A New Method for Mapping Aquatic Vegetation Especially Underwater Vegetation in Lake Ulansuhai Using GF-1 Satellite Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Remote Sensing Data and Processing
2.3. Acquisition of Field Data
2.4. Methods
2.4.1. Identification and Detection of Land and Emergent Vegetation
2.4.2. Identification and Detection of Huangtai Algae
2.4.3. Identification and Detection of Water and SAV
2.4.4. Establishment of the Classification Tree Model
3. Results
3.1. Separability of Spectral Characteristic Variables
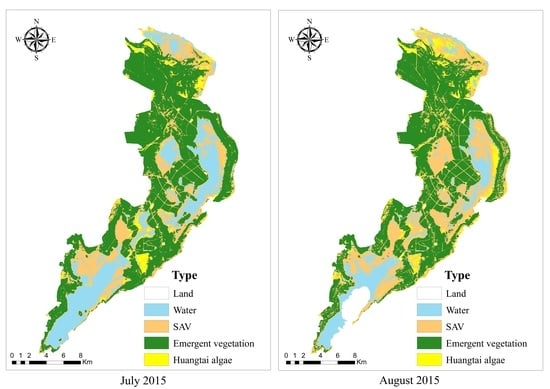
3.2. Classification Results and Validation
3.3. SAV Spectral Curve Changes with Depth under Different Transparency and Coverage
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jin, X. Lake Environment in China; China Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, R. Remote Sensing of Lake Water Environment; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, T.S.F.; Costa, M.P.F.; Melack, J.M.; Novo, E.M.L.M. Remote sensing of aquatic vegetation: Theory and applications. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 140, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, T.R.; Lee, P.F. Mapping aquatic macrophytes through digital image analysis of aerial photographs: An assessment. J. Aquat. Plant Manag. 1994, 32, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Welch, R.; Remillard, M.M.; Slack, R.B. Remote sensing and geographic information system techniques for aquatic resource evaluation. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1988, 54, 177–185. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Qin, B.; Shi, K.; Deng, J.; Zhou, Y. Aquatic vegetation in response to increased eutrophication and degraded light climate in eastern lake Taihu: Implications for lake ecological restoration. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusilli, L.; Collins, M.O.; Laneve, G.; Palombo, A.; Pignatti, S.; Santini, F. Assessment of the abnormal growth of floating macrophytes in Winam Gulf (Kenya) by using MODIS imagery time series. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 20, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackleson, S.G.; Klemas, V. Remote sensing of submerged aquatic vegetation in lower Chesapeake Bay: A comparison of Landsat MSS to TM imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 1987, 22, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, R.A. Remote sensing of submerged vegetation canopies for biomass estimation. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1993, 14, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Li, X.; Ma, R.; Li, F.; Duan, H.; Hu, W.; Qin, B.; Huang, W. Applying remote sensing techniques to monitoring seasonal and interannual changes of aquatic vegetation in Taihu Lake, China. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 60, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Sha, Z.; Yu, M. Remote sensing imagery in vegetation mapping: A review. J. Plant Ecol. 2008, 1, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, O.K.; Akyurek, Z.; Beklioglu, M. Identification and mapping of submerged plants in a shallow lake using quickbird satellite data. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2138–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, R.; Bell, S. Mapping seagrass coverage and spatial patterns with high spatial resolution IKONOS imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 54, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteside, T.; Bartolo, R. Mapping aquatic vegetation in a tropical wetland using high spatial resolution multispectral satellite imagery. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 11664–11694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolpagni, R.; Bresciani, M.; Laini, A.; Pinardi, M.; Matta, E.; Ampe, E.M.; Giardino, C.; Viaroli, P.; Bartoli, M. Remote sensing of phytoplankton-macrophyte coexistence in shallow hypereutrophic fluvial lakes. Hydrobiologia 2014, 737, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Traber, M.; Milstead, B.; Stevens, S. Terrestrial and submerged aquatic vegetation mapping in fire island national seashore using high spatial resolution remote sensing data. Mar. Geod. 2007, 30, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Gong, Z.; Zhao, W. The extraction of wetland hydrophytes types based on medium resolution TM data. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2010, 30, 6460–6469. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Lv, M.; Jiang, H.; Cai, Y.; Xu, D.; An, S. Spatio-temporal variability of aquatic vegetation in Taihu Lake over the past 30 years. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 10454–10461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davranche, A.; Lefebvre, G.; Poulin, B. Wetland monitoring using classification trees and spot-5 seasonal time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, R.; Duan, H.; Gu, X.; Zhang, S. Detecting aquatic vegetation changes in Taihu Lake, China using multi-temporal satellite imagery. Sensors 2008, 8, 3988–4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beget, M.E.; Bella, C.M.D. Flooding: The effect of water depth on the spectral response of grass canopies. J. Hydrol. 2007, 335, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Duan, H.; Gu, X. Remote sensing information extraction of hydrophytes based on the retrieval of water transparency in lake Taihu, China. J. Lake Sci. 2008, 20, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Xiao, B. Aquatic vegetation mapping based on remote sensing imagery: An application to Honghu Lake. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Remote Sensing, Environment and Transportation Engineering, Nanjing, China, 24–26 June 2011; pp. 4832–4836. [Google Scholar]
- Visser, F.; Wallis, C.; Sinnott, A.M. Optical remote sensing of submerged aquatic vegetation: Opportunities for shallow clearwater streams. Limnol. Ecol. Manag. Inland Waters 2013, 43, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alberotanza, L. Hyperspectral aerial images. A valuable tool for submerged vegetation recognition in the Orbetello Lagoons, Italy. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1999, 20, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, D.; Wu, Y.; Liu, H.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, H. Identification of algae-bloom and aquatic macrophytes in Lake Taihu from in-situ measured spectra data. J. Lake Sci. 2009, 21, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Cho, H.J.; Lu, D. A water-depth correction algorithm for submerged vegetation spectra. Remote Sens. Lett. 2010, 1, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, H.J.; Mishra, D.; Wood, J. Remote sensing of submerged aquatic vegetation. In Remote Sensing—Applications; Escalante, B., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Yang, R.; Tian, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, Y.; Mi, X. Comparative analysis of GF-1 WFV, ZY-3 MUX, and HJ-1 CCD sensor data for grassland monitoring applications. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 2089–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W. A relief-based forest cover change extraction using GF-1 images. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2014—2014 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Quebec, QC, Canada, 13–18 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Tian, Q.; Gu, X.; Yu, T.; Wang, L. Crop classification based on GF-1/WFV NDVI time series. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31, 155–161. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.; Xi, B.; Lei, H. Research on Integrated Treatment and Management Planning of Lake Ulansuhai; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, W.; Han, X.; Liu, C. Satellite remote sensing data monitoring “Huang Tai” algae bloom in lake Ulansuhai, inner Mongolia. J. Lake Sci. 2010, 22, 321–326. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, K.; Liang, S.; Gu, X.; Baret, F.; Wei, X.; Wang, X.; Yao, Y.; Yang, L.; Li, Y. Fractional vegetation cover estimation algorithm for chinese GF-1 wide field view data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 177, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yu, W. Quality evaluation of GF-1 and SPOT-7 multi-spectral image based on land surface parameter validation. J. Image Graph. 2016, 21, 1551–1561. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y. Principles and Methods of Analysis of Remote Sensing Applications; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Han, L.; Rundquist, D.C. The spectral responses of Ceratophyllum demersum at varying depths in an experimental tank. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.J.; Kirui, P.; Natarajan, H. Test of multi-spectral vegetation index for floating and canopy-forming submerged vegetation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2008, 5, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.J. Depth-variant spectral characteristics of submersed aquatic vegetation detected by Landsat 7 ETM+. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 1455–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1960, 20, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Weighted kappa: Nominal scale agreement with provision for scaled disagreement or partial credit. Psychol. Bull. 1968, 70, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, J.R. Introductory Digital Image Processing a Remote Sensing Perspective; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Liew, S.C.; Chang, C.W. Detecting submerged aquatic vegetation with 8-band worldview-2 satellite images. In Proceedings of the Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; pp. 2560–2562. [Google Scholar]











| Sensor | Band | Spectral Range (µm) | Band Type | Spatial Resolution (m) | Swath Width (km) | Revisit Period (days) | Orbit Altitude (km) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WFV (1–4) | 1 | 0.45–0.52 | Blue | 16 | 800 | 4 | 645 |
| 2 | 0.52–0.59 | Green | |||||
| 3 | 0.63–0.69 | Red | |||||
| 4 | 0.77–0.89 | NIR |
| k1 | k2 | k1 − k2 | |k1 − k2| | Obtuse Angle α | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A(X1) | −0.0763 | 0.0175 | –0.0938 | 0.0938 | 174.6333 |
| A(X2) | −0.0851 | 0.0042 | −0.0893 | 0.0893 | 174.8978 |
| A(X3) | −0.0816 | −0.0100 | −0.0716 | 0.0716 | 175.9091 |
| A(X4) | −0.0763 | −0.0117 | −0.0646 | 0.0646 | 176.3043 |
| A(X5) | −0.0482 | 0.0092 | −0.0574 | 0.0574 | 176.7127 |
| A(X6) | −0.0272 | 0.0267 | −0.0539 | 0.0539 | 176.9148 |
| A(X7) | −0.0088 | 0.0150 | −0.0238 | 0.0238 | 178.6380 |
| B(X1) | −0.0018 | −0.0283 | 0.0266 | 0.0266 | 178.4776 |
| B(X2) | −0.0123 | −0.0292 | 0.0169 | 0.0169 | 179.0329 |
| B(X3) | −0.0018 | −0.0183 | 0.0166 | 0.0166 | 179.0502 |
| B(X4) | −0.0079 | −0.0233 | 0.0154 | 0.0154 | 179.1157 |
| B(X5) | −0.0202 | −0.0308 | 0.0107 | 0.0107 | 179.3898 |
| B(X6) | −0.0044 | −0.0142 | 0.0098 | 0.0098 | 179.4397 |
| B(X7) | −0.0175 | −0.0242 | 0.0066 | 0.0066 | 179.6207 |
| Real Value | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classification Value | Land | Water | SAV | Emergent Vegetation | Huangtai Algae | Total | |||||||
| Month | 07 | 08 | 07 | 08 | 07 | 08 | 07 | 08 | 07 | 08 | 07 | 08 | |
| Land | 19 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 20 | 15 | |
| Water | 2 | 0 | 31 | 33 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 34 | 34 | |
| SAV | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 43 | 61 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 51 | 67 | |
| Emergent Vegetation | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 55 | 39 | 1 | 2 | 56 | 41 | |
| Huangtai | 2 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 52 | 42 | 56 | 50 | |
| Total | 23 | 20 | 33 | 35 | 46 | 65 | 59 | 42 | 56 | 45 | 217 | 207 | |
| Producer Accuracy (%) | 82.61 | 75.00 | 93.94 | 94.29 | 93.48 | 93.85 | 93.22 | 92.86 | 92.86 | 93.33 | |||
| User Accuracy (%) | 95.00 | 100.00 | 91.18 | 97.06 | 84.31 | 91.04 | 98.21 | 95.12 | 92.86 | 84.00 | |||
| Kappa Coefficient | 0.8995 | 0.8935 | |||||||||||
| Overall accuracy | 92.17% | 91.79% | |||||||||||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Q.; Yu, R.; Hao, Y.; Wu, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Bu, X. A New Method for Mapping Aquatic Vegetation Especially Underwater Vegetation in Lake Ulansuhai Using GF-1 Satellite Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10081279
Chen Q, Yu R, Hao Y, Wu L, Zhang W, Zhang Q, Bu X. A New Method for Mapping Aquatic Vegetation Especially Underwater Vegetation in Lake Ulansuhai Using GF-1 Satellite Data. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(8):1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10081279
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Qi, Ruihong Yu, Yanling Hao, Linhui Wu, Wenxing Zhang, Qi Zhang, and Xunan Bu. 2018. "A New Method for Mapping Aquatic Vegetation Especially Underwater Vegetation in Lake Ulansuhai Using GF-1 Satellite Data" Remote Sensing 10, no. 8: 1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10081279
APA StyleChen, Q., Yu, R., Hao, Y., Wu, L., Zhang, W., Zhang, Q., & Bu, X. (2018). A New Method for Mapping Aquatic Vegetation Especially Underwater Vegetation in Lake Ulansuhai Using GF-1 Satellite Data. Remote Sensing, 10(8), 1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10081279