A Fisheye Image Matching Method Boosted by Recursive Search Space for Close Range Photogrammetry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
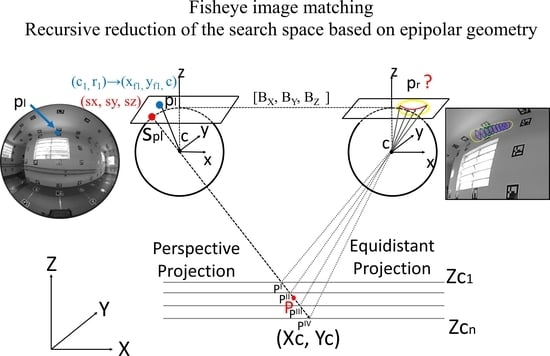
2. Recursive Search Space Method for Fisheye Images
2.1. Epipolar Geometry on the Sphere Domain
2.2. Search Space Window and Bundle Adjustment
2.3. Image Matching
3. Material and Experiments
3.1. Data Sets
3.2. Experiment I: Comparison of Omnidirectional Matching Approaches Based on SIFT
3.3. Experiment II: Sensor Position and Attitude Estimation
3.4. Performance Assessment
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Preliminary Assessment of Interest Operators on Fisheye Images
4.2. Assessment of Omnidirectional Matching Approaches (Experiment I)
4.2.1. Detection Rate and Location Correctness
4.2.2. Repeatability
4.2.3. Geometric Distribution
4.3. Sensor Pose and 3D Ground Coordinates Estimative (Experiment II)
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hasen, P.; Corke, P.; Boles, W. Wide-angle visual feature matching for outdoor localization. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2010, 29, 267–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasen, P.; Corke, P.; Boles, W.; Daniilidis, K. Scale-invariant features on the sphere. In Proceedings of the IEEE 11th International Conference on Computer Vision, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 14–21 October 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Tommaselli, A.M.G.; Berveglieri, A. Automatic orientation of multi-scale terrestrial images for 3D reconstruction. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 3020–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, T.Y.; Perng, N.H. Rectified feature matching for spherical panoramic images. Pers 2018, 84, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D.G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. (IJCV) 2004, 60, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniilidis, K.; Makadia, A.; Bulow, T. Image processing in catadioptric planes: Spatiotemporal derivatives and optical flow computation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Third Workshop on Omnidirectional Vision, Copenhagen, Denmark, 2 June 2002; pp. 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulow, T. Spherical diffusion for 3D surface smoothing. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2004, 26, 1650–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Mota, J.; Bogdanova, I.; Paquier, B.; Bierlaire, M.; Thiran, J.P. Scale invariant feature transform on the sphere: Theory and applications. Int. J. Comput. Vis. (IJCV) 2012, 98, 217–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arican, Z.; Frossard, P. Scale-invariant features and polar descriptors in omnidirectional imaging. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2012, 21, 2412–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lourenco, M.; Barreto, J.; Vasconcelos, F. sRD-SIFT: Keypoint Detection and Matching in Images with Radial Distortion. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2012, 28, 752–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig, L.; Guerrero, J.; Daniilidis, K. Scale space for camera invariant features. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 36, 1832–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaramuzza, D.; Siegwart, R. Appearance-guided monocular omnidirectional visual odometry for outdoor ground vehicles. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2008, 24, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valgren, C.; Lilienthal, A.J. SIFT, SURF & seasons: Appearance-based long-term localization in outdoor environments. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2010, 58, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, K. Photogrammetry—Geometry from Images and LASER Scans, 2nd ed.; Walter de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2007; pp. 1–459. [Google Scholar]
- Svoboda, T.; Pajdla, T.; Hlaváč, V. Epipolar geometry for panoramic cameras. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Berlin, Germany, 2–6 June 1998; pp. 218–231. [Google Scholar]
- Bunschoten, R.; Krose, B. Range Estimation from a Pair of Omnidirectional Images. In Proceedings of the IEEE-ICRA, Seul, Korea, 21–26 May 2001; pp. 1174–1179. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, S.; Forstner, W. Fish-eye-stereo calibration and epipolar rectification. ISPRS Prs 2005, 59, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiente, D.; Gil, A.; Reinoso, Ó.; Juliá, M.; Holloway, M. Improved omnidirectional odometry for a view-based mapping approach. Sensors 2017, 17, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tommaselli, A.M.G.; Tozzi, C.L. A recursive approach to space resection using straight lines. Pers 1996, 62, 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, M.B.; Tommaselli, A.M.G.; Honkavaara, E.; Prol, F.S.; Kaartinen, H.; Issaoui, A.E.; Hakala, T. A Backpack-Mounted Omnidirectional Camera with Off-the-Shelf Navigation Sensors for Mobile Terrestrial Mapping: Development and Forest Application. Sensors 2018, 18, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, M.B.; Tommaselli, A.M.G.; Marcato-Junior, J.; Honkavaara, E. Geometric model and assessment of a dual-fisheye imaging system. Photogramm. Rec. 2018, 33, 243–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellwich, O.; Heipke, C.; Tang, L.; Ebner, H.; Mayr, W. Experiences with automatic relative orientation. In Proceedings of the ISPRS symposium: Spatial Information from Digital Photogrammetry and Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 5–9 September 1994; pp. 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. Determining the epipolar geometry and its uncertainty: A review. Int. J. Comput. Vis. (IJCV) 1998, 27, 161–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, C.; Denny, P.; Jones, E.; Glavin, M. Accuracy of fish-eye lens models. Appl. Opt. 2012, 49, 3338–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, D.; Schwalbe, E.; Maas, H.G. Validation of geometric models for fisheye lenses. Isprs Prs 2009, 64, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhail, E.M.; Ackermann, F.E. Observations and Least Squares, 1st ed.; IEP—A Dun-Donnelley Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1976; pp. 1–497. [Google Scholar]
- Pope, A.J. The Statistics of Residuals and the Detection of Outliers, NOAA Technical Report; National Geodetic Survey: Rockville, MD, USA, 1976; Tech. Rep. NOS-65-NGS-1. [Google Scholar]
- Arandjelovic, R.; Zisserman, A. Three things everyone should know to improve object retrieval. In Proceedings of the IEEE-CVPR, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 2911–2918. [Google Scholar]
- The MathWorks: Statistics and Machine Learning Toolbox™ User’s Guide. Version 11.4-2018b, Sep. 2018. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/help/pdf_doc/stats/stats.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2018).
- Garrido-Jurado, S.; Muñoz-Salinas, R.; Madrid-Cuevas, F.J.; Marín-Jiménez, M.J. Automatic generation and detection of highly reliable fiducial markers under occlusion. Pattern Recognit. 2014, 47, 2280–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillo, A.C.; Guerrero, J.J.; Sagues, C. Surf features for efficient robot localization with omnidirectional images. In Proceedings of the IEEE-ICRA, Rome, Italy, 10–14 April 2007; pp. 3901–3907. [Google Scholar]
- Merkle, N.; Luo, W.; Auer, S.; Müller, R.; Urtasun, R. Exploiting deep matching and SAR data for the geo-localization accuracy improvement of optical satellite images. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.; Zhu, X.; Ren, J. Object detection on panoramic images based on deep learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE-ICCAR, Nagoya, Japan, 24–26 April 2017; pp. 375–380. [Google Scholar]
- Zbontar, J.; LeCun, Y. Stereo Matching by Training a Convolutional Neural Network to Compare Image Patches. JMLR 2016, 17, 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, J.; Läbe, T.; Förstner, W. Incremental real-time bundle adjustment for multi-camera systems with points at infinity. ISPRS Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2013, 1, W2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Interest Operator | Detection Rate | Location Correctness | Mismatches |
|---|---|---|---|
| SIFT | 164 | 70% (114/164) | 30% (50/164) |
| SURF | 155 | 63% (98/155) | 37% (57/155) |
| FAST | 59 | 64% (38/59) | 36% (21/59) |
| MOPS | 123 | 14% (19/123) | 86% (104/123) |
| Method | Detection Rate (Total/Corrected Points) | Successful Matching Rate |
|---|---|---|
| SIFTFISHEYE | 424/337 | 79.5% |
| SIFTPERSPECTIVE | 858/832 | 97% |
| SIFTRFS | 530/493 | 93% |
| σω (°) | σϕ (°) | σκ (°) | σX0 (m) | σY0 (m) | σZ0 (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.37 | 0.21 | 0.39 | 0.037 | 0.037 | 0.041 |
| Statistics | E (m) | N (m) | h (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| −0.117 | −0.071 | 0.035 | |
| σ | 0.097 | 0.069 | 0.101 |
| RMSE | 0.113 | 0.095 | 0.091 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Campos, M.B.; Tommaselli, A.M.G.; Castanheiro, L.F.; Oliveira, R.A.; Honkavaara, E. A Fisheye Image Matching Method Boosted by Recursive Search Space for Close Range Photogrammetry. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1404. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121404
Campos MB, Tommaselli AMG, Castanheiro LF, Oliveira RA, Honkavaara E. A Fisheye Image Matching Method Boosted by Recursive Search Space for Close Range Photogrammetry. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(12):1404. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121404
Chicago/Turabian StyleCampos, Mariana Batista, Antonio Maria Garcia Tommaselli, Letícia Ferrari Castanheiro, Raquel Alves Oliveira, and Eija Honkavaara. 2019. "A Fisheye Image Matching Method Boosted by Recursive Search Space for Close Range Photogrammetry" Remote Sensing 11, no. 12: 1404. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121404
APA StyleCampos, M. B., Tommaselli, A. M. G., Castanheiro, L. F., Oliveira, R. A., & Honkavaara, E. (2019). A Fisheye Image Matching Method Boosted by Recursive Search Space for Close Range Photogrammetry. Remote Sensing, 11(12), 1404. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121404