Estimation of Ground Surface and Accuracy Assessments of Growth Parameters for a Sweet Potato Community in Ridge Cultivation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Crop and Cultivation Conditions
2.2. Instrumentation and Measurement Methods
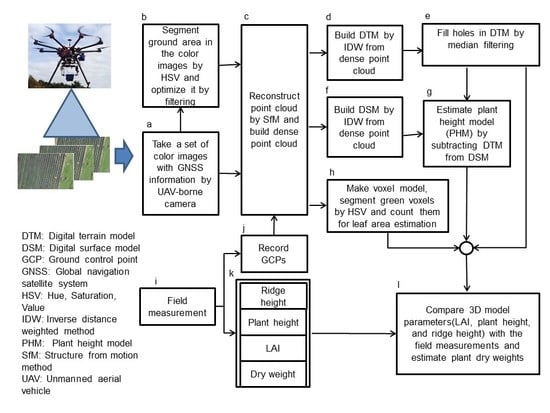
2.3. Development and Accuracy Evaluation of Ground Surface Model and Plant Height Model in Ridge Cultivation
2.4. Estimation Method of LAI and Dry Matter Weight and Their Accuracy Evaluations
3. Results
3.1. Examples of 3D Dense Point Cloud Models of the Sweet Potato Field
3.2. Effects of Plant Area Removal and Filtering Process for the Construction of Ground Surface (DTM)
3.2.1. Effects of Plant Area Removal and Enlargement Filtering
3.2.2. Effects of Median Filters
3.3. Error Evaluations of Plant Height Models (PHMs) over the Entire Growth Period
3.4. Estimation of LAI and Error Evaluation
3.5. Relationships Between LAI and Aboveground Dry Matter Weight, and Tuberous Root Yield
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Campbell, G.S.; Norman, J.M. An Introduction to Environmental Biophysics; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; ISBN 1461216265. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, H.G. Plants and Microclimate: A Quantitative Approach to Environmental Plant Physiology, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013; ISBN 9780521279598. [Google Scholar]
- Omasa, K.; Aiga, I. Environmental measurement: Image instrumentation for evaluating pollution effects on plants. In Systems & Control Encyclopedia; Singh, M.G., Ed.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1987; pp. 1516–1522. [Google Scholar]
- Omasa, K. Image instrumentation methods of plant analysis. In Modern Methods of Plant Analysis. Physical Methods in Plant Sciences; Linskens, H.F., Jackson, J.F., Eds.; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1990; pp. 203–243. [Google Scholar]
- Omasa, K. Image sensing and phytobiological information. In CIGR Handbook of Agricultural Engineering Information Technology; Munack, A., Ed.; American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2006; pp. 217–230. [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs, R.J.; Mooney, H.A. Remote Sensing of Biosphere Functioning; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 79, ISBN 146123302X. [Google Scholar]
- Sellers, P.J.; Rasool, S.I.; Bolle, H.-J. A review of satellite data algorithms for studies of the land surface. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2002, 71, 1429–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omasa, K.; Hosoi, F.; Konishi, A. 3D lidar imaging for detecting and understanding plant responses and canopy structure. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 881–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitlock, C.H.; Charlock, T.P.; Staylor, W.F.; Pinker, R.T.; Laszlo, I.; Ohmura, A.; Gilgen, H.; Konzelman, T.; DiPasquale, R.C.; Moats, C.D. First global WCRP shortwave surface radiation budget dataset. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1995, 76, 905–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, H.G.; Vaughan, R.A. Remote Sensing of Vegetation: Principles, Techniques, and Applications; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2010; ISBN 0199207798. [Google Scholar]
- Omasa, K.; Qiu, G.Y.; Watanuki, K.; Yoshimi, K.; Akiyama, Y. Accurate estimation of forest carbon stocks by 3-D remote sensing of individual trees. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 1198–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omasa, K.; Akiyma, Y.; Ishigami, Y.; Yoshimi, K. 3-D remote sensing of woody canopy heights using a scanning helicopter-borne lidar system with high spatial resolution. J. Remote Sens. Soc. 2000, 20, 394–406. [Google Scholar]
- Morsdorf, F.; Kötz, B.; Meier, E.; Itten, K.I.; Allgöwer, B. Estimation of LAI and fractional cover from small footprint airborne laser scanning data based on gap fraction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 104, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asner, G.P.; Mascaro, J.; Muller-Landau, H.C.; Vieilledent, G.; Vaudry, R.; Rasamoelina, M.; Hall, J.S.; VanBreugel, M. A universal airborne LiDAR approach for tropical forest carbon mapping. Oecologia 2012, 168, 1147–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Hyyppä, J.; Jaakkola, A. Mini-UAV-borne LIDAR for fine-scale mapping. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 8, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, L.; Lucieer, A.; Watson, C.; Turner, D. Development of a UAV-LiDAR system with application to forest inventory. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 1519–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, L.; Lucieer, A.; Malenovský, Z.; Turner, D.; Vopěnka, P. Assessment of forest structure using two UAV techniques: A comparison of airborne laser scanning and structure from motion (SfM) point clouds. Forests 2016, 7, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankey, T.; Donager, J.; McVay, J.; Sankey, J.B. UAV lidar and hyperspectral fusion for forest monitoring in the southwestern USA. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 195, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Varela, R.; dela Rosa, R.; León, L.; Zarco-Tejada, P. High-resolution airborne UAV imagery to assess olive tree crown parameters using 3D photo reconstruction: Application in breeding trials. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 4213–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandois, J.P.; Ellis, E.C. High spatial resolution three-dimensional mapping of vegetation spectral dynamics using computer vision. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 136, 259–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holman, F.H.; Riche, A.B.; Michalski, A.; Castle, M.; Wooster, M.J.; Hawkesford, M.J. High throughput field phenotyping of wheat plant height and growth rate in field plot trials using UAV based remote sensing. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Yun, H.S.; Jeong, S.; Kwon, Y.; Kim, S.; Suk, W.; Id, L.; Kim, H. Modeling and testing of growth status for chinese cabbage and white radish with UAV-based RGB Imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, A.J.; Jensen, J.L.R. Visualizing and quantifying vineyard canopy LAI using an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) collected high density structure from motion point cloud. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 2164–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badura, G.P.; Bachmann, C.M.; Tyler, A.C.; Goldsmith, S.; Eon, R.S.; Lapszynski, C.S. A novel approach for deriving LAI of salt marsh vegetation using structure from motion and multiangular spectra. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 599–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Niu, Z.; Chen, H.; Li, D.; Wu, M.; Zhao, W. Remote estimation of canopy height and aboveground biomass of maize using high-resolution stereo images from a low-cost unmanned aerial vehicle system. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 67, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.L.R.; Mathews, A.J. Assessment of image-based point cloud products to generate a bare earth surface and estimate canopy heights in a woodland ecosystem. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandois, J.P.; Olano, M.; Ellis, E.C. Optimal altitude, overlap, and weather conditions for computer vision uav estimates of forest structure. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 13895–13920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarco-Tejada, P.J.; Diaz-Varela, R.; Angileri, V.; Loudjani, P. Tree height quantification using very high resolution imagery acquired from an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) and automatic 3D photo-reconstruction methods. Eur. J. Agron. 2014, 55, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendig, J.; Bolten, A.; Bareth, G. UAV-based Imaging for Multi-Temporal, very high Resolution Crop Surface Models to monitor Crop Growth Variability. Photogramm. Fernerkund. Geoinf. 2013, 6, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendig, J.; Bolten, A.; Bennertz, S.; Broscheit, J.; Eichfuss, S.; Bareth, G. Estimating biomass of barley using crop surface models (CSMs) derived from UAV-based RGB imaging. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 10395–10412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, P.; Zhang, Y.; Shimizu, Y.; Hosoi, F.; Omasa, K. Accuracy Assessment in 3D Remote Sensing of Rice Plants in Paddy Field Using a Small UAV. Eco-Engineering 2016, 28, 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, P.; Fukumaru, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Aono, M.; Shimizu, Y.; Hosoi, F.; Omasa, K. Accuracy Assessment in 3D Remote Sensing of Japanese Larch Trees using a Small UAV. Eco-Engineering 2018, 30, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Teng, P.; Aono, M.; Shimizu, Y.; Hosoi, F.; Omasa, K. 3D monitoring for plant growth parameters in field with a single camera by multi-view approach. J. Agric. Meteorol. 2018, 74, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoshikawa, K. Encyclopedia Nipponica; Syogakukan Publ: Tokyo, Japan, 1994; Volume 12, p. 943. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, D.G. Object recognition from local scale-invariant features. In Proceedings of the Seventh IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Washington, DC, USA, 20–25 September 1999; Volume 99, pp. 1150–1157. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, D.G. Distinctive Image Features from. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 60, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasi, C.; Kanade, T. Shape and motion from image streams: A factorization method. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 9795–9802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triggs, B.; McLauchlan, P.F.; Hartley, R.I.; Fitzgibbon, A.W. Bundle Adjustment—A Modern Synthesis. Vis. Algorithms Theory Pract. 2000, 1883, 298–372. [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa, Y.; Ponce, J. Accurate, Dense, and Robust Multi-View Stereopsis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2007, 1, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa, Y.; Curless, B.; Seitz, S.M.; Szeliski, R. Towards internet-scale multi-view stereo. Proc. IEEE Comput. Soc. Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. 2010, 1434–1441. [Google Scholar]
- Hamuda, E.; Mc Ginley, B.; Glavin, M.; Jones, E. Automatic crop detection under field conditions using the HSV colour space and morphological operations. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 133, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agisoft Metashape User Manual, Professonal Edition, Version 1.5. Available online: https://www.agisoft.com/pdf/metashape-pro_1_5_en.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2019).









| From 2D Image | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Date (DAP) | Regression Line | R2 | RMSE (g/m2) |
| 10 JUN (14) | y = 0.9148x + 88.7 | 0.20 | 326.2 |
| 29 JUN (33) | y = 0.1792x + 94.7 | 0.55 | 152.0 |
| 10 AUG (75) | y = 0.0980x − 194.9 | 0.27 | 176.9 |
| 05 SEP (101) | y = 0.1046x − 75.8 | 0.39 | 247.4 |
| 15 OCT (141) | y = 0.1343x − 252.9 | 0.36 | 185.4 |
| From 3D Image | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Date (DAP) | Regression Line | R2 | RMSE (g/m2) |
| 10 JUN (14) | y = 0.7582x + 144.5 | 0.15 | 208.9 |
| 29 JUN (33) | y = 0.2281x + 51.5 | 0.69 | 125.7 |
| 10 AUG (75) | y = 0.1942x − 405.7 | 0.64 | 135.3 |
| 05 SEP (101) | y = 0.3909x − 1388.0 | 0.52 | 157.2 |
| 15 OCT (141) | y = 0.2765x − 546.2 | 0.43 | 219.3 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teng, P.; Ono, E.; Zhang, Y.; Aono, M.; Shimizu, Y.; Hosoi, F.; Omasa, K. Estimation of Ground Surface and Accuracy Assessments of Growth Parameters for a Sweet Potato Community in Ridge Cultivation. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121487
Teng P, Ono E, Zhang Y, Aono M, Shimizu Y, Hosoi F, Omasa K. Estimation of Ground Surface and Accuracy Assessments of Growth Parameters for a Sweet Potato Community in Ridge Cultivation. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(12):1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121487
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeng, Poching, Eiichi Ono, Yu Zhang, Mitsuko Aono, Yo Shimizu, Fumiki Hosoi, and Kenji Omasa. 2019. "Estimation of Ground Surface and Accuracy Assessments of Growth Parameters for a Sweet Potato Community in Ridge Cultivation" Remote Sensing 11, no. 12: 1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121487
APA StyleTeng, P., Ono, E., Zhang, Y., Aono, M., Shimizu, Y., Hosoi, F., & Omasa, K. (2019). Estimation of Ground Surface and Accuracy Assessments of Growth Parameters for a Sweet Potato Community in Ridge Cultivation. Remote Sensing, 11(12), 1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11121487