Understanding Temporal and Spatial Distribution of Crop Residue Burning in China from 2003 to 2017 Using MODIS Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. MODIS Active Fire
2.2.2. The Dataset of Land-Use and Land-Cover Change
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Extraction and Mosaic of Fire Pixels from MODIS Fire Products
2.3.2. Maximum Value Composite of Fire Pixels
2.3.3. Extraction of Fire Spots from Crop Residue Burning
3. Results
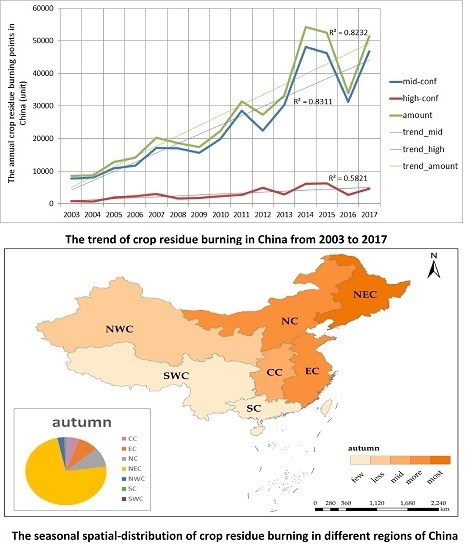
3.1. The Trend of Crop Residue Burning in China
3.2. The Temporal Distribution of Crop Residue Burning in China
3.2.1. The Temporal Distribution of Crop Residue Burning in Central China (CC)
3.2.2. The Temporal Distribution of Crop Residue Burning in East China (EC)
3.2.3. The Temporal Distribution of Crop Residue Burning in North China (NC)
3.2.4. The Temporal Distribution of Crop Residue Burning in Northeast China (NEC)
3.2.5. The Temporal Distribution of Crop Residue Burning in Northwest China (NWC)
3.2.6. The Temporal Distribution of Crop Residue Burning in South China (SC)
3.2.7. The Temporal Distribution of Crop Residue Burning in Southwest China (SWC)
3.3. The Spatial Distribution of Crop Residue Burning in China
3.3.1. Monthly Variation
3.3.2. Seasonal Variations
4. Discussion
4.1. The Attribution of the Temporal Distribution of Crop Residue Burning in Different Regions of China
4.2. The Attribution of the Spatial Distribution of Crop Residue Burning in Different Months or Seasons
4.3. Limitations and Prospect
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lal, R. World crop residues production and implication of its use as a biofuel. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, S.; Wang, X.F.; Xiao, Y.; Tani, H.; Zhong, G.S.; Sun, Z.Y. Study on spatial distribution of crop residue burning and PM2.5 change in China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 204–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zang, G.Q.; Tang, Z.H.; Chen, X.H.; Yu, Y.S. Burning straw, air pollution, and respiratory infections in China. Am. J. Infect. Control 2014, 42, 815–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehmood, K.; Chang, S.; Yu, S.C.; Wang, L.Q.; Li, P.F.; Li, Z.; Liu, W.P.; Rosenfeld, D.; Seinfeld, H.J. Spatial and temporal distributions of air pollutant emissions from open crop straw and biomass burnings in China from 2002 to 2016. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2017, 16, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.M.; Li, C.L.; Ristovski, Z.; Milic, A.; Gu, Y.; Islam, M.S.; Wang, S.; Hao, J.; Zhang, H.; He, C.; et al. A review of biomass burning: Emissions and impacts on air quality, health and climate in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 1000–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadde, B.; Bonnet, S.; Menke, C.; Garivait, S. Air pollutant emissions from rice straw open field burning in India, Thailand and the Philippines. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1554–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- THE PAPER. Available online: http://www.thepaper.cn/newsDetail_forward_1557556 (accessed on 8 November 2016).
- Chen, Z.Y.; Chen, D.L.; Zhuang, Y.; Cai, J.; Zhao, N.; He, B.; Gao, B.B.; Xu, B. Examining the influence of crop residue burning on local PM2.5 concentrations in Heilongjiang Province using ground observation and remote sensing data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 971–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Bo, Y.; Xie, S.D. Estimating emissions from crop residue open burning in China based on statistics and MODIS fire products. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 44, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.R.; Wooster, J.M.; Green, C.D.; Main, B. New field-based agricultural biomass burning trace gas, PM2.5, and black carbon emission ratios and factors measured in situ at crop residue fires in Eastern China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 121, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enkhjargal, A.; Burmaajav, B. Impact of the ambient air PM2.5 on cardiovascular diseases of Ulaanbaatar residents. Geogr. Environ. Sustain. 2015, 4, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeatts, K.; Svendsen, E.; Creason, J.; Alexis, N.; Herbst, M.; Scott, J.; Kupper, L.; Williams, R.; Neas, L.; Cascio, W.; et al. Coarse Particulate Matter (PM2.5–10) Affects Heart Rate Variability, Blood Lipids, and Circulating Eosinophils in Adults with Asthma. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, C.P.; Panigrahy, S. Characterisation of Residue Burning from Agricultural System in India using Space Based Observations. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2011, 39, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassman, W.; Ford, B.; Gan, W.R.; Pfister, G.; Magzamen, S.; Fischer, V.E.; Pierce, R.J. Spatial and temporal estimates of population exposure to wildfire smoke during the Washington state 2012 wildfire season using blended model, satellite, and in situ data. GeoHealth 2017, 1, 106–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.M.; Pereira, M.C.J.; Masiero, A.; Pirotti, F. Mapping fire regimes in China using MODIS active fire and burned area data. Appl. Geogr. 2017, 85, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.R.; Wooster, J.M.; Xu, W.D. Approaches for synergistically exploiting VIIRS I- and M-Band data in regional active fire detection and FRP assessment: A demonstration with respect to agricultural residue burning in Eastern China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 198, 407–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Siegert, F.; Goldammer, J.G.; Sukhinin, A.I. Satellite-derived 2003 wildfires in southern Siberia and their potential influence on carbon sequestration. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 1479–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramasinghe, H.C.; Jones, S.; Reinke, K.; Wallace, L. Development of a Multi-Spatial Resolution Approach to the Surveillance of Active Fire Lines Using Himawari-8. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 932–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.H.; Duan, L.; Chai, F.; Wang, S.X.; Yu, Q.; Wang, S.L. Deriving High-Resolution Emission Inventory of Open Biomass Burning in China based on Satellite Observations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 11779–11786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LAADS DACC ftp Server. Available online: ftp://ladsweb.nascom.nasa.gov (accessed on 10 October 2017).
- Giglio, L. MODIS Collection 6 Active Fire Product User’s Guide. Revision, A; Department of Geographical Sciences, University of Maryland: College Park, MD, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Justice, C.; Giglio, L.; Boschetti, L.; Roy, D.; Csiszar, I.; Morisette, J.; Kaufman, Y. Algorithm Technical Background Document MODIS FIRE PRODUCTS. MODIS Science Team: Washington, DC, USA. Available online: ftp://ladsweb.nascom.nasa.gov (accessed on 10 October 2017).
- Giglio, L.; Descloitresa, J.; Justicec, O.C.; Kaufman, J.Y. An Enhanced Contextual Fire Detection Algorithm for MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 87, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dozier, J. A Method for Satellite Identification of Surface Temperature Fields of Subpixel Resolution. Remote Sens. Environ. 1981, 11, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matson, M.; Dozier, J. Identification of Subresolution High Temperature Sources Using a Thermal IR Sensor. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1981, 47, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar]
- Resources and Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Data Center. Available online: http://www.resdc.cn (accessed on 10 October 2017).
- Liu, J.Y.; Liu, M.L.; Deng, X.Z.; Zhuang, D.F.; Zhang, Z.X.; Luo, D. The land use and land cover change database and its relative studies in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2002, 12, 275–282. [Google Scholar]
- Carroll, M.L.; Townshend, J.R.; DiMiceli, C.M.; Noojipady, P.; Sohlberg, R.A. A new global raster water mask at 250 m resolution. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2009, 2, 291–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romasanta, R.R.; Sandera, O.B.; Gaihrea, K.Y.; Alberto, C.M. How does burning of rice straw affect CH4 and N2O emissions? A comparative experiment of different on-field straw management practices. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 239, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.B.; Liu, Y.Q.; Hao, L. Contributions of open crop straw burning emissions to PM2.5 concentrations in China. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 014014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.N.; Chen, G.Y.; Cheng, Z.J.; Yan, B.B.; Hou, L.A. Air pollutant emissions from straw open burning: A case study in Tianjin. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 171, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Environmental Protection of Heilongjiang Province. Available online: http://www.hljdep.gov.cn/xwzx/hjyw/2016/04/12292.html (accessed on 1 April 2016).










© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhuang, Y.; Li, R.; Yang, H.; Chen, D.; Chen, Z.; Gao, B.; He, B. Understanding Temporal and Spatial Distribution of Crop Residue Burning in China from 2003 to 2017 Using MODIS Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10030390
Zhuang Y, Li R, Yang H, Chen D, Chen Z, Gao B, He B. Understanding Temporal and Spatial Distribution of Crop Residue Burning in China from 2003 to 2017 Using MODIS Data. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(3):390. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10030390
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhuang, Yan, Ruiyuan Li, Hao Yang, Danlu Chen, Ziyue Chen, Bingbo Gao, and Bin He. 2018. "Understanding Temporal and Spatial Distribution of Crop Residue Burning in China from 2003 to 2017 Using MODIS Data" Remote Sensing 10, no. 3: 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10030390
APA StyleZhuang, Y., Li, R., Yang, H., Chen, D., Chen, Z., Gao, B., & He, B. (2018). Understanding Temporal and Spatial Distribution of Crop Residue Burning in China from 2003 to 2017 Using MODIS Data. Remote Sensing, 10(3), 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10030390