Retrieval of Grassland Aboveground Biomass through Inversion of the PROSAIL Model with MODIS Imagery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
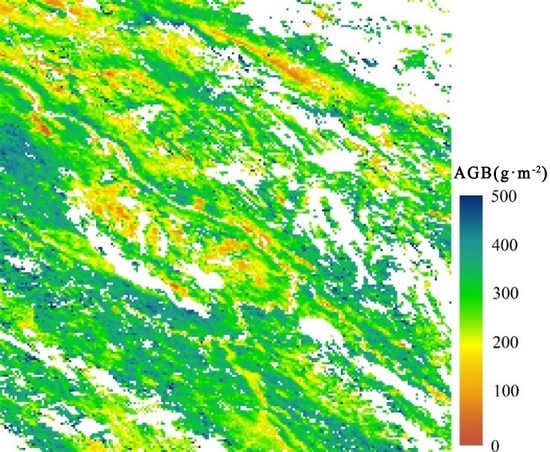
2.2.1. Field Measurements and Reference AGB Map
2.2.2. MODIS Nadir BRDF-Adjusted Reflectance
2.3. Retrieval Algorithm
2.3.1. PROSAIL Model
2.3.2. The Lookup Table (LUT) Inversion
2.3.3. Assessment of Algorithm Performance
3. Results
3.1. Comparison with Reference AGB Map
3.2. Temporal Dynamic
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dusseux, P.; Hubert-Moy, L.; Corpetti, T.; Vertès, F. Evaluation of SPOT imagery for the estimation of grassland biomass. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 38, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Tang, C.; Zhang, X.; Fu, J.; Jiang, D. An improved indicator of simulated grassland production based on MODIS NDVI and GPP data: A case study in the Sichuan province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 40, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Mutanga, O. Remote sensing of above-ground biomass. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Fang, J.; Zhou, L.; Tan, K.; Tao, S. Changes in biomass carbon stocks in China’s grasslands between 1982 and 1999. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2007, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Liu, M.; Yang, Y.; He, H.; Zhu, X.; Yang, F.; Yin, C.; Xiang, W. Estimation and uncertainty analyses of grassland biomass in Northern China: Comparison of multiple remote sensing data sources and modeling approaches. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 60, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Li, A.; Wu, C.; Wang, J.; Xie, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Nan, X.; Jin, H.; Bian, J.; Lei, G. Seamless upscaling of the field-measured grassland aboveground biomass based on gaussian process regression and gap-filled landsat 8 OLI reflectance. Int. J. Geo–Inf. 2018, 7, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoko, C.; Mutanga, O.; Dube, T. Progress in the remote sensing of C3 and C4 grass species aboveground biomass over time and space. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2016, 120, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Yang, X.; Jin, Y.; Ma, H.; Li, J.; Yu, H.; Yu, Q.; Zheng, X.; Xu, B. Spatio-temporal variation in vegetation biomass and its relationships with climate factors in the Xilingol grasslands, Northern China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Yang, X.; Qiu, J.; Li, J.; Gao, T.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, F.; Ma, H.; Yu, H.; Xu, B. Remote sensing-based biomass estimation and its spatio-temporal variations in temperate grassland, Northern China. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1496–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zeng, Y.; Luo, J.; Ma, R.; Wu, B. Modeling grassland aboveground biomass using a pure vegetation index. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 62, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Yang, S.; Feng, Q.; Liu, B.; Zhang, R.; Huang, X.; Xie, H. Multi-factor modeling of above-ground biomass in alpine grassland: A case study in the Three-River Headwaters Region, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 186, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duursma, R.A.; Marshall, J.D.; Robinson, A.P. Leaf area index inferred from solar beam transmission in mixed conifer forests on complex terrain. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2003, 118, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, L.; Xie, D.; Yin, X.; Liu, C.; Liu, G. Application of synthetic NDVI time series blended from landsat and MODIS data for grassland biomass estimation. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Sha, Z.; Yu, M.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, L. A comparison of two models with Landsat data for estimating above ground grassland biomass in Inner Mongolia, China. Ecol. Model. 2009, 220, 1810–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widlowski, J.L.; Pinty, B.; Lopatka, M.; Atzberger, C.; Buzica, D.; Chelle, M.; Disney, M.; Gastellu-Etchegorry, J.P.; Gerboles, M.; Gobron, N.; et al. The fourth radiation transfer model intercomparison (RAMI-IV): Proficiency testing of canopy reflectance models with ISO-13528. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 6869–6890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, G.F.; Li, A.N.; Zhao, W.; Jin, H.A.; Bian, J.H.; Wu, S.B.A. Modeling canopy reflectance over sloping terrain based on path length correction. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 4597–4609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, Q.; Huete, A.R.; Yin, G.; Xu, B.; Fan, W.; Zhao, J.; Yan, K.; Mu, X. A radiative transfer model for heterogeneous agro-forestry scenarios. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 4613–4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrelst, J.; Rivera, J.P.; Leonenko, G.; Alonso, L.; Moreno, J. Optimizing LUT-based RTM inversion for semiautomatic mapping of crop biophysical parameters from sentinel-2 and-3 data: Role of cost functions. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baret, F.; Weiss, M.; Lacaze, R.; Camacho, F.; Makhmara, H.; Pacholcyzk, P.; Smets, B. GEOV1: LAI and FAPAR essential climate variables and FCOVER global time series capitalizing over existing products. Part1: Principles of development and production. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 137, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquemoud, S.; Verhoef, W.; Baret, F.; Bacour, C.; Zarco-Tejada, P.J.; Asner, G.P.; Francois, C.; Ustin, S.L. PROSPECT plus SAIL models: A review of use for vegetation characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, S56–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoef, W. Light scattering by leaf layers with application to canopy reflectance modeling: The SAIL model. Remote Sens. Environ. 1984, 16, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Punalekar, S.M.; Verhoef, A.; Quaife, T.L.; Humphries, D.; Bermingham, L.; Reynolds, C.K. Application of Sentinel-2A data for pasture biomass monitoring using a physically based radiative transfer model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 218, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, X.; He, B.; Yebra, M.; Yin, C.; Liao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, X. A radiative transfer model-based method for the estimation of grassland aboveground biomass. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 54, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hunt, E.R., Jr.; Qu, J.J.; Hao, X.; Daughtry, C.S. Towards estimation of canopy foliar biomass with spectral reflectance measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 836–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Féret, J.-B.; le Maire, G.; Jay, S.; Berveiller, D.; Bendoula, R.; Hmimina, G.; Cheraiet, A.; Oliveira, J.; Ponzoni, F.; Solanki, T.; et al. Estimating leaf mass per area and equivalent water thickness based on leaf optical properties: Potential and limitations of physical modeling and machine learning. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 217, 110959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Si, Y.; Schlerf, M.; Skidmore, A.K.; Shafique, M.; Iqbal, I.A. Estimation of grassland biomass and nitrogen using MERIS data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2012, 19, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibanda, M.; Mutanga, O.; Rouget, M. Examining the potential of Sentinel-2 MSI spectral resolution in quantifying above ground biomass across different fertilizer treatments. Isprs J. Photogramm. 2015, 110, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Cheng, F.; Dong, S.; Zhao, H.; Hou, X.; Wu, X. Spatiotemporal dynamics of grassland aboveground biomass on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau based on validated MODIS NDVI. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.H.; Fang, J.Y.; Pan, Y.D.; Ji, C.J. Aboveground biomass in Tibetan grasslands. J. Arid Environ. 2009, 73, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, A.; Bian, J. Simulation of the grazing effects on grassland aboveground net primary production using DNDC model combined with time-series remote sensing data—a case study in Zoige Plateau, China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaaf, C.B.; Gao, F.; Strahler, A.H.; Lucht, W.; Li, X.W.; Tsang, T.; Strugnell, N.C.; Zhang, X.Y.; Jin, Y.F.; Muller, J.P.; et al. First operational BRDF, albedo nadir reflectance products from MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blanco-Muriel, M.; Alarcon-Padilla, D.C.; Lopez-Moratalla, T.; Lara-Coira, M. Computing the solar vector. Sol. Energy 2001, 70, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.F.; Li, J.; Liu, Q.H.; Fan, W.L.; Xu, B.D.; Zeng, Y.L.; Zhao, J. Regional leaf area index retrieval based on remote sensing: the role of radiative transfer model selection. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 4604–4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishzadeh, R.; Skidmore, A.; Schlerf, M.; Atzberger, C. Inversion of a radiative transfer model for estimating vegetation LAI and chlorophyll in a heterogeneous grassland. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 2592–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Liu, R.; Chen, J.M.; Liu, Y.; Shang, R.; Ju, W.; Wu, C.; Huang, W. Retrieving leaf chlorophyll content using a matrix-based vegetation index combination approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 224, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Taberner, M.; García-Haro, F.J.; Camps-Valls, G.; Grau-Muedra, G.; Nutini, F.; Crema, A.; Boschetti, M. Multitemporal and multiresolution leaf area index retrieval for operational local rice crop monitoring. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 187, 102–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasolli, L.; Asam, S.; Castelli, M.; Bruzzone, L.; Wohlfahrt, G.; Zebisch, M.; Notarnicola, C. Retrieval of leaf area index in mountain grasslands in the Alps from MODIS satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 165, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verger, A.; Baret, F.; Camacho, F. Optimal modalities for radiative transfer-neural network estimation of canopy biophysical characteristics: Evaluation over an agricultural area with CHRIS/PROBA observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combal, B.; Baret, F.; Weiss, M.; Trubuil, A.; Mace, D.; Pragnere, A.; Myneni, R.; Knyazikhin, Y.; Wang, L. Retrieval of canopy biophysical variables from bidirectional reflectance—Using prior information to solve the ill-posed inverse problem. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 84, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrigues, S.; Allard, D.; Baret, F.; Weiss, M. Influence of landscape spatial heterogeneity on the non-linear estimation of leaf area index from moderate spatial resolution remote sensing data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 105, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.F.; Li, A.N.; Verger, A. Spatiotemporally representative and cost-efficient sampling design for validation activities in Wanglang experimental site. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.F.; Li, J.; Liu, Q.H.; Li, L.H.; Zeng, Y.L.; Xu, B.D.; Yang, L.; Zhao, J. Improving leaf area index retrieval over heterogeneous surface by integrating textural and contextual information: A case study in the Heihe River Basin. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisette, J.T.; Baret, F.; Privette, J.L.; Myneni, R.B.; Nickeson, J.E.; Garrigues, S.; Shabanov, N.V.; Weiss, M.; Fernandes, R.A.; Leblanc, S.G.; et al. Validation of global moderate-resolution LAI products: A framework proposed within the CEOS Land Product Validation subgroup. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 1804–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Li, X.; Quan, X.; Qiu, S. Estimating the aboveground dry biomass of grass by assimilation of retrieved LAI into a crop growth model. IEEE J. Sel. Top. App. Ear. Obsev. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 550–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrelst, J.; Camps-Valls, G.; Muñoz-Marí, J.; Rivera, J.P.; Veroustraete, F.; Clevers, J.G.P.W.; Moreno, J. Optical remote sensing and the retrieval of terrestrial vegetation bio-geophysical properties—A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 108, 273–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, W.B.; Maiersperger, T.K.; Gower, S.T.; Turner, D.P. An improved strategy for regression of biophysical variables and Landsat ETM+ data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 84, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, A.M.; Darvishzadeh, R.; Skidmore, A.K. Retrieval of specific leaf area from landsat-8 surface reflectance data using statistical and physical models. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldridge, A.M.; Hook, S.; Grove, C.; Rivera, G. The ASTER spectral library version 2.0. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, F.; Chen, J.M.; Ju, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Fang, M. Improving the PROSPECT model to consider anisotropic scattering of leaf internal materials and its use for retrieving leaf biomass in fresh leaves. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 3119–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Band Number | Spectral Band | Bandwidth (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Red | 620–670 |
| 2 | NIR | 841–876 |
| 3 | Blue | 459–479 |
| 4 | Green | 545–565 |
| 5 | SWIR | 1230–1250 |
| 6 | SWIR | 1628–1652 |
| 7 | SWIR | 2105–2155 |
| Parameter | Unit | Min | Max | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Canopy | Leaf area index | m2·m−2 | 0.1 | 8.0 |
| Averaged leaf inclination angle | ° | 60 | 70 | |
| Hot spot size | Unitless | 0.05 | 0.1 | |
| Leaf | Leaf chlorophyll content | mg·cm−2 | 15 | 55 |
| leaf structure parameter | Unitless | 1.5 | 1.9 | |
| Leaf equivalent water thinness | g·cm−2 | 0.01 | 0.02 | |
| Leaf dry matter content | g·cm−2 | 0.005 | 0.01 | |
| Soil | Brightness coefficient | Unitless | 0.5 | 1.5 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, L.; Li, A.; Yin, G.; Nan, X.; Bian, J. Retrieval of Grassland Aboveground Biomass through Inversion of the PROSAIL Model with MODIS Imagery. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1597. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11131597
He L, Li A, Yin G, Nan X, Bian J. Retrieval of Grassland Aboveground Biomass through Inversion of the PROSAIL Model with MODIS Imagery. Remote Sensing. 2019; 11(13):1597. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11131597
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Li, Ainong Li, Gaofei Yin, Xi Nan, and Jinhu Bian. 2019. "Retrieval of Grassland Aboveground Biomass through Inversion of the PROSAIL Model with MODIS Imagery" Remote Sensing 11, no. 13: 1597. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11131597
APA StyleHe, L., Li, A., Yin, G., Nan, X., & Bian, J. (2019). Retrieval of Grassland Aboveground Biomass through Inversion of the PROSAIL Model with MODIS Imagery. Remote Sensing, 11(13), 1597. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11131597