An Assessment of Atmospheric and Meteorological Factors Regulating Red Sea Phytoplankton Growth
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Ocean Color Climate Change Initiative (OC-CCI) Chlorophyll-a Data
2.1.2. MODIS-Aqua SST Data
2.1.3. Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR) Pathfinder SST Data
2.1.4. Modern-Era Retrospective Analysis for Research and Applications Version 2 (MERRA-2) Dust Reanalysis Data
2.1.5. Multi-Angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer (MISR) Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) Data
2.1.6. Cloud-Aerosol Lidar and Infrared Pathfinder Satellite Observations (CALIPSO) AOD Data
2.2. Methods
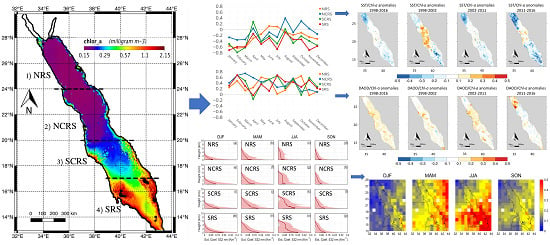
3. Results
3.1. Time Series of Scaled Values for Chl-a, DAOD, and SST
3.2. Time Series of Z-Scores for Chl-a, DAOD, and SST
3.3. Comparision of Sensors Used in OC-CCI Data
3.4. Anomaly Comparison of Chl-a Concentration and Other Factors for June 2010
3.5. Correlation Analysis of Chl-a Anomalies with SST and DAOD Anomalies
3.6. Lag (Cross) Correlation Maps of SST, Wind Speed, and DAOD with Chl-a
3.7. Calipso-Based 3D Climatology of Desert Dust Aerosol over the Red Sea
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sofianos, S.S.; Johns, W.E. Observations of the summer Red Sea circulation. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acker, J.; Leptoukh, G.; Shen, S.; Zhu, T.; Kempler, S. Remotely-sensed chlorophyll a observations of the northern Red Sea indicate seasonal variability and influence of coastal reefs. J. Mar. Syst. 2008, 69, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raitsos, D.E.; Pradhan, Y.; Brewin, R.J.W.; Stenchikov, G.; Hoteit, I. Remote Sensing the Phytoplankton Seasonal Succession of the Red Sea. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qurban, M.A.; Balala, A.C.; Kumar, S.; Bhavya, P.S.; Wafar, M. Primary production in the northern Red Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2014, 132, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; Hoteit, I.; Pratt, L.J.; Bower, A.S.; Zhai, P.; Köhl, A.; Gopalakrishnan, G. Seasonal overturning circulation in the Red Sea: 1. Model validation and summer circulation. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2014, 119, 2238–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churchill, J.H.; Bower, A.S.; McCorkle, D.C.; Abualnaja, Y. The transport of nutrient-rich Indian Ocean water through the Red Sea and into coastal reef systems. J. Mar. Res. 2014, 72, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raitsos, D.E.; Yi, X.; Platt, T.; Racault, M.-F.; Brewin, R.J.W.; Pradhan, Y.; Papadopoulos, V.P.; Sathyendranath, S.; Hoteit, I. Monsoon oscillations regulate fertility of the Red Sea: Monsoons regulate Red Sea greenness. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racault, M.-F.; Raitsos, D.E.; Berumen, M.L.; Brewin, R.J.W.; Platt, T.; Sathyendranath, S.; Hoteit, I. Phytoplankton phenology indices in coral reef ecosystems: Application to ocean-color observations in the Red Sea. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 160, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewin, R.J.W.; Raitsos, D.E.; Dall’Olmo, G.; Zarokanellos, N.; Jackson, T.; Racault, M.-F.; Boss, E.S.; Sathyendranath, S.; Jones, B.H.; Hoteit, I. Regional ocean-colour chlorophyll algorithms for the Red Sea. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 165, 64–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brindley, H.; Osipov, S.; Bantges, R.; Smirnov, A.; Banks, J.; Levy, R.; Jish Prakash, P.; Stenchikov, G. An assessment of the quality of aerosol retrievals over the Red Sea and evaluation of the climatological cloud-free dust direct radiative effect in the region: Aerosol Radiative Effect over Red Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 10862–10878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wafar, M.; Ashraf, M.; Manikandan, K.P.; Qurban, M.A.; Kattan, Y. Propagation of Gulf of Aden Intermediate Water (GAIW) in the Red Sea during autumn and its importance to biological production. J. Mar. Syst. 2016, 154, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wafar, M.; Qurban, M.A.; Ashraf, M.; Manikandan, K.P.; Flandez, A.V.; Balala, A.C. Patterns of distribution of inorganic nutrients in Red Sea and their implications to primary production. J. Mar. Syst. 2016, 156, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almahasheer, H.; Duarte, C.M.; Irigoien, X. Nutrient Limitation in Central Red Sea Mangroves. Front. Mar. Sci. 2016, 3, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreano, D.; Raitsos, D.E.; Gittings, J.; Krokos, G.; Hoteit, I. The Gulf of Aden Intermediate Water Intrusion Regulates the Southern Red Sea Summer Phytoplankton Blooms. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eladawy, A.; Nadaoka, K.; Negm, A.; Abdel-Fattah, S.; Hanafy, M.; Shaltout, M. Characterization of the northern Red Sea’s oceanic features with remote sensing data and outputs from a global circulation model. Oceanologia 2017, 59, 213–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, J.R.; Brindley, H.E.; Stenchikov, G.; Schepanski, K. Satellite retrievals of dust aerosol over the Red Sea and the Persian Gulf (2005–2015). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 3987–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qurban, M.A.; Wafar, M.; Jyothibabu, R.; Manikandan, K.P. Patterns of primary production in the Red Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2017, 169, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racault, M.-F.; Sathyendranath, S.; Brewin, R.J.W.; Raitsos, D.E.; Jackson, T.; Platt, T. Impact of El Niño Variability on Oceanic Phytoplankton. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; El-Askary, H.; ManiKandan, K.; Qurban, M.; Garay, M.; Kalashnikova, O. Synergistic Use of Remote Sensing and Modeling to Assess an Anomalously High Chlorophyll-a Event during Summer 2015 in the South Central Red Sea. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, E.A.; Roff, J.C.; Dowidar, N.M. Phytoplankton ecology and production in the Red Sea off Jiddah, Saudi Arabia. Mar. Biol. 1986, 92, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Association for the Physical Sciences of the Ocean. An outline of the weather and climate of the Red Sea. In Physical Oceanography of the Red Sea: Symposium of the International Association of Physical Sciences of the Ocean; Documentation Service, Saclay Nuclear Research Center, University of California: Oakland, CA, USA, 1974; pp. 9–27. [Google Scholar]
- Grasshoff, K. The hydrochemistry of landlocked basins and fjords. Chem. Oceanogr. 1975, 2, 455–597. [Google Scholar]
- Froese, R.; Pauly, D. (Eds.) World Wide Web Electronic Publication, www.fishbase.org, Version (02/2017); FishBase: Los Banos, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Price, A.R.G.; Ghazi, S.J.; Tkaczynski, P.J.; Venkatachalam, A.J.; Santillan, A.; Pancho, T.; Metcalfe, R.; Saunders, J. Shifting environmental baselines in the Red Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 78, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Transboundary Water Assessment Programme. LME 33—Red Sea; Transboundary Water Assessment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cantin, N.E.; Cohen, A.L.; Karnauskas, K.B.; Tarrant, A.M.; McCorkle, D.C. Ocean Warming Slows Coral Growth in the Central Red Sea. Science 2010, 329, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berumen, M.L.; Hoey, A.S.; Bass, W.H.; Bouwmeester, J.; Catania, D.; Cochran, J.E.M.; Khalil, M.T.; Miyake, S.; Mughal, M.R.; Spaet, J.L.Y.; et al. The status of coral reef ecology research in the Red Sea. Coral Reefs 2013, 32, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raitsos, D.E.; Brewin, R.J.W.; Zhan, P.; Dreano, D.; Pradhan, Y.; Nanninga, G.B.; Hoteit, I. Sensing coral reef connectivity pathways from space. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jickells, T.D. Global Iron Connections Between Desert Dust, Ocean Biogeochemistry, and Climate. Science 2005, 308, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brewin, R.J.W.; Raitsos, D.E.; Pradhan, Y.; Hoteit, I. Comparison of chlorophyll in the Red Sea derived from MODIS-Aqua and in vivo fluorescence. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 136, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mélin, F.; Vantrepotte, V.; Chuprin, A.; Grant, M.; Jackson, T.; Sathyendranath, S. Assessing the fitness-for-purpose of satellite multi-mission ocean color climate data records: A protocol applied to OC-CCI chlorophyll-a data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 203, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mélin, F.; Sclep, G. Band shifting for ocean color multi-spectral reflectance data. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathyendranath, S.; Brewin, R.J.W.; Jackson, T.; Mélin, F.; Platt, T. Ocean-colour products for climate-change studies: What are their ideal characteristics? Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 203, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, T.; Sathyendranath, S.; Mélin, F. An improved optical classification scheme for the Ocean Colour Essential Climate Variable and its applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 203, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewin, R.J.W.; Ciavatta, S.; Sathyendranath, S.; Jackson, T.; Tilstone, G.; Curran, K.; Airs, R.L.; Cummings, D.; Brotas, V.; Organelli, E.; et al. Uncertainty in Ocean-Color Estimates of Chlorophyll for Phytoplankton Groups. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evers-King, H.; Martinez-Vicente, V.; Brewin, R.J.W.; Dall’Olmo, G.; Hickman, A.E.; Jackson, T.; Kostadinov, T.S.; Krasemann, H.; Loisel, H.; Röttgers, R.; et al. Validation and Intercomparison of Ocean Color Algorithms for Estimating Particulate Organic Carbon in the Oceans. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocean Biology Processing Group. MODIS Aqua Level 3 SST Thermal IR Monthly 4 km Daytime v2014.0; PO.DAAC: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2015.
- National Oceanographic Data Center and Rosen Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science. AVHRR Pathfinder Level 3 Monthly Daytime SST Version 5; PO.DAAC: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2003.
- Kilpatrick, K.A.; Podestá, G.P.; Evans, R. Overview of the NOAA/NASA advanced very high resolution radiometer Pathfinder algorithm for sea surface temperature and associated matchup database. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2001, 106, 9179–9197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrick, S.W.; Leptoukh, G.; Farley, J.D.; Rui, H. Giovanni: A Web Service Workflow-Based Data Visualization and Analysis System. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Modeling and Assimilation Office. MERRA-2 tavgM_2d_adg_Nx: 2d, Monthly Mean, Time-Averaged, Single-Level, Assimilation, Aerosol Diagnostics (Extended) V5.12.4; Goddard Earth Sciences Data and Information Services Center (GES DISC): Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2015.
- Global Modeling and Assimilation Office. MERRA-2 tavgM_2d_aer_Nx: 2d, Monthly Mean, Time-Averaged, Single-Level, Assimilation, Aerosol Diagnostics V5.12.4; Goddard Earth Sciences Data and Information Services Center (GES DISC): Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2015.
- Diner, D. MISR Level 3 Component Global Aerosol Product Covering a Month HDF-EOS File—Version 4; NASA Langley Atmospheric Science Data Center (DAAC): Hampton, VA, USA, 2009. [CrossRef]
- Abdou, W.A. Comparison of coincident Multiangle Imaging Spectroradiometer and Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer aerosol optical depths over land and ocean scenes containing Aerosol Robotic Network sites. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marey, H.S.; Gille, J.C.; El-Askary, H.M.; Shalaby, E.A.; El-Raey, M.E. Study of the formation of the “Black Cloud” and its dynamics over Cairo, Egypt using MODIS and MISR sensors. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winker, D.M.; Hunt, W.H.; McGill, M.J. Initial performance assessment of CALIOP. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, W.H.; Winker, D.M.; Vaughan, M.A.; Powell, K.A.; Lucker, P.L.; Weimer, C. CALIPSO Lidar Description and Performance Assessment. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 1214–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winker, D.M.; Vaughan, M.A.; Omar, A.; Hu, Y.; Powell, K.A.; Liu, Z.; Hunt, W.H.; Young, S.A. Overview of the CALIPSO Mission and CALIOP Data Processing Algorithms. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 2310–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, A.H.; Winker, D.M.; Vaughan, M.A.; Hu, Y.; Trepte, C.R.; Ferrare, R.A.; Lee, K.-P.; Hostetler, C.A.; Kittaka, C.; Rogers, R.R.; et al. The CALIPSO Automated Aerosol Classification and Lidar Ratio Selection Algorithm. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 1994–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, S.A.; Vaughan, M.A. The Retrieval of Profiles of Particulate Extinction from Cloud-Aerosol Lidar Infrared Pathfinder Satellite Observations (CALIPSO) Data: Algorithm Description. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 1105–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansmann, A.; Bösenberg, J.; Chaikovsky, A.; Comerón, A.; Eckhardt, S.; Eixmann, R.; Freudenthaler, V.; Ginoux, P.; Komguem, L.; Linné, H.; et al. Long-range transport of Saharan dust to northern Europe: The 11–16 October 2001 outbreak observed with EARLINET: SAHARAN DUST TRANSPORT OVER EUROPE. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balis, D.S.; Amiridis, V.; Nickovic, S.; Papayannis, A.; Zerefos, C. Optical properties of Saharan dust layers as detected by a Raman lidar at Thessaloniki, Greece: Optical Properties of Dust Layers at Thessaloniki. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mona, L.; Liu, Z.; Müller, D.; Omar, A.; Papayannis, A.; Pappalardo, G.; Sugimoto, N.; Vaughan, M. Lidar Measurements for Desert Dust Characterization: An Overview. Adv. Meteorol. 2012, 2012, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiridis, V.; Wandinger, U.; Marinou, E.; Giannakaki, E.; Tsekeri, A.; Basart, S.; Kazadzis, S.; Gkikas, A.; Taylor, M.; Baldasano, J.; et al. Optimizing CALIPSO Saharan dust retrievals. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 12089–12106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Omar, A.; Vaughan, M.; Hair, J.; Kittaka, C.; Hu, Y.; Powell, K.; Trepte, C.; Winker, D.; Hostetler, C.; et al. CALIPSO lidar observations of the optical properties of Saharan dust: A case study of long-range transport. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesche, M.; Ansmann, A.; Müller, D.; Althausen, D.; Engelmann, R.; Freudenthaler, V.; Groß, S. Vertically resolved separation of dust and smoke over Cape Verde using multiwavelength Raman and polarization lidars during Saharan Mineral Dust Experiment 2008. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiridis, V.; Marinou, E.; Tsekeri, A.; Wandinger, U.; Schwarz, A.; Giannakaki, E.; Mamouri, R.; Kokkalis, P.; Binietoglou, I.; Solomos, S.; et al. LIVAS: A 3-D multi-wavelength aerosol/cloud database based on CALIPSO and EARLINET. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 7127–7153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinou, E.; Amiridis, V.; Binietoglou, I.; Tsikerdekis, A.; Solomos, S.; Proestakis, E.; Konsta, D.; Papagiannopoulos, N.; Tsekeri, A.; Vlastou, G.; et al. Three-dimensional evolution of Saharan dust transport towards Europe based on a 9-year EARLINET-optimized CALIPSO dataset. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 5893–5919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proestakis, E.; Amiridis, V.; Marinou, E.; Georgoulias, A.K.; Solomos, S.; Kazadzis, S.; Chimot, J.; Che, H.; Alexandri, G.; Binietoglou, I.; et al. 9-year spatial and temporal evolution of desert dust aerosols over South-East Asia as revealed by CALIOP. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2017, 18, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, M.; Prospero, J.M.; Baker, A.R.; Dentener, F.; Ickes, L.; Liss, P.S.; Mahowald, N.M.; Nickovic, S.; García-Pando, C.P.; Rodríguez, S.; et al. Atmospheric Transport and Deposition of Mineral Dust to the Ocean: Implications for Research Needs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 10390–10404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahowald, N.M.; Baker, A.R.; Bergametti, G.; Brooks, N.; Duce, R.A.; Jickells, T.D.; Kubilay, N.; Prospero, J.M.; Tegen, I. Atmospheric global dust cycle and iron inputs to the ocean: ATMOSPHERIC IRON DEPOSITION. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2005, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WMO Statement on the State of the Global Climate in 2017. Available online: https://public.wmo.int/en/wmo-statement-state-of-global-climate-2017 (accessed on 18 January 2018).
- Notaro, M.; Alkolibi, F.; Fadda, E.; Bakhrjy, F. Trajectory analysis of Saudi Arabian dust storms: SAUDI ARABIAN DUST STORMS. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 6028–6043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginoux, P.; Prospero, J.M.; Gill, T.E.; Hsu, N.C.; Zhao, M. Global-scale attribution of anthropogenic and natural dust sources and their emission rates based on MODIS Deep Blue aerosol products: Anthropogenic and Natural Dust Sources. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prospero, J.M. Environmental characterization of global sources of atmospheric soil dust identified with the NIMBUS 7 Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer (TOMS) absorbing aerosol product. Rev. Geophys. 2002, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedler, S.; Schepanski, K.; Knippertz, P.; Heinold, B.; Tegen, I. How important are atmospheric depressions and mobile cyclones for emitting mineral dust aerosol in North Africa? Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 8983–9000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsham, J.H.; Parker, D.J.; Grams, C.M.; Taylor, C.M.; Haywood, J.M. Uplift of Saharan dust south of the intertropical discontinuity. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knippertz, P. Dust emissions in the West African heat trough the role of the diurnal cycle and of extratropical disturbances. Meteorol. Z. 2008, 17, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepanski, K.; Tegen, I.; Todd, M.C.; Heinold, B.; Bönisch, G.; Laurent, B.; Macke, A. Meteorological processes forcing Saharan dust emission inferred from MSG-SEVIRI observations of subdaily dust source activation and numerical models. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roberts, A.J.; Knippertz, P. The formation of a large summertime Saharan dust plume: Convective and synoptic-scale analysis. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 1766–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomos, S.; Kallos, G.; Mavromatidis, E.; Kushta, J. Density currents as a desert dust mobilization mechanism. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 11199–11211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalenderski, S.; Stenchikov, G. High-resolution regional modeling of summertime transport and impact of African dust over the Red Sea and Arabian Peninsula: High-Resolution Regional Modeling. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 6435–6458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jish Prakash, P.; Stenchikov, G.; Kalenderski, S.; Osipov, S.; Bangalath, H. The impact of dust storms on the Arabian Peninsula and the Red Sea. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 199–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duce, R.A.; Liss, P.S.; Merrill, J.T.; Atlas, E.L.; Buat-Menard, P.; Hicks, B.B.; Miller, J.M.; Prospero, J.M.; Arimoto, R.; Church, T.M.; et al. The atmospheric input of trace species to the world ocean. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1991, 5, 193–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryor, S.C.; Gallagher, M.; Sievering, H.; Larsen, S.E.; Barthelmie, R.J.; Birsan, F.; Nemitz, E.; Rinne, J.; Kulmala, M.; Grönholm, T.; et al. A review of measurement and modelling results of particle atmosphere–surface exchange. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2008, 60, 42–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gittings, J.A.; Raitsos, D.E.; Krokos, G.; Hoteit, I. Impacts of warming on phytoplankton abundance and phenology in a typical tropical marine ecosystem. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











| Sensor Number | Sensor Name | Start Time | End Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SeaWiFS | September 1997 | December 2010 |
| 2 | MODIS (Aqua) | July 2002 | On-going |
| 3 | MERIS | April 2002 | April 2012 |
| 4 | VIIRS | January 2012 | On-going |
| NRS | NCRS | SCRS | SRS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| January | SST/Chl-a | −0.562 | −0.268 | −0.496 | −0.703 |
| DAOD/Chl-a | +0.244 | +0.407 | +0.310 | +0.314 | |
| February | SST/Chl-a | −0.639 | −0.355 | −0.785 | −0.592 |
| DAOD/Chl-a | +0.473 | +0.669 | +0.670 | +0.678 | |
| March | SST/Chl-a | −0.617 | −0.341 | −0.618 | −0.592 |
| DAOD/Chl-a | +0.138 | +0.736 | +0.479 | +0.294 | |
| April | SST/Chl-a | −0.301 | +0.042 | +0.266 | −0.138 |
| DAOD/Chl-a | +0.243 | +0.588 | −0.160 | −0.027 | |
| May | SST/Chl-a | −0.151 | −0.410 | −0.419 | −0.497 |
| DAOD/Chl-a | 0.597 | +0.436 | +0.370 | +0.360 | |
| June | SST/Chl-a | +0.122 | −0.091 | −0.223 | −0.296 |
| DAOD/Chl-a | +0.531 | +0.521 | +0.528 | +0.122 | |
| July | SST/Chl-a | +0.102 | −0.263 | −0.484 | −0.672 |
| DAOD/Chl-a | +0.020 | +0.250 | +0.651 | +0.674 | |
| August | SST/Chl-a | −0.083 | +0.391 | +0.015 | −0.099 |
| DAOD/Chl-a | +0.147 | +0.294 | +0.219 | +0.442 | |
| September | SST/Chl-a | −0.182 | −0.096 | −0.464 | −0.339 |
| DAOD/Chl-a | +0.509 | +0.562 | +0.526 | +0.431 | |
| October | SST/Chl-a | −0.107 | +0.292 | −0.228 | −0.339 |
| DAOD/Chl-a | +0.647 | +0.103 | −0.017 | +0.260 | |
| November | SST/Chl-a | −0.256 | +0.034 | −0.392 | −0.705 |
| DAOD/Chl-a | −0.030 | +0.169 | +0.578 | +0.500 | |
| December | SST/Chl-a | −0.319 | −0.151 | −0.542 | −0.569 |
| DAOD/Chl-a | +0.095 | +0.083 | +0.269 | +0.212 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; El-Askary, H.; Qurban, M.A.; Proestakis, E.; Garay, M.J.; Kalashnikova, O.V.; Amiridis, V.; Gkikas, A.; Marinou, E.; Piechota, T.; et al. An Assessment of Atmospheric and Meteorological Factors Regulating Red Sea Phytoplankton Growth. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10050673
Li W, El-Askary H, Qurban MA, Proestakis E, Garay MJ, Kalashnikova OV, Amiridis V, Gkikas A, Marinou E, Piechota T, et al. An Assessment of Atmospheric and Meteorological Factors Regulating Red Sea Phytoplankton Growth. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(5):673. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10050673
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Wenzhao, Hesham El-Askary, Mohamed A. Qurban, Emmanouil Proestakis, Michael J. Garay, Olga V. Kalashnikova, Vassilis Amiridis, Antonis Gkikas, Eleni Marinou, Thomas Piechota, and et al. 2018. "An Assessment of Atmospheric and Meteorological Factors Regulating Red Sea Phytoplankton Growth" Remote Sensing 10, no. 5: 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10050673
APA StyleLi, W., El-Askary, H., Qurban, M. A., Proestakis, E., Garay, M. J., Kalashnikova, O. V., Amiridis, V., Gkikas, A., Marinou, E., Piechota, T., & Manikandan, K. P. (2018). An Assessment of Atmospheric and Meteorological Factors Regulating Red Sea Phytoplankton Growth. Remote Sensing, 10(5), 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10050673