Qu, X.; Jing, R.; Xiong, K. Spatio-temporal variation of vegetation coverage and its response to climate change in North China plain in the last 33 years. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 53, 103–117. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Zhang, H.; Chen, B.; Zhang, H.; Innes, J.; Wang, G.; Yan, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Myneni, R. Changes in vegetation growth dynamics and relations with climate over China’s landmass from 1982 to 2011. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 3263–3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, B.; Wu, W. Monitoring and dynamic analysis of fractional vegetation cover in the Hai River Basin based on MODIS data. Resour. Sci. 2010, 32, 1417–1424. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, N.; Macpherson, A.; Rosemblatt, K.A.N. A course in theoretical statistics: For sixth forms, Technical Colleges, Colleges of Education, Universities: Charles Griffin & Company Limited; Charles Griffin & Company Limited: London, UK, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Pearson, K. Note on regression and inheritance in the case of two parents. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1895, 58, 240–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Drought-induced reduction in global terrestrial net primary production from 2000 through 2009. Science 2010, 329, 940–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Xie, Z. A new surface runoff parameterization with subgrid-scale soil heterogeneity for land surface models. Adv. Water Resour. 2001, 24, 1173–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhenghui, X.; Fengge, S.; Xu, L.; Qingcun, Z.; Zhenchun, H.; Yufu, G. Applications of a surface runoff model with horton and dunne runoff for vic. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2003, 20, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- People.cn. Available online: http://bj.people.com.cn/n/2015/0528/c82840-25035935.html (accessed on 3 September 2017).









| Variable | t-Test | Mann-Kendall Test | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slope | T | Tc | H0 | Kendall’s Tau | Z | Zc | H0 | |
| ET * | 3.70 | 2.28 | 2.16 | R | 0.43 | 2.18 | 1.96 | R |
| Precipitation | 3.00 | 0.79 | 2.16 | N.R. | 0.20 | 0.99 | 1.96 | N.R. |
| Water surplus | −0.65 | −0.21 | 2.16 | N.R. | −0.01 | 0.00 | 1.96 | N.R. |
| NDVI * | 0.002 | 5.26 | 2.16 | R | 0.66 | 3.40 | 1.96 | R |
| HUMD | −0.04 | −0.30 | 2.16 | N.R. | −0.09 | −0.40 | 1.96 | N.R. |
| PRE | 0.37 | 0.55 | 2.16 | N.R. | 0.09 | 0.40 | 1.96 | N.R. |
| SUNT | −0.08 | −0.32 | 2.16 | N.R. | −0.12 | −0.59 | 1.96 | N.R. |
| Tavg | 0.07 | 0.19 | 2.16 | N.R. | −0.03 | −0.10 | 1.96 | N.R. |
| Winv | −0.04 | −0.59 | 2.16 | N.R. | −0.18 | −0.89 | 1.96 | N.R. |
| Variable | t-Test | Mann-Kendall Test | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slope | T | Tc | H0 | Kendall’s Tau | Z | Zc | H0 | |
| ET * | 0.01 | 24.48 | 1.97 | R | 0.75 | 15.50 | 1.96 | R |
| Albedo * | 9.4 × 10−5 | 2.84 | 1.97 | R | 0.18 | 3.63 | 1.96 | R |
| Relative humidity * | 0.05 | 3.25 | 1.97 | R | 0.16 | 3.22 | 1.96 | R |
| NDVI * | 1.9 × 10−3 | 38.74 | 1.97 | R | 0.80 | 16.45 | 1.96 | R |
| Air pressure * | −1.17 | −20.66 | 1.97 | R | −0.63 | −12.98 | 1.96 | R |
| Sunshine hours * | 0.13 | 3.43 | 1.97 | R | 0.17 | 3.60 | 1.96 | R |
| Temperature * | 0.18 | 33.06 | 1.97 | R | 0.74 | 15.17 | 1.96 | R |
| Wind speed | 0.01 | 1.78 | 1.97 | N.R. | 0.08 | 1.73 | 1.96 | N.R. |
| Variable | ET (Original) (mm) | ET (Detrended) (mm) | Difference (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Albedo | 219.31 | 229.38 | −10.08 |
| HUMD | 219.31 | 219.29 | 0.02 |
| NDVI | 219.31 | 93.95 | 125.35 |
| PRE | 219.31 | 234.15 | −14.84 |
| SUNT | 219.31 | 202.01 | 17.29 |
| Tavg | 219.31 | 30.58 | 188.73 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, N.; Tian, F.; Wu, B.; Zhu, W.; Yu, M. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Actual Evapotranspiration and Its Causes in the Hai Basin. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10020332
Yan N, Tian F, Wu B, Zhu W, Yu M. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Actual Evapotranspiration and Its Causes in the Hai Basin. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(2):332. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10020332
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Nana, Fuyou Tian, Bingfang Wu, Weiwei Zhu, and Mingzhao Yu. 2018. "Spatiotemporal Analysis of Actual Evapotranspiration and Its Causes in the Hai Basin" Remote Sensing 10, no. 2: 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10020332
APA StyleYan, N., Tian, F., Wu, B., Zhu, W., & Yu, M. (2018). Spatiotemporal Analysis of Actual Evapotranspiration and Its Causes in the Hai Basin. Remote Sensing, 10(2), 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10020332