Relating X-band SAR Backscattering to Leaf Area Index of Rice in Different Phenological Phases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. TerraSAR-X ScanSAR: Multitemporal Image Acquisition and Processing
2.3. Monitoring of Sites and Field Data Collection
2.4. In situ LAI Measurement
2.5. Interpolation of LAI (from the in situ LAI Measurements)
2.6. Analysis of the Relationship of Backscatter Coefficient (σ°) and LAI
3. Results
3.1. Interpolated LAI
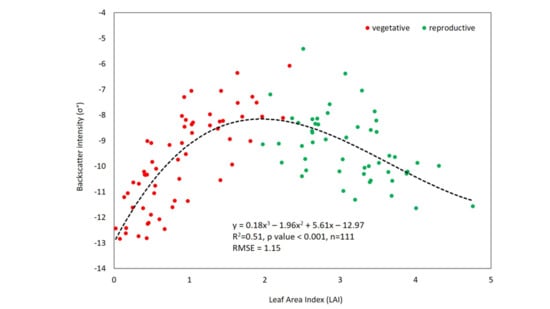
3.2. Relationship Between Backscatter Intensity (σ°) and Interpolated LAI
4. Discussion
Relationship between Backscatter Intensity (σ°) and Interpolated LAI
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- LAI-2200 Plant Canopy Analyzer. Available online: https://www.licor.com/documents/6n3conpja6uj9aq1ruyn (accessed on 12 December 2018).
- González Sanpedro, M. Optical and Radar Remote Sensing Applied to Agricultural Areas in Europe; Universitat de València: Valencia, Spain, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ulaby, F.; Allen, C.; Eger Iii, G.; Kanemasu, E. Relating the Microwave Backscattering Coefficient to Leaf Area Index. Remote Sens. Environ. 1984, 14, 113–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S. Fundamentals of Rice Crop Science; IRRI: Los Banos, Philippines, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Campos-Taberner, M.; García-Haro, F.J.; Camps-Valls, G.; Grau-Muedra, G.; Nutini, F.; Crema, A.; Boschetti, M. Multitemporal and Multiresolution Leaf Area Index Retrieval for Operational Local Rice Crop Monitoring. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 187, 102–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoefsloot, P.; Ines, A.; van Dam, J.; Duveiller, G.; Kayitakiret, F.; Hansen, J. Combining Crop Models and Remote Sensing for Yield Prediction: Concepts, Applications and Challenges for Heterogeneous Smallholder Environments; CGIAR: Montpellier, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bouman, B.; Van Keulen, H.; Van Laar, H.; Rabbinge, R. The ‘School of De Wit’crop Growth Simulation Models: A Pedigree and Historical Overview. Agric. Syst. 1996, 52, 171–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulin, S.; Bondeau, A.; Delecolle, R. Combining Agricultural Crop Models and Satellite Observations: From Field to Regional Scales. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 1021–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouman, B. Crop Modelling and Remote Sensing for Yield Prediction. NJAS Wagening. J. Life Sci. 1995, 43, 143–161. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, G.; Moskal, L.M. Retrieving Leaf Area Index (LAI) Using Remote Sensing: Theories, Methods and Sensors. Sensors 2009, 9, 2719–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopez-Sanchez, J.M.; Cloude, S.R.; Ballester-Berman, J.D. Rice Phenology Monitoring by Means of SAR Polarimetry at X-Band. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 2695–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuzugullu, O.; Erten, E.; Hajnsek, I. Estimation of Rice Crop Height from X-and C-Band Polsar by Metamodel-Based Optimization. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y.; Sakaiya, E. Relationship between X-Band Backscattering Coefficients from High-Resolution Satellite SAR and Biophysical Variables in Paddy Rice. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 4, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishzadeh, R.; Skidmore, A.; Schlerf, M.; Atzberger, C. Inversion of a Radiative Transfer Model for Estimating Vegetation LAI and Chlorophyll in a Heterogeneous Grassland. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 2592–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.H. Earth Observation for Rice Crop Monitoring and Yield Estimation: Application of Satellite Data and Physically Based Models to the Mekong Delta; Faculty of Geo-information Science and Earth Observation, University of Twente: Enschede, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, Y.; Sakaiya, E.; Wang, C. Capability of C-Band Backscattering Coefficients from High-Resolution Satellite SAR Sensors to Assess Biophysical Variables in Paddy Rice. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Sanchez, J.M.; Ballester-Berman, J.D. Potentials of Polarimetric SAR Interferometry for Agriculture Monitoring. Radio Sci. 2009, 44, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Special Features of ASAR. Available online: https://earth.esa.int/handbooks/asar/CNTR1-1-5.html#eph.asar.ug.choos.specfeat.selincang (accessed on 1 April 2019).
- Lopez-Sanchez, J.M.; Vicente-Guijalba, F.; Ballester-Berman, J.D.; Cloude, S.R. Influence of Incidence Angle on the Coherent Copolar Polarimetric Response of Rice at X-Band. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 12, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.-H.; Hong, S.Y.; Lee, H. Radar Backscattering Measurement of a Paddy Rice Field Using Multi-Frequency (L, C and X) and Full-Polarization. In Proceedings of the Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Boston, MA, USA, 6–11 July 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Lin, H.; Huang, C.; Fang, C. The Relationship between the Leaf Area Index (LAI) of Rice and the C-Band SAR Vertical/Horizontal (VV/HH) Polarization Ratio. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 2149–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y.; Kurosu, T.; Maeno, H.; Uratsuka, S.; Kozu, T.; Dabrowska-Zielinska, K.; Qi, J. Season-Long Daily Measurements of Multifrequency (Ka, Ku, X, C, and L) and Full-Polarization Backscatter Signatures over Paddy Rice Field and Their Relationship with Biological Variables. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 81, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y.; Sakaiya, E.; Wang, C. Potential of X-Band Images from High-Resolution Satellite SAR Sensors to Assess Growth and Yield in Paddy Rice. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 5995–6019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirooka, Y.; Homma, K.; Maki, M.; Sekiguchi, K. Applicability of Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) to Evaluate Leaf Area Index (LAI) and Its Growth Rate of Rice in Farmers’ Fields in Lao Pdr. Field Crop. Res. 2015, 176, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Datta, S.K. Principles and Practices of Rice Production; IRRI: Los Banos, Philippines, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.; Kumari, M.; Saha, S.K. Leaf Area Index Estimation of Lowland Rice Using Semi-Empirical Backscattering Model. Appres 2013, 7, 073474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Quilang, E.; Alosnos, E.; Finnigan, J. Rice Area Mapping, Yield, and Production Forecast for the Province of Nueva Ecija Using Radarsat Imagery. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 37, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deparment of Agriculture, Bureau of Soils and Water Management. Land Resources Evaluation Project of Nueva Ecija: The Physical Environment; Deparment of Agriculture, Bureau of Soils and Water Management: Quezon City, Philippines, 2005.
- Palay and Corn. Area Harvested; Philippine Statictics Authority: Quezon City, Philippines, 2017. Available online: http://openstat.psa.gov.ph/PXWeb/pxweb/en/DB/ DB__2E__CS/0022E4EAHC0.px/?rxid=bdf9d8da-96f1-4100-ae09-18cb3eaeb313 (accessed on 23 February 2017).
- Climate of the Philippines. Available online: https://www1.pagasa.dost.gov.ph/index.php/climate-of-the-philippines (accessed on 15 August 2018).
- Asilo, S.; de Bie, K.; Skidmore, A.; Nelson, A.; Barbieri, M.; Maunahan, A. Complementarity of Two Rice Mapping Approaches: Characterizing Strata Mapped by Hypertemporal Modis and Rice Paddy Identification Using Multitemporal SAR. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 12789–12814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GADM Maps and Data. Version 2.8 Ed. Available online: https://gadm.org/ (accessed on 25 August 2015).
- Liew, S.C.; Kam, S.P.; Tuong, T.P.; Chen, P.; Minh, V.Q.; Lim, H. Application of Multitemporal Ers-2 Synthetic Aperture Radar in Delineating Rice Cropping Systems in the Mekong River Delta, Vietnam. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 1412–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, A.; Setiyono, T.; Rala, A.; Quicho, E.; Raviz, J.; Abonete, P.; Maunahan, A.; Garcia, C.; Bhatti, H.; Villano, L.; et al. Towards an Operational SAR-Based Rice Monitoring System in Asia: Examples from 13 Demonstration Sites across Asia in the Riice Project. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 10773–10812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SARMAP. MAPscape-RICE. Version 5.064; SARMAP: Cascine de Barico, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Daily TRMM and Other Satellites Precipitation Product (3b42 V6 Derived). Available online: https://pmm.nasa.gov/data-access/downloads/trmm (accessed on 10 August 2015).
- AccuPAR PAR/LAI Ceptometer. Available online: http://manuals.decagon.com/Manuals/10242_Accupar%20LP80_Web.pdf (accessed on 19 April 2018).
- Maclean, J.; Hardy, B.; Hettel, G. Rice Almanac: Source Book for One of the Most Important Economic Activities on Earth; IRRI: Los Banos, Philippines, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Baret, F. Contribution Au Suivi Radiometrique de Cultures de Cereales; Universite de Paris-Sud: Paris, France, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Koetz, B.; Baret, F.; Poilvé, H.; Hill, J. Use of Coupled Canopy Structure Dynamic and Radiative Transfer Models to Estimate Biophysical Canopy Characteristics. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 95, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA Prediction of Worldwide Energy Ressources: Climatology Resource for Agroclimatology. Available online: https://power.larc.nasa.gov/ (accessed on 16 October 2017).
- Biostatistics Open Learning Textbook. Available online: http://bolt.mph.ufl.edu/6050-6052/unit-1/case-q-q/scatterplots/ (accessed on 3 January 2018).
- Loevinsohn, M.E. Asynchrony in Cultivation among Philippine Rice Farmers: Causes and Prospects for Change. Agric. Syst. 1992, 41, 419–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loevinsohn, M.E.; Litsinger, J.A.; Bandong, J.P.; Alviola, A.; Kenmore, P. Synchrony of Rice Cultivation and the Dynamics of Pest Populations: Experimentation and Implementation; IRRI: Los Banos, Philippines, 1982; p. 20. [Google Scholar]
- Bouvet, A.; Le Toan, T.; Dao, N.L. Estimation of Agricultural and Biophysical Paramters of Rice Fields in Vietnam Using X-Band Dual-Polarization SAR. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 13–18 July 2014. [Google Scholar]







| Frequency Band | Sensor | Wavelength (cm) | Incident Angle (◦) | Polarisation | Spatial Resolution/Antenna Height (m) | Temporal Resolution (days) | Growth Phase Studied | Relationship with LAI | R2 | Sample Size | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ka | scatterometer | 1.18 | 25°, 35°, 45°, 55° | HH, HV, VV, and VH | 5 m height | Daily | Transplanting to harvest | Poor correlation | <0.7 | not mentioned | Inoue et al., 2002 [22] |
| Ku | scatterometer | 1.88 | 25°, 35°, 45°, 55° | HH, HV, VV, and VH | 5 m height | Daily | Transplanting to harvest | Poor correlation | <0.7 | not mentioned | Inoue et al., 2002 [22] |
| X | scatterometer | 3.12 | 25°, 35°, 45°, 55° | HH, HV, VV, and VH | 5 m height | Daily | Transplanting to harvest | Poor correlation | <0.7 | not mentioned | Inoue et al., 2002 [22] |
| X | scatterometer | 3.11 | 20°–60° | HH, HV, VV, and VH | 4.16 m height | not mentioned | Before transplanting to late maturing stage | Poor correlation | not mentioned | not mentioned | Kim et al., 2008 [20] |
| X | COSMO-SkyMed (Spotlight mode) | 3.11 | 54° | VV | 1 | Single image acquired | Late maturing stage | Poor correlation | 0.0064 | 58 | Inoue et al., 2012 [13] |
| X | TSX and CSK (Spotlight mode) | 3.11 | 44°, 50°, 55° | VV | 1.7 x 1.48 and 1 x 1 respectively | Once per season | Transplanting and late maturing stage | Poor correlation (maturing stage) | −0.21 (maturing stage) | 128 | Inoue et al, 2014 [23] |
| X | CSK (ScanSAR Wide Region mode) | 3.11 | 45° | HH | 30 | 16 | Between transplanting and heading stage | Statistically significant correlation | 0.34 (r = 0.58, p < 0.001) | 30 | Hirooka et al. 2015 [24] |
| Frequency Bands | Sensor | Wavelength (cm) | Incident Angle (◦) | Polarisation | Spatial Resolution/Antenna Height (m) | Temporal Resolution (days) | Growth Phase Studied | Relationship with LAI | R2 | Sample Size | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | scatterometer | 5.21 | 25°, 35°, 45°, 55° | HH, HV, VV, and VH | 5 m height | Daily | Transplanting to harvest | Best correlated with LAI at HH and HV | 0.96–0.97 | not mentioned | Inoue et al., 2002 [22] |
| C | scatterometer | 5.66 | 20°–60° | HH, HV, VV, and VH | 4.16 m height | not mentioned | Before transplanting to late maturing stage | Strong correlation at HH and HV at > 45° | 0.88–0.94 | not mentioned | Kim et al., 2008 [20] |
| C | ENVISAT ASAR | 5.62 | 31°–39° | VV/HH | 30 | Image acquired at selected growth stages | Seedling to maturing stage | Strongest correlation at seedling stage | 0.62–0.88 | 32 | Chen et al., 2009 [21] |
| C | Radarsat-2 | 5.4 | 28°–37° | HH, HV, VH, VV, HH/VV, HV/HH | not mentioned | Image acquired for two years for important growth stages | Tillering to maturing stage | Strongest correlation at HV and HH/VV | 0.88 and 0.84 | 14 and 20 per growth stage | Kumar et al., 2013 [26] |
| C | Radarsat-2 | 5.55 | 25°–35° | VH | 1 × 1 | Image acquired at selected growth stages | Vegetative to ripening | Strong correlation | 0.84–0.85 | 41, 52, 12, 24 (2009–2012 respectively) | Inoue et al., 2014 [16] |
| L | scatterometer | 23.79 | 25°, 35°, 45°, 55° | HH, HV, VV, and VH | 5 m height | Daily | Transplanting to harvest | High correlation but only second best compared to C-band | 0.88–0.91 | not mentioned | Inoue et al., 2002 [22] |
| L | scatterometer | 23.61 | 20°–60° | HH, HV, VV, and VH | 4.16 m height | not mentioned | Before transplanting to late maturing stage | Strong correlation at HH and 50° | 0.94 | not mentioned | Kim et al., 2008 [20] |
| Frequency Bands | Sensor | Wavelength (cm) | Incident Angle (◦) | Polarisation | Spatial Resolution (m) | Temporal Resolution (days) | Crop Growth Phase Studied | Relationship with LAI | R2 | Sample Size | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | TSX (ScanSAR) | 3.11 | 45° | HH | 18.5 | 11 | Vegetative to reproductive phase (seedling to flowering stage) | Statistically significant non-linear relationship and moderate correlation | 0.51 | 111 | this study |
| Ripening phase (milking to maturing stage) | Poor correlation | 0.02 | 36 | ||||||||
| X | CSK (Spotlight mode) | 3.11 | 54° | VV | 1 | Single image acquired | Late maturing stage | Poor correlation | 0.0064 | 58 | Inoue et. al., 2012 [13] |
| X | TSX and CSK (Spotlight mode) | 3.11 | 44°, 50°, 55° | VV | 1.7 × 1.48, 1x1 | Once per season | Transplanting and late maturing stage | Poor correlation | −0.21 (maturing) | not mentioned | Inoue et al, 2014 [23] |
| X | CSK (ScanSAR Wide Region mode) | 3.11 | 45° | HH | 30 | 16 | Before the heading stage | Statistically significant correlation | 0.34 | 30 | Hirooka et al. 2015 [24] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Asilo, S.; Nelson, A.; de Bie, K.; Skidmore, A.; Laborte, A.; Maunahan, A.; Quilang, E.J.P. Relating X-band SAR Backscattering to Leaf Area Index of Rice in Different Phenological Phases. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121462
Asilo S, Nelson A, de Bie K, Skidmore A, Laborte A, Maunahan A, Quilang EJP. Relating X-band SAR Backscattering to Leaf Area Index of Rice in Different Phenological Phases. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(12):1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121462
Chicago/Turabian StyleAsilo, Sonia, Andrew Nelson, Kees de Bie, Andrew Skidmore, Alice Laborte, Aileen Maunahan, and Eduardo Jimmy P. Quilang. 2019. "Relating X-band SAR Backscattering to Leaf Area Index of Rice in Different Phenological Phases" Remote Sensing 11, no. 12: 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121462
APA StyleAsilo, S., Nelson, A., de Bie, K., Skidmore, A., Laborte, A., Maunahan, A., & Quilang, E. J. P. (2019). Relating X-band SAR Backscattering to Leaf Area Index of Rice in Different Phenological Phases. Remote Sensing, 11(12), 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121462