Estimation of Translational Motion Parameters in Terahertz Interferometric Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar (InISAR) Imaging Based on a Strong Scattering Centers Fusion Technique
Abstract
:1. Introduction
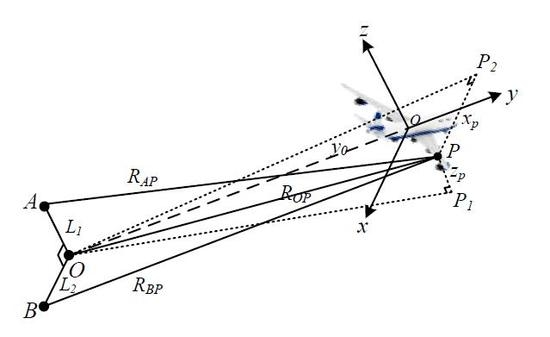
2. Signal Model of Interferometric Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar (InISAR) Imaging
3. The Strong Scattering Centers Fusion (SSCF) Technique
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. The Point Target Simulation Results
4.2. Experimental Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, X.; Narayanan, R.M. Three-dimensional interferometric ISAR imaging for target scattering diagnosis and modeling. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2001, 10, 1094–1102. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Xia, X.; Chen, V.C. Three-dimensional ISAR imaging of maneuvering targets using three receivers. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2001, 10, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Given, J.A.; Schmidt, W.R. Generalized ISAR—Part II: Interferometric techniques for three-dimensional location of scatterers. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2005, 14, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biao, T.; Na, L.; Yang, L. A Novel image registration method for InISAR imaging system. SPIE Secur. Def. 2014, 9252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; He, F.; Gao, X. Novel reference range selection method in InISAR imaging. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2012, 23, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Shi, S.; Liu, Y. Image registration of interferometric inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging system based on joint respective window sampling and modified motion compensation. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2015, 9, 095097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yeo, T.S.; Du, G. Estimation of three-dimensional motion parameters in interferometric ISAR imaging. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felguera-Martin, D.; Gonzalez-Partida, J.T.; Almorox-Gonzalez, P. Interferometric inverse synthetic aperture radar experiment using an interferometric linear frequency modulated continuous wave millimeter-wave radar. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2011, 5, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.H.; Tran, H.T.; Martorella, M. Estimation of the total rotational velocity of a non-cooperative target with a high cross-range resolution three-dimensional interferometric inverse synthetic aperture radar system. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2017, 11, 1020–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Xing, M.; Xia, X.G. 3D geometry and motion estimations of maneuvering targets for interferometric ISAR with sparse aperture. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 25, 2005–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martorella, M.; Stagliano, D.; Salvetti, F. 3D interferometric ISAR imaging of non-cooperative targets. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2014, 50, 3102–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dengler, R.J.; Cooper, K.B.; Chattopadhyay, G. 600 GHz Imaging Radar with 2 cm Range Resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE/MTT-S International Microwave Symposium, Honolulu, HI, USA, 3–8 June 2007; pp. 1371–1374. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, K.B.; Dengler, R.J.; Chattopadhyay, G. A high-resolution imaging radar at 580 GHz. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2008, 18, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, K.B.; Dengler, R.J.; Llombart, N. Penetrating 3-D imaging at 4 and 25 meter range using a submillimeter-wave radar. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2008, 56, 2771–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llombart, N.; Cooper, K.B.; Dengler, R.J. Time-delay multiplexing of two beams in a terahertz imaging radar. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2010, 58, 1999–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, K.B.; Dengler, R.J.; Llombart, N. THz imaging radar for standoff personnel screening. IEEE Trans. Terahertz Sci. Technol. 2011, 1, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazquez, B.; Cooper, K.B.; Llombart, N. Time-delay multiplexing with linear arrays of THz radar transceivers. IEEE Trans. Terahertz Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheen, D.M.; Mcmakin, D.L.; Thomas, E.H. Active Millimeter-Wave Standoff and Portal Imaging Techniques for Personnel Screening. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Technologies for Homeland Security, Waltham, MA, USA, 11–12 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sheen, D.M.; Hall, T.E.; Severtsen, R.H. Active wideband 350 GHz imaging system for concealed-weapon detection. Proc. SPIE 2009, 7309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Li, C.; Gu, S. Design, Analysis and Measurement of a Millimeter Wave Antenna Suitable for Stand off Imaging at Checkpoints. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2011, 32, 1314–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Li, C.; Gao, X. Terahertz aperture synthesized imaging with fan-beam scanning for personnel screening. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2012, 60, 3877–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Li, C.; Gu, S. Fast Three-Dimensional Image Reconstruction of Targets Under the Illumination of Terahertz Gaussian Beams with Enhanced Phase-Shift Migration to Improve Computation Efficiency. IEEE Trans. Terahertz Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.B.; Cui, Z.M.; Lu, B. 340 GHz 3-D imaging radar with 4Tx-16Rx MIMO array. IEEE Trans. Terahertz Sci. Technol. 2018, 5, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Cui, Z.M.; Cheng, B.B. Fast Three-Dimensional Image Reconstruction of a Standoff Screening System in the Terahertz Regime. IEEE Trans. Terahertz Sci. Technol. 2018, 4, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essen, H.; Wahlen, A.; Sommer, R. High-Bandwidth 220 GHz Experimental Radar. Electron. Lett. 2007, 43, 1114–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanko, S.; Caris, M.; Wahlen, A. Millimeter Resolution with Radar at Lower Terahertz. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Radar Symposium, Dresden, Germany, 19–21 June 2013; pp. 235–238. [Google Scholar]
- Caris, M.; Stanko, S.; Palm, S. 300 GHz radar for high resolution SAR and ISAR applications. In Proceedings of the 16th International Radar Symposium, Dresden, Germany, 24–26 June 2015; pp. 577–580. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Fan, R.; Dominski, F. A 235 GHz Radar for Airborne Applications. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Radar Conference, Oklahoma City, USA, 23–27 April 2018; pp. 1549–1554. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, B.B.; Jiang, G.; Wang, C. Real-time imaging with a 140 GHz inverse synthetic aperture radar. IEEE Trans. Terahertz Sci. Technol. 2013, 3, 594–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Kahl, M.; Loffeld, O. THz 3-D image formation using SAR techniques: Simulation, processing and experimental results. IEEE Trans. Terahertz Sci. Technol. 2013, 3, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danylov, A.A.; Goyette, T.M.; Waldman, J. Terahertz Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar (ISAR) Imaging with a Quantum Cascade Laser Transmitter. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 16264–16272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Pi, Y.; Li, J. Terahertz Imaging Radar with Inverse Aperture Synthesis Techniques: System Structure, Signal Processing, and Experiment Results. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Qin, Y.L.; Zhang, K. Experimental research on vehicle-borne SAR imaging with THz radar. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2017, 59, 2048–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Yeo, T.S.; Bao, Z. Weighted least square estimation of phase errors for SAR/ISAR autofocus. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 2487–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, P.; Xing, M.; Sun, G. Minimum Entropy via Subspace for ISAR Autofocus. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2010, 7, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, D.E.; Eichel, P.H.; Ghiglia, D.C. Phase gradient autofocus—A robust tool for high resolution SAR phase correction. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1994, 30, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Parameter | Setting Value |
|---|---|
| Carrier frequency | 220 GHz |
| Bandwidth | 5 GHz |
| Pulse width | 50 us |
| Pulse repetition frequency | 1000 Hz |
| Pulse number | 1000 |
| Sampling frequency | 20 MHz |
| Target speed | (300, 0, and 0 m/s) |
| Antenna O location | (0, 20,000, and 0 m) |
| Antenna A location | (0.5, 20,000, and 0 m) |
| Antenna B location | (0, 20,000, and 0.5 m) |
| Method | Reconstruction Time | Number of Channels | Anti-Noise Ability | Need Ranging Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency domain Searching (FDS) | 23.145 s | 3 | Strong | No |
| Respective Reference Distance Compensation (RRDC) | 0.699 s | 3 | Strong | Yes |
| Angular Motion Parameters Estimation (AMPE) | 0.744 s | 9 | Weak | No |
| Strong Scattering Centers Fusion (SSCF) | 1.657 s | 3 | Strong | No |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Deng, B.; Qin, Y.; Wang, H. Estimation of Translational Motion Parameters in Terahertz Interferometric Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar (InISAR) Imaging Based on a Strong Scattering Centers Fusion Technique. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11101221
Zhang Y, Yang Q, Deng B, Qin Y, Wang H. Estimation of Translational Motion Parameters in Terahertz Interferometric Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar (InISAR) Imaging Based on a Strong Scattering Centers Fusion Technique. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(10):1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11101221
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ye, Qi Yang, Bin Deng, Yuliang Qin, and Hongqiang Wang. 2019. "Estimation of Translational Motion Parameters in Terahertz Interferometric Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar (InISAR) Imaging Based on a Strong Scattering Centers Fusion Technique" Remote Sensing 11, no. 10: 1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11101221
APA StyleZhang, Y., Yang, Q., Deng, B., Qin, Y., & Wang, H. (2019). Estimation of Translational Motion Parameters in Terahertz Interferometric Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar (InISAR) Imaging Based on a Strong Scattering Centers Fusion Technique. Remote Sensing, 11(10), 1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11101221