Assessing Single-Polarization and Dual-Polarization TerraSAR-X Data for Surface Water Monitoring
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data Description and Methodology
2.1. Study Area and Data Description
2.2. Classification Methods
3. Results
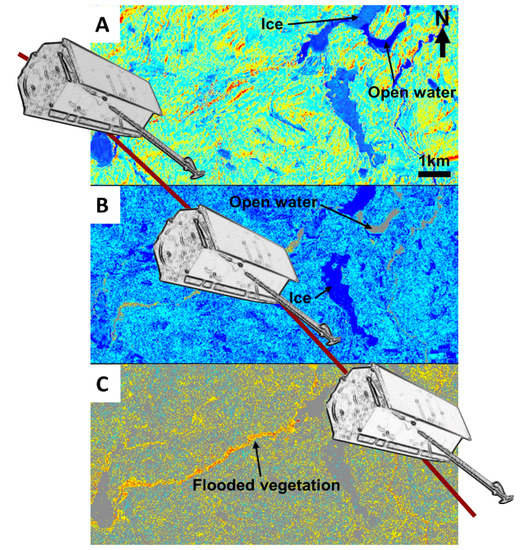
3.1. Single Polarization Classification
3.2. Dual-Polarization Classification: H-Alpha–Wishart
3.3. Dual-Polarization Classification: Kennaugh Element Framework
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, J.-S.; Pottier, E. Polarimetric Radar Imaging: From Basics to Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; 422p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-S.; Grunes, M.R.; Pottier, E. Quantitative Comparison of Classification Capability: Fully Polarimetric versus Dual and Single-Polarization SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 2343–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisco, B.; Touzi, R.; van der Sanden, J.J.; Charbonneau, F.; Pultz, T.J.; D’Iorio, M. Water Resource Applications with RADARSAT-2—A Preview. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2008, 1, 130–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, L.; Brisco, B.; Dabboor, M.; Schmitt, A.; Pratt, A. A Collection of SAR Methodologies for Monitoring Wetlands. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 7615–7645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuenzer, C.; Guo, H.; Huth, J.; Leinenkugel, P.; Li, X.; Dech, S. Flood Mapping and Flood Dynamics of the Mekong Delta: ENVISAT-ASAR-WSM Based Time Series Analyses. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 687–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schlaffer, S.; Matgen, P.; Hollaus, M.; Wagner, W. Flood Detection from Multi-Temporal SAR Data Using Harmonic Analysis and Change Detection. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 38, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, L.; Brisco, B.; Pregitzer, M.; Tedford, B.; Boychuk, L. RADARSAT-2 Beam Mode Selection for Surface Water and Flooded Vegetation Mapping. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 40, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinis, S.; Kersten, J.; Twele, A. A Fully Automated TerraSAR-X Based Flood Service. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 104, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, D.C.; Speck, R.; Devereux, B.; Schumann, G.; Neal, J.C.; Bates, P.D. Flood Detection in Urban Areas Using TerraSAR-X. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 882–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matgen, P.; Schumann, G.; Henry, J.B.; Hoffmann, L.; Pfister, L. Integration of SAR-Derived River Inundation Areas, High-Precision Topographic Data and a River Flow Model toward near Real-Time Flood Management. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2007, 9, 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Jezek, K.C. Automated Extraction of Coastline from Satellite Imagery by Integrating Canny Edge Detection and Locally Adaptive Thresholding Methods. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 937–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhoff, M.L.; Vermillion, L.; Story, M.H.; Choudhury, A.M.; Gafoor, A.; Polcyn, F. Monsoon Flood Boundary Delineation and Damage Assessment Using Space Borne Imaging Radar and Landsat Data. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1987, 53, 405–413. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, D.C.; Horritt, M.S.; Dall’Amico, J.T.; Scott, T.R.; Bates, P.D. Improving River Flood Extent Delineation from Synthetic Aperture Radar Using Airborne Laser Altimetry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 3932–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinis, S.; Twele, A.; Voigt, S. Towards Operational near Real-Time Flood Detection Using a Split-Based Automatic Thresholding Procedure on High Resolution TerraSAR-X Data. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 9, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustarini, L.; Chini, M.; Hostache, R.; Pappenberger, F.; Matgen, P. Flood Hazard Mapping Combining Hydrodynamic Modeling and Multi Annual Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 14200–14226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, K.; Beaulne, D.; Braun, A.; Fotopoulos, G. Fusion of SAR, Optical Imagery and Airborne LiDAR for Surface Water Detection. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gstaiger, V.; Huth, J.; Gebhardt, S.; Wehrmann, T.; Kuenzer, C. Multi-Sensoral and Automated Derivation of Inundated Areas Using TerraSAR-X and ENVISAT ASAR Data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 7291–7304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, A.; Brisco, B. Wetland Monitoring Using the Curvelet-Based Change Detection Method on Polarimetric SAR Imagery. Water 2013, 5, 1036–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mermoz, S.; Allain-Bailhache, S.; Bernier, M.; Pottier, E.; Van Der Sanden, J.J.; Chokmani, K. Retrieval of River Ice Thickness from C-Band PolSAR Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 3052–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisco, B.; Schmitt, A.; Murnaghan, K.; Kaya, S.; Roth, A. SAR Polarimetric Change Detection for Flooded Vegetation. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2011, 6, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallant, A.L.; Kaya, S.G.; White, L.; Brisco, B.; Roth, M.F.; Sadinski, W.; Rover, J. Detecting Emergence, Growth, and Senescence of Wetland Vegetation with Polarimetric Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Data. Water 2014, 6, 694–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, S.; Jang, H.; Kim, N.; Sohn, H.G. Water Area Extraction Using RADARSAT SAR Imagery Combined with Landsat Imagery and Terrain Information. Sensors 2015, 15, 6652–6667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Betbeder, J.; Rapinel, S.; Corgne, S.; Pottier, E.; Hubert-Moy, L. TerraSAR-X Dual-Pol Time-Series for Mapping of Wetland Vegetation. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 107, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dabboor, M.; White, L.; Brisco, B.; Charbonneau, F. Change Detection with Compact Polarimetric SAR for Monitoring Wetlands. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 41, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, L.; Schmitt, A.; Wendleder, A.; Roth, A. Monitoring of the Lac Bam Wetland Extent Using Dual-Polarized X-Band SAR Data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, A.; Leichtle, T.; Huber, M.; Roth, A. On the Use of Dual-Co-Polarized TerraSAR-X Data for Wetland Monitoring. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. ISPRS Arch. 2012, 39, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, A.; Wendleder, A.; Hinz, S. The Kennaugh Element Framework for Multi-Scale, Multi-Polarized, Multi-Temporal and Multi-Frequency SAR Image Preparation. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 102, 122–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, L.L.; Melack, J.M.; Filoso, S.; Wang, Y. Delineation of Inundated Area and Vegetation along the Amazon Floodplain with the SIR-C Synthetic Aperture Radar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1995, 33, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgeau-Chavez, L.L.; Kasischke, E.S.; Brunzell, S.M.; Mudd, J.P.; Smith, K.B.; Frick, L. Analysis of Space-Borne SAR Data for Wetland Mapping in Virginia Riparian Ecosystems. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 3665–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, P. A Synthetic Aperture Radar–based Model to Assess Historical Changes in Lowland Floodplain Hydroperiod. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjusree, P.; Kumar, L.P.; Bhatt, C.M.; Rao, G.S.; Bhanumurthy, V. Optimization of Threshold Ranges for Rapid Flood Inundation Mapping by Evaluating Backscatter Profiles of High Incidence Angle SAR Images. Int. J. Disaster Risk Sci. 2012, 3, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisco, B.; Short, N.; Van Der Sanden, J.; Landry, R.; Raymond, D. A Semi-Automated Tool for Surface Water Mapping with RADARSAT-1. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 35, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasischke, E.S.; Melack, J.M.; Dobson, M.C. The Use of Imaging Radars for Ecological Applications—A Review. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 59, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.R. The Dual Polarisation Entropy/Alpha Decomposition. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on Science and Applications of SAR Polarimetry and Polarimetric Interferometry, Frascati, Italy, 22–26 January 2007; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Cloude, S.R.; Pottier, E. A Review of Target Decomposition Theorems in Radar Polarimetry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1996, 34, 498–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalite, K.; Voormansik, K.; Olesk, A.; Noorma, M.; Reinart, A. Effects of Inundated Vegetation on X-Band HH-VV Backscatter and Phase Difference. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 1402–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, A. Multiscale and Multidirectional Multilooking for SAR Image Enhancement. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 5117–5134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mleczko, M.; Mróz, M. Wetland Mapping Using SAR Data from the Sentinel-1A and TanDEM-X Missions: A Comparative Study in the Biebrza Floodplain (Poland). Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heine, I.; Jagdhuber, T.; Itzerott, S. Classification and Monitoring of Reed Belts Using Dual-Polarimetric TerraSAR-X Time Series. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wdowinski, S.; Hong, S.H. Wetland InSAR: A review of the technique and applications. In Remote Sensing of Wetlands Applications and Advances; Tiner, R.W., Lang, M.W., Klemas, V.V., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullmann, T.; Banks, S.N.; Schmitt, A.; Jagdhuber, T. Scattering characteristics of X-, C- and L-band PolSAR data examined for the tundra environment of the Tuktoyaktuk Peninsula, Canada. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| ID | Date (2016) | Mode | Polarization | Product | Look Direction | Path | Incidence Angle (o) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 April | stripmap | HH/VV | SSC | Right | Descending | 39 |
| 2 | 24 April | stripmap | HH/VV | SSC | Right | Descending | 39 |
| 3 | 5 May | stripmap | HH/VV | SSC | Right | Descending | 39 |
| 4 | 18 June | stripmap | HH/VV | SSC | Right | Descending | 39 |
| Date (2016) | Threshold Value (dB) | Water (%) | Other (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 April | −17.38 | 8 | 92 |
| 24 April | −19.68 | 9 | 91 |
| 5 May | −18.56 | 10 | 90 |
| 18 June | −18.87 | 10 | 90 |
| Date (2016) | Water (%) | Flooded Vegetation (%) | Other (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 April | 17 | 5 | 78 |
| 24 April | 15 | 6 | 79 |
| 5 May | 16 | 2 | 82 |
| 18 June | 12 | 6 | 82 |
| Date (2016) | Water (%) | Flooded Vegetation (%) | Other (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 April | 16 | 13 | 72 |
| 24 April | 12 | 13 | 75 |
| 5 May | 13 | 5 | 82 |
| 18 June | 12 | 5 | 83 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Irwin, K.; Braun, A.; Fotopoulos, G.; Roth, A.; Wessel, B. Assessing Single-Polarization and Dual-Polarization TerraSAR-X Data for Surface Water Monitoring. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10060949
Irwin K, Braun A, Fotopoulos G, Roth A, Wessel B. Assessing Single-Polarization and Dual-Polarization TerraSAR-X Data for Surface Water Monitoring. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(6):949. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10060949
Chicago/Turabian StyleIrwin, Katherine, Alexander Braun, Georgia Fotopoulos, Achim Roth, and Birgit Wessel. 2018. "Assessing Single-Polarization and Dual-Polarization TerraSAR-X Data for Surface Water Monitoring" Remote Sensing 10, no. 6: 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10060949
APA StyleIrwin, K., Braun, A., Fotopoulos, G., Roth, A., & Wessel, B. (2018). Assessing Single-Polarization and Dual-Polarization TerraSAR-X Data for Surface Water Monitoring. Remote Sensing, 10(6), 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10060949