Method Based on Edge Constraint and Fast Marching for Road Centerline Extraction from Very High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (a)
- Edge information of remote sensing imagery has been studied extensively and widely used in the extraction and tracking of linear objects, such as roads and rivers, in medium-/low-resolution remote sensing imagery. The present study indicates that the synergy of edge information, road centerline probability map, and road spectral feature can overcome the shortcomings of the bias of the road centerline extracted by the fast marching method, which uses spectral feature only. Moreover, our method is robust to road extraction in shaded areas.
- (b)
- Another contribution of this study is that the proposed method needs only a few road seed points when extracting an S-shaped or U-shaped road. This characteristic leads to the efficiency of the widespread practical application of road centerline extraction from remote sensing images.
2. Related Work
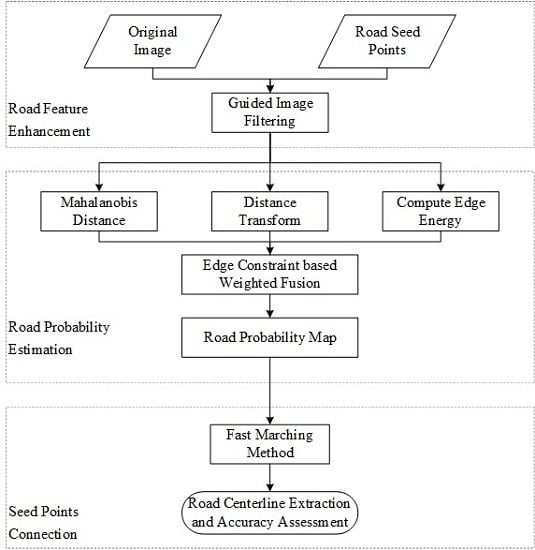
3. Methodology
3.1. Road Feature Enhancement
3.2. Road Probability Estimation
3.2.1. Mahalanobis Distance
3.2.2. Edge Energy
3.2.3. Road Probability Estimation
3.3. Seed-Point Connection
4. Experimental Study
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Experimental Setup and Parameter Setting
- (1)
- For all methods, as few seed points are selected as possible to improve the efficiency of road extraction while ensuring integrity.
- (2)
- For an occluded road area, road seed points that are not occluded by shadows or automobiles are selected as much as possible to ensure the accuracy of road extraction.
4.3. Results and Quantitative Evaluation
4.3.1. Test of the Edge Constraint
4.3.2. Experiment on Centerline Extraction from U-Shaped Roads
4.3.3. Experiment on An IKONOS Image
4.3.4. Experiment on A QuickBird Image
4.3.5. Experiment on A WorldView-2 Image
4.3.6. Experiment on An IKONOS Grayscale Image
5. Discussion
5.1. Parameter Sensitivity Analysis
5.2. Computational Cost Analysis
5.3. Number and Location of Seed Points Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, W.; Zhu, C.; Wang, Y. Road feature extraction from remotely sensed image: Review and Prospects. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2001, 30, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Miao, Z.; Debayle, J. An integrated method for urban main-road centerline extraction from optical remotely sensed imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 3359–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena, J.B. State of the art on automatic road extraction for GIS update: A novel classification. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2003, 24, 3037–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, F.; Cao, T.; Eklund, P. A review of road extraction from remote sensing images. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. (Engl. Ed.) 2016, 3, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.; Shi, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X. Road centerline extraction from high-resolution imagery based on shape features and multivariate adaptive regression splines. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, P. Classification and extraction of spatial features in urban areas using high-resolution multispectral imagery. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2007, 4, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Stein, A.; Bijker, W.; Zhan, Q. Region-based urban road extraction from VHR satellite images using Binary Partition Tree. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 44, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shi, W.; Wang, Q.; Miao, Z. Extracting man-made objects from high spatial resolution remote sensing images via fast level set evolutions. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 883–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.; Shi, W.; Gamba, P.; Li, Z. An object-based method for road network extraction in VHR satellite images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, L. Road centreline extraction from high-resolution imagery based on multiscale structural features and support vector machines. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 1977–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtrai, L.; Lefèvre, S. Morphological path filtering at the region scale for efficient and robust road network extraction from satellite imagery. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2016, 83, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Y.; Wang, C.; Cao, L.; Yu, Y.; Li, J. Road network extraction via aperiodic directional structure measurement. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 3322–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butenuth, M.; Heipke, C. Network snakes: Graph-based object delineation with active contour models. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2012, 23, 91–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruen, A.; Li, H. Road extraction from aerial and satellite images by dynamic programming. ISPRS-J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 1995, 50, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtarzade, M.; Zoej, M.J.V. Road detection from high-resolution satellite images using artificial neural networks. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2007, 9, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panboonyuen, T.; Jitkajornwanich, K.; Lawawirojwong, S.; Srestasathiern, P.; Vateekul, P. Road segmentation of remotely-sensed images using deep convolutional neural networks with landscape metrics and conditional random fields. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirnalinee, T.T.; Das, S.; Varghese, K. An integrated multistage framework for automatic road extraction from high resolution satellite imagery. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2011, 39, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, J.D.; Montoya-Zegarra, J.A.; Schindler, K. A higher-order CRF model for road network extraction. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; IEEE CSP: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; pp. 1698–1705. [Google Scholar]
- Zang, Y.; Wang, C.; Yu, Y.; Luo, L.; Yang, K. Joint enhancing filtering for road network extraction. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 1511–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maboudi, M.; Amini, J.; Hahn, M.; Saati, M. Road network extraction from VHR satellite images using context aware object feature integration and tensor voting. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.; Shi, W.; Samat, A.; Lisini, G.; Gamba, P. Information fusion for urban road extraction from VHR optical satellite images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Razdan, A.; Femiani, J.C.; Cui, M.; Wonka, P. Road network extraction and intersection detection from aerial images by tracking road footprints. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 4144–4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.G.; Zhang, J.X.; Liu, Z.J.; Shen, J. Semi-automatic extraction of ribbon roads form high resolution remotely sensed imagery by cooperation between angular texture signature and template matching. In Proceedings of the ISPRS Congress, Beijing, China, 3–11 July 2008; pp. 539–544. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.; Mirnalinee, T.T.; Varghese, K. Use of salient features for the design of a multistage framework to extract roads from high-resolution multispectral satellite images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3906–3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Zhu, F.; Xiang, S.; Wang, Y.; Pan, C. Accurate urban road centerline extraction from VHR imagery via multiscale segmentation and tensor voting. Neurocomputing 2016, 205, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, G.; Wang, Y.; Gong, Y.; Zhu, F.; Pan, C.B.I. Urban road extraction via graph cuts based probability propagation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Paris, France, 27–30 October 2014; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 5072–5076. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Tao, C.V. A robust method for semi-automatic extraction of road centerlines using a piecewise parabolic model and least square template matching. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2004, 70, 1393–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.; Wang, B.; Shi, W.; Zhang, H. A semi-automatic method for road centerline extraction from VHR images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 1856–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Bischof, W.F.; Caelli, T. Robust and efficient road tracking in aerial images. In Proceedings of the Joint Workshop of ISPRS and DAGM (CMRT’05) on Object Extraction for 3D City Models, Road Databases and Traffic Monitoring—Concepts, Algorithms and Evaluation, Vienna, Austria, 29–30 August 2005; pp. 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Movaghati, S.; Moghaddamjoo, A.; Tavakoli, A. Road extraction from satellite images using particle filtering and extended Kalman filtering. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 2807–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y. An adaptive multifeature sparsity-based model for semiautomatic road extraction from high-resolution satellite images in urban areas. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 1238–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Poz, A.P.; Gallis, R.A.B.; Silva, J.F.C.D.; Martins, E.F.O. Object-space road extraction in rural areas using stereoscopic aerial images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 9, 654–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, C. Multi-points fast marching: A novel method for road extraction. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Geoinformatics, Beijing, China, 18–20 June 2010; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Osher, S.; Sethian, J.A. Fronts propagating with curvature-dependent speed: Algorithms based on Hamilton-Jacobi formulations. J. Comput. Phys. 1988, 79, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jbabdi, S.; Bellec, P.; Toro, R.; Daunizeau, J.; Pelegrini-Issac, M.; Benali, H. Accurate anisotropic fast marching for diffusion-based geodesic tractography. Int. J. Biomed. Imaging 2008, 2008, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Xue, Z.; Cui, K.; Wong, S. Diffusion tensor-based fast marching for modeling human brain connectivity network. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2011, 35, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barzohar, M.; Cooper, D.B. Automatic finding of main roads in aerial images by using geometric-stochastic models and estimation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1996, 18, 707–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinz, S.; Baumgartner, A. Automatic extraction of urban road networks from multi-view aerial imagery. ISPRS-J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2003, 58, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, K.; Sun, J.; Tang, X. Guided Image Filtering. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 35, 1397–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, S.; Nie, F.; Zhang, C. Learning a Mahalanobis distance metric for data clustering and classification. Pattern Recognit. 2008, 41, 3600–3612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, A.; Pfaltz, J.L. Distance functions on digital pictures. Pattern Recognit. 1968, 1, 33–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, W.H.; Schmidt, K.S. Hyperspectral edge filtering for measuring homogeneity of surface cover types. ISPRS-J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2002, 56, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamada, I.; Flachaire, E. Non-Parametric Econometrics; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2010; ISBN 9780199578009. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, D.J.; Shah, M. A Fast algorithm for active contours and curvature estimation. CVGIP Image Underst. 1992, 55, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türetken, E.; Benmansour, F.; Fua, P. Automated reconstruction of tree structures using path classifiers and Mixed Integer Programming. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 566–573. [Google Scholar]
- VPLab Data. Available online: http://www.cse.iitm.ac.in/~vplab/satellite.html (accessed on 16 April 2017).
- Wiedemann, C.; Heipke, C.; Mayer, H.; Jamet, O. Empirical evaluation of automatically extracted road axes. In Empirical Evaluation Techniques in Computer Vision, 1st ed.; Bowyer, K., Phillips, P.J., Eds.; IEEE CSP: Los Alamitos, CA, USA, 1998; pp. 172–187. ISBN 0818684011. [Google Scholar]














| Hu et al.’s Method | Miao et al.’s Method | Proposed ECFM Method | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | |||
| Completeness (%) | 89.76 | 83.26 | 90.95 |
| Correctness (%) | 93.54 | 84.04 | 94.93 |
| Quality (%) | 85.34 | 79.78 | 85.91 |
| Number of seed points | 8 | 2 | 2 |
| Case 2 | |||
| Completeness (%) | 96.68 | 97.81 | 99.82 |
| Correctness (%) | 97.47 | 98.67 | 99.91 |
| Quality (%) | 94.32 | 96.54 | 99.73 |
| Number of seed points | 9 | 2 | 2 |
| Hu et al.’s Method | Miao et al.’s Method | Proposed ECFM Method | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Experiment on IKONOS image | |||
| Completeness (%) | 96.24 | 97.94 | 98.39 |
| Correctness (%) | 96.99 | 97.07 | 97.83 |
| Quality (%) | 93.45 | 95.13 | 96.30 |
| Number of seed points | 442 | 279 | 264 |
| Experiment on QuickBird image | |||
| Completeness (%) | 94.91 | 90.80 | 95.58 |
| Correctness (%) | 95.16 | 93.57 | 97.82 |
| Quality (%) | 90.54 | 85.47 | 93.60 |
| Number of seed points | 8 | 8 | 5 |
| Hu et al.’s Method | Miao et al.’s Method | Proposed ECFM Method | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Experiment on WorldView-2 image | |||
| Completeness (%) | 95.63 | 94.01 | 97.56 |
| Correctness (%) | 95.25 | 92.03 | 96.84 |
| Quality (%) | 91.28 | 86.94 | 94.55 |
| Number of seed points | 249 | 249 | 249 |
| Experiment on IKONOS grayscale image | |||
| Completeness (%) | 93.16 | 91.28 | 92.58 |
| Correctness (%) | 86.01 | 88.62 | 90.29 |
| Quality (%) | 80.90 | 81.71 | 84.20 |
| Number of seed points | 67 | 67 | 67 |
| Hu et al.’s Method | Miao et al.’s Method | Proposed ECFM Method | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Experiment on IKONOS image (size: 3500 pixels × 3500 pixels) | |||
| Time (s) | 1643 s | 1307 s | 1273 s |
| Number of seed points | 442 | 279 | 264 |
| Experiment on QuickBird image (size: 1200 pixels × 1600 pixels) | |||
| Time(s) | 40 s | 43 s | 29 s |
| Number of seed points | 8 | 8 | 5 |
| Hu et al.’s Method | Miao et al.’s Method | Proposed ECFM Method | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Experiment on WorldView-2 image (size: 3000 pixels × 3000 pixels) | |||
| Time (s) | 759 s | 621 s | 720 s |
| Number of seed points | 249 | 249 | 249 |
| Experiment on IKONOS grayscale image (size: 725 pixels × 1018 pixels) | |||
| Time(s) | 108 s | 79 s | 97 s |
| Number of seed points | 67 | 67 | 67 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, L.; Shi, W.; Miao, Z.; Lv, Z. Method Based on Edge Constraint and Fast Marching for Road Centerline Extraction from Very High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 900. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10060900
Gao L, Shi W, Miao Z, Lv Z. Method Based on Edge Constraint and Fast Marching for Road Centerline Extraction from Very High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(6):900. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10060900
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Lipeng, Wenzhong Shi, Zelang Miao, and Zhiyong Lv. 2018. "Method Based on Edge Constraint and Fast Marching for Road Centerline Extraction from Very High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images" Remote Sensing 10, no. 6: 900. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10060900
APA StyleGao, L., Shi, W., Miao, Z., & Lv, Z. (2018). Method Based on Edge Constraint and Fast Marching for Road Centerline Extraction from Very High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sensing, 10(6), 900. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10060900